

Volume 100
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEIPI 2025 Symposium: Understanding Religious Identity in Educational Contexts

Campus place spirit is the core carrier that nourishes campus cultural identity and emotional connection. Its essence lies in using spatial design and cultural symbols to make teachers and students feel a sense of direction, identity and belonging. This paper takes the campus landscape of Jiaqing style in Jimei University, Xiamen City, Fujian Province, China as the research object, and based on the theory of place spirit, explores how the Jiaqing architectural complex constructs a unique campus cultural field from the three dimensions of historical context, regional characteristics and spatial functions. The research finds that the Jiaqing style buildings, relying on the design language of combining Chinese and Western elements, the adoption of traditional materials from southern Fujian, and the integration of function and aesthetics, not only inherit Chen Jiaqing's concept of "education for national rejuvenation", but also achieve the contemporary relevance of place spirit through modern technological innovation. This study provides theoretical support and practical reference directions for the cultural inheritance and innovative design of university campus landscapes.

 View pdf
View pdf


The sharing economy optimizes resource allocation through internet technologies and offers new opportunities for traditional agricultural development. This paper focuses on the "sharing + platform agriculture" business model by examining the shared fishpond project in Village W. It analyzes the mechanisms of agricultural supply-demand integration and social interaction under the trend of urban-rural integration. By establishing interest-based virtual communities, the shared fishpond model efficiently integrates urban and rural resources, creating a closed loop from production to sales. This model overcomes the bottlenecks of traditional agricultural production and distribution and innovates social relations between urban and rural communities. It broadens agricultural product sales channels, increases farmers’ income, and promotes rural revitalization. Despite its significant value in enhancing urban-rural development and reshaping social relations, the model still faces practical challenges such as poor management, low levels of digitalization, and insufficient infrastructure. Institutional innovation and technological support are urgently needed to foster sustainable development.

 View pdf
View pdf


In an era of evolving educational concepts, the critical importance of early childhood language development, and advancing kindergarten curriculum reforms, exploring how to apply cognitive development theories to young children's Chinese language teaching not only enriches the theoretical system of early childhood education and promotes interdisciplinary integration between psychology and education but also helps teachers optimize educational methods based on children's cognitive characteristics and language development laws, providing direction for innovative educational practices and addressing traditional educational drawbacks. This paper, grounded in Piaget's theory of cognitive development stages and Vygotsky's "Zone of Proximal Development " theory, focuses on their applications in young children's Chinese language teaching. Using a systematic literature review, it examines the research status and practical progress of these theories in early childhood language education. The study aims to provide new path references for the scientific and personalized development of young children's Chinese language teaching, exploring teaching design, classroom interaction, language practice, and evaluation feedback in conjunction with current hot topics in early childhood language education, such as core literacy cultivation and gamified teaching. The study reveals that cognitive development theories have abundant achievements in kindergarten language education, with numerous practices showing that their rational application—through teaching methods, environmental design, and other approaches—can significantly enhance children's language learning effects and capabilities.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, the growing disconnect between traditional education and labor market demands has become increasingly evident. Conventional classroom teaching methods are no longer adequate to meet the needs of modern talent development. As a result, project-based learning, a new teaching mode distinct from traditional classroom teaching, has received extensive attention in the education field. Based on the constructivist learning theory and the mastery learning theory, this paper employs a literature review to conduct an in-depth analysis of two "interdisciplinary - project-based" cases in junior high school mathematics teaching. It also explores their implementation status, main characteristics and existing problems. This research reveals that project-based learning can effectively promote the integration of interdisciplinary knowledge, enhance students' mathematical literacy, autonomous learning ability and comprehensive practical ability. However, it also faces practical difficulties such as a shortage of teachers, large individual differences among students and limited hardware facilities. Furthermore, the current evaluation mechanism is mainly based on mutual evaluation between teachers and students, lacking diversity and scientificity. Meanwhile, issues such as procedural design and unreasonable time arrangement in task design are noted.

 View pdf
View pdf


Anxiety in language interaction has long been a challenge in second language learning. Learners who experience high levels of anxiety often avoid real-time communication, missing valuable opportunities to practice. Fortunately, digital tools—such as online forums, AI chatbots, and avatar systems—now offer low-pressure environments by allowing learners to respond at their own pace. This study investigates how these tools enhance language skills while addressing ethical concerns, such as overdependence on technology.Key findings reveal that interactions through avatars reduce stress-related brain activity by 28% and boost participation rates by 58% . However, heavy reliance on AI tools comes with a cost: learners’ ability to internalize grammar rules declines by 5.3% monthly. To address these challenges, the study emphasizes balancing technology with ethical guidelines. For example, platforms designed to respect cultural norms—like adapting interfaces for learners from collectivist societies—can foster inclusivity. Collaboration between educators, technologists, and neuroscientists is also critical to creating supportive learning environments.This research ultimately charts a path forward: embracing tools that let learners set their own pace—empowering their growth while safeguarding their unique identities and cultural roots. By balancing innovation with ethical grounding, People can ensure technology acts as a supportive partner in language learning, keeping the warmth of human connection alive behind screens rather than letting sterile algorithms dictate how people connect.

