1. Introduction and Rationale
Since the introduction of the first computer 60 years ago, the world in this century has dramatically transitioned from an industrial age to an information age [1]. There are now numerous kinds of technology and software that far exceeds the capacity for any one business to adopt [1; 2; 3]. [4] and [5] state that the fast pace in digital technologies development plays a significant role in changing the way that businesses work more than ever before. Digital technology has become a part of many businesses as it enables new capabilities and brings competitive advantages to businesses in various ways [6]. Outcomes from [7]’s study show that digital technologies are penetrating almost into every industry and [8] reveals that the companies in Fortune 500 are focusing on integrating technologies into their businesses and becoming Digital 500. [8] further asserts that executives of these Fortune 500 embrace the fact that digital transformation is a key for businesses to survive throughout this digitization age.
The swift development of digital technologies does not only impact businesses but also affect individuals, societies, and the economy as a whole. According to [9], the fast spread of information and communication technologies (ICTs) on a global basis in this century has transformed the way that individuals perceive information and interact with each other. This viewpoint complements the views from [10] and [11] which remarked that the demands of customers are now changing toward products and services with more technological and mobile capabilities on digital platforms. Also, the intensity of competition amongst businesses is on the rise due to the fact that more and more businesses adopt digital technologies to generate digital business models with the aim of acquiring more market share and gaining new revenue streams on digital platforms [5].
1.1. Study Context
As mentioned previously, the fast pace of digital technologies development has caused the world economy to shift towards a digital economy. [12] emphasize that the Asian region is a leader in embracing digital changes. Thailand is one of the countries in the Asian region that recognizes the potential benefits of digital changes [13]. Thus, as a measure to enable businesses to become attentive towards digital transformation, the Thailand government launched a new economic model called Thailand 4.0. The Thailand 4.0 is aimed at encouraging businesses in the country to be more innovative and to integrate more digital technologies into their organization [14; 15]. It is important to note that implementing digital transformation in businesses requires radical changes in all aspects of the organization [16]. [3] and [17] posit that digital transformation as a time-span process requires integrating digital technologies into the facilitation and transformation of the foundational components of a business. While previous and current studies are constantly discussing the changes that are needed for an organization to succeed in implementing digital transformation, there is dearth of research on the factors, strategies and frameworks that make businesses successful in implementing digital transformation.
Therefore, this study aims to fulfil this lack of empirical studies by exploring the importance of pursuing digital transformation for businesses under Thailand 4.0 economic model, defining key factors that businesses should consider in their decision to adopt digital transformation, and subsequently provide insights & recommendations on appropriate digital transformation strategies/ framework that businesses may use for the successful implementation of digital transformation.
2. A Review on Digital Transformation
2.1. Digitization Age
According to [18], [19], and [20], globalization, which originated about half-century ago, became a buzzword that commonly describes the world economic and business environment that shifted from local trading and internal exchange to international integration and cultural exchange. These studies indicate that globalization significantly enriched the world both economically and culturally and it increased volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity to the world and business environment, bringing tough challenges for businesses to survive. However, insights from more recent articles like [3], [4], [5] and [7] reveal that the acceleration of digital technologies since the beginning of the 21st century have brought a new wave of revolution to the world and is shifting the entire world from globalization to the ‘Digitization age’ in which digital technology have become a fundamental element for businesses and people’s everyday lives. These studies imply that the speedy pace of digital technologies will continue to play a significant role in leveraging the world economy, transforming people’s lives, changing the way that businesses work as well as bringing bigger challenges to businesses than globalization.
The argument on the significant role and implication of digital transformation is supported by statistics from [21]’s study, which shows exponential growth of internet users around the world from 1995 to 2015 (Fig 1) and from [7]’s study that demonstrates most industries that are faced with digital disruption in form of percentage of digital penetration by industry (Fig 2). [22] and [23] assert that more than half the companies on the Fortune 500 list prior to this century disappeared or went bankrupt while struggling to respond to digital disruption. Furthermore, [8] indicates that all CEOs from Fortune 500 companies nowadays admitted that the greatest challenge for their businesses is the rapid pace of digital technologies and recognized that it is also the cause of the ‘sweeping’ transformations across entire industries and suggested that digital transformation is a key for any business that aims to survive in the 21st century.
Therefore, it is necessary for today’s businesses who aim to remain throughout this digitization age to consider the impacts of the swift development of digital technologies and to understand what digital transformation is and why it is important for business in this century.
2.2. Digital Technology
The rapid growth of technological development in the digitization era and its impacts have been studied and discussed by many scholars, businesses and Information Technology (IT) experts in the last few years. For example, [8], [9], [24], [25], and [26] argue that the emergence of ICTs is the main cause of the drastic changes in the world. Outcomes from these studies indicate that Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile technologies are the major contributors in allowing everything to connect with anything at any time and in any place, which subsequently makes the world, businesses and people more connected than ever before. Thus, the fast spread of ICTs to all over the world impacts on businesses, and the economy by enabling enormous opportunities for value creation and performance improvement to businesses in all industries [27; 28].
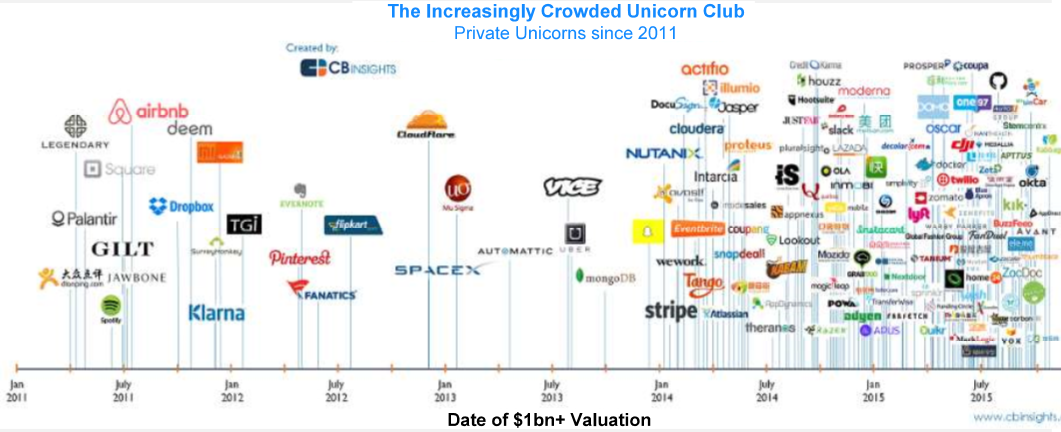
Figure 3: Increase in entrepreneurial businesses with ICT [29].
