1.Introduction
The emergence of yield curve control policy has existed for many years. It has demonstrated practical effects in diversified aspects, such as stimulating economic growth, promoting consumer demand, reducing capital outflows, and alleviating unemployment rates. The Federal Reserve became the first central bank to adopt a yield curve control policy in 1942, providing valuable insights into Japan's adoption of this policy.
Facing significant blows from the bubble economy, Japan fell into a deflationary quagmire in the 1980s and 1990s. In response to this challenge, Japan implemented policies like quantitative and qualitative monetary easing (QQE) and zero interest rates, continuously increasing purchases of government bonds. As a result, the Japanese economy gradually emerged from deflationary pressures around 2006 [1]. However, after the 2008 global financial crisis outbreak, Japan again experienced an economic downturn and had to reintroduce unconventional monetary policies such as QQE and negative interest rates. Although these policies facilitated the decline in long-term government bond yields and boosted economic growth, the actual yield levels still deviated from the central bank's expectations [1]. Therefore, on September 21, 2016, Japan adjusted the focus of QQE, shifting from quantity-based control to yield curve control [2]. While this policy achieved the central bank's targeted yield in the short term and led to an increase in price levels, its adverse effects gradually emerged, evident from Japan's continuous adjustments of specific target interest rates in recent years. Various controversies surrounding the yield curve control policy have also been expanding.
What is the specific content of the yield curve control policy, its direct impact on the Japanese yen, its correlation relationship with yen price, and its positive and negative effects? Understanding the above information is critical, especially in adapting to today's financial markets and the constantly changing global landscape. Additionally, exploring its implications for China's economic development and economic policy formulation holds significant importance and value in studying Japan's monetary policy and investment market.
2.The Policy Content
Academic research on the yield curve control policy can be traced back to 1955 when Robinson published an article titled "Federal Debt Management: Civil War, World War I, and World War II" in the American Economic Association. In this article, Robinson explored how the Federal Reserve formulated policies during World War II to sell more government bonds with different durations and upper-interest rate limits and indicated that the yield curve control policy created a trigger mechanism for generating new bank reserves [3]. Other countries may have varying specific requirements for the yield curve control policy due to different historical contexts and economic market conditions. Just as Robinson's exploration of the yield curve control policy was based on the specific circumstances of the United States, what are the areas in which Japan's implementation of the yield curve control policy has continued and innovated?
Japan formally introduced the yield curve control policy on September 21, 2016. According to Liu, the yield curve control policy is a new type of open market operation that controls short- and long-term interest rates by purchasing government bonds at a fixed rate [4]. Higgins and Klitgaard further specified that the Bank of Japan set the target yield of 10-year government bonds at "around zero" and would continue to rapidly purchase assets until the price stability target reached around 2% [5]. Koeda and Ueno analyzed the yield curve control policy based on the Preferred Habitat Theory and the theoretical foundation of the asset pricing framework, interpreting the degree of price elasticity of central bank government bond demand as the strictness of the target yield curve control [6]. Lu mentioned that the yield curve control policy not only includes plans to purchase assets other than long-term government bonds but also involves the purchase of short-term financing bills [7].
From the different definitions of the yield curve control policy by these economists, it can be observed that the yield curve control policy implemented by the Bank of Japan continues the framework of the Federal Reserve's policy of controlling government bond yields, such as using open market operations to increase government bond sales and changing the previous reliance on discount rates as the primary monetary tool. However, in a specific implementation, it innovates by setting an apparent bond maturity, namely, targeting a zero-interest rate for 10-year government bonds while maintaining the short-term deposit rate policy at around -0.1%. At the same time, while the United States implemented the yield curve control policy to reduce government financing costs and increase war funding, Japan implemented the yield curve control policy to overcome deflation and the rapid decline in GDP, aiming to achieve economic recovery.
Furthermore, Koeda and Ueno noted that the Bank of Japan's yield curve control policy, while effectively influencing long-term interest rates, may face challenges in responding quickly to economic conditions because of Japan's focus on a specific target for maintaining 10-year government bond yields [6]. The rigid target may limit the policy's response to changing economic conditions and market volatility, which shows less flexibility in Japan's policy. On the other hand, research by Higgins and Klitgaard highlighted the discretionary nature of the Fed's yield curve control policies and their ability to adapt to specific economic circumstances [5]. By comparing the research of Koeda and Ueno with Higgins and Klitgaard, the American yield curve control policy's flexibility is significantly higher than Japan's. It also illustrates the importance of continuously adjusting monetary policies to suit the specific economic development of each country.