 View pdf
View pdf


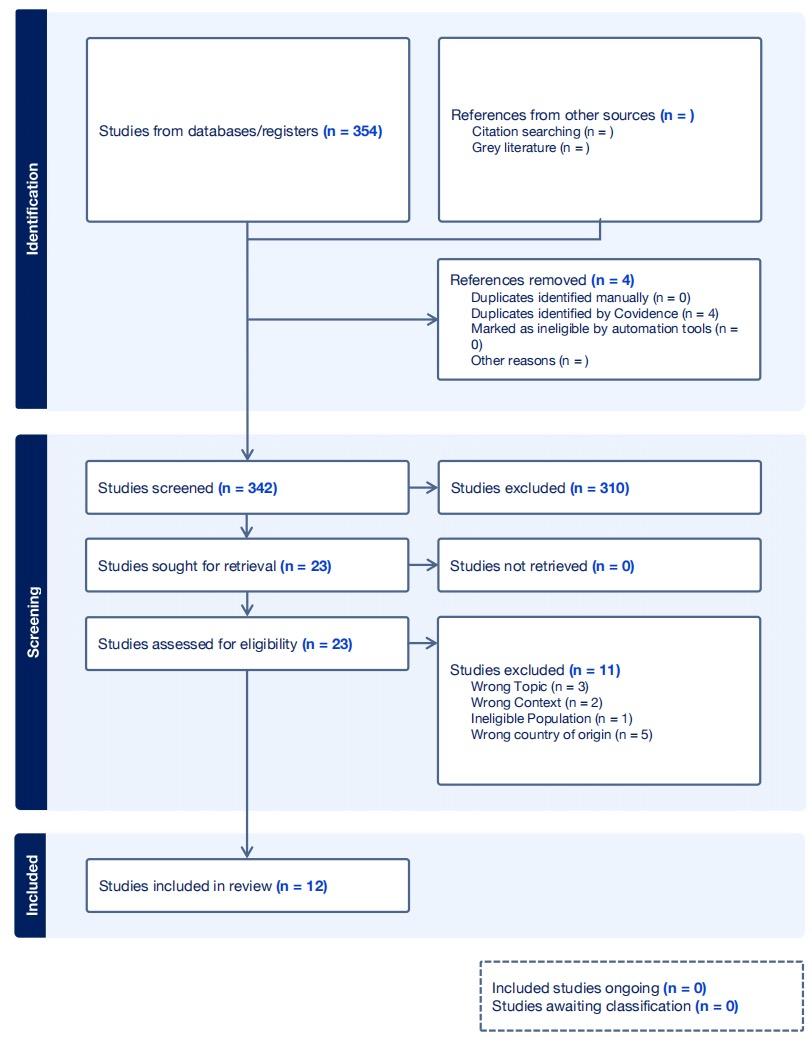
This systematic review evaluates how contemporary research on educational achievement engages with the broader discussion of socioeconomic inequality in the United States, highlighting the impact of individual family background and socioeconomic status upon shaping their educational trajectories with inequality. Therefore, by analyzing 329 academic research studies, 12 of them provide us a clear understanding of the causal relationship between educational achievement and socioeconomic status, with deeper interconnections of specific mediating and moderating variables that are derived from different levels of institutional forces, situationally affecting students’ performance, especially in college admissions. Through the lens of ecological system theory, we are better able to classify those factors and precisely apply them to the discussion of the causal mechanism, and the results offer important information for future research.