Digital technology impacts individuals and society such that customer behaviours are transformed as customers tend to search for, purchase, or consume products and services through digital-based channels [10; 11). Hence, the traditional marketing channels, or business models of analogue businesses that worked decades ago no longer help such businesses to grow or remain sustainable in this digitization age [29]. Also, [5] observed that the steep growth of emerging technologies to significantly increase market competitiveness enables new types of competitors with new business models to compete with and even become much more successful than analogue businesses. This can be seen in the dramatic rise in entrepreneurial businesses with an ICT base and digital business models that reached a market capitalization of 1 billion USD in 2015 [29]: Fig 3. Hence, these impacts and the continuing evolution of digital technologies at an exponential rate are the main drivers for any analogue business in this century to adopt digital transformation [30; 31; 32).
2.3. Digital Transformation
To adopt digital transformation, it is necessary for businesses to have clear understanding of what it is. According to [32] and [33], businesses often fall into a pitfall of thinking of digital transformation as a replacement of operational activities and processes with digital technologies or an adoption of digital technologies to boost efficiency or cut cost. Consequently, this could trap businesses into heavily investing into new technologies to partially bolster parts of the firms to transform their organisations and gain competitive advantage in digital age [30; 34]. However, [16] indicates that digital technology, on its own, does not provide the competitive advantage or transform the firms but requires radical changes in all aspects of the organization.
According to [1; 16; 30], digital transformation or digital business transformation is a transforming process that requires deeper or profound changes of an organization in a wider scope and bigger scale rather than merely embracing emerging technologies to leverage the organization’s performance or create a new competitive advantage. Furthermore, [3] and [17] argue that it is a continuous time-span process for businesses to integrate digital technologies into its foundational components for the purpose of facilitating and transforming its culture, business models, operating models, organizational structure, infrastructure, as well as people’s skills and knowledge from the top to the bottom levels of the organization.
Therefore, the definition of digital transformation can be a transformation process that requires profound changes in the foundational components of an organization to integrate digital technologies in all areas and all levels of the organization.
2.4. Thailand 4.0
According to [5] and [9], the rapid pace of emerging technologies drastically impacts the economic growth of many countries around the world. As mentioned earlier, many Asian governments have recognized the impact and the advantages of the swift development of digital technologies on their economies and so have consequently put technological development on their economic agenda. More specifically, Thailand is one of the developing countries that realized the impact of digitization and digital disruption in its economy; therefore, in late 2016, Thailand’s government initiated a new economic model called Thailand 4.0 to transform its economic structure toward digital and technology focus [13; 14; 15]. The government emphasized that this economic model will be focusing on encouraging and fostering creativity, innovation, and technologies on 10 target industries, which include Automotive, Automation and Robotics, Argo Processing, Aerospace, Digital, Electrical and Electronics, Medical, Petrochemicals, Textile, and Tourism. Thus, it is important for businesses that operate in the country which fall into these industries to gain an understanding on the importance of digital transformation and how to adopt digital transformation into their companies with a well-defined digital transformation strategy and framework. This study is designed to provide insights on why digital transformation is critical to businesses in Thailand; as well as insights on the transformation strategies and framework that businesses should pursue in order to avoid failure in implementing digital transformation in their businesses.
3. Methodology
3.1. Approach
In order to identify and understand the reasons why digital transformation is critical for business in this century, especially in Thailand 4.0 era and finding appropriate digital transformation strategy and framework for businesses to pursue, this study embraces the Qualitative Research Methodology. According to [35], Qualitative research method is a descriptive or contextual approach that uses interpretive/theoretical frameworks to address the meanings of the data to answer the questions or problems under consideration. [36] stated that qualitative data can be a robust source for data analysis in circumstances where what is known about the problems or issues are relatively little.
This methodology enabled the preliminary exploration of digital transformation experience in Thailand, in-depth evaluation of the importance of digital transformation for businesses in the country and intimate assessment of the appropriate digital transformation strategies and framework that should be considered in business practice.
3.2. Participants
This study, carried out within a Public Limited Company, in Bangkok, Thailand, is based on the investigation of the working experience of 10 current workers from various departments who have been providing different digital technologies for digital business transformation or digital enterprise solutions to large and medium enterprises in Thailand at an average of 9years amongst them. The technologies that they provide are either Business Intelligence, Big Data, Digital Automation systems, Digital Collaboration systems and Digital Infrastructure. An overview of the 10 participants is shown in Table 1.
The company is positioned as an advanced professional IT service provider who specialize in network computing, e-business and integrated digital technologies for business innovation. In addition, the company has been serving large enterprises and industry leaders in government and private sectors in Thailand for more than 2 decades. Therefore, investigating and collecting data from the current workers who have been working in the company for more than 8 years and have experience in providing digital transformation to large enterprises supported this study in discovering the reasons why digital transformation is critical for businesses in this century especially in Thailand 4.0 era as well as finding the appropriate strategy and framework that should be used in business practice for any business which aims to pursue digital transformation.
Table 1: Study Participants.