After reviewing multiple articles on the yield curve control policies implemented by the United States and Japan, this paper provides a more detailed exposition and differentiation of the divergent aspects of yield curve control policy through tabular representation (Table 1).
Table 1: Comparison of yield curve control policies in the United States and Japan.
|
United States |
Japan |
|
|
Specific implementation time |
Late 1950s |
September 21, 2016 |
|
Main objective |
Increase war financing and stabilize prices |
Addressing deflationary pressures |
|
Policy Duration |
Federal Reserve's YCC policy is generally considered a short-term crisis response tool |
The policy implementation time is longer |
|
Target Interest Rates |
The federal funds rate |
Focus on the yield of a specific maturity, such as the 10-year Japanese Government bond (JGB) yield |
|
Flexibility |
Greater flexibility, allowing the yield curve to move within a range to reflect changing economic conditions |
Implement a more rigid form of yield curve control and stricter targets |
3.Comparison of Yield Curve and Inspiration
3.1.Relationship with the Yen
Through an analysis of the fluctuation of Japan's Consumer Price Index in different months, Wen and Li found that after the implementation of the yield curve control policy for government bonds, inflation rapidly increased in the short term, and the depreciation of the Japanese yen accelerated [8]. However, for a long time, the trend of yen depreciation may not persist continuously; at some point, the yen's trajectory could reverse to appreciation, which would also vary with the scale of intervention by the Japanese government [8]. Furthermore, due to the requirement of maintaining long-term government bond yields at nearly zero levels, the yield curve control policy could lead to yen depreciation against other currencies when interest rates in other major economies are relatively higher. It is because investors seek higher yields and shift their funds to other countries, increasing the supply of yen and thereby devaluing the exchange rate. This trend is evident from the data on the exchange rates of the Chinese Yuan and the US Dollar against the Japanese yen in Figure 1.
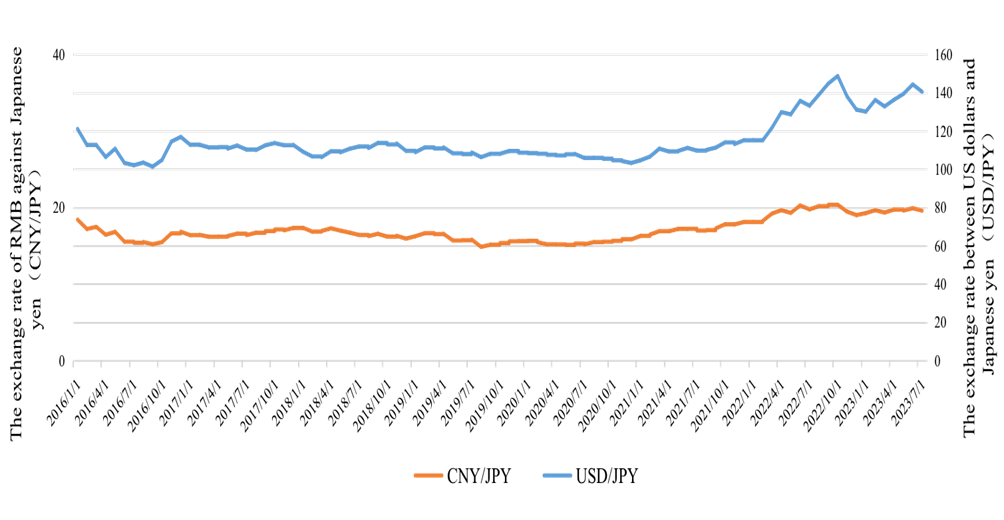
Figure 1: The exchange rate of RMB and US dollar against Japanese yen.
