

Volume 140
Published on October 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2025 Symposium: Interdisciplinary Frontiers in Pharmaceutical Sciences
Adolescence marks a phase of drastic physiological and psychological transformations in individuals, characterized by the development of secondary sexual characteristics, significant hormone fluctuations, a heightened sense of independence, and shifts in social roles. This period is often plagued by health issues such as acne, obesity, and depression, which can profoundly impact adolescents' quality of life and future prospects. Given the potential drawbacks of traditional pharmacological treatments, including side effects, poor adherence, and high costs, it is imperative to seek out safe, effective, and easily incorporable supplementary or preventive strategies for daily life. This article delves into the mechanisms and clinical evidence supporting the Mediterranean diet pattern (centered around olive oil, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish) in mitigating acne severity, tackling obesity and its metabolic complications, and alleviating depressive symptoms. Research has shown that the Mediterranean diet exerts a synergistic protective effect on common adolescent ailments through various pathways, including modulating the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway, enhancing lipid metabolism, decreasing systemic chronic inflammation, and optimizing gut microbiota composition. Moreover, it encapsulates the essence of sustainable healthy living and offers a pivotal pathway for the comprehensive management of adolescent conditions.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous development of the digitalization process in oral medicine, digital oral scanning, 3D printing and artificial intelligence technologies are gradually integrating and driving the transformation of the diagnostic model in oral restoration. This article, through systematic literature retrieval and analysis, integrates recent domestic and international research findings and clinical data on relevant digital technologies in the field of oral restoration, and explores the characteristics and applications of these three technologies in oral restoration. The results show that digital oral scanning can improve the accuracy of impression taking and clinical efficiency, 3D printing realizes the efficient personalized manufacturing of restorations, and AI technology can further optimize the design.

 View pdf
View pdf


Penile erection demonstrates how psychological influences and hormonal balance modulate microcirculation. It results from a highly coordinated neurovascular process involving the integration and synchronisation of vascular endothelium, smooth muscle, and psychological, neurological, and endocrine systems. Therefore, the proper functioning of these processes is essential for maintaining penile flaccidity or achieving an erection, whereas disturbances in any component can result in erectile dysfunction (ED). ED is a common health condition with a substantial impact on men’s quality of life worldwide. Currently, this disease is considered a multifactorial condition involving a complex interplay of social, psychological, and physiological factors, necessitating the adoption of multiple treatment strategies. This paper offers an overview of the mechanisms of erections, etiological factors contributing to ED—including psychological, neurological, endocrinological, and vasculogenic aspects—diagnostic approaches and treatments.

 View pdf
View pdf


Emerging studies challenge the popular view that dairy products unanimously promote inflammation. This review synthesizes current research on how variations in fermentation status and fat content influence the inflammatory potential of dairy. Through enrichment with probiotics and postbiotics, fermented dairy products demonstrate dual regulatory effects: modulating gut microbiota composition while suppressing pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. Conversely, non-fermented and high-fat dairy products exhibit heterogeneous inflammatory responses—particularly among individuals with metabolic dysfunction—where outcomes range from neutral to markedly pro-inflammatory. The inconsistencies arise from variations in bacteria strains, fat composition, processing methods, and host metabolic status. This review underscores the need for more standardized interventions and broader participant diversity in the future to clarify dairy’s role in inflammation.

 View pdf
View pdf


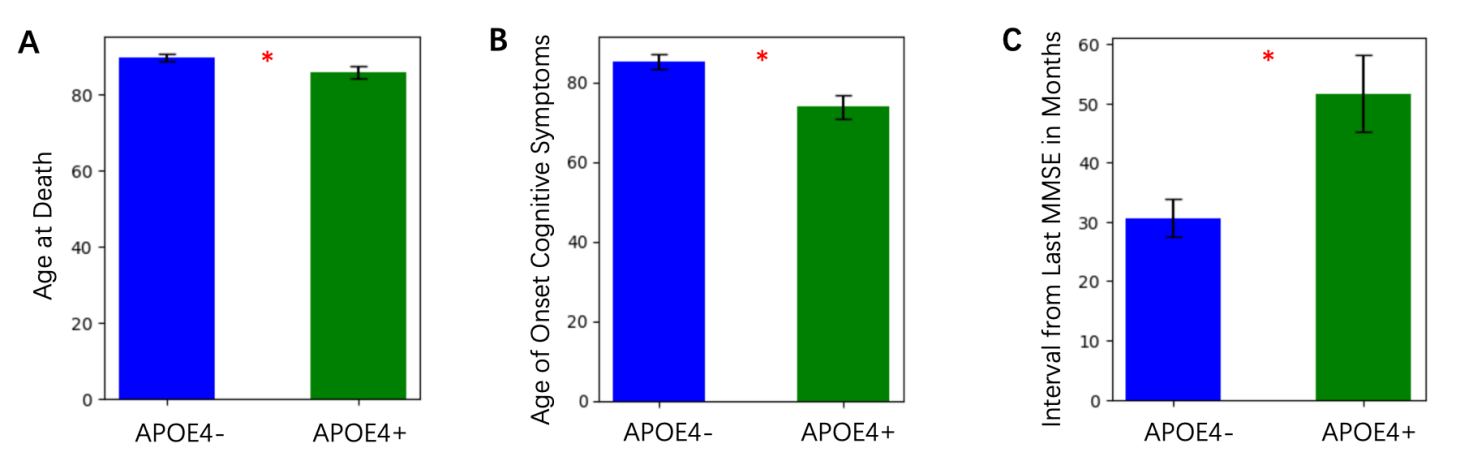
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline, amyloid plaque accumulation, and tau pathology. The Apolipoprotein E4 (ApoE4) allele is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset AD, contributing to increased amyloid burden, neuroinflammation, and brain atrophy. However, the cellular and structural mechanisms underlying ApoE4’s impact on disease progression remain incompletely understood. In this paper, we analyzed multi-modal datasets from the Seattle Alzheimer’s Disease Brain Cell Atlas (SEA-AD) to investigate differences between ApoE4+ and ApoE4- individuals. 116 parameters were assessed, including neuropathology, imaging, and clinical outcomes and we identified 15 key parameters that are more significant and representative between the groups. ApoE4+ individuals exhibited earlier cognitive decline, greater tau and amyloid pathology, and accelerated brain atrophy, particularly in cortical and subcortical regions. RNA sequencing of the Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) and Middle Temporal Gyrus (MTG) revealed significant reductions in Sst Chodl, Sncg, and Vip interneurons in ApoE4+ individuals. These findings suggest that ApoE4 carriers experience widespread neurodegenerative changes, including altered inhibitory neuron composition, which may contribute to disease progression. Understanding how ApoE4 affects inhibitory networks could provide new insights into Alzheimer’s pathology and potential therapeutic targets.

 View pdf
View pdf




