1. Introduction
Research has shown as the difficulty of math increases, students often experience heightened pressure, anxiety, and feelings of failure, which can erode their self-efficacy, form learning difficulties, and gradually diminish their interest in learning math [1,2]. This negative emotional cycle not only affects current academic performance but can also hinder long-term mathematical skill development. Therefore, it is crucial to explore methods to enhance both interest and effectiveness in math learning. Game-based learning (GBL), which incorporates game elements into education, has emerged as a promising approach to improving student motivation and learning experiences. Research has shown that games can positively impact cognitive development, attitudes toward learning, and emotional well-being, leading to the development of numerous educational games to enhance math learning [3]. However, many studies focus on the design of standalone digital games, neglecting the integration of both online and offline gaming experiences. This limitation restricts the broader application and effectiveness of game-based learning in real educational settings. In the classroom, relying solely on digital games may not fully meet students' diverse learning needs and often lacks alignment with offline teaching activities. This research aims to address this gap by exploring innovative ways to combine the strengths of digital and non-digital games, creating a hybrid game-based learning model that integrates both online and offline game activities. The goal is to maximize the potential of games in promoting mathematics learning in students' daily lives.
2. Game-based Learning and Learning Science
2.1. Game-based Learning
Games, characterized by structured rules and competitive activities aimed at specific goals, differ from playfulness, which is more free-form, improvisational, and often involves a spontaneous or even "chaotic" recombination of behaviors and meanings. Games are also defined as a complex genre of learning environments [4]. Due to the immense appeal of games, researchers have begun to focus on purposes other than pure entertainment such as education, training, health, and management. Different concepts such as serious games, gamification, and game-based learning were proposed by researchers. Deterding systematically investigates the industry origins of “Gamification” in relation to precursors and similar concepts. It concluded that"Gamification" is the use of game design elements in non-game contexts [5]. Plass differentiates Gamification and game-based learning. Games with boring activities but game elements such as stars, badges, and leaderboards may be divided into gamification, while game-based learning means redesigning the activities, using artificial conflict and rules of play [4]. Game-based learning is also a type of gameplay with specific learning outcomes [6].
2.2. Learning Game Design Elements and Models
There is no doubt that games are positive to learning, but what elements selected and what degree of design complexity can contribute to meaningful learning should be figured out. Many educational games fail to engage students and only provide repetitive practice and stress memorization [7,8]. Many scholars have categorized game elements and discussed the structures and models in game design. Jabbar considered the effects of game elements on players and categorized the elements into Motivational elements (Usefulness), Interactive elements (interaction), Fun elements (Playfulness), and Multimedia elements (Attractiveness) [9]. Others categorized the game elements into three primary dimensions (game mechanism, game fantasy, and game value) and seven secondary dimensions [10]. Plass discussed the theoretical foundation of game-based learning and emphasized key elements such as game mechanics, visual aesthetic design, narrative design, musical score, incentive systems, and content and skills. There are a lot of models like the GBL design model [10], the MDA framework (Mechanics, Dynamics, and Aesthetics) [11], and the integrated design framework [4]. The classification of game elements typically revolves around several core dimensions, interface, and sensory design (how players are experienced), gameplay mechanic design (how games are built), and user experience design (how players experience).
2.3. Learning Science
Learning science is an interdisciplinary field (psychology, neuroscience, education, computer science, and so on) that studies how people learn and how to design effective learning environments. Game-based learning should be guided by general learning principles improving retention, and understanding, and making meaningful learning occur. In the paper, we focus on multiple representations and scaffolding.
As the brain matures, human numerical cognition undergoes continuous refinement, evolving from an approximate sense of numbers to the precise manipulation and comprehension of quantities through the use of language and Arabic numerals. The triple-code theory posits that students must not only acquire proficiency in different representational systems but also develop the ability to seamlessly translate between them [12]. Games provide students with an external representation thereby offering an enhanced understanding of numerical concepts and operations [13].
