

Volume 6
Published on July 2024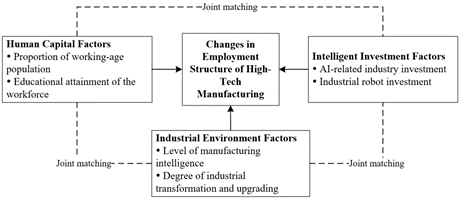
This study investigates the impact pathway and mechanisms of multi-factor artificial intelligence investment on the proportion of high-tech manufacturing labor force, drawing upon the theory of skill-biased technological changes (SBTC). Employing a mixed qualitative and quantitative research design, we identify key resource factors influencing changes in the employment structure within the high-tech manufacturing industry. Our analysis employs fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) on a provincial dataset from China, spanning the years 2018 to 2020. Findings reveal the following insights: (1) There exists a configurational effect among antecedent factors influencing changes in the employment structure of the manufacturing industry. Specifically, investments in AI-related industries, industrial robots, industry transformation and upgrading, industrial intelligence, working-age population proportion, and educational attainment of the workforce are not individually necessary conditions. (2) There are three paths that drive the increase of the proportion of high-tech manufacturing labor force, including comprehensive development type, capital-led type, and education-led type. (3) Investments in industrial robots and advancements in industrial intelligence emerge as pivotal factors driving the increase in the proportion of high-tech manufacturing labor force. This research contributes to advancing a multidimensional perspective on biased technological change, laying the groundwork for regional management strategies to invest in AI for fostering the healthy development of high-tech manufacturing.

 View pdf
View pdf


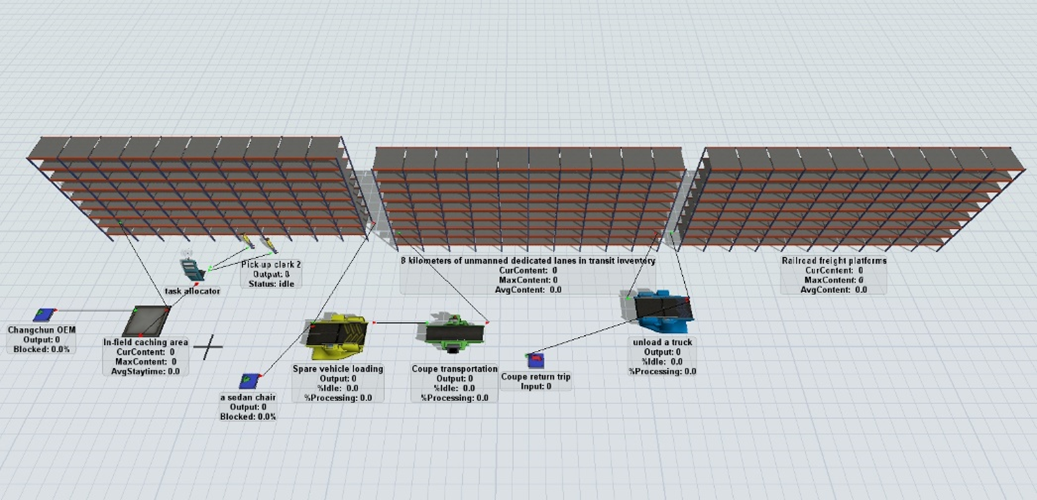
Against the backdrop of the rapid development of the shuttle transport industry, the selection of car transporters and resource allocation has become the focus of enterprises. Based on the actual operations of FAW Logistics Company, we used FlexSim simulation software to construct a highly realistic shuttle transport model. This model conducted a comprehensive simulation analysis of the performance of three mainstream car transporters over an 8-kilometer shuttle transport route. Through detailed mathematical processing, we derived the optimal scheme with the lowest procurement cost. This scheme was not only validated through FlexSim simulation but also provided a feasible solution for car companies in selecting car transporters and allocating resources in shuttle transport, with significant theoretical and practical guiding significance.

