

Volume 214
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2025 Symposium: Resilient Business Strategies in Global Markets
In the era of rapid globalization and accelerating digital transformation, understanding how external openness interacts with domestic digital development has become a pressing research question. Drawing on panel data from 29 Chinese provinces covering 2012-2022, this study examines the influence of opening-up on the development of the digital economy from the perspective of policy support, using a panel threshold effect model. The empirical results indicate three key findings: (1) opening-up exerts a significant negative impact on digital economy growth; (2) fiscal expenditure on science and technology acts as the sole threshold variable in this relationship—once such spending surpasses the identified threshold, the adverse effect of opening-up is markedly alleviated; (3) notable regional disparities exist, with strong negative effects observed in the eastern, western, and northeastern regions, while the impact in central China is statistically insignificant. These findings offer practical insights for optimizing the spatial layout of opening-up and refining policy support frameworks to foster high-quality development of the digital economy.

 View pdf
View pdf


The ongoing digital transformation is accelerating the thorough incorporation of digital technologies into the economy, society, and education. As a result, entrepreneurial activities among university students are profoundly impacted by emerging technologies and business models, thus presenting both new opportunities and challenges. In this context, the paper explores university students’ digital entrepreneurship to analyze the opportunities and challenges posed by digitalization and to investigate methods for improving entrepreneurial capabilities and management approaches. By reviewing and analyzing relevant literature and examining typical cases, the study summarizes replicable management experiences and strategies. The results demonstrate that university students can utilize digital technologies to boost team management and resource allocation in their entrepreneurial ventures, yet they also encounter challenges such as limited experience, deficiencies in technical and business knowledge, and compliance risks. Accordingly, this paper proposes strategies to enhance entrepreneurial capabilities, strengthen external support, and foster technological integration, offering guidance for university entrepreneurship education and practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study examines the distinct impacts of greenfield investment and cross-border mergers and acquisitions (M&A) on host countries’ economic growth through case-study approach. Focusing on sectoral differences, it finds that greenfield investment is more effective in manufacturing industries, where it drives capital formation, employment, and technology transfer. In contrast, cross-border M&A better supports service-sector growth by transferring managerial expertise, organizational knowledge, and access to international networks. The case studies also reveal regional patterns: Southeast Asian countries depend heavily on greenfield manufacturing investments, whereas Latin American economies increasingly rely on M&A-service synergies. These findings suggest that FDI strategies should be tailored to national priorities—developing economies focusing on industrialization should attract greenfield investment, while service-oriented and advanced economies should adopt regulatory frameworks to maximize knowledge-intensive M&A benefits.

 View pdf
View pdf


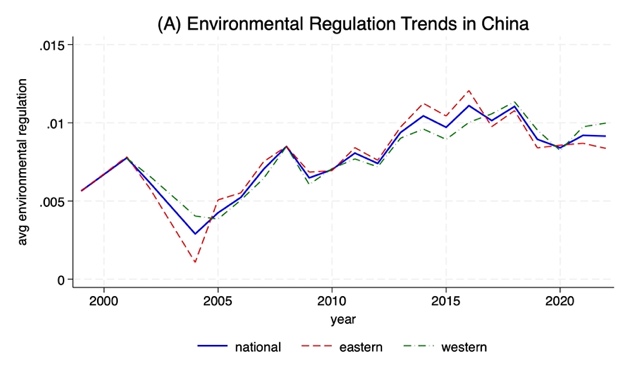
This study investigates the impact of environmental regulation on housing prices in China from 1999 to 2023. Using the empirical method, we find that stricter environmental regulations can lead to a significant rise in real estate prices, and this positive correlation is significant at 1% level for several specifications of the regression model. Theoretically, green policies appear to influence the housing market by improving property quality, while simultaneously reducing the local labor supply and raising construction costs, thereby altering market demand and supply. Regionally, the higher-priced housing markets in eastern China are less sensitive to these regulatory costs, whereas the lower-priced markets in the west exhibit a stronger positive price response. These findings offer a more thorough assessment of environmental legislation and important insights for policymakers aiming to balance sustainable development with housing affordability. Furthermore, the paper proposes differentiated regulations that can be adopted in response to local housing market conditions.

