1. Introduction
A real-time data warehouse updates and queries indices in real-time or near real-time. Real-time data acquisition enables enterprises to quickly comprehend current business conditions and trends, allowing for timely decisions and adjustments [1]. For instance, traditional data warehouses typically operate on a T+1 basis, meaning that data collected today is processed and available for analysis the following day. This delay is no longer sufficient for organizations that require instant data processing. As a result, real-time data warehouse architectures have been developed to provide immediate data processing capabilities, allowing businesses to access and analyze data as soon as it is collected. In Internet companies, operations are generally divided into two broad categories: offline and real-time tasks. Real-time tasks require higher data precision and have lower fault tolerance compared to offline tasks. Constructing a real-time data warehouse often involves significant real-time computation and storage efforts to facilitate the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes [2].
The current big data computing mode is mainly divided into batch computing (also known as offline computing) and stream computing (also known as real-time computing), interactive computing, graph computing, etc. Among them, stream computing and batch computing are the two main big data computing modes, which are respectively suitable for different big data application scenarios. Table 1 illustrates the key differences between batch processing and stream processing:
Table 1. The key differences between batch processing and stream processing
Batch processing | Stream processing | |
Data timeliness | Non-real-time, high latency | Real-time, low latency |
Data characteristics | Generally static data | Generally dynamic and boundary-free |
Application scenario | It is used in the scenario of low real-time requirement and offline calculation, data analysis | Real-time scenarios, such as real-time recommendation and service monitoring, require high timeliness |
Mode of operation | Completed once | Continuous task execution (7 * 24) |
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) is a crucial element of real-time data warehousing. OLAP is a technique that enables quick and flexible analysis of multi-dimensional data. By organizing data into a multidimensional model, OLAP facilitates complex queries and analytical operations like slicing, dicing, drilling, and pivoting. With the support of OLAP technology, real-time data warehouse provides real-time, flexible and high-performance multi-dimensional analysis capabilities to help decision makers gain insight into business dynamics and make more accurate decisions.
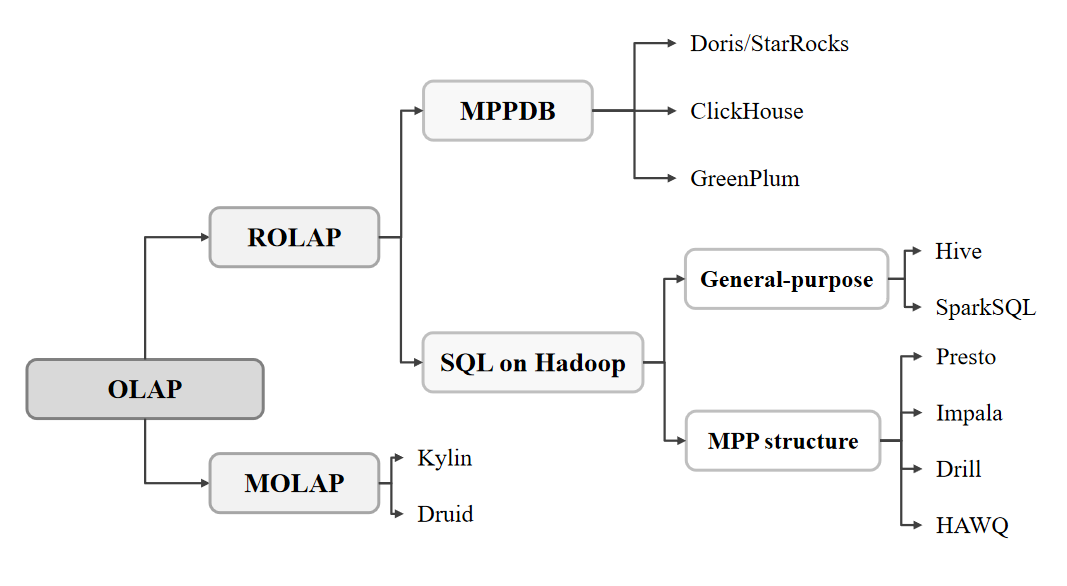
Figure 1. Classification of OLAP (Online Analytical Processing)
The Figure 1 outlines the OLAP classification, with ROLAP (Relational OLAP) and MOLAP(Multidimensional OLAP) being the two main subcategories. In addition, it illustrates a set of complementary technologies, such as SQL on Hadoop, Kylin, Druid, etc., that make up the broader OLAP ecosystem.