Scaffolding is derived from Vygotsky's concept of the "Zone of Proximal Development" (ZPD), which describes the gap between what a learner can do independently and what they can achieve with guidance. Providing learning support on GBL is a type of value-added approach for scaffolding [14]. Cognitive support involves breaking down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable steps, providing illustrative examples, and offering visual aids such as diagrams and charts. Metacognitive support encourages students to reflect on their learning processes, develop effective problem-solving strategies, and monitor their progress. Motivational support aims to maintain student engagement and motivation through positive reinforcement, encouragement, and the adaptation of tasks to align with students' interests and skill levels. Adaptive scaffolding in games offers personalized learning experiences by adjusting challenges to align with the learner's current skill level. This tailored approach ensures that learners receive the appropriate scaffolding required for gradual skill development, building their confidence and ensuring steady progress [4].
3. Game-based Learning in Math Learning
3.1. Effects of Game-Based Learning for Mathematics
Mathematics abstracts quantitative relationships and spatial forms from the real world. Therefore, learning mathematics requires developing the ability to think abstractly and have strong logical thinking abilities. Mathematical knowledge is highly systematic and cumulative, with earlier knowledge often forming the foundation for later content, thus a lot of practice is needed. Making the process of math learning easier and more engaging is very important. The effects of game-based learning for math can be divided into two aspects: cognitive domain and affective domain.
Educational math games were identified as an appealing strategy to promote mathematic achievements. Research shows games have a positive effect on developing strategic and reasoning abilities and flexible and adaptive mathematical skills. Besides games, they can also improve geometry skills, problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity.
Affective affordances in games, such as engaging narratives, interactive elements, and rewarding experiences, evoke positive emotions, reducing anxiety and fostering a supportive learning environment. It is said when a player is so involved in gameplay that the sense of time is lost [15], this is called game flow which indicates learners' immersion degree [16]. Games can have an influence on students' motivation, beliefs, and attitudes towards mathematics and teaching [17]. We should also remain vigilant about the potential negative impacts of game-based learning. Poorly Designed Games can lead to risks such as distractions, superficial learning, and short-term motivation with overreliance on external incentives.
3.2. Categories of Math Games
Games designed for learning mathematics exhibit remarkable diversity and innovation across various dimensions, including gameplay, technology, and player scale. Within the broad field of math learning games, they can be categorized by gameplay type. Role-playing games (RPGs) like Math Kingdom Adventures have players take on heroic roles in a fantasy kingdom, solving math problems such as arithmetic challenges to progress through the narrative. Action-adventure games (AAVs) like Geometry Dash: Math Edition integrate geometric concepts into fast-paced, precision-based gameplay, allowing players to learn geometry while enjoying an adrenaline-filled experience. Simulation games (SIMs) like Math City Builder require players to use mathematical skills to manage city layouts and resource allocation, fostering a thriving math-based metropolis. Strategy games (SLGs) such as Number Battlefields challenge players to use strategic thinking and mathematical calculations to lead armies to victory on the battlefield.
From a technological perspective, these games range from traditional analog games to modern PC and console platforms. Classic math learning analog games like Math Bingo are widely popular in homes and classrooms due to their simple rules and engaging design, while modern technology has breathed new life into math learning games. For example, Algebra Touch is a math learning app specifically designed for touch-screen devices, allowing players to experience math learning interactively at their fingertips [18]. Regarding player scale, games can be single-player or multiplayer. Single-player games such as Math Quest Solo offer individual challenges that help players improve their math skills through independent problem-solving. On the other hand, multiplayer online games like Math Team Challenge promote teamwork by encouraging players to solve complex math problems together, enjoying the shared success of collaborative problem-solving.
Role-playing games offer distinct advantages when used for game-based learning for math [19]. They immerse students in imaginative and exploration virtual worlds, significantly enhancing engagement. Additionally, the rich storylines and varied challenges in RPGs encourage sustained involvement in math learning. Role-playing games with rich scenarios can make students more engaged and interested in math learning. However, students complain digital games may be too hard and complicated in the classroom and usually hard to access [15]. Conversely, tabletop analog games provide unique benefits due to their intuitive design and cost-effectiveness. The allure of tabletop analog games lies in their tangible nature and face-to-face interaction. By offering physical, tangible tools such as game boards, cards, and blocks, analog games allow students to directly interact with math concepts, making abstract ideas more concrete. Their low dependence on technology and reusability makes them easily integrated into regular classroom learning, broadening access to math games for a larger number of students.