 View pdf
View pdf


The contemporary art market places significant emphasis on the value attributed to symbols. These symbolic values act as mirrors, reflecting how political economy interprets the artistic landscape and defines its dynamics within the market. This paper engages in modeling the process of elevating symbols as mutual osmosis equilibrating the supply and the demand, delving into their communal accumulation within cultural contexts, and examining their pivotal roles in shaping the contemporary art markets. The study introduces a comprehensive model that unveils a feedback loop encompassing the elevation of symbols, the collective recognition of their symbolic value, and the diffusion of cultural capital. This framework offers insights into the perpetual evolution of art markets and the multifaceted influences they exert.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the 21st century, the global economy and society face unprecedented challenges and opportunities, with environmental issues like climate change and resource depletion threatening sustainable development. Green finance emerges as a novel financial model, emphasizing the integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into financial decisions and investments. This study explores the connotation, characteristics, and global practices of green finance, highlighting its role in promoting economic sustainability through tools like green bonds and sustainable development loans. The literature review identifies key themes and research findings in green finance, including its impact on sustainable development and the challenges it faces, such as information asymmetry and lack of standardized evaluation systems. The development and challenges of green finance in China are also examined, noting significant progress driven by government policies and the growth of the green bond market, alongside persistent issues like inconsistent standards and transparency. This comprehensive analysis underscores green finance's potential in fostering international cooperation, enhancing financial stability, and driving the green transformation of the economy, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable global future.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper explores the impacts of affordable housing on community health and well-being in China, focusing on urbanization's role in providing affordable housing. The study uses qualitative methodology and use systemic review and meta-analysis to analyze health indicators and socioeconomic improvements directly linked to access to affordable housing. Among the findings is that the mental health implication is that affordable housing reduces stress and, therefore, encourages social stability and economic resilience. This study, thus, allows regional housing policy diversification, innovative housing solutions, and the subjective experiences of the residents. This results in an overall understanding of the effects that affordable housing brings to one's health and well-being. The insights are critical to the development of practical policies regarding housing and effective policies that are centered on community development towards the improvement of life quality.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper aims to explore the current state, challenges, and optimization pathways of policy coordination mechanisms in the process of integrating the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region. By analyzing the degree of coordination among various levels of government in policy formulation and implementation, this study evaluates its impact on achieving regional integration goals and proposes recommendations to promote policy coordination. The study finds that policy coordination mechanisms play a crucial role in achieving regional integration but face several challenges at present, including institutional barriers, conflicts of interest, and uneven resource distribution. Establishing a unified coordination agency, promoting the unification of laws and regulations, designing a reasonable benefit-sharing mechanism, and achieving integrated resource allocation can effectively promote policy coordination, thereby advancing regional integration development.

 View pdf
View pdf


Enhancing corporate innovation capabilities in complex and uncertain environments is a focal point of societal concern. This study examines the impact of executive compensation performance sensitivity on corporate innovation against the backdrop of environmental uncertainty, using a sample of listed companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen A-shares market from 2015 to 2020. Empirical results indicate that executive compensation performance sensitivity significantly inhibits corporate innovation; however, this inhibitory effect varies with the characteristics of the environment and the industry in which the company operates. As environmental uncertainty increases, this inhibitory effect becomes insignificant. High-tech enterprises, due to their strong motivation for innovation, can offset the inhibitory effect of executive compensation performance sensitivity on corporate innovation. Nevertheless, in highly uncertain environments, where resource constraints and risks are heightened, the inhibitory effect of executive compensation performance sensitivity on corporate innovation in high-tech enterprises becomes significant. The conclusions of this study contribute to the understanding of the motivational effects of executive compensation contracts in uncertain environments, provide a reference for evaluating the effectiveness of performance-based compensation from the perspective of corporate innovation, and offer insights for companies in designing and refining executive compensation incentive plans according to the times and industry characteristics.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper takes the Yangtze River Delta integration as the research object, deeply explores the application and importance of the dual-layer governance model in the process of China’s regional integration. Through the analysis of the practice of Yangtze River Delta integration, it expounds the connotation and characteristics of the dual-layer governance model, as well as the key role played by the leadership and coordination bodies in it. Meanwhile, it analyzes the current challenges and problems, and puts forward corresponding countermeasures and suggestions, aiming to provide theoretical reference and practical guidance for promoting the development of China’s regional integration.

 View pdf
View pdf


The digital economy significantly promotes fundamental innovation activities and impacts environmental pollution through mechanisms such as optimizing resource allocation, accelerating knowledge flow, and enhancing innovation service efficiency. Based on panel data from 29 provinces in China from 2010 to 2020, this paper employs a panel threshold regression model to investigate the relationship between the digital economy, fundamental innovation, and environmental pollution. The study finds a significant negative correlation between the level of digital economy development and environmental pollution. As the digital economy level increases, the environmental pollution levels in the relevant provinces significantly decrease. Additionally, the impact of technological innovation on the relationship between the digital economy and environmental pollution exhibits nonlinear characteristics. When the level of technological innovation exceeds a specific threshold, the effect of the digital economy on reducing environmental pollution is significantly enhanced. There are regional differences in how digital economy development and technological innovation levels affect environmental pollution. In the eastern coastal regions, where the digital economy and technological innovation are more advanced, the reduction effect on environmental pollution is more pronounced, whereas the effect is relatively limited in the central and western regions. This study provides theoretical support and decision-making references for the construction of ecological civilization and green, low-carbon development.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study examines the dual impact of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) on environmental quality in host countries, differentiating between developing and developed nations. Linear regression analysis of income-segmented data reveals that FDI reduces greenhouse gas emissions globally but increases pollution in middle-income countries while reducing it in high-income countries. Robustness checks validate these findings. FDI's environmental impacts vary with the host country's regulatory environment and development status. Positive impacts include advanced technology transfer and improved resource efficiency, while negative impacts involve the "pollution haven" effect and resource over-exploitation by foreign investors. To maximize benefits and minimize drawbacks, host governments should provide incentives for environmentally friendly investments, promote knowledge exchange, and enforce robust environmental regulations with clear policies and self-reporting mechanisms. These strategies can help host countries harness FDI's advantages while mitigating its environmental risks.

 View pdf
View pdf