Participants’ Identifier | Years of Experience in IT/ Digital Transformation | Gender |
P1 | 9 | Male |
P2 | 9 | Female |
P3 | 13 | Female |
P4 | 7 | Male |
P5 | 13 | Male |
P6 | 7 | Female |
P7 | 8 | Male |
P8 | 7 | Female |
P9 | 10 | Male |
P10 | 6 | Female |
3.2.1. Procedure for Data Collection
The interview technique was adopted to capture the workers’ perceptions on the importance of digital transformation and the reasons why it is important to businesses in Thailand 4.0 period. All the interview sessions were carried out between December 2017 and January 2018, when the workers were not under any form of pressure such as immediate project deadlines. In addition, all interview sessions were carried out in Thai context to avoid language barrier and misunderstandings. Furthermore, all interview sessions were carried out online through Skype, which is a telecommunication application software that provides video chat and voice calls between computers; Skype was used because the researchers and the participants were in different geographical locations/ countries.
Prior to the interview sessions, appropriate ethical approval was sought and obtained. Accordingly, formal consent letters were drafted for the participants. Therefore, each interview session was preceded by a participant information sheet, which outlined the study’s aim and objectives, the reason why the participant was being invited to the interview and the potential benefits of the study to businesses in Thailand. Participation was completely voluntary. Consequently, as stated in the participant information sheet, issues of strict confidentiality, risks associated with the study and participant’s informed consent were established.
Even though the interviews were conducted by Skype, the interviews were approached on video call to simulate a face-to-face experience. On average, each interview session lasted approximately 30 minutes. During the interview sessions, simpler opening questions in Thai context were used to avoid jargons and ease the interviewees into the process, thereby ensuring that any form of tension was reduced, and any form of misunderstanding was eliminated. All participants were basically presented with similar questions, which focused on the following:
• The participants’ opinions on the importance of digital transformation to businesses in Thailand and the reasons of its importance
• The participants’ experience in providing digital transformation to the incumbents and large enterprises in Thailand
• The participants’ perceived factors or strategies in implementing digital transformation to the incumbents and large enterprises in Thailand
• The participants’ suggestions on appropriate digital transformation strategies and framework for businesses in Thailand 4.0 era
3.2.2. Procedure for Data Analysis
According to [37], thematic analysis is one of the methods for examining, analyzing, and interpreting patterns of the meaning of qualitative data as it provides systematic procedures for generating codes and themes from the data. [38] states that a theme is a pattern found in the information that can be used in describing, organizing, or interpreting aspects of the phenomenon and it can be generated inductively from raw data or deductively from theory and prior research. [39] posits that thematic analysis provides a way to analyse rich details and complex data in both manifest and latent aspects in a case where there are no previous studies dealing with the phenomenon before. Thus, since there is little or no previous studies on this topic in Thailand, thematic analysis is a great tool that was used in analyzing the data to identify themes and answer questions for this study. The generated data was analyzed by using reduction and coding technique to manage, classify and categorize the data. In this regard, meaningful textual sections were derived based on similar and/or different viewpoints of this study’s participants on the digital business transformation in Thailand.
Following the interview sessions/ discussions with the participants on their experiences in providing digital transformation and IT solutions to large enterprises and medium businesses in Thailand, the first pattern of experience (the reasons why digital transformation is critical for businesses in Thailand 4.0 era) was identified. The second pattern of experience was the opinions the interviewees have towards key factors that make businesses succeed in implementing the digital transformation. The third pattern of experience was the presumptions the interviewees have towards digital transformation strategy in terms of the strategies that businesses should have for the successful adoption of digital transformation. Lastly, the forth pattern of experience was the viewpoints the interviewees have towards conceptual frameworks that make businesses successful in transforming themselves into digital businesses. Thus, there were four categories which composed of ‘Why Digital Transformation is Important’, ‘Key Factors for Successful implementation of Digital Transformation’, ‘Strategies for Successful implementation of Digital Transformation’, and ‘Conceptual Framework for the Successful implementation of Digital Transformation’.
4. Findings and Discussions
The evaluation of the results of this study is focused on discussions on the reasons why digital transformation is important for businesses in Thailand 4.0 era and the discovery of the factors, strategies, and frameworks that underpin the success of adopting digital transformation in businesses in Thailand 4.0 era. The main points of arguments from the participants are presented and highlighted in verbatim quotes (in italics format). The participants’ identifier numbers are written next to the quotes. The findings are presented in the four sub-sections as follows:
• Why digital transformation is important
• Key factors for the successful implementation of digital transformation
• Strategies for the successful implementation of digital transformation
• Way Forward for the successful implementation of digital transformation: A Conceptual Framework
It is important to note that the themes and codes used in this study were defined based on the focus and goal of the study (which is stated in the Study Context section of this paper). Essentially, the themes and codes were analyzed under the scope of this study to gain insights on the importance of digital transformation to businesses that operate in Thailand in Thailand 4.0 era and identify the reasons of the importance as well as determine key factors and strategies that businesses should consider or pursue for the successful adoption of digital transformation to their business.
4.1. Why Digital Transformation is Important
The study identified the degree of the importance and a number of themes/ reasons associated with implementing digital transformation in analogue businesses in Thailand 4.0 era based on the experience of the participants on digital transformation. The degree of the importance is high shown by 60% of the participants indicating that it is ‘very important’ and 40% indicating that it is ‘important’. Some of the participants’ comments that reflect this high degree of importance include:
“…bring lots of opportunities for businesses to grow or generate new revenue streams, complement with the promotion of Thailand 4.0 from the government, therefore, this is a great chance of businesses in almost every industry to change themselves…” (P1)
“…transformed customer behaviour to consume things toward digital channels or digital platform…there are increasing of magazine or newspaper companies that gone bankrupt or disappeared because people tend to consume news or read things through…applications on their mobile devices...” (P2)
“…there are more and more of digital data…into digital platform every day… 90% of data is in digital format” (P3).