4. The Systematic Game Design for Mathematics: A Case of Fraction
Elementary mathematics is a crucial component of basic education. The concept of fractions plays an indispensable role in understanding the continuity and indivisibility of numbers, making fraction learning a milestone in the development of students' numerical cognition and number sense. Research has shown that proficiency in fractions has a significant impact on students' future mathematical achievement. However, students face several challenges when learning fractions. First, while whole numbers are represented linearly with a single number, the meaning of fractions is multifaceted. For example, fractions can be defined as the ratio between a whole and its parts, where concepts such as area, segmented lines, and discrete objects can represent the "part-whole" relationship. Fractions can also be viewed as the result of division; in which case the fraction signifies a quotient. The measurement interpretation of fractions also positions them as points on a continuous number line, requiring students to shift from a natural number framework to a rational number framework, thereby expanding their understanding of numbers. Second, there are misconceptions about understanding the whole. For instance, 1/4 can represent dividing 1 into 4 equal parts and taking 1 of those parts, or it can represent 5 out of 20. Third, when comparing the sizes of fractions, larger numbers do not necessarily imply larger fractions. In fraction multiplication, the product does not always increase, and in fraction division, the quotient does not necessarily decrease. Fourth, students encounter difficulties in understanding fraction division, particularly as the strategies employed for division differ when the denominators are the same versus when they are different.
As Figure 1 shows, this study designed a game design model that combined the advantages of both digital and analog games. The learning strategies adopted are deeply rooted in both constructivist and cognitivist educational theories. The games are set in a series of rich scenarios, such as running a farm, planning a party, and managing a store. Different and interesting external representations will be designed according to the triple-code theory. Students can learn about fractions through various representations and models, applying the knowledge they have gained to solve problems and experience how mathematics is widely used in real-life situations. Detailed design is shown below.
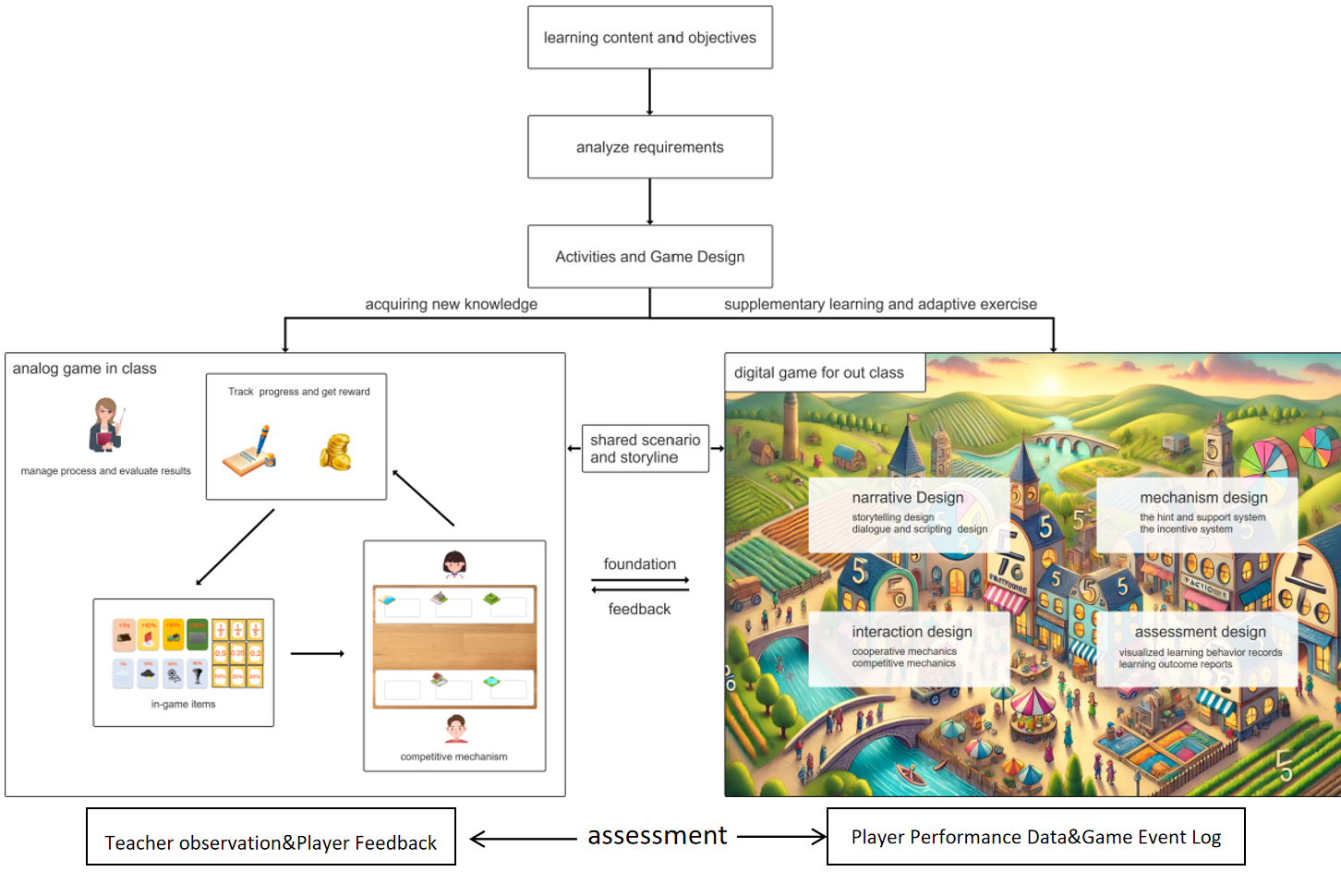
Figure 1: Design model combined digital and analog games
4.1. Learning Content and Objectives