This article reviews different types of real-time data warehouses and their advantages and disadvantages across various industries, with a particular focus on the Internet industry, including companies like ByteDance, Alibaba and Huawei. It also discusses the selection and construction of new real-time data warehouses, examining specific use cases and challenges faced by these industry leaders. Our goal is to provide Internet-based companies with valuable insights into the implementation and effectiveness of real-time data warehousing.
2. Industry Applications
In the realm of real-time data warehouses, the traditional architecture is chiefly categorized into two models: Lambda and Kappa. Each model offers a unique approach to handling real-time and offline data, which are foundational in defining the technology selections in this field.
2.1. Lambda architecture
2.1.1. Overview of Lambda Architecture. The Lambda architecture, introduced by Nathan Marz.the founder of Apache Storm, is a robust data processing framework designed to handle massive quantities of data by dividing it into two distinct paths: real-time and batch processing[3]. Use a streaming computing engine (such as Flink) for real-time data and a batch computing engine (such as Spark) for offline data. The results are then stored separately on different storage engines to provide external data services that combine streaming and batch processing to process large-scale data. The architecture delivers accurate data through batch processing while leveraging streaming for low latency, striking a balance between latency, throughput, and fault tolerance. The two processing results are combined to support subsequent Ad-hoc query requirements.
2.1.2. Components of Lambda Architecture
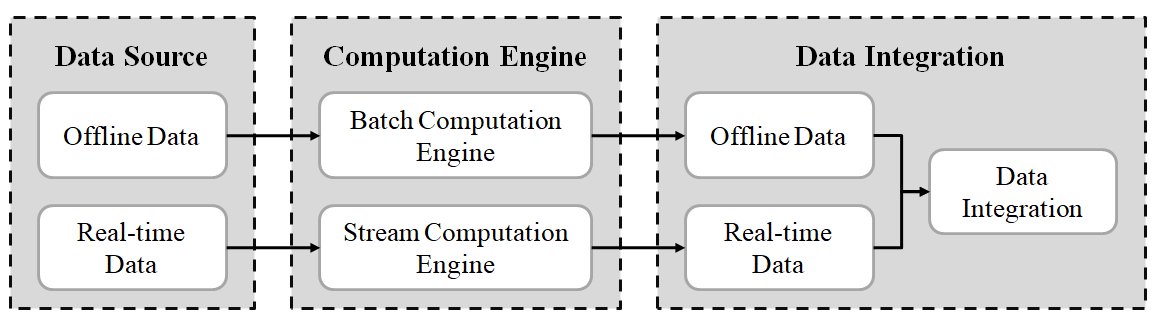
Figure 2. Example of the Lambda Architecture
Figure 2 presents an example of the Lambda architecture that combines both batch and stream processing to provide low-latency responses. The Lambda architecture consists of three main layers: First, batch computation engines, such as Apache Spark, are employed for processing offline data in the batch layer, which manages large volumes of historical data to produce comprehensive and accurate results. Second, streaming computation engines like Apache Flink handle real-time data, enabling quick decision-making and real-time analytics by processing data as it arrives. Third, the serving layer integrates outputs from both the real-time and batch processing layers, providing access to both historical insights and real-time data analytics. This integration is essential for applications that require ad-hoc querying capabilities for immediate and historical data analysis [4].
Also, maintaining data consistency between the real-time and batch layers is a significant challenge in this architecture. The batch layer often needs to correct or update discrepancies found in real-time data to ensure overall consistency. Additionally, the architecture's dual processing nature introduces complexity, making it challenging to implement and maintain. This complexity arises from the need to synchronize between different systems, which can increase resource requirements and complicate system management and troubleshooting.