In Zhang and Li's research (2023), it is also explicitly pointed out that the aggressive rate hikes by the Federal Reserve in 2022 significantly widened the yield spread between the US and Japanese ten-year government bonds, leading to numerous international investors borrowing yen to subsequently sell it in the foreign exchange market and invest in higher-yield assets, such as purchasing US Treasury bonds for carry trade. It greatly exacerbated the speed of yen depreciation [1]. Based on the data provided by the Bank of Japan, the central bank adjusted the fluctuation range of long-term yield rates from ±0.1% to ±0.2% in July 2018, then to ±0.25% in March 2021, and most recently to ±0.5% in December 2022. These adjustments indicate the necessity for the Bank of Japan to adopt the specific fluctuation range of yield curve control due to the rapid pace of yen depreciation [9]. According to data from CEIC on the particular bond yields of the US and Japan from 2016 to 2023 in different months, Figure 2 is constructed. The area range in Figure 2 shows that under the combined effects of Japan's yield curve control policy and the US rate hike policy, the yield spread between the US and Japan gradually widened, intensifying the sustained trend of yen depreciation.
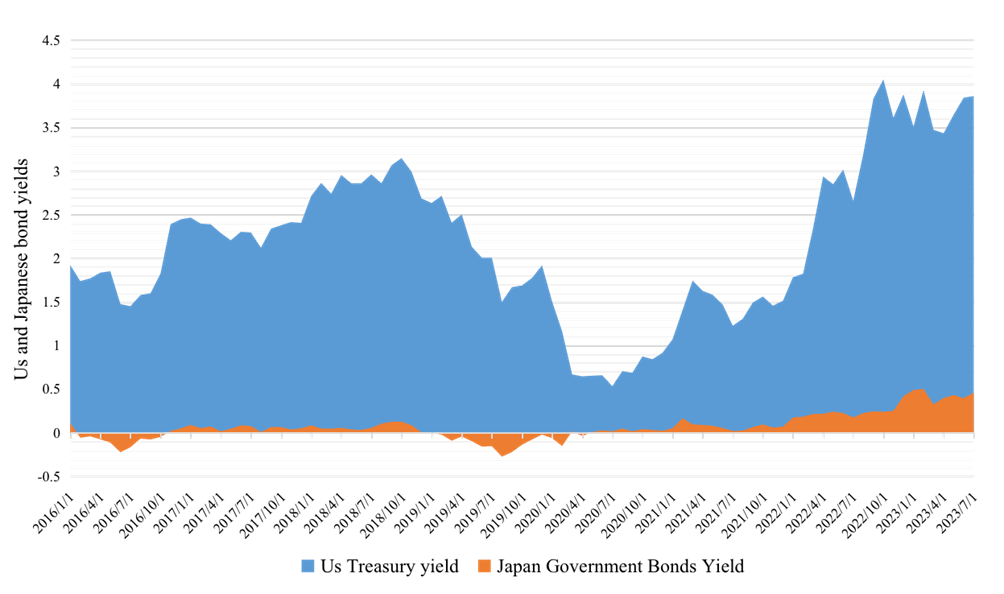
Figure 2: U.S. and Japanese government bond yields from 2016 to 2023.
Honda and Inoue's research indicated that after November 2016, the exchange rate of the yen began to depreciate, influenced by the Federal Reserve's upward adjustment of the federal fund's target rate from 0.5% to around 0.75%, which promoted a significant appreciation of the US dollar and increased the US-Japan yield spread [10]. These studies collectively highlight that the yield curve control policy for long-term government bonds directly accelerated the yen's depreciation process. Additionally, the yield curve control policy influenced capital flows, further contributing to yen depreciation, as investors expected the Bank of Japan to maintain long-term government bond yields at low levels. Consequently, they were more likely to invest funds in other countries and sell off the yen in large volumes to seek higher returns, leading to an outflow of capital from Japan and harming the yen price.
Table 2: Normality test of independent variable (Japan government bonds yield).