For declarative knowledge, Students will understand that a fraction represents a part of a whole and can be used to describe parts of a group or a quantity. This concept is often linked to students' experiences with dividing objects. Students also need to understand the measurement interpretation and be able to identify and explain the roles of the numerator (top number) and denominator (bottom number) in a fraction. For procedural knowledge, students are required to develop proficiency in skills such as comparing and ordering fractions, identifying and simplifying equivalent fractions, and performing operations including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions.
4.2. Analyze Requirements
Students have already learned the concepts of place value, the decimal scale, and the operations with whole numbers, but their understanding remains at the stage of natural numbers. They do not yet have a clear grasp of the meaning and operations of fractions. Their logical thinking skills are gradually maturing, but their understanding of abstract mathematical concepts still requires the use of intuitive representations. Students are assigned math homework to reinforce their understanding of the content, but they show low interest in math exercises. Computers and the internet are accessed in the classroom, but students are familiar with technology and have access to touchscreen devices such as tablets or smartphones, which they primarily use for entertainment. The target learners for this educational module are upper elementary students who exhibit a low level of interest in learning math. These learners are often unengaging and struggling when dealing with numbers and algebra.
4.3. Activities and Game Design
The game takes place in a small town called Fractionville, a magical and wise place where residents use fractions to manage every aspect of their lives—from planting crops to hosting celebrations. However, one day, the town's only mathematician, the Fraction Sage, mysteriously disappears. As the Sage vanishes, the knowledge of fractions begins to fade from the townspeople's memories, plunging the town into chaos. The daily activities of the town fall into disarray. The player takes on the role of an outsider who accidentally arrives in Fractionville. As the only person who still remembers the basics of fractions, the player is tasked with restoring order to the town. By learning and mastering more advanced fraction concepts, the player must help the townspeople solve their problems and eventually uncover the mystery behind Sage's disappearance, restoring peace and prosperity to the town.
Chapter 1: The Chaotic Farm: The town's farmers are in desperate need of help because they don't know how to evenly distribute seeds and fertilizer. The player will learn the basics of fractions (such as 1/2, 1/4, etc.) and help the farmers plant crops in different plots proportionately. In this mission, the player will assist in distributing land, watering crops, and calculating feed portions for animals to ensure the farm runs smoothly.
