1. Introduction
With the change in modern lifestyles, obesity has become a global health problem. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), as of 2022, more than 1 billion people worldwide are obese, and the data also shows that 43% of adults are overweight [1]. Obesity is closely related to the occurrence of a variety of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and some cancers, such as obesity, which can lead to metabolic disorders in the human body and cause metabolic syndrome, causing hyperlipidemia[2]; Obesity can also lead to fat accumulation in the body, abnormal lipid metabolism, and finally an increase in blood lipids, resulting in arteriosclerosis and plaque formation in blood vessels. Therefore, obesity poses a significant threat to human health. As a treasure of traditional medicine in China, traditional Chinese medicine possesses a unique theoretical system and rich treatment experience, and holds potential advantages and application value in the treatment of obesity. In contemporary China, it is of great importance to inherit, innovate, and broaden the scope of applications of TCM nutrition[3]. The topic of this paper is the dietary treatment of obesity and the role of herbal medicine and acupuncture in the treatment of obesity. In terms of research methods, the combination of literature review and case analysis of modern medical research data is mainly adopted. By reviewing the historical background of TCM principles, including the theory of Yin and Yang, the concept of qi, and the theory of blood, the perception of obesity in TCM is deeply analyzed. At the same time, combined with the specific modern medical research data, such as comparative studies for different populations, randomized controlled trials, epidemiological investigation and clinical research, etc., respectively examined the traditional Chinese medicine diet advice (whole grains, lean protein, fruits and vegetables), herbs (lotus leaf, hawthorn, Poria cocos, etc.), and the mechanism of acupuncture in the treatment of obesity and curative effect.
2. Historical Background of TCM Principles
2.1. The perspective of the Huangdi Neijing
The Yellow Emperor's Neijing divides obesity into three categories: greasy people, fatty people, and muscular people. Greasy people have a visibly fat waist, back, and abdomen (resembling a beer belly), with relatively thin buttocks and limbs. Their waist and abdomen circumference exceeds their hip circumference, resulting in a protruding belly; Fatty people have an even distribution of fat throughout their body and limbs, with soft muscles lacking strength. They are fat but not muscular, appearing loose and flabby, particularly in the chest and buttocks; Muscular people possess strong bones and muscles, compact flesh and skin, as well as dense texture. In the medical classic The Yellow Emperor's Neijing, the Su Wen: Tong Commentary on Fiction and Reality states: "Obese yellow people, the words of anointing Liang are also[4]. It means that obese and affluent people are more prone to diseases due to excessive intake of highly nutritious and calorie-dense foods. It believes that obesity is mostly caused by excessive fat eating and lack of exercise.
2.2. The doctrine of Yin and Yang
As one of the core concepts of TCM theory, the theory of yin and yang can be traced back to ancient Chinese philosophy. Zhang Jingyue, a medical scientist in the Ming Dynasty, mentioned in the Jingyue Quanshu that "there are many people who are cold, and the reason for the deficiency in the system"[5].
Qi and Yang deficiencies indicate a depletion of Yang energy in the body, resulting in disrupted production, distribution and excretion of body fluids. This ultimately leads to the formation of phlegm and dampness, contributing to obesity. Therefore, maintaining the balance and coordination of yin and yang is crucial for human health. Any imbalance in yin and yang can lead to the onset of diseases. In the context of obesity, the imbalance of yin and yang may manifest as insufficient yang qi and excessive yin qi, which affects the body's metabolism and energy balance[6].
2.3. Theories and concepts of Qi and Blood
It is widely believed that Qi, blood, and body fluid circulate or traverse through the channel system[7]. The relationship between qi and blood, as qi is considered the master of blood. It serves as the basic substance that constitutes the human body and sustains life activities, and it has a variety of functions such as propulsion, warmth, defense, and fixation[7].
Blood is considered the mother of qi in traditional Chinese medicine, and it is known to have a nourishing and moisturizing effect. The heart governs the main blood, the lungs control the main qi, while the spleen and liver are responsible for regulating blood flow. When there is an imbalance in Qi, it can lead to a deficiency in both Qi and blood, resulting in a decreased metabolic rate. This can lead to a slower breakdown of body fat, causing an accumulation of fat in the body. In TCM dietary therapy, you can promote the flow of qi and blood by eating some foods that replenish qi and activate blood, such as red dates, longan, black fungus, etc.