2.2. Kappa Architecture
2.2.1. Components of Kappa Architecture. In contrast, the Kappa architecture simplifies the data processing landscape by treating all data as streaming data, processed by a unified streaming computing engine. This approach reduces architectural complexity but demands that all data must be handled in real-time; offline data must also be converted into streaming data for processing. While this model simplifies the processing pipeline, it places stringent requirements on data timeliness[5].
The specific architecture can be viewed in combination with Figure 3.
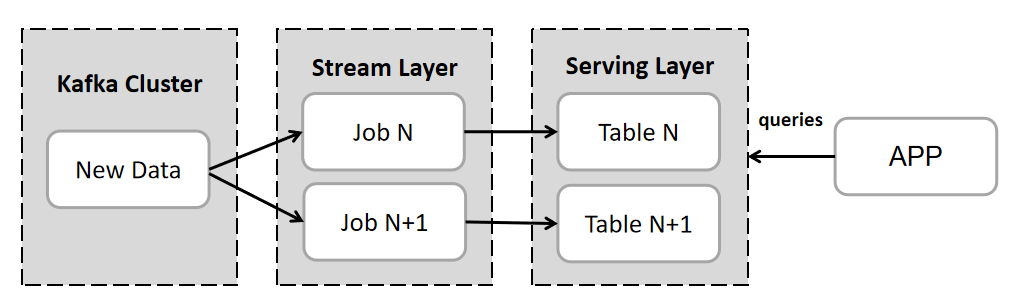
Figure 3. Example of the Kappa Architecture[6]
2.2.2. Compare with Lambda Architecture. The Kappa architecture represents a significant advancement in big data technologies by focusing solely on stream processing, thereby simplifying the data processing workflow. By treating all data as a continuous stream, Kappa architecture reduces system complexity and enhances the efficiency of real-time data processing. This unified approach makes data management and maintenance more straightforward. However, compared to the Lambda architecture, Kappa may face challenges in handling historical data and data replay. This highlights areas where further improvements could be made to enhance the architecture’s comprehensiveness and flexibility for various application scenarios. Table 2 clearly outlines the differences between the Lambda and Kappa architectures:
Table 2. Comparison of Lambda Architecture and Kappa Architecture
Lambda | Kappa | |
Consumption | Batch and stream processing simultaneously, high resource consumption | Only stream processing, low resource consumption |
throughput | Batch reprocessing, high throughput | Stream reprocessing, relatively low throughput |
Maintenance | Requires two sets of codes, harder to develop and test[6] | Requires one set of code, easier to develop and test |
Operational Costs | Maintenance of two systems, high operational costs | Maintenance of one system, relatively lower operational costs |
2.3. Data Lake Architecture (2011)
2.3.1. Overview of Data Lake Architecture. With the rise of big data, enterprises face increasing data volume and diversity. To effectively leverage these data resources, data lakes have emerged as a new data storage and management architecture. The data lake concept was first proposed by James Dixon in 2011, who believed traditional data warehouses and marts lead to data silos, while the open and flexible nature of data lakes can help resolve this issue[7]. Centered around raw data, they adopt a unified storage and access mechanism, supporting diverse formats and types, providing enterprises a unified data platform. The core concepts, architectures, and applications of data lakes will be explored in the following sections, to help enterprises better understand and apply this technology to optimize data resource utilization.