|
Tests of Normality |
||||||
|
|
Kolmogorov-Smirnova |
Shapiro-Wilk |
||||
|
|
Statistic |
df |
Sig. |
Statistic |
df |
Sig. |
|
Japan Government Bonds Yield |
0.165 |
91 |
0.000 |
0.936 |
91 |
0.000 |
a. Lilliefors Significance Correction
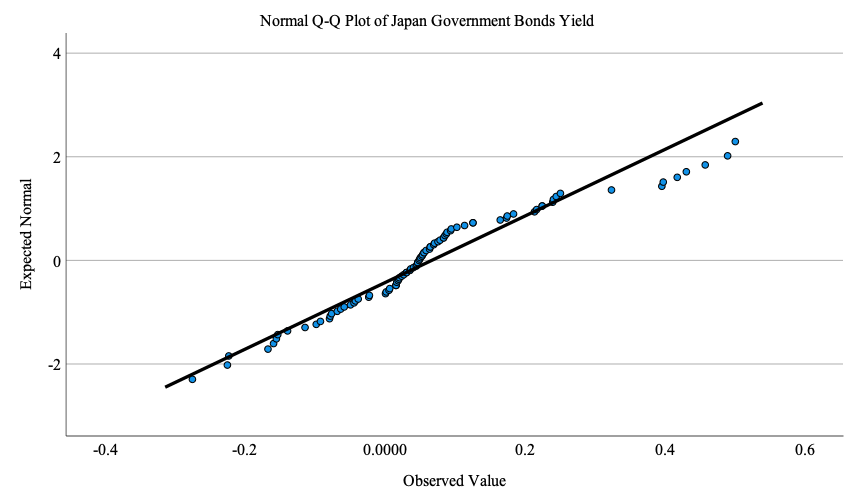
Figure 3: Normal Q-Q plot of independent variable (Japan government bonds yield).
To further explore the impact of the yield curve control policy on the Japanese yen, this article uses SPSS software to analyze its correlation relationship based on representative sample data (91 in total) selected from the daily data of Japanese government bond yields and the daily exchange rates of the US dollar against the Japanese yen provided by the Bank of Japan and CEIC from 2016 to 2023 (1,092 in total), respectively, as shown in Table 2 and 3. Given the objective of investigating the influence of yield curve control policy on the Japanese yen's price, this article adopts Japanese government bond yields as the independent variable and the daily exchange rates of the US dollar against the Japanese yen as the dependent variable. Before conducting the correlation analysis, the normality of the Japanese government bond yields and the daily exchange rates of the US dollar against the Japanese yen are examined. The Shapiro-Wilk test is applied considering the sample size of 91, less than 100. Based on the obtained significance level below 0.05 and the corresponding Q-Q plots, it is evident that neither the Japanese government bond yields nor the daily exchange rates of the US dollar against the Japanese yen adhere to a normal distribution (Figure 3 and 4).
Table 3: Normality test of dependent variable (USD/JPY).
|
Tests of Normality |
||||||
|
|
Kolmogorov-Smirnova |
Shapiro-Wilk |
||||
|
Statistic |
df |
Sig. |
Statistic |
df |
Sig. |
|
|
USD/JPY |
0.272 |
91 |
0.000 |
0.777 |
91 |
0.000 |
|
a. Lilliefors Significance Correction |
||||||
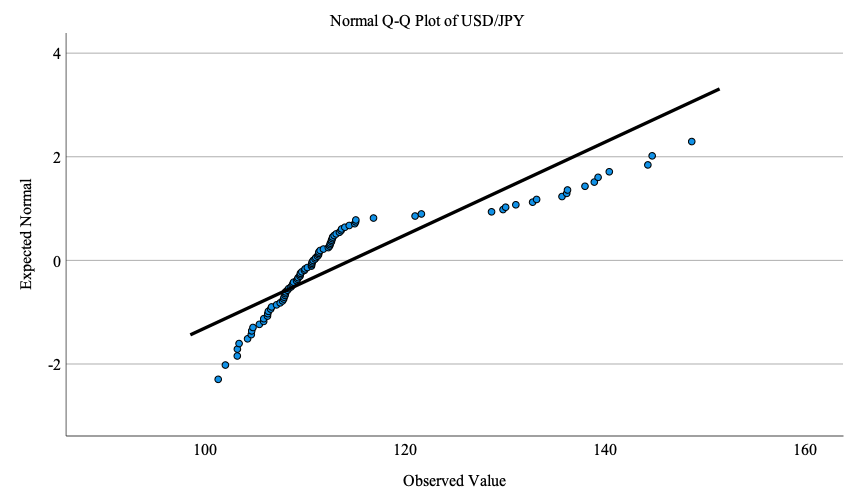
Figure 4: Normal Q-Q plot of dependent variable (USD/JPY).