3. Perception of Obesity in Traditional Chinese medicine
3.1. Energy imbalance view
In the view of traditional Chinese medicine, obesity is considered a disorder of the human body. The inability to reduce it may be due to insufficient blood and qi energy in the body, leading to inadequate energy for excreting waste products. As a result, these accumulated waste products cannot be discharged and accumulate in the gaps between internal tissues of the body. With the gradual increase in the accumulation of waste, people may experience a slow weight gain. Following this logic, obesity can be seen not as an excess of energy, but rather as a deficiency of energy, as the body lacks sufficient energy to properly eliminate waste. Cells are the fundamental units of tissues in the body, and each cell independently absorbs nutrients and excretes waste. The waste excreted by the cells must be returned to the veins through the microvessels, carried by body fluids, and then filtered out of the body by the liver and kidneys. Any disruption in this process can lead to a buildup of waste between cells, initially in small amounts, which becomes suspended in tissue fluid. This accumulation can result from any malfunction at any stage of this process, preventing normal excretion of waste. In the research on energy metabolism pathways in obesity, it has been observed that obese individuals often have a lower basal metabolic rate compared to those of normal weight, and the energy expenditure is not proportional to their intake, indicating excessive caloric consumption and inadequate excretion[8]. In conclusion, a thorough understanding of energy imbalance is essential for the treatment of obesity. Implementing comprehensive measures such as dietary intervention, increased physical activity, and behavioral intervention can help to restore energy balance, achieve weight loss, and maintain a healthy weight over the long term.
3.2. Imbalance in organ function
In fact, obesity often originates from the dysfunction of the spleen and stomach. According to traditional Chinese medicine theory, the spleen and taste are closely interconnected, and a healthy spleen enables us to fully appreciate the five flavors. The Treatise on the Spleen and Stomach, an ancient medical classic of Chinese medicine, clearly points out that "the spleen is the foundation of nurture[9]. It means that the spleen and stomach play a vital role in the growth, development, and nutrient absorption of the human body. They not only convert food into nutrients to nourish the entire body but also regulate water metabolism. The spleen is responsible for processing clear substances, while the stomach processes turbid substances. When the functions of these two organs are compromised, metabolic waste cannot be effectively eliminated from the body. Over time, it can lead to the accumulation of fat throughout the body, which not only manifests externally but also reflects internal organ dysfunction. There are several factors in life that can lead to damage to the spleen and stomach, such as an irregular diet, overwork, or a long-term lack of physical activity, which can result in a deficiency of qi in the spleen and stomach. It is worth mentioning that obese people tend to prefer greasy and heavy foods, which can contribute to dampness in the body. When the spleen is deficient, its transport function becomes imbalanced, resulting in abnormal water drainage in the body and the formation of phlegm. Therefore, obese individuals often exhibit the presence of internal dampness or damp heat, which is also associated with them. TCM weight loss involves comprehensive conditioning that promotes overall body health, regulates the internal environment and balances yin and yang, adjusts disordered metabolism and endocrine systems, and normalizes the functions of the liver, spleen, and kidneys so as to achieve the goal of weight loss.
4. TCM Diet Advice and Its Impact on Weight Loss
4.1. The role of whole grains
Traditional Chinese medicine holds that whole grains have the ability to strengthen the spleen and stomach, as well as nourish the body and qi. Whole grain staples offer numerous benefits, including providing sustained energy and a strong feeling of satiety, making them particularly suitable for weight loss. In addition, whole grains are rich in dietary fiber and vitamins, which can increase bowel movements and reduce possible constipation. Furthermore, it is rich in gamma-oryzanol and B vitamins, which can improve sleep quality. A study by researchers from Tufts University in Boston monitored 3,000 people in their mid-50s.Those who ate three servings of whole grains a day had waist sizes two inches (about 5 centimeters) less than those who didn't consume the same amount, and they also had lower blood pressure and lower blood sugar levels[10].