“Oh…I think it is really important…the plummeting cost of digital technologies enables start-up business to start…at much lower cost with much faster time than the analogue businesses…Physical store…become less important to customers in this century” (P4)
“…digital technologies enable opportunities for businesses to generate new value creations internally such as improve collaboration and performance among employees by having Performance Management system and support better decision making in executive level with Business Intelligence system and externally such as enhance customer engagement and customer loyalty by having Line Official Account…” (P5)
“Nowadays…more businesses are changing themselves to be more digital in order to serve the changes in customer demands and grow their market share…to retain their revenue or want to survive, then they need to change to be more digital.” (P6)
“…We have to accept that the whole world is already changed by the coming of technologies. People already transformed their behaviour to consume things toward digital channels or digital platform….it is important for businesses to transform if they still want to compete and survive in this digitization era” (P7)
“…Depends on where are we talking about. If we talk about businesses in the big cities…I think it is really important but for other small cities, I don’t think it is that important…people in those cities still need at least 2-3 years to adjust and access to full functionalities of digital technologies…” (P8)
“…Digital technologies bring lots of opportunities for businesses to grow or generate new value creations. Adopting digital technologies into business operation makes them work faster, easier and achieve better performance…” (P9)
“…I think it is very important because many businesses that gone bankrupt or disappeared are actually due to not adjust or transform themselves to the changes…digital technologies are already shifting the entire world…will play a significant role in driving the whole world to move much faster pace…any businesses…not moving forward to follow…will die or extinct soon….” (P10)
The themes/ reasons for digital transformation being important were grouped into three sub-categories which are ‘Opportunity to Grow’(OG), ‘The Changes in Customer Behaviour and Demands’(CCD) and ‘Increase of Competition’(IC). OG includes the workers’ comments that relate to the potential benefits that digital technologies bring to businesses that enables the businesses to improve their operations and gain competitive advantage over their competitors while CCD includes the participants’ comments that relate to the spreading of digital technologies, which result in changes in customer behaviour and their demands towards digital technology trends. IC includes the participants’ opinions on the increase in the intensity of competition in the business environment and the changes of business trends toward digital transformation.
As shown in the above comments and in Fig 4, six of the ten participants mentioned the potential benefits of digital technologies in improving business internally in terms of increasing the ease of work, reducing complexity and time-savings in operational practices, enhancing communication and collaboration amongst employees and fostering better decision-making at the executive level. Also, the participants believe that digital technologies enable businesses to generate new value creations in terms of creating new digital business models to gain more revenue, adding new digital marketing channels and generating new digital payment channels.
In discussing CCD sub-category, 90% of the participants remarked that the changes in customer demands and behaviour are due to the spreading of digital technologies, the internet and mobile devices in particular; interest or preference to digital channels and platforms in comparison to physical channels.
Figure 4: Reasons why digital transformation is important for businesses in Thailand 4.0 era.
An evaluation of the IC sub-category show that half of the interviewees agree with the view that analogue businesses that resist digital transformation are continuing to lose their revenues and market shares to competitors as there are increasing number of businesses in this century who have already changed or transformed into digital businesses and serve customer demands better than the analogue businesses. These participants also suggested that adopting digital transformation is the way for analogue businesses to survive and compete with others.
The findings on the degree of the importance of transforming a business from analogue to digital for businesses in Thailand 4.0 era show very strong opinions from the participants. An exploration of the participants’ opinions/ comments show that the comments are broadly around customer demands and ability to remain sustainable in this digitization age, which highlights ‘Internet of Things’ and ‘mobile technologies’ as the main technologies that channel customer behaviour and demands towards digital platforms in comparison to analogue platforms. This can further be seen in recent research, which shows that the two technologies (internet of things and mobile technologies) are indeed changing the customer demands and behaviour [10; 11].
As demonstrated earlier, the degree of the importance associated with digital transformation is also channeled towards the ‘Opportunity to Grow’, which particularly highlights benefit of digital technologies for internal improvement and value creations. In addition, a recent study shows that digital technologies enable enormous opportunities for value creation and performance improvement to businesses in all industries [27]. Given that the participants are digital transformation providers or IT solution providers who implement IT or digital transformation projects to businesses in various industries in Thailand, the benefits of digital technologies that bring opportunities for businesses to grow in business practice can be seen in their comments, example:
“You can see from the success story of Kasikorn bank that they are the first bank in Thailand that started mobile banking application and they are getting a lot of customers from it” (P2).
The participant further added:
“People switching to open accounts with them because they want to have convenient experience in doing transactions online that can save a lot of time compare to going to bank branch and wait in the queue. Many banks tried to do the same but Kasikorn bank is still number 1 in Thailand because they moved first…” (P2).
Similarly, another participant stated:
“Even cafés and restaurants around my office are already changed, many of them allow customers to pay money using their mobile phone instead of paying by cash only and from my observation” (P4).
The participant further accentuated:
“…those businesses who adjusted themselves to the changes and the trend of digital technologies are getting more money and more customers and the one who resist to change keep losing their customers and their profit because they are no longer support what customer want.” (P4)
Correspondingly, another interviewee commented:
“For example, WorkPoint is a large entertainment enterprise who succeed in shifting from Digital Terrestrial TV channel that has main revenue stream from broadcast entertainment contents on television to be through online channels… They gain numerous customers from various continents around the world and gain much more revenue according to the bold change that they made” (P10).
4.2. Key Factors for Successful Implementation of Digital Transformation
With respect to key factors that contribute to the successful adoption of digital transformation, findings from the interviews identified eight themes grouped under three sub-categories which include ‘Business Resources’(BR), ‘Business Competencies’(BC), and ‘Executives’ Vision’(EV) as shown in Fig 5.
Figure 5: Key factors for the successful implementation of digital transformation.
With respect to Business Resources, half of the participants remarked that in order to succeed in implementing digital transformation, sufficient business resources are required. These participants particularly emphasized the relevance of human resources and stated that employees in the organization need to have enough knowledge and skills for digital technologies and digital transformation in order to efficiently follow the company's digital transformation vision, framework, and strategy.
With respect to Business Competencies, comments from 30% of the interviewees suggest that a business needs a clear insight on its core competencies and business model to determine whether their business model and competencies are consistent with emerging technologies or not. This will then help them decide what technology to adopt, and which area of the business will benefit most with the implementation of digital transformation.
