

Volume 89
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Education Innovation and Psychological Insights
Music therapy has emerged as a promising intervention for enhancing the emotional regulation and social reciprocity of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), their cognitive development, and fostering good relations between them and their parents. ASD has an impact on social interaction, emotional regulation, and cognitive development, which in turn affects individuals and their families. Music therapy can deal with these challenges. It promotes emotional expression, social interaction, cognitive abilities, and parent-child cooperation, enabling families to support the overall development of the child. This literature review discusses the use of music therapy to help manage the emotions of children with autism, helping with reciprocal social interactions, building up stronger cognitive functions, and relationships within a family. It synthesizes current research findings, highlighting how music therapy creates opportunities for meaningful emotional engagement, supports the development of social skills, promotes cognitive growth, and empowers parents through family-centered interventions. Additionally, music therapy improves joint attention and imitation by improving core social and emotional development abilities. It also strengthens the cognitive skills necessary for adaptive functioning. Moreover, family members participating in music therapy sessions can better understand their child’s abilities and learn effective strategies to promote developmentally appropriate skill acquisition within the home.

 View pdf
View pdf


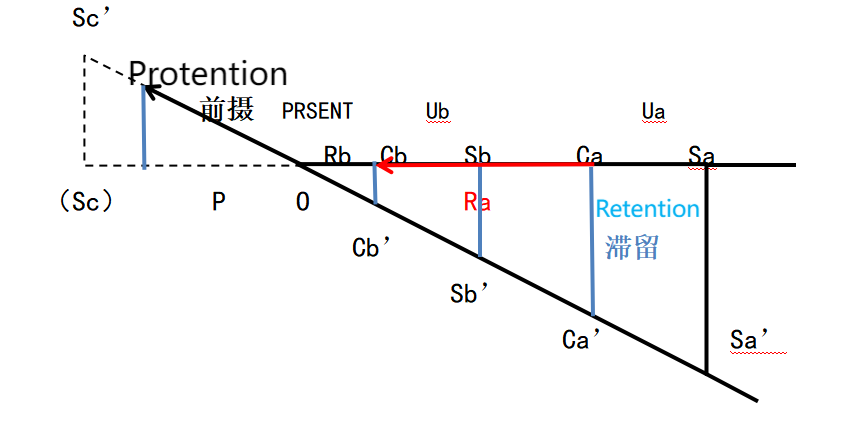
Building upon Heidegger's profound conception of time, Lacan ingeniously developed a sociologically grounded framework of 'intersubjectivity'. Notably, the key distinction between Lacanian intersubjectivity and Husserl's concept is stark. Lacanian intersubjectivity lacks the epistemological substance that is inherently present in Husserl's idea. Through a meticulous comparative analysis of Lacan's and Husserl's temporal frameworks, complemented by a detailed phenomenological reconstruction of Lacan's theory of time, this in - depth study thoroughly elucidates the application of Lacanian logical time at the microscopic epistemological scale. The paper strikingly reveals that this temporal mechanism functions independently of intersubjective interactions, vividly demonstrating how the subject attains cognitive mastery over the object by establishing its unique logical time.

 View pdf
View pdf


Artificial intelligence is important because it has the potential to influence every aspect of our daily lives. From solving problems to creating new opportunities, artificial intelligence will be a huge part of the future society. This study aims to explore Chinese high school students’ AI literacy from the four dimensions: awareness, usage, evaluation, and ethics by using the expectancy-value theory. A mixed-methods approach was employed, including surveys of 478 students to assess their understanding of artificial intelligence and how much they know about it, along with qualitative interviews to explore specific suggestions towards the improvement of AI courses in school and AI applications in their schoolwork. Quantitative findings revealed that there are significant differences in the four dimensions of AI literacy that are: ethics, awareness, usage, and evaluation with tenth grade students showing higher scores. Students’ AI literacy was influenced by their expectancy and value beliefs. There is no significant difference between school types for awareness, evaluation, usage but ethics. These findings highlight the impact of AI-related resources on students’ ethical perceptions. The structural equation modelling revealed the hypothesized model is a good representation of the data. Then the multi group equation modelling revealed the hypothesized model fits well across groups. Here, the groups mean students who participated in AI clubs or not. Qualitative themes highlighted the benefits of AI in enhancing productivity and learning, challenges in evaluating AI-generated information, ethical concerns about artificial intelligence usage, as well as the desire for more support and education to enhance AI literacy. The study emphasizes the importance of integrating AI literacy education into school curricula to enhance students' understanding and practical application of AI.

 View pdf
View pdf


In order to explore the impact of the multi-school zoning policy on the level of educational equity, this article uses a questionnaire survey to collect data on parents’ demographics, perception of the policy, its impact, satisfaction levels, and suggestions for improvement. The study finds that the multi-school zoning policy has improved the equitable allocation of educational resources to a certain extent, alleviated the pressure on popular schools, and increased the quality of education in other schools. However, there are also some problems during its implementation. For example, parents’ satisfaction with school choice is low, and some parents believe that the multi-school zoning policy does not fairly consider the interests of all students. Based on the survey results, this article puts forward some recommendations for improving the multi-school zoning policy, with the aim of further promoting educational equity.