Chapter 2: Party Troubles: The town's mayor is hosting the annual town celebration, but the party is on the verge of failure because no one knows how to divide cakes and drinks. The player must learn fraction addition and subtraction to help the mayor slice the cakes evenly and calculate drink portions so that every townsperson gets their fair share. The player will apply fractions in real-life scenarios of food and drink distribution.
Chapter 3: Managing the Store: The local shopkeeper is unable to calculate discounts, leading to chaotic transactions. The player will use fraction multiplication and division to help the store calculate discounts, manage inventory, and adjust prices using fractions. For example, there are different zones; Drink Mixing Area where students need to follow customer requests, properly allocate the ingredients, and calculate the final ratio using fractions. Food Preparation Area where students must proportion the ingredients correctly based on recipes, calculating the right amounts to make pastries or other dishes. Students also need to adjust the price of the drinks or dishes to run the store successfully. In this mission, the player will develop their fraction skills further by simulating business operations and exercising logical thinking.
Chapter 4: Repairing the Bridge: One of the town's bridges has broken down due to old age, and the craftsmen can't figure out how to evenly distribute the materials needed for repairs. The player must master more complex fraction operations to help the craftsmen calculate the right proportions of materials to restore the bridge and reestablish transportation. The player will learn how to distribute, split, and combine fractions in this task, enhancing their arithmetic abilities.
Chapter 5: Uncovering the Mystery: After completing various tasks around the town, the player gradually discovers that the Fraction Sage's disappearance was no accident. By unlocking a series of clues, the player finds out that the Sage is trapped in an ancient, mysterious library within the town. To unlock the Sage's room, the player must apply all the fraction knowledge they've learned to solve the ultimate puzzle. In this final chapter, the player will integrate all of their previously learned fraction skills to complete math challenges and rescue the Sage, restoring peace to Fractionville.
4.4. Game Mechanics
The Hint and support system: The Hint System aims to give the players more support and scaffolding deeply rooted in constructivist principles when students feel confused and struggling in the activities. There are two parts to the hint system, first is the tour guidance in which students can get the strategies or methods and solutions. Second is a real-time feedback system such as visual Cues and automatic error correction by the NPC. If the player answers incorrectly, the NPC will engage with the player and guide them toward the correct thinking. By engaging learners in this reflective practice, the system encourages them to internalize and personalize their learning. The hint system is designed to foster resilience and persistence even when learners face challenges.
The incentive system: By learning and mastering math knowledge, players get more skills and functional tools which can help players unlock new levels of games and more abilities, in-game items, and currency, advancing the storyline as players progress. Players can also invite others to form teams to solve puzzles in cooperative missions or compete with others via a leaderboard system. We also introduce periodic challenges or tournaments, where top-ranking players receive extra rewards. For the cooperative mechanics, Players can either enjoy the game via split-screen on the same device or team up online. Each character has complementary tasks. For example, one player conducts geometric analysis on a math problem, while another player completes the algebraic calculation task. Both players must work together to progress. It's impossible to play the game solo, making teamwork crucial. For the competitive mechanics(1V1) players compete against each other with the goal of achieving victory, often based on skill, strategy, or quick reflexes. Students need to master proficient fraction operation skills and problem-solving strategies, and by competing in speed and accuracy, they can achieve success in the game.
4.5. Implementation and Evaluation
Lastly, the assessment mechanic is seamlessly integrated into the gameplay, automatically analyzing players' learning outcomes and providing continuous feedback on the learner's progress. These assessments are designed to be non-intrusive, all of which help learners track their progress and identify areas for improvement. Besides the game will generate a visual learning report for players according to player performance records and game event log, helping them understand their mastery of the knowledge. For classroom assessment, both teacher observations and peer feedback will contribute to the evaluation process. The final assessment will combine the two parts.
5. Conclusion
This study highlights the critical role that games play in enhancing mathematics education. Both digital and analog games are shown to stimulate interest, sustain engagement, and promote effective learning. The design model proposed offers a structured approach for integrating games into both online and offline math learning environments, providing a balance between educational learning in class and out of class. A game case for learning fractions was designed based on this model. The proposed design model may need further validation through large-scale empirical studies to assess its effectiveness in different educational contexts. Future research could explore the long-term impact of the model on student learning outcomes, and investigate its adaptability across diverse subject areas and age groups. Additionally, qualitative studies involving student and teacher experiences could provide deeper insights into the model's strengths and areas for improvement.