In discussing Executives’ Vision, nine of ten participants elucidated that the board of directors’ vision is an important factor that determines the success or the failure of businesses in adopting digital transformation. These participants stated that individuals at the executive level must have “sufficient knowledge and understanding in digital transformation, digital technologies and its trends” as well as foresee the changes in customer demands and behaviour in order to drive appropriate digital transformation vision, framework, and strategy for the whole organization.
As demonstrated in the findings, leaders’ knowledge and understanding towards digital transformation, digital technologies and trends as well as customer demands and behaviour (Figure 5), drive the vision that determines success in the implementation of digital transformation. Thus, one of the interviewees stated:
“Those successful businesses understand…these changes and even foreseen on what they might want in the future…they foreseen that customer trend in spending money in Thailand is changing toward e-money or contactless payment. Thus, the company generated a digital business model for e-money trend and launched the mobile application just in time.” (P3).
On the contrary, an unfocussed or wrong vision in digital transformation implementation, possibly due to lack of knowledge and understanding on digital transformation at management/ executive level, could lead to failure in the business as noted by one participant:
“…They thought that the current trend of customer demand is everything included… but it isn’t the same when it comes to when they consume things through their mobile devices.” (P10).
The participant further added:
“The application mainly provides customer to do banking transactions but provide other features like explore on new movies and music charts because they thought that act like one stop service that include everything in one application will make them gain more customers. Instead, people complain a lot on the application… too many garbage features that they don’t want for mobile banking application.” (P10).
4.2.1. Strategies for Successful Implementation of Digital Transformation
The study outcomes reveal several digital transformation strategies that make businesses in Thailand successful in implementing digital transformation as well as the recommended strategies that analogue businesses should pursue based on the participants’ perspectives. The two main themes identified as findings from this study as successful implementation strategies for digital transformation were mentioned by 80% of the participants; the participants’ comments are broadly categorized as ‘Executive Empowerment’ coded as ExE and ‘Employee Empowerment’ coded as EE. As shown in Fig 6, other successful strategies or recommended strategies highlighted by the participants were categorized into five themes including: ‘Balance Investment’(BI), ‘Risk Taking’(RT), ‘Agility’(AG), ‘Study from others’(SO), and ‘Core Competencies Focus’(CCF).
Figure 6: Strategies for the successful implementation of digital transformation.
With respect to ExE sub-category, nine of the ten participants remarked that from their experiences in implementing digital transformation in medium and large enterprises in Thailand, successful enterprises started with either having a Chief Innovation Officer /Chief Digital Officer who has innovative thinking and in-depth knowledge in digital transformation and emerging technologies or partner with IT expertise companies to empower IT knowledge of individuals in the executive level to foster insights in both the IT and the business aspects before deciding to drive forward with the digital transformation vision and framework for the companies. These interviewees further highlighted that executive empowerment should be the first strategy that businesses should pursue because the company’s vision and framework are the main factors that determine the success or failure of the company in developing digital transformation.
Specifically, executives who have digital maturity or IT experts who have in-depth knowledge in technologies are highlighted in the participants’ comments as being vital in the pursuit and right implementation of the vision of digital transformation:
“…not realized the…real advantages of the transformation make those executives generate the wrong vision and framework for their company. And if you start with the wrong things, how can you expect the right result…” (P7).
“Because digital transformation starts from top to bottom. Start with the right people or the right person at the top level will make the organization have the right vision and the right framework.” (P9).
With regards to EE sub-category, eight of ten interviewees stated that knowledge of employees in the lower levels or positions in the company is also important. They accentuated that employee empowerment throughout the entire organization can be facilitated by training them to have sufficient knowledge and skills in adopting digital technologies; the participants also added that having clear communication in the company vision and framework is needed for efficient digital transformation.
Additional strategies, which may seem understated were uncovered in the findings as shown in figure 6. Below are the some of the participants’ corresponding comments:
“Like an example of banking industry that I'm focusing on for several years… I would say agility is the strategy that make them succeed.” (P4).
“…if think in terms of Big data technology only, I would say 100% of my clients are successful… Employee empowerment in terms of skills, knowledge to be ready…are the main strategies of those who succeed.” (P3).
4.2.2. Way Forward for the Successful Implementation of Digital Transformation: A Conceptual Framework
In view of the purpose of this study, which is to identify the factors, strategies, and framework that make businesses succeed in implementing digital transformation, nine of the ten participants stated that a single business framework cannot be defined as the fundamental elements such as business model, operation model, and business resources of each company are different, thus, each business needs to define a unique framework that is suitable in consideration of their operational models and resources. However, analyses from this study identified themes, which were subsequently used to define a conceptual framework (Fig 7) aimed at making businesses succeed in implementing digital transformation. Three themes of the conceptual framework include ‘Change for Getting Better’ (CGB), ‘Think Out of the Box’(TOB), and ‘Not Afraid to Fail’(NAF). In discussing CGB theme, all the participants mentioned that the act of ‘thinking’ in the direction for change towards digital transformation is a fundamental practice for businesses who are successful in the implementation of digital transformation. The interviewees also emphasized that the ‘change for better’ practice should be promoted throughout the whole organization in order to make people in the organization move forward in the same direction.
Figure 7: Conceptual Framework for the successful implementation of digital transformation.
With respect to the NAF theme, 40% of the participants remarked that risk taking or not being afraid to fail is the main concept that the businesses who succeed in implementing digital transformation had when they tried to integrate emerging technologies into their businesses through digital transformation projects. In addition, the participants stressed that those businesses learned from their failures and kept trying until they achieved success with digital transformation.
The two participants who mentioned the TOB theme stated that the businesses who succeed in the implementation of digital transformation think beyond the scope of the businesses’ fundamental elements and consequently generate new value creations over their competitors.
The conceptual framework is consonant with the key factors and the strategies required for the successful implementation of digital transformation, which can be seen from some of the participants’ comments:
“I think it is…‘Change for better things’… Such companies realised the trend of digital technologies and customer demands as well as understand the potential benefits of adopting emerging technologies. They are not afraid to explore or try to invest in new technologies.” (P8).