 View pdf
View pdf


Anxiety and academic procrastination are general among university students. And experiencing anxiety has been claimed to be related to academic procrastination. This study aims to conduct a cross-sectional investigation on the relationship in college students in China. A cross-sectional study was conducted in colleges and universities in China. Anxiety symptoms were assessed using the self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) and academic procrastination was determined by procrastination assessment scale for students (PASS). Potential confounders included age, gender, major, study program, birth place, and place of residence. Participants were divided into anxiety and non- anxiety group based on SAS score. Pearson’s correlation test was used to explore association between anxiety and academic procrastination. We further performed the multivariate linear regression analysis to estimate the relationship before and after adjusting with potential confounders. A total of 523 students participated the survey and completed the questionnaire. Based on SAS threshold of 50, 258 (49.3%) subjects were classified as Non anxiety group (SAS score <50), 185 cases (35.4%) were divided into Mild anxiety group (SAS score 50-59), and 58 cases (11.1%) were divided into Moderate anxiety group (SAS score 60-69).The remaining 22 participants (4.2%) were in the Severe anxiety group (SAS score ≥ 70). Academic procrastination was positively associated with anxiety, additionally. This indicated that more anxious people went through more severe academic procrastination. The findings of this study provide evidence that anxiety is positively related to academic procrastination in college students in China. Higher levels of anxiety were linked to increased procrastination behaviors, particularly in academic tasks such as exam preparation and thesis writing.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study examines the fairness of inclusive education in vocational training, focusing on challenges faced by students with disabilities and analyzing global policies aimed at improving inclusivity. Through a comprehensive literature review, the research explores five key aspects: policy support, resource allocation, curriculum adaptation, teacher training, and employment support. Additionally, This paper introduces inclusive policies from various countries and the current state of vocational education for individuals with disabilities. While various measures, such as accessible teaching resources and vocational training programs, have been implemented, issues like unequal resource distribution, inadequate teacher preparation, and employer bias persist. To address these challenges, it suggests that teacher training should be improved, that the use of assistive technology should be broadened, and that there should be increased collaboration between educational institutions, manufacturing companies, and government agencies. The study emphasizes the need for stronger policy enforcement, interdisciplinary collaboration, and technological advancements to enhance vocational education opportunities for students with disabilities.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, the education sector is undergoing profound changes, particularly in curriculum design and educational equity. The growing use of AI, including adaptive learning platforms, intelligent tutoring systems, virtual tutors, and immersive education technologies (VR/AR), is driving personalized learning and improving the efficient use of teaching and learning resources. However, the impact of AI in education is not all positive, as it can either create new educational opportunities or exacerbate existing inequities. Through a systematic literature review, this study explores the core applications of AI in curriculum design and analyses its contribution to modern educational equity, while revealing the challenges of the digital divide, algorithmic bias, and technological thresholds that AI may bring. This study aims to provide policymakers, educators and technology developers with a comprehensive understanding of AI's dual impact on educational equity, emphasizing both its benefits and potential risks, to guide the development of policies that enhance the role of AI in promoting educational equity, while preventing it from exacerbating existing inequities.

 View pdf
View pdf


Self-regulatory fatigue has now appeared to emerge as a significant challenge in our contemporary society. This comprehensive review takes a comprehensive overview of its wide-ranging impacts on human function and performance. The analysis includes the discussions of the effects on cognition, social behavior, physical health, and achievement across various domains. Key findings have shown how differences between individuals and some contextual factors moderate fatigue severity. Neuroscience studies and advances in these days demonstrate some complex changes in brain network organization and neurotransmitter function during self-regulation fatigue states. These various insights make a suggestion on the need for sophisticated models to incorporate not only physiological but also without ignoring psychological factors. The review makes some discussions on the implications for education, workplace management, and healthcare settings. Recommendations for future research emphasize improved measurement methods and intervention development. It is crucial to understand these aspects in order to address self-regulatory fatigue in modern life.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, the application of constructivism theory in courses has grown remarkably. Given the diverse teaching conditions and the varying needs of students, teachers frequently struggle to select suitable teaching approaches. It is essential to determine how teachers can effectively apply these methods to transition to a student-centered learning environment, enabling students to genuinely master what they have learned. Thus, a comprehensive analysis of the advantages and limitations of these methods is essential for teachers to make informed decisions. This study combines literature review with case analysis to explore these aspects. The results show that firstly, the scaffolding instruction is flexible but demands much from teachers, which has limited impact on student motivation, and presents more flaws in online courses. Secondly, the anchored instruction boosts confidence and grades, yet it requires complex evaluation and specific scenarios. Finally, the random access instruction stimulates interest and independent thinking but does not lead to improved grades, lacks teacher-student interaction, and needs strict evaluation.

 View pdf
View pdf


The development of AI has energised society as a whole and higher education needs to reconsider the role of AI. This study explores the definition of AI literacy, examines its framework within Chinese universities by reviewing domestic and international literature, as well as the influencing factors and measures suggested. The study finds that, although AI literacy education has brought more opportunities to the development of higher education in China, there are still some challenges, including regional disparities, insufficiently targeted policies, and students' misuse of AI tools. In response, it is essential to foster students’ critical thinking skills and rethink traditional educational approaches in the AI era. Therefore, Chinese higher education leaders need to improve policies, optimise curricula, focus on students' personal development, and develop ethical standards to advance higher education. This review provides theoretical support for Chinese scholars and enriches the literature base at the intersection of AI and education.

 View pdf
View pdf