4.2. Selection of High-quality proteins
High-quality proteins such as chicken, fish, beans, etc., are considered to have the effect of nourishing the body and replenishing righteous qi in TCM dietary recommendations. From the perspective of modern nutrition, high-quality protein is those proteins whose amino acid composition is highly consistent with the pattern in our human blood, and these amino acids can promote muscle synthesis and improve basal metabolic rate, so as to achieve the purpose of weight loss. Among the many plant-based foods, although most of the protein does not fully meet our body's needs, the soybean family, including the well-known black beans, soybeans, and green beans, is an exception, and their amino acid pattern is very similar to our blood pattern, so they are also outstanding representatives of high-quality protein. In addition, animal-derived meat, eggs, and milk are all essential sources of high-quality protein in our daily diet. With the deepening of the relationship between nutrition and health, exploring the effects of specific nutrients on body weight and body fat becomes a research hotspot. In this context, this 12-week study was conducted aiming to determine the effect of increasing leptin intake on body weight and on body fat percentage. A 12-week study found that the experimental group that increased their lean protein intake lost an average of 3% of their body weight and significantly reduced their body fat percentage[9].
4.3. Consumption of fruits and vegetables
In traditional Chinese medicine theory, fruits and vegetables are believed to primarily have the functions of clearing heat and dampness, as well as promoting regular bowel movements. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber and antioxidants, which can promote intestinal peristalsis, remove toxins and waste products from the body, reduce the burden on the body, and achieve the purpose of weight loss. Studies have shown that a daily intake of adequate amounts of vegetables and fruits can reduce the risk of obesity by about 20%[11]. In general, the recommended daily intake of vegetables and fruits for adults is 300 ~ 500g/d and 200~400g/d[12].
5. The Role of Herbal Medicine in the Treatment of Obesity in TCM
5.1. Commonly used herbal formulas for weight loss
5.1.1. Lotus leaf and hawthorn tea
The lotus leaf is known for its ability to clear heat, relieve heat, raise Yang, cool blood, and stop bleeding. Modern research has also shown that it can effectively lower fat and aid in weight reduction. Additionally, hawthorn has the ability to promote digestion and reduce adipose accumulation by eliminating a food-healthy stomach, regulating qi to disperse blood stasis, and transforming turbidity to drop fat. A healthy liver, clear eyes, and well-hydrated intestines are essential for eliminating toxins and excess waste from the body.
5.1.2. Wax gourd sand coix seed Ttea
Wax gourd has cool skin and a sweet taste, with the effect of clearing away heat and benefiting water, reducing swelling, and detoxifying. Job's tears have the effect of promoting water infiltration, spleen, and alleviating diarrhea. It also aids in detoxification and dispersing pus, which can enhance water metabolism in the body, reduce edema and moisture, and contribute to weight loss.
It is widely recognized that plants serve as a valuable source of preventive, curative, and therapeutic substances[13]. