

Volume 21
Published on October 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
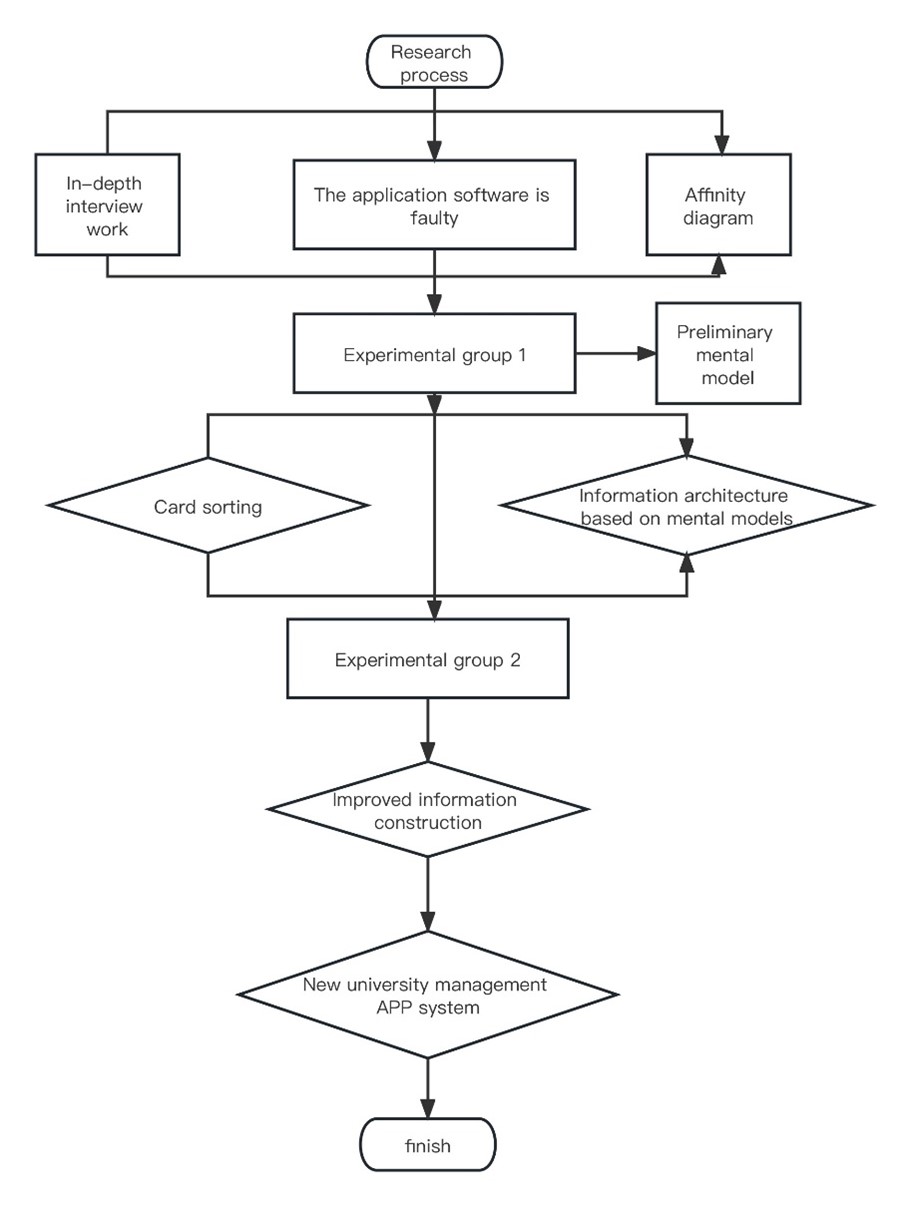
Based on the results of interviews conducted with university students in a certain university in Yunnan Province, this study identifies the problems of excessive information navigation, complex interface layout, and difficulty in locating the school system within the university management system APP. From the perspective of information architecture, this study designs a cognitive model that is suitable for the university management system APP of a certain university in Yunnan Province. By conducting tracking surveys and interviews with students from different majors, the study utilizes the affinity diagram method to construct a cognitive model for student users, which is further categorized by involving 10 participants. The data obtained after categorization is analyzed using hierarchical cluster analysis, and the information construction of the university management system APP is restructured accordingly. Through experiments, the characteristics and existing problems of the informationization construction of the university management system APP are determined, and the navigation label information of the management system is improved. The cognitive model of the university management system APP is reconstructed, resulting in the development of navigation names and classification methods for information construction that align with the cognitive models of student users. The research findings provide a basis and reference for other university management system APPs.