“…makes them have innovative thinking and not stop trying to integrate emerging technologies into their businesses because technologies are developing, and it will be many more technologies that can make them better than the current position” (P9).
5. Conclusion and Recommendations
This study was aimed at exploring the reasons why digital transformation is critical for businesses in this century, especially in Thailand 4.0 era, as well as finding out the key factors, strategies, concepts and current practice that make businesses successful in implementing digital transformation. This study makes a contribution to this research area by providing insights on the experiences of digital transformation/IT solution providers of a large IT provider enterprise in Thailand, in terms of investigating their viewpoints toward digital transformation.
The findings and discussions presented in this study show that digital transformation is important for businesses in Thailand 4.0 era and show three reasons why it is important which include digital technologies bring opportunity to grow, the changes in customer demands and behaviour, and the increase of competition in business environment. The outcomes resulted in several recommendations to businesses in Thailand 4.0 era, which are summarized below:
• To successfully transform a business from analogue to digital, the business should pay close attention to its three key factors which are Executives’ Vision, Business Resources, and Business Competencies and determine whether these three factors are fully prepared for adopting digital transformation
• After carefully thinking of the readiness of the above three factors, the business should then consider which of the seven strategies: Executive Empowerment, Employee Empowerment, Balance Investment, Risk Taking, Agility, Study from Other, Core Competencies Focus they should pursue with careful consideration of the readiness of the aforementioned three key factors
• Subsequently, to ensure that the chosen strategy or strategies are efficiently adopted throughout the whole organization, the business should consider which of the three concepts including Change for Getting Better, Think Out of the Box, and Not Afraid to Fail they should pursue in consideration of their chosen strategies and key factors
While the findings of this study and the highlighted recommendations contribute to businesses in terms of exploring and identifying the key factors, the strategies and the frameworks that make businesses successful in adopting digital transformation from digital transformation providers’ viewpoints, the findings create the need to further explore the same topic with a larger sample of participants from different companies. Also, the further study on the same topic under the viewpoints of the executives (insiders’ viewpoints) of the businesses in Thailand that are successful in transforming themselves from analogue to digital is needed to get a more balanced outlook; this study was conducted based on the digital transformation providers’ experience (outsiders' viewpoints).
References
[1]. Abolhassan, F.: The Drivers of Digital Transformation: Why There’s no Way around the Cloud. Springer International, Germany (2016).
[2]. Andal-Ancion, A., Cartwright, P.A., Yip, G.S.: The digital transformation of traditional business, MIT Sloan Management Review, 44, 34-41 (2003).
[3]. Berman, S.J.: Digital transformation: opportunities to create new business models, Strategy & Leadership, 40(2), 16-24 (2012).
[4]. Press, G.: A Very Short History of Digitization, Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/gilpress/2015/12/27/a-very-short-history-of-digitization/#3e4ad8d649ac, last accessed 2018/02/07 (2015).
[5]. Manyika, J., Lund, S., Bughin, J., Woetzel, J. Stamenov, K, Dhingra, D.: Digital Globalisation: The New Era of Global Flows, McKinsey Global Institute, https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/digital-mckinsey/our-insights/digital-globalization-the-new-era-of-global-flows, last accessed 2018/01/05 (2016).
[6]. Bowersox, D.J., Closs, D.J., Drayer, R.W.: The digital transformation: technology and beyond, Supply Chain Management Review, 9(1), 22-29 (2005).
[7]. Bughin, J., LaBerge, L., Mellbye, A.: The Case for Digital Reinvention, McKinsey Quarterly, https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/digital-mckinsey/our-insights/the-case-for-digital-reinvention last accessed 2018/01/17 (2017).
[8]. Anand, M.: Why the Fortune 500 is Fast Becoming the Digital 500, Cisco, https://blogs.cisco.com/news/why-the-fortune-500-is-fast-becoming-the-digital-500, last accessed 2020/12/06. (2015)
[9]. Hernandez, K., Faith, B., Prieto Martín, P., Ramalingam, B.: The Impact of Digital Technology on Economic Growth and Productivity, and its Implications for Employment and Equality: An Evidence Review (No. IDS Evidence Report; 207). IDS (2016).
[10]. EY Global Financial Services Institute: The impact of digital technology on consumer purchase behavior, The Journal of Financial Perspectives, 3(3), 1-13 (2015).
[11]. Narwal, M., Sachdeva, G.: Impact of information technology (it) on consumer purchase behavior, Researchers World, l.4, 41 (2013).
[12]. Deloitte University Press: Asia winning the race on innovation, growth and connectivity—powered by digital engagement Deloitte, https://www2.deloitte.com/insights/us/en/economy/voice-of-asia/may-2017/winning-the-race.html, last accessed 2018/01/10 (2017).
[13]. Thailand Board of Investment: Thailand 4.0 means opportunity Thailand - BOI [online]. Thailand Board of Investment, http://www.boi.go.th/upload/content/TIR_Jan_32824.pdf, last accessed 2017/12/11 (2017).
[14]. Thailand’s Government Public Relations Department: Developing the Country toward Thailand 4.0, Thailand’s Government Public Relations Department, http://thailand.prd.go.th/ewt_news.php?nid=4498&filename=index, last accessed 2017/12/08 (2016).
[15]. Royal Thai Embassy: Thailand 4.0, Royal Thai Embassy, http://thaiembdc.org/thailand-4-0-2/, last accessed 2017/12/08 (2017).
[16]. Cray, P.: The Digital Transformation of Business, Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/resources/pdfs/comm/microsoft/the_digital_transformation_of_business.pdf, last accessed 2019/05/02 (2015).
[17]. Matt, C., Hess, T., Benlian, A.: Digital transformation strategies, Business & Information Systems Engineering, 57(5), 39-343 (2015).
[18]. Bennett, N., Lemoine, G.J.: What a difference a word makes: Understanding threats to performance in a VUCA world, Business Horizons, 57(3), 311-317 (2014).
[19]. The Economist: When did globalisation start, The Economist, https://www.economist.com/blogs/freeexchange/2013/09/economic-history-1, last accessed 2018/01/04 (2013).