References
[1]. Yamani, M., Almala, A., Elbedour, S., Woodson, K., & Reed, G. (2018). Math anxiety: Trends, issues, and challenges. Journal of Psychology and Clinical Psychiatry, 9(1), 00503.
[2]. Hoffman, B. (2010). “I think I can, but I'm afraid to try”: The role of self-efficacy beliefs and mathematics anxiety in mathematics problem-solving efficiency. Learning and individual differences, 20(3), 276-283.
[3]. Hui, H. B., & Mahmud, M. S. (2023). Influence of game-based learning in mathematics education on the student's cognitive and affective domain: A systematic review. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1105806.
[4]. Plass, J. L., Homer, B. D., & Kinzer, C. K. (2015). Foundations of game-based learning. Educational psychologist, 50(4), 258-283.
[5]. Deterding, S., Khaled, R., Nacke, L.E., and Dixon, D. (2011). Gamification: toward a definition. In CHI 2011 gamification workshop proceedings Vancouver, BC, Canada: ACM.
[6]. Shaffer, D. W., Squire, K. R., Halverson, R., & Gee, J. P. (2005). Video games and the future of learning. Phi delta kappan, 87(2), 105-111.
[7]. Villalta, M., Gajardo, I., Nussbaum, M., Andreu, J. J., Echeverría, A., & Plass, J. L. (2011). Design guidelines for classroom multiplayer presential games (CMPG). Computers & Education, 57(3), 2039-2053.
[8]. Young, M. F., Slota, S., Cutter, A. B., Jalette, G., Mullin, G., Lai, B., et al. (2012). Our princess is in another castle: a review of trends in serious gaming for education. Review of Educational Research, 82, 61-89.
[9]. Abdul Jabbar, A. I., & Felicia, P. (2015). Gameplay engagement and learning in game-based learning: A systematic review. Review of educational research, 85(4), 740-779.
[10]. Shi, Y. R., & Shih, J. L. (2015). Game factors and game‐based learning design model. International Journal of Computer Games Technology, 2015(1), 549684.
[11]. Hunicke, R., LeBlanc, M., & Zubek, R. (2004, July). MDA: A formal approach to game design and game research. In Proceedings of the AAAI Workshop on Challenges in Game AI, 4(01), p. 1722).
[12]. Dehaene, S., & Cohen, L. (1995). Towards an anatomical and functional model of number processing. Mathematical Cognition, 1,83–120.
[13]. Mulligan, J. T., & Mitchelmore, M. C. (2013). Early awareness of mathematical patterns and structure. Reconceptualizing early mathematics learning, 29-45.
[14]. Chen, C. H., & Law, V. (2016). Scaffolding individual and collaborative game-based learning in learning performance and intrinsic motivation. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 1201-1212.
[15]. Squire, K. (2005). Changing the game: What happens when video games enter the classroom? Innovate: Journal of online education, 1(6).
[16]. Hou, H. T., & Keng, S. H. (2021). A dual-scaffolding framework integrating peer-scaffolding and cognitive scaffolding for an augmented reality-based educational board game: An analysis of learners' collective flow state and collaborative learning behavioral patterns. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 59(3), 547–573. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633120969409
[17]. Chen, Z. H., Liao, C. C., Cheng, H. N., Yeh, C. Y., & Chan, T. W. (2012). Influence of game quests on pupils' enjoyment and goal-pursuing in math learning. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 15(2), 317-327.
[18]. Ottmar, E., Landy, D., Weitnauer, E., & Goldstone, R. (2015). Graspable mathematics: Using perceptual learning technology to discover algebraic notation. In Integrating touch-enabled and mobile devices into contemporary mathematics education (pp. 24-48). IGI Global.
[19]. Wan Ahmad, W. F., Shafie, A., & A Latif, M. H. A. (2010). Role-playing game-based learning in mathematics. The Electronic Journal of Mathematics and Technology. 4(02):184-196.