Since both variables do not adhere to a normal distribution, the article applies Spearman correlation analysis to examine the relationship between the two variables. As indicated in Table 4, with a significance level (sig) of less than 0.01, a highly significant correlation exists between the variables. Furthermore, upon gathering a correlation coefficient of 0.749, it is evident that the two variables exhibit a strong positive correlation. However, it is essential to note that when the daily exchange rate of the US dollar against the Japanese yen increases, it implies a decrease in yen price. Consequently, the study concludes that a negative correlation exists between the yield curve control policy and the Japanese yen's price. In other words, when the daily yields of Japanese government bonds rise, the day-to-day exchange rate of the US dollar against the Japanese yen increases, causing a decrease in the Japanese yen's price. This conclusion is also consistent with the results of Zhang and Li's research and Honda and Inoue's research.
Table 4: Correlation analysis of independent variable and dependent variable.
|
Correlations |
||||
|
Spearman's rho |
USD/JPY |
Correlation Coefficient |
1.000 |
.749** |
|
Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
0.000 |
||
|
N |
91 |
91 |
||
|
Japan Government Bonds Yield |
Correlation Coefficient |
.749** |
1.000 |
|
|
Sig. (2-tailed) |
0.000 |
|
||
|
N |
91 |
91 |
||
|
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). |
||||
3.2.Advantages and Disadvantages
Han and Xu argued that the yield curve control policy reduces the scarcity of the Japanese yen, leading to its depreciation against major currencies. The price advantage enhances the competitiveness of Japanese export enterprises, promoting the export of various Japanese products [11]. Fukuda empirically showed that the yield control policy encourages Japanese insurance companies to expand overseas investments, increase the proportion of overseas markets, and seek new profit opportunities [12]. Zhang pointed out that the yield curve control policy maintains long-term interest rates at low levels over several years, prompting increased borrowing activities by the private sector, stimulating personal consumption and investment, and facilitating a short-term economic recovery [2].
Based on previous studies, controlling government bond yields allows the central bank to reduce government financing costs, which not only helps alleviate the government's debt burden but also provides more fiscal space for social welfare and infrastructure investments. Moreover, setting specific targets for government bond yields allows the central bank to stabilize long-term interest rate levels to some extent, preventing excessive rate fluctuations, reducing market uncertainty, and forming stable expectations for borrowers and investors, leading to adjustments in investment and decision-making based on these expectations [7]. Hui et al. explored the spillover effects of yield curve policy based on the target-zone model, including the long-term low-interest rates that increase money supply and credit activities, thereby avoiding deflation risks [13].
Despite its advantages, scholars have also identified drawbacks and potential issues with the yield curve control policy. Bernanke pointed out that while the yield curve control policy stimulates investors to seek high-return assets, it may also lead to a rapid increase in asset prices, promoting an economy detached from its real fundamentals and potentially creating asset bubbles. When these bubbles burst, it could trigger more severe economic crises and hinder the recovery of the real economy [14]. Xu, Ji, Li, and other economists also noted that excessive intervention by central banks due to political pressure has eroded the unity of decision-making within the central bank. The intervention and constraints on target interest rates seriously undermine the independence of central banks [15]. Han and Xu further highlighted concerns about the jeopardized independence of central bank monetary policy [11]. They pointed out that Abe once considered amending the "Bank of Japan Law" if the central bank did not set a price target [11]. These developments indicate that the will of the Japanese government has taken precedence over the central bank's independence in formulating monetary policy, leading to the loss of central bank independence. Additionally, long-term low-interest rate policies may create expectations of currency depreciation. While accelerated yen depreciation benefits exports, it can also lead to rising import prices, causing import-driven inflation.
3.3.Implications for China
Zong and Luo mentioned that the Chinese government should continue to prioritize establishing a sound benchmark interest rate and market-oriented interest rate system while maintaining the decisive role of the market in resource allocation [16]. Establishing a monetary policy that aligns with China's national conditions and market demands is crucial while maintaining coordination and coherence among various guidelines, such as enhancing the synergy between monetary and fiscal policies [16]. Fu explicitly pointed out that the yield curve control policy is unsuitable for China's current economic market. As an unconventional monetary policy, this policy is applicable in exceptional situations such as war, major pandemics, or severe economic recession, showing that only a few countries have adopted and implemented it [17]. China's economic development has remained stable recently, and the COVID-19 pandemic has been essentially controlled. Consumer consumption levels have steadily grown. Accordingly, an ordinary monetary policy is more appropriate for China's current environment, which involves maintaining an upward-sloping yield curve.