[20]. O'Rourke, K.H., Williamson, J.G.: When Did Globalization Begin, w7632. National Bureau of Economic Research (2000).
[21]. Murphy, J., Roser, M.: Internet: Our World in Data, https://ourworldindata.org/internet, last accessed 2018/12/15 (2017).
[22]. Capgemini Consulting: When Digital Disruption Strikes: How Can Incumbents Respond? Capgemini Consulting, https://www.capgemini.com/consulting/wp-content/uploads/sites/30/2017/07/digital_disruption_1.pdf, last accessed 2018/02/08 (2017).
[23]. Nanterme, P.: Digital disruption has only just begun, World Economic Forum, https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/01/digital-disruption-has-only-just-begun/ last accessed 201810/05 (2016).
[24]. Becerra, J.: The digital revolution is not about technology — it’s about people, World Economic Forum, https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/03/the-digital-revolution-is-not-about-technology-it-s-about-people/ last accessed 2019/03/08 (2017)
[25]. Thomas, I, Rosewell, D.: Whitepaper: The Four Essential Pillars of Digital Transformation, Fujitsu, http://www.fujitsu.com/uk/Images/White-Paper-the-four-essential-pillars-of-digital-transformation.pdf, last accessed 2018/12/07 (2017).
[26]. Hanna, N.K. (Ed.): Mastering digital transformation: Towards a smarter society, economy, city and nation, In Mastering Digital Transformation: Towards a Smarter Society, Economy, City and Nation (pp. i-xxvi). Emerald Group Publishing Limited (2016).
[27]. Rodríguez, T.: Every Business is a Digital Business (The small shop too), Accenture, https://www.accenture.com/gb-en/success-every-business-digital-business, last accessed 2018/01/10 (2018).
[28]. World Bank Group: World Development Report 2016: Digital Dividend, World Bank Group, http://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/wdr2016, last accessed 2018/12/07 (2016).
[29]. World Economic Forum: World Economic Forum White Paper Digital Transformation of Industries: Digital Enterprise, World Economic Forum, http://reports.weforum.org/digital-transformation/wp-content/blogs.dir/94/mp/files/pages/files/digital-enterprise-narrative-final-january-2016.pdf, last accessed 2018/12/08 (2016).
[30]. Rashid, B.: Digital Transformation and Innovation In Today's Business World, Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/brianrashid/2017/06/13/digital-transformation-and-innovation-in-todays-business-world/#79ea936b4905, last accessed 2018/01/22 (2017).
[31]. Libert, B., Beck, M., Wind, Y. J.: How to Navigate a Digital Transformation, Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/2016/06/how-to-navigate-a-digital-transformation, last accessed 2018/01/04 (2016).
[32]. King, H.: What is digital transformation? The Guardian, https://www.theguardian.com/media-network/media-network-blog/2013/nov/21/digital-transformation, last accessed 2019/02/01 (2013).
[33]. Kane, G.C., Palmer, D., Phillips, A.N., Kiron, D., Buckley, N.: Strategy, not technology, drives digital transformation, MIT Sloan Management Review and Deloitte University Press, 14 (2015).
[34]. Grossman, R.: The Industries That Are Being Disrupted the Most by Digital, Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/2016/03/the-industries-that-are-being-disrupted-the-most-by-digital, last accessed 2018/03/06 (2016).
[35]. Creswell, J.: Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. 3rd edn. SAGE, London (2013).
[36]. Gray, D.: Doing research in the real world. 3rd edn., SAGE, London (2014).
[37]. Clarke, V., Braun, V.: Thematic analysis, The Journal of Positive Psychology, 12(3), 297-298 (2017).
[38]. Boyatzis, R.: Transforming qualitative information: Thematic analysis and code development, SAGE, London (1998).
[39]. Vaismoradi, M., Turunen, H., Bondas, T.: Content analysis and thematic analysis: Implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study, Nursing & Health Sciences, 15(3), 398-405 (2013).
Cite this article
Nzekwe-Excel,C.;Pongvikrant,C. (2023). Is Digital Transformation Vital for Business in Thailand 4.0 Era: An Exploratory Study. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,6,354-371.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis (ICFTBA 2022), Part 2
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Abolhassan, F.: The Drivers of Digital Transformation: Why There’s no Way around the Cloud. Springer International, Germany (2016).
[2]. Andal-Ancion, A., Cartwright, P.A., Yip, G.S.: The digital transformation of traditional business, MIT Sloan Management Review, 44, 34-41 (2003).
[3]. Berman, S.J.: Digital transformation: opportunities to create new business models, Strategy & Leadership, 40(2), 16-24 (2012).
[4]. Press, G.: A Very Short History of Digitization, Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/gilpress/2015/12/27/a-very-short-history-of-digitization/#3e4ad8d649ac, last accessed 2018/02/07 (2015).
[5]. Manyika, J., Lund, S., Bughin, J., Woetzel, J. Stamenov, K, Dhingra, D.: Digital Globalisation: The New Era of Global Flows, McKinsey Global Institute, https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/digital-mckinsey/our-insights/digital-globalization-the-new-era-of-global-flows, last accessed 2018/01/05 (2016).
[6]. Bowersox, D.J., Closs, D.J., Drayer, R.W.: The digital transformation: technology and beyond, Supply Chain Management Review, 9(1), 22-29 (2005).
[7]. Bughin, J., LaBerge, L., Mellbye, A.: The Case for Digital Reinvention, McKinsey Quarterly, https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/digital-mckinsey/our-insights/the-case-for-digital-reinvention last accessed 2018/01/17 (2017).
[8]. Anand, M.: Why the Fortune 500 is Fast Becoming the Digital 500, Cisco, https://blogs.cisco.com/news/why-the-fortune-500-is-fast-becoming-the-digital-500, last accessed 2020/12/06. (2015)
[9]. Hernandez, K., Faith, B., Prieto Martín, P., Ramalingam, B.: The Impact of Digital Technology on Economic Growth and Productivity, and its Implications for Employment and Equality: An Evidence Review (No. IDS Evidence Report; 207). IDS (2016).