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the urgent need to address obesity through scientific research and development of herbal medicines. Firstly, herbs can play a role in regulating energy metabolism. The components in some herbs can activate lipase and promote the decomposition of triglycerides in adipocytes into free fatty acids and glycerol, ultimately reducing fat accumulation. For example, catechins found in green tea have been shown to enhance the activity of lipooxidase and accelerate the process of lipolysis. Additionally, certain herbs can inhibit key enzymes such as fatty acid synthases, thereby reducing the production of new lipogenesis. For example, curcumin in turmeric has been shown to inhibit the differentiation of adipocytes and the synthesis of fat[14]. Furthermore, certain herbs have the potential to enhance energy expenditure by increasing basal metabolic rate. For instance, ephedrine present in ephedra can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system and improve the metabolism. Secondly, herbal medicine can also regulate the endocrine system. Obesity is often accompanied by insulin resistance, resulting in increased insulin secretion(Figure 1)[15]. Some herbal medicines can improve insulin sensitivity and lower insulin levels. For example, mosaic in moma can enhance the activity of insulin receptors and regulate blood glucose and insulin levels. Thyroid hormones have an important effect on the metabolism. Certain herbs can regulate thyroid function and increase thyroid hormone levels, thereby increasing energy expenditure. For example, iodine in seaweed can promote the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
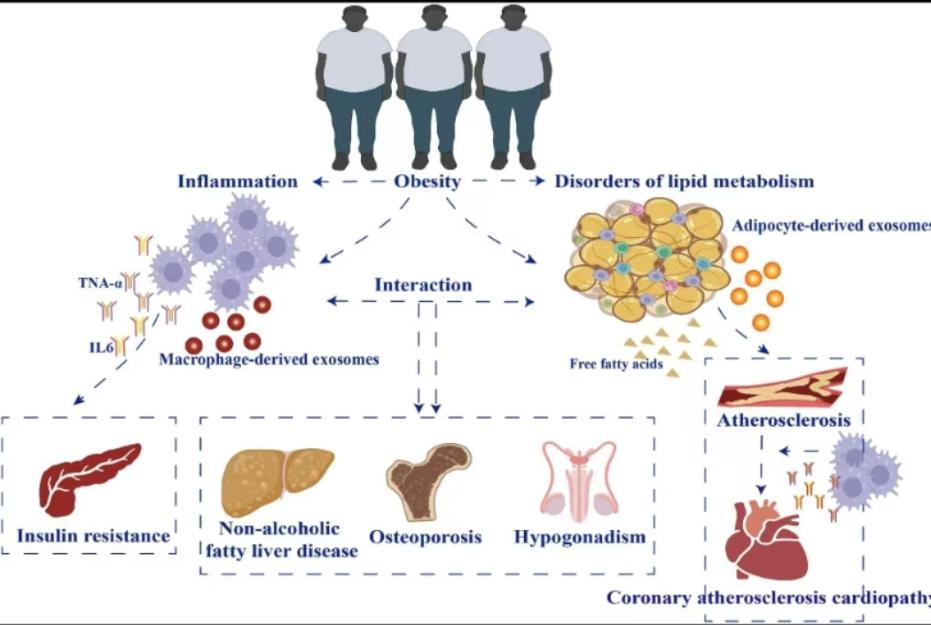
Figure 1. Biomarkers of obesity-mediated insulin resistance: focus on microRNAs [15]
These herbs may exert weight loss effects by regulating gastrointestinal function, improving lipid metabolism, regulating the endocrine system, and improving the body's antioxidant capacity. Therefore, an in-depth understanding of the potential mechanisms through which herbal medicine regulates the gut microbiota in the treatment of obesity can provide insight into the pathogenesis of obesity from a new perspective and propose innovative therapeutic strategies for obesity[16].
6. Application of Acupuncture in the Treatment of Obesity in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Acupuncture point selection and stimulation methods Commonly used acupuncture points include Zusanli, Zhongguan, and Tianshu, which are known for their ability to regulate the flow of meridian qi and blood, and these points can also improve the function of internal organs through various stimulation methods such as acupuncture, moxibustion, and electroacupuncture [17]. The mechanism of acupuncture in treating obesity may involve several factors, including appetite suppression, regulation of gastrointestinal hormone secretion, promotion of fat breakdown and metabolism, and improvement of insulin resistance. According to a clinical study, obese patients who received acupuncture treatment lost an average of 4.5 kg in weight and approximately 3 cm in waist circumference over a period of three months [18].
7. Conclusion
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) provides a unique perspective on the treatment of obesity and has explored many effective methods and treatments. By combining the wisdom of traditional Chinese medicine and applying the theories of yin and yang, as well as qi and blood balance, the disorders of human metabolism caused by imbalances in energy and organ function can be explored, thereby inducing obesity. Based on these problems, traditional Chinese medicine can effectively regulate the balance of energy and organ function of the human body by rationally adjusting the diet and leveraging the benefits of traditional Chinese herbal medicine acupuncture, and other treatment methods, in order to achieve the goal of weight loss and maintain a healthy weight. In the future, it is essential to further uphold and advance the theories and methodologies of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in treating obesity. There is a need for in-depth exploration of the mechanisms and effectiveness of TCM in managing obesity, in order to provide robust evidence and support for comprehensive obesity treatment.