Cite this article
Zhang,L. (2024). The Design of Game-based Learning for Elementary Mathematic Based on Learning Science Perspective. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,74,66-73.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICILLP 2024 Workshop: Today's College Students and Faculty: How AI is Transforming Their Behaviors, Legally
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Yamani, M., Almala, A., Elbedour, S., Woodson, K., & Reed, G. (2018). Math anxiety: Trends, issues, and challenges. Journal of Psychology and Clinical Psychiatry, 9(1), 00503.
[2]. Hoffman, B. (2010). “I think I can, but I'm afraid to try”: The role of self-efficacy beliefs and mathematics anxiety in mathematics problem-solving efficiency. Learning and individual differences, 20(3), 276-283.
[3]. Hui, H. B., & Mahmud, M. S. (2023). Influence of game-based learning in mathematics education on the student's cognitive and affective domain: A systematic review. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1105806.
[4]. Plass, J. L., Homer, B. D., & Kinzer, C. K. (2015). Foundations of game-based learning. Educational psychologist, 50(4), 258-283.
[5]. Deterding, S., Khaled, R., Nacke, L.E., and Dixon, D. (2011). Gamification: toward a definition. In CHI 2011 gamification workshop proceedings Vancouver, BC, Canada: ACM.
[6]. Shaffer, D. W., Squire, K. R., Halverson, R., & Gee, J. P. (2005). Video games and the future of learning. Phi delta kappan, 87(2), 105-111.
[7]. Villalta, M., Gajardo, I., Nussbaum, M., Andreu, J. J., Echeverría, A., & Plass, J. L. (2011). Design guidelines for classroom multiplayer presential games (CMPG). Computers & Education, 57(3), 2039-2053.
[8]. Young, M. F., Slota, S., Cutter, A. B., Jalette, G., Mullin, G., Lai, B., et al. (2012). Our princess is in another castle: a review of trends in serious gaming for education. Review of Educational Research, 82, 61-89.
[9]. Abdul Jabbar, A. I., & Felicia, P. (2015). Gameplay engagement and learning in game-based learning: A systematic review. Review of educational research, 85(4), 740-779.
[10]. Shi, Y. R., & Shih, J. L. (2015). Game factors and game‐based learning design model. International Journal of Computer Games Technology, 2015(1), 549684.
[11]. Hunicke, R., LeBlanc, M., & Zubek, R. (2004, July). MDA: A formal approach to game design and game research. In Proceedings of the AAAI Workshop on Challenges in Game AI, 4(01), p. 1722).
[12]. Dehaene, S., & Cohen, L. (1995). Towards an anatomical and functional model of number processing. Mathematical Cognition, 1,83–120.
[13]. Mulligan, J. T., & Mitchelmore, M. C. (2013). Early awareness of mathematical patterns and structure. Reconceptualizing early mathematics learning, 29-45.
[14]. Chen, C. H., & Law, V. (2016). Scaffolding individual and collaborative game-based learning in learning performance and intrinsic motivation. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 1201-1212.
[15]. Squire, K. (2005). Changing the game: What happens when video games enter the classroom? Innovate: Journal of online education, 1(6).
[16]. Hou, H. T., & Keng, S. H. (2021). A dual-scaffolding framework integrating peer-scaffolding and cognitive scaffolding for an augmented reality-based educational board game: An analysis of learners' collective flow state and collaborative learning behavioral patterns. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 59(3), 547–573. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633120969409
[17]. Chen, Z. H., Liao, C. C., Cheng, H. N., Yeh, C. Y., & Chan, T. W. (2012). Influence of game quests on pupils' enjoyment and goal-pursuing in math learning. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 15(2), 317-327.
[18]. Ottmar, E., Landy, D., Weitnauer, E., & Goldstone, R. (2015). Graspable mathematics: Using perceptual learning technology to discover algebraic notation. In Integrating touch-enabled and mobile devices into contemporary mathematics education (pp. 24-48). IGI Global.
[19]. Wan Ahmad, W. F., Shafie, A., & A Latif, M. H. A. (2010). Role-playing game-based learning in mathematics. The Electronic Journal of Mathematics and Technology. 4(02):184-196.