Over the years, China has adopted a prudent monetary policy with innovative features that align well with the country's actual conditions. This policy aims not only to prevent inflation but also to prevent deflation. Considering the rapid development of the national economy, a prudent monetary policy is a more feasible approach. Therefore, although the yield curve control policy implemented by the Bank of Japan has been successful in the United States and Australia, China should carefully consider the dual nature of policy when adopting the same strategy. Maintaining the independence of China's monetary policy, primarily interest rate policy, is crucial, particularly during significant changes in the global economy and financial markets. China needs to retain control over its interest rate policy to adopt a monetary policy that best fits the development of the socialist economy with Chinese characteristics.
While adhering to the fundamental stability of China's monetary policy, partial adoption of a successful yield curve control policy can be considered, such as addressing deflationary pressures and achieving targeted long-term government bond interest rates. It can better equip China to respond to international situations, especially in coping with specific circumstances like potential COVID-19 resurgence.
4.Conclusion
After experiencing multiple shocks, such as the bubble economy and global economic crises, the Bank of Japan gradually explored a suitable interest rate model to rescue Japan from deflationary pressures, the yield curve control policy, and maintaining long-term interest rates at low levels for an extended period. The yield curve control policy directly led to the depreciation of the Japanese yen. The policy-induced increase in the yield spread between the US and Japan, capital outflows from Japan, and increased arbitrage activities by investors further accelerated the yen's rapid depreciation. Meantime, Through the empirical analysis of the daily yield of Japanese government bonds and the exchange rate between the US dollar and yen, the article finds that the yield control policy of Japanese government bonds has a significant negative correlation with the price of yen. In recent years, Japan's measures to continuously increase the yield of government bonds have also contributed to the further decline in the yen price.
Faced with the phenomenon of the yen's accelerated depreciation, the Japanese government has taken intervention measures in recent years, adjusting the upper limit of long-term yields to stabilize inflation. However, the effectiveness of these measures has been insignificant. Whether the yen will continue to depreciate at the current speed or potentially reverse into appreciation depends on whether the Japanese government will persist in pursuing the yield curve control policy.
Furthermore, the yield curve control policy not only impacted the Japanese yen but also positively affected Japan's export volumes and encouraged the expansion of overseas market investments. It stimulated private sector consumption, borrowing, and expansion activities. However, it also generated specific adverse effects, such as asset bubbles and a decrease in the independence of the Bank of Japan. Moreover, this unconventional monetary policy has had a constructive influence on China's interest rate adjustments, serving as a valuable reference. Nevertheless, China's path follows various factors, including differences in consumer consumption levels, unique historical backgrounds, and changes in the international situation that influence the road of socialist characteristics and monetary policy. Thus, while drawing lessons from Japan's yield curve control policy, China must adhere to its independent monetary policy with Chinese characteristics, embracing an innovative approach that selects the essence and discards the gross.
References
[1]. Zhang, X. and Li, H. (2023). The Dilemma of Japan’s Yield Curve Control Policy. Financial Market Research, 2, 82-88.
[2]. Zhang, Q. (2021). The Historical Evolution, Theoretical Basis, and Impact of Yield Curve Control. Financial Theory and Practice, 42(03), 20-27.
[3]. Robinson, M. A. (1955). Federal Debt Management: Civil War, World War I, and World War II. The American Economic Review, 45(2), 388-401.
[4]. Liu, R. (2017). Japan’s New Framework of Quantitative and Qualitative Monetary Easing: An Analysis of Yield Curve Control Policy. Northeast Asian Studies, 6, 31-37.
[5]. Higgins, M. and Klitgaard, T. (2020). Japan’s Experience with Yield Curve Control. Federal Reserve Bank of New York. No. 20200622.
[6]. Koeda, J. and Ueno, Y. (2022). A Preferred Habitat View of Yield Curve Control. Bank of Japan. No. 22-E-7.
[7]. Lu, Y. (2020). Analysis of Japan’s Yield Curve Control Policy. Financial Horizon, 8, 42-47.
[8]. Wen, B. and Li, X. (2022). Analysis of Japan’s Monetary Policy and Outlook for the Yen. Tsinghua Financial Review, 12, 30-34.
[9]. Bank of Japan. (2023). Retrieved from https://www.boj.or.jp/en/.
[10]. Honda, Y. and Inoue, H. (2019). The Effectiveness of the Negative Interest Rate Policy in Japan: An Early Assessment. Journal of the Japanese and International Economies, 52, 142-153.
