

Volume 86
Published on April 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Educational Innovation and Philosophical Inquiries
This essay examines distinction made by David Hume between the "vulgar system" and the "philosophical system" as explanations for belief in the continued and distinct existence of objects. Via a reconstruction of the arguments by Hume, the essay analyzes how these systems attempt to account for human perceptual experience. The vulgar system conflates perceptions with objects, while the philosophical system posits a double existence of both, yet neither can adequately explain the causal link between them. Furthermore, the study engages with interpretations of readings on Hume by considering the double existence counterargument by Pears and the systematic explanatory hypothesis proposed by Mackie to circumvent the need for naive realism. Finally, the essay evaluates the strength of these criticisms and considers their implications for Hume's overall skeptical position regarding external objects. The skepticism of Hume regarding the possibility of establishing a firm foundation for epistemic belief in external objects remains potent, even in light of these attempts at providing alternative explanations.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid digitalization of education, artificial intelligence (AI) has gained significant attention for its potential to transform teaching and learning. In the context of A-Level Biology, AI presents both opportunities and challenges. However, research specifically focusing on AI’s application in A-Level Biology teaching remains limited. This study, employing interviews as the primary method, aims to explore how AI can address specific challenges in A-Level Biology teaching. The main objectives are to understand how AI-assisted teaching differs from traditional teaching, its impact on teaching practices, and the potential benefits and drawbacks for teachers. The research used qualitative interviews with three A-Level Biology teachers from different teaching backgrounds to explore the influence in teaching when AI is used in A-Level Biology. The research finds that teachers acknowledged both the advantages, such as personalized resources and increased efficiency, and the challenges, such as potential loss of creativity and autonomy.

 View pdf
View pdf


The family environment plays a pivotal role in shaping children's educational outcomes. This paper examines how socioeconomic status, parental involvement, emotional climate, and material resources within households influence academic achievement, cognitive development, and socioemotional skills. Drawing on empirical studies and theoretical frameworks, the analysis highlights the interplay between familial factors and educational trajectories. For instance, children from low-income families often face systemic barriers such as limited access to tutoring and technology, while parental over-involvement may inadvertently harm intrinsic motivation. Additionally, the emotional dynamics of households—such as conflict resolution and parental warmth—mediate children’s stress levels and executive functioning, further impacting learning capacities. The findings underscore the need for holistic interventions, including equitable resource allocation and culturally responsive pedagogies, to mitigate disparities arising from unequal family environments. Notably, cultural capital, manifested through non-material assets like educational aspirations and social networks, also perpetuates inequalities by aligning certain groups with institutional norms. By synthesizing multidisciplinary perspectives from psychology, sociology, and education, this study provides actionable insights for policymakers, educators, and families, emphasizing the importance of addressing both material and psychosocial dimensions of child development. Practical recommendations include expanding early childhood education programs, fostering school-community partnerships, and implementing trauma-informed teaching practices to support vulnerable students. These strategies aim to dismantle systemic inequities and create inclusive pathways for academic success across diverse socioeconomic contexts.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the increasing of adolescents' mental health problems, especially the rising incidence of depression, the potential impact of family parenting style on adolescents' mental health has been widely concerned. This paper mainly studies the influence of family parenting style on adolescent depression and the effect of psychological counseling. The purpose of this study is to explore the relationship between different parenting styles and adolescent mental health, and to analyze the effective psychological intervention methods. This study uses the method of literature review to sort out the recent and past research results in related fields. The subjects included adolescents and their families, and the main tools were psychological research literature, statistical data and clinical case studies. Through the comparative analysis of the authoritative, authoritarian, permissive (liberal) loving, permissive uninvolved style and other different parenting styles, combined with the treatment cases of adolescent depression, to reveal the internal relationship between family parenting mode and adolescent depression. The findings suggest that authoritative parenting is the most beneficial for adolescent mental health, while parenting that is overly controlling or emotionally apathetic may increase the risk of depression. In addition, multimodal treatment regimes-such as a combination of cognitive behavioral therapy and medication-were significantly more effective than monotherapy in the intervention of adolescent depression. This paper emphasizes the important role of family parenting style in adolescent mental health, and provides theoretical support for related psychological intervention.

 View pdf
View pdf


Shadow education, also known as private tutoring or supplementary education, has attracted increasing research attention in the past two decades. In an effort o promote equity in education, the Chinese government has implemented a "Double reduction" policy to normalize tutoring institution and moderate the strained atmosphere caused by the educational race. However, This policy may exacerbate rather than reduce educational inequality. So far, studies have systematically reviewed the literature on the impact of shadow education from the perspective of educational inequality is relatively scarce. Therefore, based on literature search method and interviews with 5 parents, this paper provide a comprehensive overview of the implications of the "Double reduction" policy on shadow education and summarizes the implications for future practice and research. Research has found that the policy has triggered new educational equity pitfalls, including a surge in covert tutoring, and an increase in anxiety among some families, in the context of the "scores-only" theory in the college entrance examination.

 View pdf
View pdf


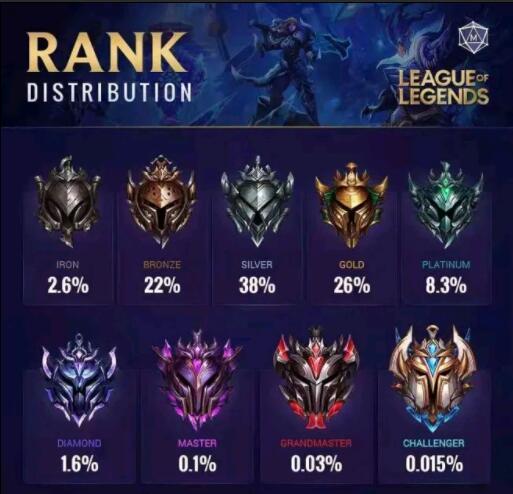
The League of Legends has been recognized as one of the most popular and influential games worldwide for many years. The success of the Riot team in designing and maintaining the game is both commendable and worth in-depth studying. This study examines the application of game psychology in League of Legends, highlighting how it fulfills a wide range of players’ psychological needs while fostering a sense of identity through its design and associated cultural products. These elements contribute to the remarkable level of engagement and its widespread appeal over time. By adopting a psychological perspective, the study expands the understanding of how League of Legends creates a fulfilling gaming experience. Furthermore, the findings aim to provide valuable theoretical guidance for future game development, helping developers design games that not only entertain but also connect with players on a deeper emotional and psychological level.

 View pdf
View pdf


The minors’ engagement with video games has become a global phenomenon. Meanwhile, in relevant research and psychological health interventions, the impact of video games on minors’ mental health has been confirmed to exist, and the impact is significant for their development. Based on existing findings, this study will analyze the mechanisms through which gaming behavior affects adolescents' mental health. From the perspective of how the impacts on the minors present, the articles that author reviewed can be categorized into three main themes regarding the mechanisms of affects: Mechanisms of Negative Impacts, Protective and Mitigating Factors, and Cultural and Demographic Variations. The study shows that video gaming’s impact on adolescent mental health is shaped by intricate interactions between individual behaviors, social contexts, and cultural influences. Emotional dysregulation and social withdrawal resulting from Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) can lead to significant risks. Appropriately designed gaming interventions can promote the minors’ mental health, enhancing emotional regulation and cognitive abilities.

 View pdf
View pdf