 View pdf
View pdf



In the VUCA (Volatile, Uncertain, Complex, Ambiguous) era, construction management faces unique challenges, particularly in the realm of workload assessment. This paper proposes an innovative solution to address these challenges: a blockchain-based GameFi model for construction workload assessment. This model leverages blockchain Non-Fungible Token (NFT) technology to issue various badges, reliably representing employees' workload. The technology ensures the authenticity and tamper-proof nature of the badges, thereby fostering employee motivation through a distributed trust system. This study provides fresh insights into the construction industry's digital transformation and is anticipated to lay the groundwork for similar applications in other sectors.

 View pdf
View pdf



Facial expression recognition with significant implications across fields such as psychology, computer science, and artificial intelligence. This paper proposes a combination of a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) and a Residual Network (ResNet) to construct a recognition model. The main objective of the proposed model is to refine the multi-level feature representation of facial expressions. This approach aims to provide a more holistic understanding of the diverse and complex nature of facial expressions, recognizing the intricate interplay between macro and micro-expressions. Experimental results underscore the model's considerable superiority over traditional methods, particularly in terms of accuracy and adaptability to objects of varying sizes and complexities. This comprehensive approach to facial expression recognition showcases the potential of integrating different neural network architectures, furthering our understanding of the subtleties of facial expressions. The research, therefore, presents a significant contribution to the field of facial expression recognition, demonstrating the efficacy of integrating multi-scale feature extraction techniques to improve model performance. It sets the stage for future research directions in this domain, paving the way for more sophisticated emotion recognition systems that can be deployed in real-world applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


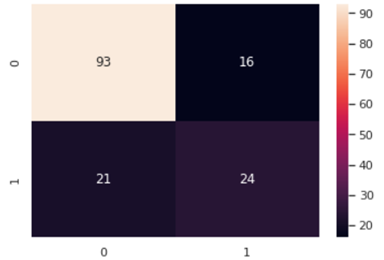
Diabetes is now a common disease for modern people. Diabetes will cause some serious symptoms. Diabetes patients will face a painful life, high cure cost, and even death. So, it is necessary to correctly diagnose diabetes and analyze the factors that mainly cause diabetes to prevent the happen of diabetes. This essay mainly focuses on training the computer to help the doctor to train the computer. Three Naive Bayes classifications will be used to train the computer to do the prediction, including the Gaussian Naïve Bayes, Bernoulli Naïve Bayes, and Multinomial Naïve Bayes. To compare each method’s result, accuracy will be the main index to measure whether a method is good enough to put into use. Not only the accuracy, classification report, and confusion matrix also assist to measure the prediction. Finally, the Gaussian Naïve Bayes has the highest accuracy and when combined with the confusion matrix and the classification report, the Gaussian Naïve Bayes has a huge advantage over the other two models. The accuracy of these models still does not satisfy medical demand. Some deep learning and high-level model are expected to optimize this project.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the increasing use of social media in our daily lives, it is crucial to maintain safe and inclusive platforms for users of diverse backgrounds. Offensive content can inflict emotional distress, perpetuate discrimination towards targeted individuals and groups, and foster a toxic online environment. While natural language processing (NLP) has been employed for automatic offensive language detection, most studies focus on English only, leaving languages other than English understudied due to limited training data. This project fills this gap by developing a novel multilingual model for offensive language detection in 100 languages, leveraging existing English resources. The model employs graph attention mechanisms in transformers, improving its capacity to extend from English to other languages. Moreover, this work breaks new ground as the first study ever to identify the specific individuals or groups targeted by offensive posts. Statistical analysis using F1 scores shows high accuracy in offensive language classification and target recognition across multiple languages. This innovative model is expected to enable multilingual offensive language detection and prevention in social media settings. It represents a significant step forward in the field of offensive language detection, paving the way for a safer and more inclusive social media experience for users worldwide.