2.3.2. Components of Data Lake
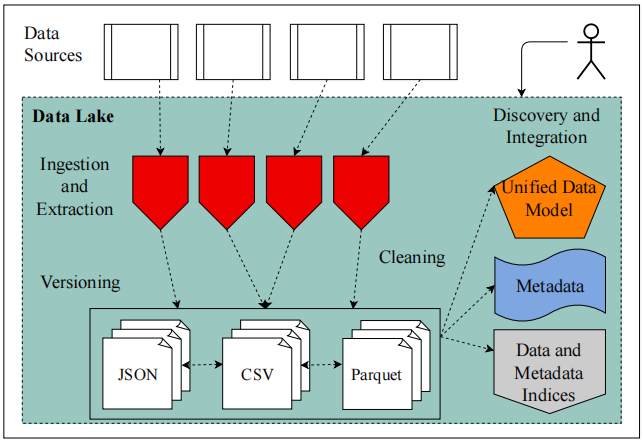
Figure 4. Example Data Lake System[7]
Figure 4 illustrates a typical data lake system architecture, which functions as a centralized repository for storing large volumes of raw data in its native format. The architecture encompasses several key components: Data Sources and Ingestion involve integrating various data formats such as JSON, CSV, and Parquet from different systems through both batch and real-time streaming processes; Data Lake and Storage centers on a distributed storage system designed to handle vast amounts of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data efficiently; Data Cleaning and Versioning ensure data quality by removing noise, handling missing values, and standardizing formats, while managing different versions to support data governance and traceability; and Discovery, Integration, and Unified Data Model focus on exploring relationships between data sources and integrating them into a unified model, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of data analysis by providing a consistent representation of data from diverse sources.
2.3.3. Example of Data Lakes: Apache Hudi (2016). Apache Hudi is a transactional data lake platform that enhances the power of a data lake by combining features commonly found in databases and data warehouses[8]. It introduces a modern approach to data processing, replacing traditional batch processing with an efficient incremental processing framework. The framework enables near-real-time analysis with low latency, allowing for minute-level analysis. Table 3 outlines the primary differences between Apache Hudi and traditional data warehouses
Table 3. Comparison of Apache Hudi and Traditional Data Warehouse
Apache Hudi(Data Lakes) | Traditional Data Warehouse | |
Data Storage | Stores large amounts of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data without prior formatting or schema definition | Primarily stores structured data, requiring predefined data schemas |
Flexibility | Avoids the limitations of needing predefined data schemas, supports fast ingestion of new data sources and changing data requirements over time | Requires predefined data schemas, less flexible with changing data requirements |
Cost | Using open source Hadoop and cloud storage technologies, big data can be stored and managed at lower cost | Higher construction and operation costs |
Advanced Analytics | Provides raw data sources for advanced analytics such as machine learning and deep learning, which require rich data sources | Supports basic reporting and analytics but not as supportive of advanced analytics as data lakes |
The primary challenge with data lake architecture is the lack of oversight in managing and storing raw data. For a data lake to be effective, it needs well-defined mechanisms for cataloging and safeguarding data. Without these mechanisms, data can become difficult to locate and trust, leading to a "data swamp" scenario where data is neither usable nor reliable. Although the open and flexible nature of data lakes helps in breaking down data silos, it also introduces the risk of unchecked data accumulation. This lack of proper data management and quality control can undermine the data lake's purpose of enabling efficient data utilization. To ensure that data lake initiatives are successful and deliver their intended benefits, enterprises must implement robust governance frameworks, ensure semantic consistency, and establish effective access control measures.
2.4. Data Lakehouse(2020)
2.4.1. Overview of Data Lakehouse. In 2020, the company Databricks first introduced the concept of the Data Lakehouse, aiming to integrate data lake and data warehouse technologies into a unified solution. The Data Lakehouse encompasses the advantages of both data lakes and data warehouses, enabling data analysts and data scientists to operate on data within a single data storage environment. Furthermore, the Data Lakehouse model offers enhanced convenience for data governance within organizations.
2.4.2. Example of Data Lakehouse: Huawei FusionInsight . Huawei's data lakehouse solution is built on an integrated architecture that enables storage and computing separation[9] . This approach allows a single data platform to support a variety of analytical needs, from SQL-based queries to business intelligence (BI) and artificial intelligence (AI) applications. According to a recent study, the FusionInsight architecture possesses several key advantages over traditional database systems. The authors note that "it can process structured and unstructured data, and the data processing capacity is above PB-level, which is far stronger than the processing capacity of traditional database". Moreover, "it can simply complete the storage and operation functions by adding nodes without modifying the system architecture, thus reducing the operation and maintenance cost[10] ".