[11]. Han, H. and Xu, B. (2018). Analysis and Evaluation of Japan’s Quantitative Easing Monetary Policy. Northeast Asian Economic Research, 2(04), 112-120.
[12]. Fukuda, S. I. (2017). The Impacts of Japan’s Negative Interest Rate Policy on Asian Financial Markets. Pacific Economic Review, 23(1), 67-79.
[13]. Hui, C. H., Wong, A. and Lo, C. F. (2022). A note on modelling yield curve control: A target-zone approach. Finance Research Letters, 49, 103076.
[14]. Bernanke, B. S. (2017). Monetary Policy in a New Era. In Evolution or revolution: Rethinking macroeconomic policy after the great recession, 3-48.
[15]. Xu, Z., Ji, M. and Li, H. (2018). Monetary Policy with Yield Curve as an Operational Target: Historical Experience and Policy Reflection. International Economic Review, 5, 91-103+6.
[16]. Zong, L. and Luo, Q. (2023). The Main Characteristics, Impact, and Implications of Changes in Japan’s Government Bond Yield Curve. Bonds, 4, 86-91.
[17]. Fu, Y. (2021). Yield Curve Control: Theoretical Origins, Historical Experience, and Policy Implications. Financial Market Research, 2, 89-98.
Cite this article
Xu,K. (2023). The Yield Curve Control of the Central Bank of Japan and the Yen Price. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,53,270-278.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhang, X. and Li, H. (2023). The Dilemma of Japan’s Yield Curve Control Policy. Financial Market Research, 2, 82-88.
[2]. Zhang, Q. (2021). The Historical Evolution, Theoretical Basis, and Impact of Yield Curve Control. Financial Theory and Practice, 42(03), 20-27.
[3]. Robinson, M. A. (1955). Federal Debt Management: Civil War, World War I, and World War II. The American Economic Review, 45(2), 388-401.
[4]. Liu, R. (2017). Japan’s New Framework of Quantitative and Qualitative Monetary Easing: An Analysis of Yield Curve Control Policy. Northeast Asian Studies, 6, 31-37.
[5]. Higgins, M. and Klitgaard, T. (2020). Japan’s Experience with Yield Curve Control. Federal Reserve Bank of New York. No. 20200622.
[6]. Koeda, J. and Ueno, Y. (2022). A Preferred Habitat View of Yield Curve Control. Bank of Japan. No. 22-E-7.
[7]. Lu, Y. (2020). Analysis of Japan’s Yield Curve Control Policy. Financial Horizon, 8, 42-47.
[8]. Wen, B. and Li, X. (2022). Analysis of Japan’s Monetary Policy and Outlook for the Yen. Tsinghua Financial Review, 12, 30-34.
[9]. Bank of Japan. (2023). Retrieved from https://www.boj.or.jp/en/.
[10]. Honda, Y. and Inoue, H. (2019). The Effectiveness of the Negative Interest Rate Policy in Japan: An Early Assessment. Journal of the Japanese and International Economies, 52, 142-153.
[11]. Han, H. and Xu, B. (2018). Analysis and Evaluation of Japan’s Quantitative Easing Monetary Policy. Northeast Asian Economic Research, 2(04), 112-120.
[12]. Fukuda, S. I. (2017). The Impacts of Japan’s Negative Interest Rate Policy on Asian Financial Markets. Pacific Economic Review, 23(1), 67-79.
[13]. Hui, C. H., Wong, A. and Lo, C. F. (2022). A note on modelling yield curve control: A target-zone approach. Finance Research Letters, 49, 103076.
[14]. Bernanke, B. S. (2017). Monetary Policy in a New Era. In Evolution or revolution: Rethinking macroeconomic policy after the great recession, 3-48.
[15]. Xu, Z., Ji, M. and Li, H. (2018). Monetary Policy with Yield Curve as an Operational Target: Historical Experience and Policy Reflection. International Economic Review, 5, 91-103+6.
[16]. Zong, L. and Luo, Q. (2023). The Main Characteristics, Impact, and Implications of Changes in Japan’s Government Bond Yield Curve. Bonds, 4, 86-91.
[17]. Fu, Y. (2021). Yield Curve Control: Theoretical Origins, Historical Experience, and Policy Implications. Financial Market Research, 2, 89-98.









