

Volume 244
Published on November 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2025 Symposium: Strategic Human Capital Management in the Era of AI
This paper examines the strategic dynamics of soybean trade between the United States and China through a static Nash Equilibrium (NE) framework. Using data from 2008 to 2023 on trade volumes and world soybean prices, we estimate a multivariate regression linking global prices to the import and export behavior of major countries. The estimated elasticities show that China’s imports significantly raise world prices, while U.S. exports exert a strong downward pressure. Based on these relationships, we construct a payoff matrix and identify the equilibrium strategies of both nations. The model predicts that, absent strategic motives, China would import a low volume while the U.S. would export heavily—contradicting observed behavior. To reconcile this gap, we introduce a “strategic benefit” term for China, reflecting food security, forest protection, and long-term supply stability. Incorporating this factor shifts the NE to one consistent with reality: China maintains high imports while the U.S. limits exports. The results highlight that global agricultural trade cannot be explained by price mechanisms alone; strategic and policy considerations play a decisive role. Our findings underscore the importance of integrating security-oriented objectives into economic models of international commodity trade.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study investigates how ownership—proxied by listing status—shapes firms’ choices of internationalization strategy, the efficiency of execution, and longer-run outcomes. Focusing on Chinese firms operating under the “dual-circulation” policy setting, we argue that public and private firms face distinct combinations of governance arrangements, resource endowments, and institutional constraints. These differences produce systematic variation in entry modes, pacing, and performance of international expansion. Board characteristics—size, composition, and directors’ backgrounds—offer additional explanatory power for this heterogeneity. Based on these mechanisms, we derive three policy-relevant implications: expand cross-border financing options for non-listed firms to ease capacity and timing constraints; refine evaluation frameworks for state-owned enterprises so that internationalization is assessed on strategic fit and learning outcomes rather than scale alone; and encourage listed firms to commit to longer-horizon internationalization roadmaps to reduce short-termism. Conceptually, the paper places “listing status” as a central institutional variable in the analysis of internationalization and shows that equity structure moderates the interaction between internationalization and innovation.

 View pdf
View pdf


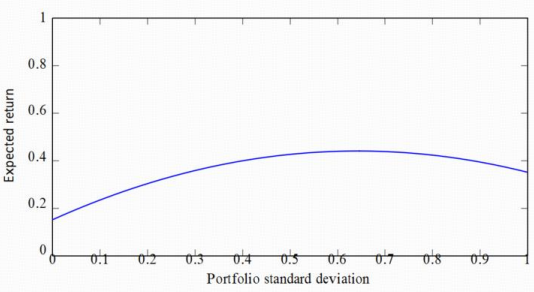
Modern economies confront pervasive uncertainty from stochastic demand, volatile prices, heterogeneous preferences, and incomplete information. Probability theory provides a coherent language and tools to quantify and manage such uncertainty across investment, forecasting, insurance, and consumer analytics. This study synthesizes foundational probability concepts with economic decision problems, develops a unifying framework that integrates expected value, variance, and Bayesian updating with portfolio selection and risk control, and demonstrates the approach through case analyses in tourism demand planning and insurance pricing. Methodologically, the paper combines conceptual modeling, stylized numerical examples, and references to empirical practices in the literature. The results suggest that (i) expected-value-based rules are necessary yet insufficient without explicit variance and tail-risk considerations; (ii) probability-guided forecasting improves allocation and inventory choices; and (iii) transparent probability models enhance consumer-behavior inference, pricing, and resilience under uncertainty. Its contribution is to provide an analytically feasible blueprint with tables and diagrams for the application of probability to economic management problems and to highlight research gaps related to model uncertainty and non-ergodicity.

 View pdf
View pdf


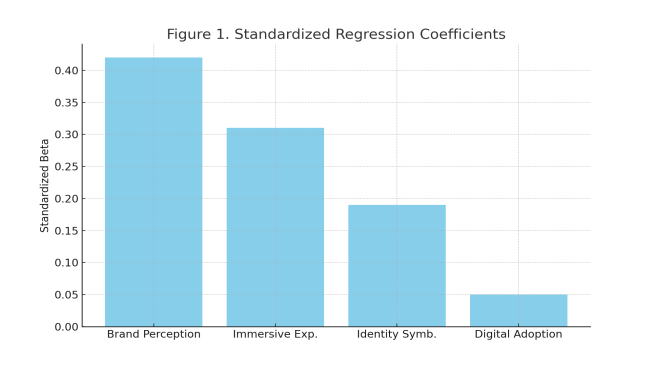
The rise of the metaverse has provided luxury brands with a brand-new immersive digital marketing approach. However, there are still relatively few empirical studies on the impact of metaverse marketing on consumers' brand preferences for luxury brands, especially a lack of case studies taking Gucci as an example. This study takes Gucci as a case study, focusing on the digital marketing strategies of luxury brands in the context of the metaverse, and explores how the new experiences provided by the metaverse, such as virtual interaction, immersion, and digital scarcity, can integrate with the traditional attractions of luxury goods (such as vanity satisfaction, identity recognition, and aesthetic experience), jointly influencing consumers' brand preferences and loyalty. This study employs quantitative research methods and collects data through structured questionnaires to verify the impact of metaverse digital marketing strategies on Gucci brand preferences. The research results show that the virtual interaction, immersion and digital scarcity in the metaverse digital marketing strategy have significantly enhanced consumers' sense of identity and satisfaction of vanity towards the Gucci brand, thereby increasing brand preference and loyalty.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the digital-native era, collectible toys such as Pop Mart’s Labubu have gained tremendous popularity. However, limited studies explore how celebrity influence and short-form videos create explosive market phenomena, especially in Chinese brands exporting culturally resonant IPs. This study investigates the Labubu phenomenon, focusing on its role in Pop Mart’s growth through celebrity endorsements, online virality, and hype-driven sales. Using a mixed-methods approach, combining qualitative case study analysis of viral content and endorsements with quantitative data review of sales figures and social media metrics from 2024-2025, the study draws on industry reports and academic literature. Findings show that Labubu generated $670 million in H1 2025, accounting for 34.7% of Pop Mart's revenue, with profits increasing by 396.5%. This growth is attributed to scarcity tactics and social proof. The study highlights the risks of overconsumption and suggests that brands balance hype with sustainability to ensure long-term viability.

 View pdf
View pdf


As the organizational environment becomes increasingly complex, leaders often need to deal with paradoxical demands in their management practices. Paradoxical leadership behavior (PLB) is a new type of leadership behavior that aims to enhance leadership effectiveness by simultaneously resolving and integrating the paradoxical demands of the organization and its employees. This study conducted a systematic review and synthesis of the relevant research on PLB. First, this study reviewed the definition and measurement scales of PLB. Second, this study has systematically reviewed the main theoretical perspectives of the PLB research. Furthermore, this study has reviewed the research results on the antecedents and the impacts of PLB. The research on the impacts of PLB covers the impacts at the individual, team and organizational levels. Finally, this study has proposed the future directions for the PLB research, such as further exploring its antecedent variables, investigating the impacts of PLB at the team and organizational levels, and exploring its influence on leaders themselves.

 View pdf
View pdf