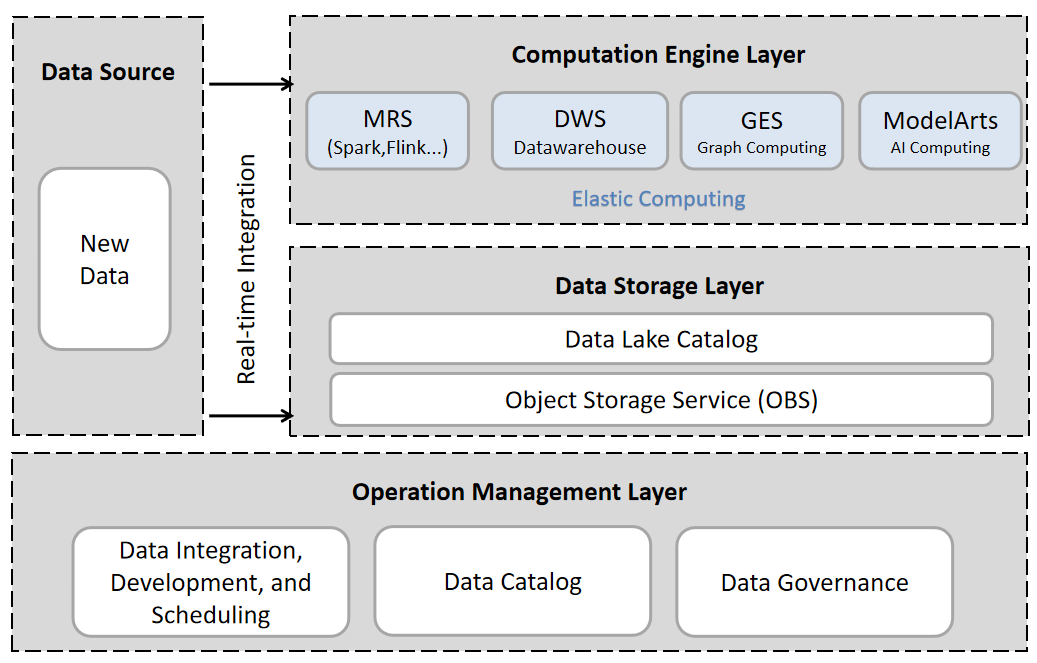
Figure 5. Components of the FusionInsight Architecture
Figure 5 illustrates the components of the FusionInsight architecture, which includes three key layers. The Data Storage Layer employs a cloud-native storage architecture that separates storage and computing to lower total cost of ownership (TCO). It features a unified metadata management service, creating a centralized data storage resource pool and supporting various analytical and computational tools, thus forming the foundation for lake and warehouse convergence. The Computation Engine Layer incorporates a transactional computation engine to enhance data lake transactional processing and improve data quality. It utilizes a standard SQL access engine for unified access to cross-domain multi-source data, supports integrated analysis and collaborative computation, and includes a fusion analytics and AI computation framework for machine learning model training and real-time analysis. The Operation Management Layer provides a unified data development and governance environment with robust security management, supporting task orchestration across multiple computation engines, data modeling, and quality monitoring. This layer ensures a consistent experience for lake and warehouse management, crucial for operationalizing "Lake-Warehouse Convergence." Through these technological innovations, the architecture effectively eliminates traditional boundaries between data lakes and warehouses, addressing enterprises' needs for comprehensive and efficient data processing.
2.5. Hybrid Transaction & Analytical processing (HTAP)
2.5.1. Overview of HTAP system. HTAP can be simply understood as completing OLAP and OLTP business tasks within a unified database system[11]. Compared to traditional TP databases, HTAP databases have an additional computing engine that can accelerate SQL execution efficiency. And based on traditional AP databases, HTAP databases also have a transaction engine that allows "write-to-read" and provides high data timeliness. It breaks down the wall between transaction processing and analysis, supporting more information and real-time business decision-making.