[10]. EY Global Financial Services Institute: The impact of digital technology on consumer purchase behavior, The Journal of Financial Perspectives, 3(3), 1-13 (2015).
[11]. Narwal, M., Sachdeva, G.: Impact of information technology (it) on consumer purchase behavior, Researchers World, l.4, 41 (2013).
[12]. Deloitte University Press: Asia winning the race on innovation, growth and connectivity—powered by digital engagement Deloitte, https://www2.deloitte.com/insights/us/en/economy/voice-of-asia/may-2017/winning-the-race.html, last accessed 2018/01/10 (2017).
[13]. Thailand Board of Investment: Thailand 4.0 means opportunity Thailand - BOI [online]. Thailand Board of Investment, http://www.boi.go.th/upload/content/TIR_Jan_32824.pdf, last accessed 2017/12/11 (2017).
[14]. Thailand’s Government Public Relations Department: Developing the Country toward Thailand 4.0, Thailand’s Government Public Relations Department, http://thailand.prd.go.th/ewt_news.php?nid=4498&filename=index, last accessed 2017/12/08 (2016).
[15]. Royal Thai Embassy: Thailand 4.0, Royal Thai Embassy, http://thaiembdc.org/thailand-4-0-2/, last accessed 2017/12/08 (2017).
[16]. Cray, P.: The Digital Transformation of Business, Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/resources/pdfs/comm/microsoft/the_digital_transformation_of_business.pdf, last accessed 2019/05/02 (2015).
[17]. Matt, C., Hess, T., Benlian, A.: Digital transformation strategies, Business & Information Systems Engineering, 57(5), 39-343 (2015).
[18]. Bennett, N., Lemoine, G.J.: What a difference a word makes: Understanding threats to performance in a VUCA world, Business Horizons, 57(3), 311-317 (2014).
[19]. The Economist: When did globalisation start, The Economist, https://www.economist.com/blogs/freeexchange/2013/09/economic-history-1, last accessed 2018/01/04 (2013).
[20]. O'Rourke, K.H., Williamson, J.G.: When Did Globalization Begin, w7632. National Bureau of Economic Research (2000).
[21]. Murphy, J., Roser, M.: Internet: Our World in Data, https://ourworldindata.org/internet, last accessed 2018/12/15 (2017).
[22]. Capgemini Consulting: When Digital Disruption Strikes: How Can Incumbents Respond? Capgemini Consulting, https://www.capgemini.com/consulting/wp-content/uploads/sites/30/2017/07/digital_disruption_1.pdf, last accessed 2018/02/08 (2017).
[23]. Nanterme, P.: Digital disruption has only just begun, World Economic Forum, https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/01/digital-disruption-has-only-just-begun/ last accessed 201810/05 (2016).
[24]. Becerra, J.: The digital revolution is not about technology — it’s about people, World Economic Forum, https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/03/the-digital-revolution-is-not-about-technology-it-s-about-people/ last accessed 2019/03/08 (2017)
[25]. Thomas, I, Rosewell, D.: Whitepaper: The Four Essential Pillars of Digital Transformation, Fujitsu, http://www.fujitsu.com/uk/Images/White-Paper-the-four-essential-pillars-of-digital-transformation.pdf, last accessed 2018/12/07 (2017).
[26]. Hanna, N.K. (Ed.): Mastering digital transformation: Towards a smarter society, economy, city and nation, In Mastering Digital Transformation: Towards a Smarter Society, Economy, City and Nation (pp. i-xxvi). Emerald Group Publishing Limited (2016).
[27]. Rodríguez, T.: Every Business is a Digital Business (The small shop too), Accenture, https://www.accenture.com/gb-en/success-every-business-digital-business, last accessed 2018/01/10 (2018).
[28]. World Bank Group: World Development Report 2016: Digital Dividend, World Bank Group, http://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/wdr2016, last accessed 2018/12/07 (2016).
[29]. World Economic Forum: World Economic Forum White Paper Digital Transformation of Industries: Digital Enterprise, World Economic Forum, http://reports.weforum.org/digital-transformation/wp-content/blogs.dir/94/mp/files/pages/files/digital-enterprise-narrative-final-january-2016.pdf, last accessed 2018/12/08 (2016).
[30]. Rashid, B.: Digital Transformation and Innovation In Today's Business World, Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/brianrashid/2017/06/13/digital-transformation-and-innovation-in-todays-business-world/#79ea936b4905, last accessed 2018/01/22 (2017).
[31]. Libert, B., Beck, M., Wind, Y. J.: How to Navigate a Digital Transformation, Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/2016/06/how-to-navigate-a-digital-transformation, last accessed 2018/01/04 (2016).
[32]. King, H.: What is digital transformation? The Guardian, https://www.theguardian.com/media-network/media-network-blog/2013/nov/21/digital-transformation, last accessed 2019/02/01 (2013).
[33]. Kane, G.C., Palmer, D., Phillips, A.N., Kiron, D., Buckley, N.: Strategy, not technology, drives digital transformation, MIT Sloan Management Review and Deloitte University Press, 14 (2015).
[34]. Grossman, R.: The Industries That Are Being Disrupted the Most by Digital, Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/2016/03/the-industries-that-are-being-disrupted-the-most-by-digital, last accessed 2018/03/06 (2016).
[35]. Creswell, J.: Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. 3rd edn. SAGE, London (2013).
[36]. Gray, D.: Doing research in the real world. 3rd edn., SAGE, London (2014).
[37]. Clarke, V., Braun, V.: Thematic analysis, The Journal of Positive Psychology, 12(3), 297-298 (2017).
[38]. Boyatzis, R.: Transforming qualitative information: Thematic analysis and code development, SAGE, London (1998).
[39]. Vaismoradi, M., Turunen, H., Bondas, T.: Content analysis and thematic analysis: Implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study, Nursing & Health Sciences, 15(3), 398-405 (2013).









