

Volume 227
Published on October 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
Driven by the "dual-carbon" strategic goals and strong support from national policies, the scale of the new energy vehicle industry has expanded rapidly, gradually becoming an important force promoting economic transformation. However, development trends such as intensified homogeneous market competition and rapid technological iteration have led new energy vehicle enterprises to face multi-dimensional financial risks. Based on the industry status quo and the practices of typical enterprises, this paper analyzes the dimensions of financing, investment, operation, and profitability, and proposes risk response strategies, providing theoretical support for solving enterprise problems and maintaining the stable development of the industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


The research paper develops a China Climate Policy Uncertainty Index and analyzes how this uncertainty affects corporate risk behaviors. By leveraging data from publicly-traded companies in China, I've discovered that a rise in climate policy uncertainty is directly tied to more risky corporate actions. Even when I swapped out key variables, omitted outlier years, included additional control factors, adjusted for fixed effects, and introduced lagged models, this conclusion held steadfast.Continued examination shows that sustained growth in climate policy ambiguity increases corporate risk-taking due to decreased investment effectiveness and decreased credit access. Additionally, the impact is notably greater among privately held businesses, companies with significant pollution, and those reliant on substantial capital investment. This study broadens the existing research on the link between climate policy uncertainty and corporate risk-taking, offering practical insights for business strategy, government policy formulation, and regulatory oversight.

 View pdf
View pdf


Driven by the Digital China Strategy, process industries represented by the chemical industry are currently facing core propositions of safety and controllability, green and low-carbon development, and high-end breakthroughs. Through new-generation information technologies such as the industrial internet and artificial intelligence (AI), digital transformation reconstructs the entire R&D-production-service chain, serving as a key path to address the "bottleneck" dilemma. Taking Wanhua Chemical as a case study, this paper explores the specific path of its digital transformation and evaluates the transformation effect from both financial and non-financial dimensions, aiming to provide practical experience for the digital transformation of chemical enterprises. The study finds that Wanhua Chemical has carried out digital transformation at three levels—foundation, application, and ecology—achieving improvements in financial performance such as operational capacity and growth capacity, while also benefiting from non-financial aspects including organizational structure, R&D innovation, and green and low-carbon development.

 View pdf
View pdf


The coordinated advancement of the digital economy and rural economic resilience is a new dynamic engine for high-quality rural and agricultural development. To quantitatively evaluate the degree of coordinated development between the digital economy and rural economic resilience, this paper selects provincial panel data from 10 Chinese provinces for 2016–2023, and constructs an indicator system for the digital economy that reflects digital infrastructure and industrial digitalization, as well as a chained economic-resilience evaluation system reflecting “resistance–adaptation–transformation.” Indicator weights are determined comprehensively using the entropy-weight method. Based on a coupling-coordination-degree model, a comparative analysis is then conducted on the coupling-coordination types of urban digital economy and ecological resilience across 30 provinces nationwide. The study finds that: in terms of temporal evolution, the coupling-coordination degree of the provinces has grown steadily, although many provinces remain in a state of disequilibrium; overall the development trend is positive. Spatially, the coupling-coordination degree exhibits an “east-high, west-low; south-high, north-low” pattern. By 2023, most regions were in a coordinated state.

 View pdf
View pdf


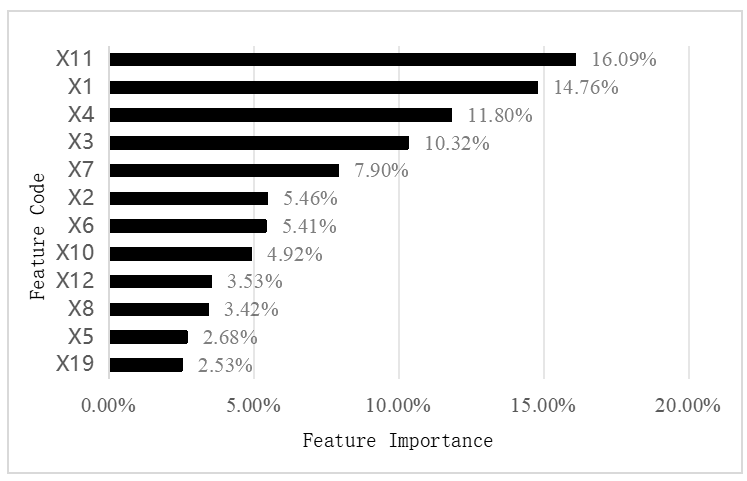
Aiming at the problem that traditional default early warning models have insufficient discriminative power and robustness under the scenario of strong correlation among high-dimensional indicators and unbalanced samples, this study proposes a serial fusion model integrating Random Forest (RF) and Back Propagation (BP) Neural Network. First, RF is used for feature selection: the minimum sufficient feature set is screened out based on the criterion of cumulative contribution ≥ 90%, which corresponds to the input layer nodes of the BP Neural Network. Subsequently, the BP Neural Network is applied to perform nonlinear fitting on the selected features. During the training phase, ADASYN (Adaptive Synthetic Sampling Approach) oversampling is only implemented on the training set to balance samples while preventing information leakage. The model is trained and evaluated using samples from the wholesale and retail industry, and its early warning effect is verified by predicting the default probability of Gome Electrical Appliances. The results show that the RF-BP model has strong early warning capability for small to medium-sized samples and can issue risk early warning signals in advance.

 View pdf
View pdf


Under the impetus of global carbon neutrality goals, quality management in the new energy vehicle (NEV) battery supply chain has become a central focus of national policy agendas. This study systematically analyzes policy documents and industry data from China, the European Union, and the United States between 2015 and 2024, with emphasis on three aspects. First, regarding differences in policy instruments: China’s mandatory coding and traceability system (GB/T34014) has reduced defect recall rates by 32%; the EU’s market-oriented carbon footprint labeling scheme under the New Battery Regulation increased compliance costs by 15% but reduced accident rates by 28%; and U.S. state-level legislation (e.g., California’s AB-2832) requiring ESG disclosure has influenced corporate quality practices. Second, concerning the dilemma of lagging standards: emerging technologies such as fast charging and solid-state batteries lack internationally unified standards, compelling firms to establish independent testing systems at a 40% higher cost (with CATL as a case example). Third, in terms of policy synergy and innovation: Guangdong Province’s traceability platform enables cross-departmental sharing of full life-cycle battery data, raising the efficiency of dispute resolution by 60%. This study advances three recommendations: (1) establish a dynamic standards framework combining “basic national standards” with “technical consortium standards”; (2) implement a dual-carbon assessment system for battery supply chain quality; and (3) strengthen mutual recognition of China–EU policies. The findings provide theoretical support for constructing a global governance framework for battery quality.

 View pdf
View pdf