2.5.2. Components of HTAP system. HTAP databases include an efficient computing engine that accelerates SQL query execution and enhances analytical performance, a transaction engine based on traditional AP databases that provides transaction processing capabilities and "write-to-read" functionality for high data timeliness, and the ability to support real-time business decision-making by breaking down the barriers between transaction processing and analysis, eliminating the need to replicate data from OLTP to OLAP systems.
2.5.3. Example of HTAP system: ByteHTAP
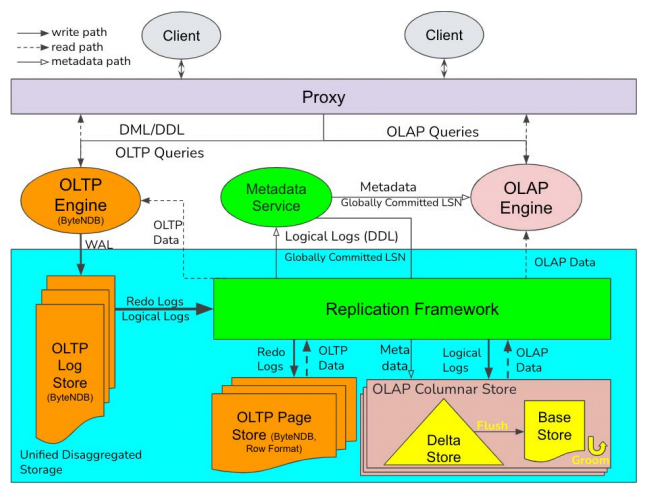
Figure 6. An illustration of ByteHTAP architecture[12]
As shown in Figure 6, HTAP (Hybrid Transaction/Analytical Processing) systems like ByteHTAP are designed to handle both transactional (OLTP) and analytical (OLAP) workloads efficiently. ByteHTAP uses separate engines over shared storage, with a unified API and a smart proxy that directs queries to either the OLTP engine (ByteNDB) or the OLAP engine (Flink). Simple transactional queries go to the OLTP engine, while complex analytical queries are handled by the OLAP engine, avoiding interference between workloads and ensuring optimal query processing[12].
2.6. Hybrid Serving & Analytical processing (HSAP)
2.6.1. Overview of HSAP System. Hybrid Serving & Analytical Processing (HSAP) systems are designed to bridge the gap between real-time data serving and complex analytical processing. Traditional HTAP (Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing) systems excel at real-time data analysis but often struggle with large-scale data processing. The HSAP system builds upon the HTAP paradigm by integrating advanced capabilities for both transactional and analytical workloads, addressing the challenges of big data environments.
2.6.2. Example of HSAP System: Hologres by Alibaba. Hologres is a cloud-native, real-time analytical data warehouse launched by Alibaba Cloud, which is built upon the Apache Hudi. It provides high-performance, scalable, and real-time data storage and analytics capabilities, supporting features such as cloud-native architecture, real-time data processing, high scalability, and SQL compatibility, enabling organizations to manage their entire data ecosystem within a unified platform.
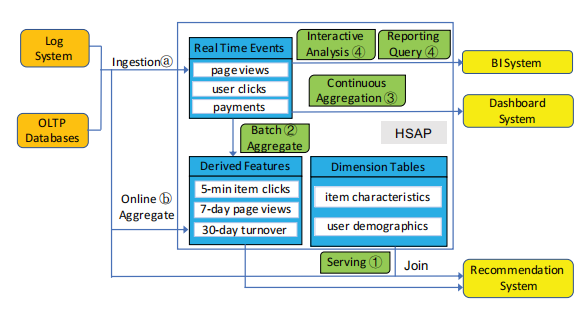
Figure 7. An Example HSAP Scenario[13]
Figure 7 illustrates the High-Scale Analytical Processing (HSAP) architecture of the big data technology stack supporting a recommendation service [13]. This architecture integrates various components to efficiently process and analyze large-scale data in both real-time and batch modes. Ingestion and Aggregation involves processing data through online aggregation for immediate use in applications like recommendation systems, and batch aggregation for deriving features and updating dimension tables for longer-term analytics. Derived Features are generated from aggregated data, such as item clicks over different time intervals, to enhance recommendation algorithms, while Dimension Tables store static data about items and users, essential for joining and analyzing data from various sources. Real-Time Events like page views and user clicks are processed instantly for immediate analytics and updates, complemented by Continuous Aggregation, which performs ongoing data aggregation to provide up-to-date insights. Finally, Interactive Analysis enables real-time data exploration, and Reporting Queries support the generation of reports and dashboards for business intelligence insights.