 View pdf
View pdf


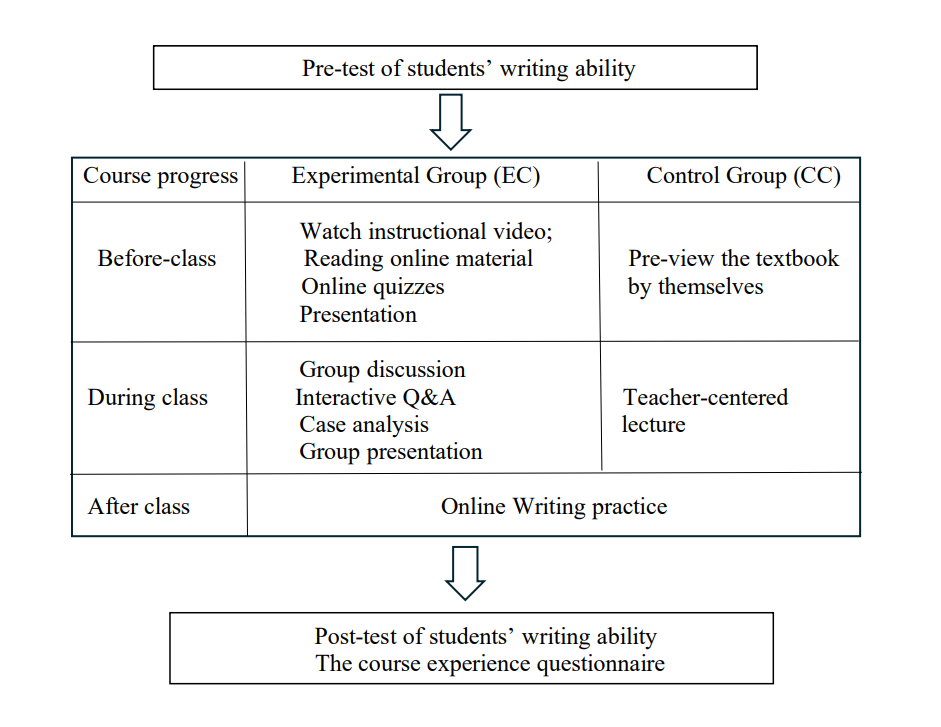
With the popularity of technology aiding teaching, the blended teaching mode is one of the easiest ways to implement at first, which can also cultivate students’ independent thinking ability and critical thinking ability. In order to know whether blended teaching mode have a positive effect on improving students’ writing skill and how it realize the effect, especially for EFL learners, this article attempted to analyze the course experience questionnaire scores using descriptive statistics and independent sample t-tests in order to determine whether students' writing outcomes had improved and received a higher average score than conventional ones under the mode of blended teaching by altering their perception of the course from six scales. According to the final results, compared to traditional teaching mode, it has been proved that blended teaching mode can improve students’ writing ability by letting students have clear goals, independent thinking ability, and good teaching, while a heavy workload given by the teacher damages the good impression of the course to some extent in the EFL learning background.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study explores how social media(SM) affects language anxiety in English as a foreign language (EFL) learners. In recent years, SM was widely used in language learning, and its influence on learning anxiety (LA) has aroused extensive interest from scholars. This research focuses on the application of SL in second language learning, as well as its dual effect on LA. This article used the method of literature review, selecting and analysing 17 high-quality literatures published in the past 10 years from Google Scholar and the Web of Science database. The study found that the use of SL can alleviate EFL's foreign language anxiety (FLA) and improved their language skills to a certain extent. However, excessive use of SL may aggravate anxiety and foster their perfectionism tendency. The relationship between SL and LA is complex, which requires comprehension from different aspects. This study has refined the theoretical framework of second language learning, which offered guidence to educational practice. Future researches are supposed to concentrate on the influence of factors such as individual differences and cultural background, and formulate strategies to maximize the positive impact of SM.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article explores the application of gamified teaching in Chinese English education and its positive impacts on students' learning motivation, language application ability, and core literacy. In the context of globalization, English proficiency is crucial for Chinese students. However, traditional exam - oriented education often leaves them lacking in practical language use, and there is also the issue of uneven distribution of educational resources in China. As an emerging model, gamified teaching transforms the learning process by incorporating elements like feedback, challenges, points, rewards, leaderboards, and levels. It creates an experience that combines fun and challenge, effectively sparking students' interest and enhancing their classroom participation and motivation to learn. Gamification in education, through interactive tasks and activities, exposes students to new vocabulary repeatedly across various scenarios for better memory and association. Its immediate feedback mechanism boosts students' sense of achievement and learning motivation, promotes teacher-student interaction, and enlivens the learning process. Moreover, this approach encourages student interaction and collaboration, fostering teamwork and competition. To complete tasks or earn rewards, students must communicate and work together, enhancing their social skills and creating a positive learning environment. This article highlights the importance of teacher training and school technical support. Teachers should undergo systematic training to master designing and implementing gamification in education. Schools must offer technical support for gamified teaching tools. Challenges like urban-rural resource disparities exist. The paper suggests improvements for wider student benefits. Future research can explore its application in different settings and its role in education.

 View pdf
View pdf


The field of education is now being more attentive to the emotions of learners when studying foreign languages, more emotions besides anxiety, boredom, and enjoyment have been gradually discovered by researchers. The focus of this study is on the impact of anxiety, shame, and pleasure on student motivation and academic grades (AG) in Chinese high schools, and aims to help educators guide students to acquire second language from the psychological aspect. A mixture of methods was employed to obtain data from 105 students at a Chinese high school via questionnaires and AG records. The findings reveal that foreign language anxiety and shame is significantly negatively linked to students' English learning motivation (ELM) and AG. In contrast, foreign language pleasure positively influences motivation and academic outcomes. The study suggests that educators should focus on students' learning emotions towards English subjects more, and use interesting classroom activities and other measures to minimize negative emotions and increase positive emotions. In this way, those approaches can promote the generation of students' ELM and the improvement of academic performance.

 View pdf
View pdf