Acknowledgment
First and foremost, I would like to express gratitude towards myself. Despite not being outstanding and never giving up, I am thankful for my efforts. Perhaps everyone desires to conquer the sea, but most of us are merely a small stream. There will always be moments of discontent, as life is a mixture of both joy and hardship. With genuine sincerity, we must move forward at our own pace, taking small steps towards progress. I am deeply grateful for the resilience and courage of those who never give up on themselves. The journey has been filled with obstacles, and I acknowledge the countless difficult days and nights, as well as moments of self-healing and tears that have sustained me. These experiences will ultimately become an integral part of my life's journey. Secondly, I would like to express my deepest gratitude to the teachers and professors of my university, who have provided me with valuable guidance at all stages of my thesis writing. Finally, I also want to thank my parents. "How to get mugwort," as the saying goes, "say the heart of the tree, raising grace cannot return." My greatest wish is for you to always be healthy and happy! As this paper nears completion, I am filled with excitement. From the beginning of the project to the final paper's completion, countless friends have offered me their help. Please accept my sincere thanks!
References
[1]. Obesity and overweight — World Health Organization (WHO). 01.3. 2024, https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
[2]. Wang Xiaojian's research group at Zhejiang University has discovered a new mechanism for regulating obesity-related metabolic syndrome. 06 Jun. 2021, https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_12915779.
[3]. Zhao, X., Tan, X., Shi, H. et al. Nutrition and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): a system’s theoretical perspective. Eur J Clin Nutr 75, 267–273 (2021).
[4]. The Huangdi Neijing: Obesity and Health. 23 Sep. 2017, https://www.sohu.com/a/193980648_534427.
[5]. Jing Yue Quanshu. A Database of Ancient Books of Traditional Chinese Medicine." https://www.qihuang.vip/book-227.html
[6]. Wang, W., Huang, Y. Philosophical Bases of TCM. In: Huang, Y., Zhu, L. (eds) Textbook of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Springer, Singapore. (2024).
[7]. Varker KA, Ansel A, Aukerman G, Carson WR. Review of complementary and alternative medicine and selected nutraceu-ticals: background for a pilot study on nutrigenomic intervention in patients with advanced cancer. Alter Ther Health M. 18:26-34. Maciocia G. 2012.
[8]. Research Progress of Energy Metabolism Signaling Pathway in the Mechanism of Obesity · El Shati Rehe Jiang, Ekbar Aili, Kelimu· Abdureim, Research Progress in Energy Metabolism Signaling Pathway[J], Clinical Medicine Advances, 14(3). 2024.
[9]. Li Gao. Treatise on the Spleen and Stomach[J], Chinese Medicine Books, Chinese Medicine Family" https://www.zysj.com.cn/lilunshuji/piweilun/
[10]. Abstracts from the 2023 Annual Meeting of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J GEN INTERN MED 38 (Suppl 2), 81–799 (2023).
[11]. Zhang Y, Tabung FK, Smith-Warner SA, Giovannucci E. High-quality fruit and vegetable characterized by cardiometabolic biomarkers and its relation to major chronic disease risk: results from 3 prospective United States cohort studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2024 May 25:S0002-9165 (24) 00514-8.
[12]. Shang Yi, Li Ling & Shang Yuhan. On the importance of diet concept balance to residents' nutrition and health — Comment The Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents. The Chinese Journal of Social Medicine (04), 430. 2024. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstrac
[13]. Krishnaswamy, S. Phytopharmaceutical Biotechnology: Integration of Botany, Pharmacology and Plant Biotechnology to Deliver the Best Therapeutic Potential of Herbs. In: Bose, S., Shukla, A.C., Baig, M.R., Banerjee, S. (eds) Concepts in Pharmaceutical Biotechnology and Drug Development . Interdisciplinary Biotechnological Advances. Springer, Singapore. 2024.
[14]. Bianconi, V. et al. The Multifaceted Actions of Curcumin in Obesity. In: Sahebkar, A., Sathyapalan, T. (eds) Natural Products and Human Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology(), vol 1328. Springer, Cham. 2021.
[15]. Cai, Y., Liu, P., Xu, Y. et al. Biomarkers of obesity-mediated insulin resistance: focus on microRNAs. Diabetol Metab Syndr 15, 167. (2023).
[16]. Guan, Y., Tang, G., Li, L.et al. Herbal medicine and gut microbiota: exploring untapped therapeutic potential in neurodegenerative disease management. Arch. Pharm. Res. 47, 146–164 (2024).