Besides, the HSAP system encounters significant challenges due to high variability in data ingestion and query workloads, necessitating dynamic resource allocation to sustain performance. HSAP architectures must handle and serve massive data volumes, processing hundreds of millions of events per second with stringent latency requirements that exceed traditional OLAP needs. Furthermore, HSAP platforms must support extremely high concurrency, with queries reaching tens of millions per second, while simultaneously managing complex analytical workloads. This demands advanced resource management techniques to ensure efficient operation.
3. Conclusion
In conclusion, this paper systematically reviews the technical characteristics of various types of real-time data warehouses and their application scenarios across multiple industries, with a particular focus on the Internet sector. By deeply analyzing the considerations for selecting new real-time data warehouses, architectural design, and typical application cases, it provides valuable insights and guidance for Internet companies in technology selection and system construction related to real-time data warehouses.
In terms of technical architecture, we conducted an in-depth comparison of the widely used Lambda and Kappa architectures, analyzing their strengths and weaknesses in key performance metrics such as data throughput, processing latency, and system scalability. The Lambda architecture, which combines batch and stream processing, offers high fault tolerance and flexibility but comes with increased complexity and higher latency. The Kappa architecture simplifies data processing by focusing solely on stream processing, yet it faces limitations in data replay and historical data handling.
With the continuous advancement of emerging technologies, innovations such as Apache Hudi and the rise of lakehouse architectures present new opportunities for performance optimization and functional expansion of real-time data warehouses. Data lake technologies enhance data warehouses' processing capabilities and flexibility by providing efficient data storage and management solutions. Meanwhile, the lakehouse architecture integrates the advantages of data lakes and data warehouses, enabling more efficient data querying and analytical processing.
In terms of hybrid architectures, the emergence of HTAP (Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing) and HSAP (Hybrid Serving/Analytical Processing) architectures has driven the deep integration of transactional and analytical processing. This integration not only enhances the system's real-time capabilities and consistency but also simplifies data management and application development through a unified data platform. HTAP architecture improves data consistency and real-time capabilities by supporting both transactional and analytical processing within a single database, while HSAP architecture achieves more efficient business processing and data insights by combining online serving with analytical processing.
Despite these insights, this study has certain limitations. It may not thoroughly the latest advancements in these architectures, which offer new possibilities for performance optimization and functional expansion. Looking ahead, with the continuous progress of cloud computing and big data technologies, real-time data warehouses will further develop towards intelligence, automation, and integration. The deep penetration of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning will endow real-time data warehouses with more powerful analytical and predictive capabilities, helping enterprises uncover valuable insights hidden in vast amounts of data. Intelligent data processing and automated operation management will significantly reduce system complexity and operational costs, enhancing enterprises' data-driven decision-making capabilities.
References
[1]. Sousa, R., Miranda, R., Moreira, A., Alves, C., Lori, N., & Machado, J. (2021). Software tools for conducting real-time information processing and visualization in industry: An up-to-date review. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 4800.
[2]. Gorhe, S. (2020). ETL in Near-Real Time Environment: Challenges and Opportunities. no. April.
[3]. Warren, J., & Marz, N. (2015). Big data: Principles and best practices of scalable realtime data systems. Simon and Schuster.
[4]. Hasani, Z., Kon-Popovska, M., & Velinov, G. (2014). Lambda architecture for real time big data analytic. In ICT Innovations (pp. 133–143).