 View pdf
View pdf


Behavioral biases, such as overconfidence, loss aversion, confirmation bias, and anchoring, significantly distort individual decision-making processes. These biases lead to suboptimal portfolio performance, characterized by excessive trading, delayed loss realization, and inefficient information processing. At the market level, these biases aggregate into systemic anomalies like herding, overreaction, and momentum effects. These anomalies undermine market efficiency due to limits to arbitrage and the influence of noise trader sentiment. This paper examines the profound impact of behavioral biases on both investor performance and market efficiency, challenging the traditional financial theories that assume market rationality. Empirical evidence reveals significant negative impacts on investor returns and prolonged mispricing durations. These findings highlight the necessity for a multidisciplinary approach that integrates cognitive psychology and financial economics to better understand and address these pervasive issues in financial markets. By bridging these disciplines, this research aims to provide actionable insights for portfolio management and regulatory design, ultimately enhancing market efficiency and investor outcomes.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the ESG investment wave, capital markets are highly concerned about corporate environmental performance. However, this creates a significant paradox with the increasingly covert and technological upgrading of corporate "greenwashing" behavior. This paper takes non-financial listed companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share markets in China from 2014 to 2023 as samples, constructs indicators of greenwashing and patient capital, and combines empirical methods such as the two-way fixed effects model to deeply explore the impact of patient capital on corporate greenwashing and its mechanism of action. The study found that patient capital can effectively curb corporate greenwashing behavior. The action pathways mainly include correcting the short-termism tendencies of management, enhancing the degree of green innovation of enterprises, and improving the transparency of information. Heterogeneity analysis shows that the effect varies under different financial conditions, governance structures, and institutional environments. This study reveals new mechanisms to curb corporate greenwashing from the perspective of the capital supply side, providing important theoretical and empirical evidence for investment institutions to optimize ESG strategies, enterprises to introduce long-term capital to drive real transformation, and regulators to build long-term governance mechanisms.

 View pdf
View pdf


In today's highly competitive market environment, enterprises must innovate their project management approaches to enhance core competitiveness. This paper examines the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with the application of information management cloud platforms in enterprise management innovation. Through a comprehensive analysis of these factors, the paper also explores strategic directions for future development. The study finds that the strengths of information management cloud platforms lie in enabling data-driven decision-making and automating management processes. However, their weaknesses include risks related to data security and privacy, high hidden costs, and uncertain return on investment (ROI). At the same time, these platforms are presented with opportunities stemming from rising customer expectations for digitalization and China’s leadership in digital infrastructure. Nevertheless, they also face threats such as conflicts in data sovereignty legislation and the existence of a significant digital divide.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of enterprises expanding overseas, digital transformation offers a strategic pathway for improving quality, reducing costs, and enhancing operational efficiency, thereby supporting long-term sustainable development. Drawing on panel data from A-share listed companies between 2014 and 2023, this study employs both baseline regression model and mediating effect model to examine the interplay among corporate digital transformation, ESG performance, and international expansion. The findings reveal that corporate digital transformation can significantly boost ESG performance; overseas expansion plays a crucial mediating role between digital transformation and ESG performance; and the impact of corporate digital transformation on ESG performance varies by region, industry, ownership type, and performance dimension. Manufacturing firms, non-eastern regions, and state-owned enterprises benefit more significantly, and among ESG dimensions, the effect on environmental indicators is particularly notable. Consequently, to elevate corporate ESG performance, it is necessary to strengthen the development of mechanisms for corporate digital transformation and overseas expansion, as well as enhance cooperation between regions and industries.

 View pdf
View pdf


Nowadays, sports events are becoming increasingly popular with people, and large-scale sports events are often held all over the world. This study aims to explore the role of large-scale sports events in promoting host city’s economic development, taking the FIFA world cup as an example. The research motivation stems from interest in the potential impact of sporting events on host countries' economies. This article adopts the method of literature review and collects primary and secondary materials to conduct an in-depth analysis of previous cases of holding large-scale sports events and their post-match utilization. Large-scale sports events can not only drive growth in various fields such as tourism, catering, and retail, but also enhance a city's image and popularity. However, these advantages often come with substantial financial risks, as cities may face budget overruns and underwhelming attendance. Furthermore, environmental considerations play a crucial role in shaping sustainable practices for future events. By analyzing both positive and negative outcomes, this study aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how hosting major sports events can shape the economic landscape of cities and contribute to their long-term growth.

 View pdf
View pdf