[17]. Wang Li. Clinical research of Yin and Yang conditioning moxibustion combined with electroacupuncture to improve phlegm and dampness constitution of patients with simple obesity (master's thesis, Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine). 2019.
[18]. "Research progress on acupuncture in the treatment of simple obesity." https://www.hanspub.org/journal/PaperInformation?paperID=81867.
Cite this article
Zhang,S. (2024). Obesity Treatment from the Unique Perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Theoretical and Natural Science,66,17-23.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Obesity and overweight — World Health Organization (WHO). 01.3. 2024, https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
[2]. Wang Xiaojian's research group at Zhejiang University has discovered a new mechanism for regulating obesity-related metabolic syndrome. 06 Jun. 2021, https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_12915779.
[3]. Zhao, X., Tan, X., Shi, H. et al. Nutrition and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): a system’s theoretical perspective. Eur J Clin Nutr 75, 267–273 (2021).
[4]. The Huangdi Neijing: Obesity and Health. 23 Sep. 2017, https://www.sohu.com/a/193980648_534427.
[5]. Jing Yue Quanshu. A Database of Ancient Books of Traditional Chinese Medicine." https://www.qihuang.vip/book-227.html
[6]. Wang, W., Huang, Y. Philosophical Bases of TCM. In: Huang, Y., Zhu, L. (eds) Textbook of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Springer, Singapore. (2024).
[7]. Varker KA, Ansel A, Aukerman G, Carson WR. Review of complementary and alternative medicine and selected nutraceu-ticals: background for a pilot study on nutrigenomic intervention in patients with advanced cancer. Alter Ther Health M. 18:26-34. Maciocia G. 2012.
[8]. Research Progress of Energy Metabolism Signaling Pathway in the Mechanism of Obesity · El Shati Rehe Jiang, Ekbar Aili, Kelimu· Abdureim, Research Progress in Energy Metabolism Signaling Pathway[J], Clinical Medicine Advances, 14(3). 2024.
[9]. Li Gao. Treatise on the Spleen and Stomach[J], Chinese Medicine Books, Chinese Medicine Family" https://www.zysj.com.cn/lilunshuji/piweilun/
[10]. Abstracts from the 2023 Annual Meeting of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J GEN INTERN MED 38 (Suppl 2), 81–799 (2023).
[11]. Zhang Y, Tabung FK, Smith-Warner SA, Giovannucci E. High-quality fruit and vegetable characterized by cardiometabolic biomarkers and its relation to major chronic disease risk: results from 3 prospective United States cohort studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2024 May 25:S0002-9165 (24) 00514-8.
[12]. Shang Yi, Li Ling & Shang Yuhan. On the importance of diet concept balance to residents' nutrition and health — Comment The Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents. The Chinese Journal of Social Medicine (04), 430. 2024. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstrac
[13]. Krishnaswamy, S. Phytopharmaceutical Biotechnology: Integration of Botany, Pharmacology and Plant Biotechnology to Deliver the Best Therapeutic Potential of Herbs. In: Bose, S., Shukla, A.C., Baig, M.R., Banerjee, S. (eds) Concepts in Pharmaceutical Biotechnology and Drug Development . Interdisciplinary Biotechnological Advances. Springer, Singapore. 2024.
[14]. Bianconi, V. et al. The Multifaceted Actions of Curcumin in Obesity. In: Sahebkar, A., Sathyapalan, T. (eds) Natural Products and Human Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology(), vol 1328. Springer, Cham. 2021.
[15]. Cai, Y., Liu, P., Xu, Y. et al. Biomarkers of obesity-mediated insulin resistance: focus on microRNAs. Diabetol Metab Syndr 15, 167. (2023).
[16]. Guan, Y., Tang, G., Li, L.et al. Herbal medicine and gut microbiota: exploring untapped therapeutic potential in neurodegenerative disease management. Arch. Pharm. Res. 47, 146–164 (2024).
[17]. Wang Li. Clinical research of Yin and Yang conditioning moxibustion combined with electroacupuncture to improve phlegm and dampness constitution of patients with simple obesity (master's thesis, Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine). 2019.
[18]. "Research progress on acupuncture in the treatment of simple obesity." https://www.hanspub.org/journal/PaperInformation?paperID=81867.