[5]. Lin, J. (2017). The lambda and the kappa. IEEE Internet Computing, 21(05), 60–66.
[6]. Feick, M., Kleer, N., & Kohn, M. (2018). Fundamentals of real-time data processing architectures lambda and kappa. In SKILL 2018-Studierendenkonferenz Informatik (pp. 55-66). Gesellschaft für Informatik eV.
[7]. Nargesian, F., Zhu, E., Miller, R. J., et al. (2019). Data lake management: challenges and opportunities. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 12(12), 1986-1989.
[8]. Apache Hudi. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://hudi.apache.org/
[9]. Huawei Cloud. (n.d.). FusionInsight. Retrieved from https://www.huaweicloud.com/product/FusionInsight.html
[10]. Lin, Q. I. (2021). Analysis and discussion of component in the ecosphere of Hadoop from Huawei’s FusionInsight. In 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE) (pp. 713-717). IEEE.
[11]. Huang, D., Liu, Q., Cui, Q., et al. (2020). TiDB: a Raft-based HTAP database. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 13(12), 3072-3084.
[12]. Chen, J., Ding, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). ByteHTAP: Bytedance's HTAP system with high data freshness and strong data consistency. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 15(12), 3411-3424.
[13]. Jiang, X., Hu, Y., Xiang, Y., Jiang, G., Jin, X., Xia, C., Jiang, W., Yu, J., Wang, H., Jiang, Y., et al. (2020). Alibaba Hologres: A cloud-native service for hybrid serving/analytical processing. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 13(12), 3272–3284.
Cite this article
Qu,J.;Wang,J. (2024). Real-time data warehousing in the big data environment: A comprehensive review of implementation in the internet industry. Applied and Computational Engineering,88,105-114.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Sousa, R., Miranda, R., Moreira, A., Alves, C., Lori, N., & Machado, J. (2021). Software tools for conducting real-time information processing and visualization in industry: An up-to-date review. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 4800.
[2]. Gorhe, S. (2020). ETL in Near-Real Time Environment: Challenges and Opportunities. no. April.
[3]. Warren, J., & Marz, N. (2015). Big data: Principles and best practices of scalable realtime data systems. Simon and Schuster.
[4]. Hasani, Z., Kon-Popovska, M., & Velinov, G. (2014). Lambda architecture for real time big data analytic. In ICT Innovations (pp. 133–143).
[5]. Lin, J. (2017). The lambda and the kappa. IEEE Internet Computing, 21(05), 60–66.
[6]. Feick, M., Kleer, N., & Kohn, M. (2018). Fundamentals of real-time data processing architectures lambda and kappa. In SKILL 2018-Studierendenkonferenz Informatik (pp. 55-66). Gesellschaft für Informatik eV.
[7]. Nargesian, F., Zhu, E., Miller, R. J., et al. (2019). Data lake management: challenges and opportunities. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 12(12), 1986-1989.
[8]. Apache Hudi. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://hudi.apache.org/
[9]. Huawei Cloud. (n.d.). FusionInsight. Retrieved from https://www.huaweicloud.com/product/FusionInsight.html
[10]. Lin, Q. I. (2021). Analysis and discussion of component in the ecosphere of Hadoop from Huawei’s FusionInsight. In 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE) (pp. 713-717). IEEE.
[11]. Huang, D., Liu, Q., Cui, Q., et al. (2020). TiDB: a Raft-based HTAP database. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 13(12), 3072-3084.
[12]. Chen, J., Ding, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). ByteHTAP: Bytedance's HTAP system with high data freshness and strong data consistency. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 15(12), 3411-3424.
[13]. Jiang, X., Hu, Y., Xiang, Y., Jiang, G., Jin, X., Xia, C., Jiang, W., Yu, J., Wang, H., Jiang, Y., et al. (2020). Alibaba Hologres: A cloud-native service for hybrid serving/analytical processing. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 13(12), 3272–3284.