 View pdf
View pdf


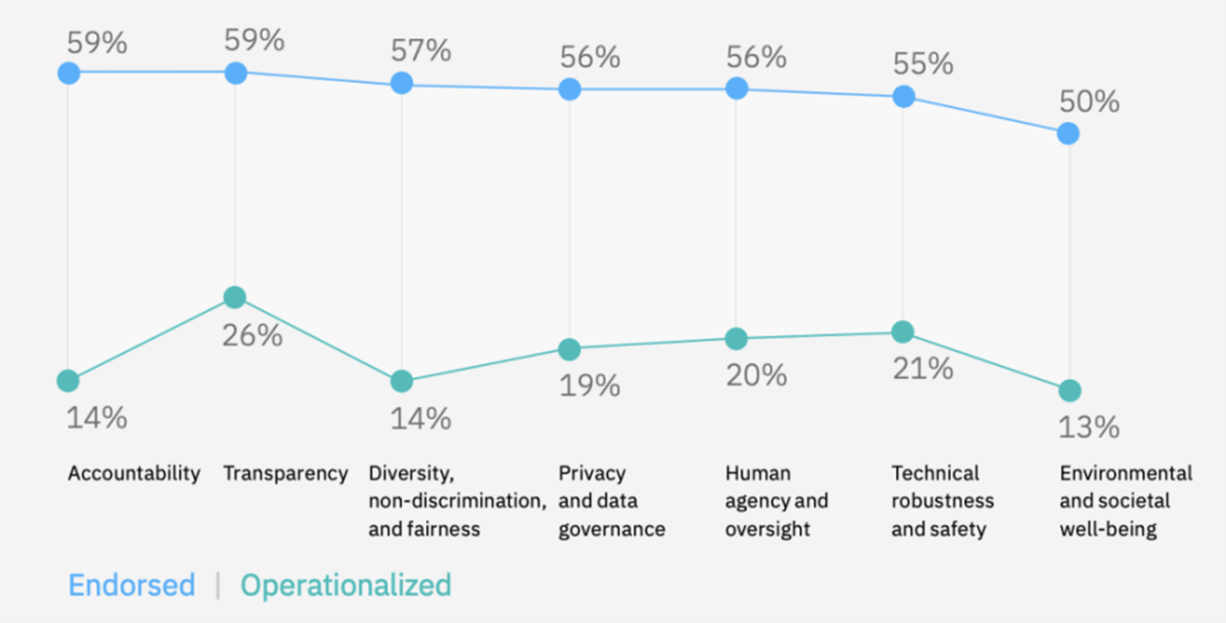
With the rapid development of Artificial intelligence (AI), the rapid development of AI also brings many new problems. Among them, the ethical and moral issues brought by AI have attracted people's attention. Due to the rapid renewal of artificial intelligence, many moral problems that have never been envisaged have also emerged. To avoid such problems and provide solutions for the future, this paper mainly analyzes the possible moral and ethical problems brought by artificial intelligence in the future, and adopted solutions and the results after adopting solutions. The research data are taken from published research, reports, government legislation, etc. This research believes that AI should comply with the current moral principles and be released after having solutions that can solve possible moral and ethical problems.

 View pdf
View pdf


Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease afflicting over 10 million patients worldwide, most commonly the elderly, that causes tremors, stiffness, movement loss, and other symptoms. Since symptoms are often mild and difficult to notice in the early stages of the condition, it can be hard to notice and diagnose until the condition has already become more severe. An earlier diagnosis of PD will allow treatment to begin earlier and lessen the impact of the disease. The goal of this work is to develop an affordable, non-intrusive, and accessible way of diagnosing PD. This neurodegenerative disorder leads to loss of movement control and other symptoms. Since there is no known cure for PD yet, early diagnosis would allow timely treatment and prevent the symptoms from worsening too quickly. Doing so in an affordable and non-intrusive way will minimize costs and maximize efficiency — removing the need for lengthy consulting with doctors and possibly expensive testing and medical equipment. This work presents the FaceTell system, which combines and optimizes traditional machine learning and deep learning to make predictions on the patient’s PD status based on video data of their faces. By analyzing a variety of attributes such as facial expressions and emotion prevalence/intensity, the model was able to achieve a more thorough examination of the patient’s condition and make predictions of similar accuracy compared to prior results. One main innovation was collecting data affordably: sampling publicly available videos from platforms like YouTube. This serves as a proof-of-concept to show that simple, affordable, and non-intrusive data collection methods can still produce viable results. Using methods and tools such as hyperparameter tuning, data cleaning, and Face++, the performance of the system readily improved. The ultimate results obtained include an F1 score of 0.86 and an accuracy of 89%, compared to prior results which reached up to 95% accuracy.

 View pdf
View pdf


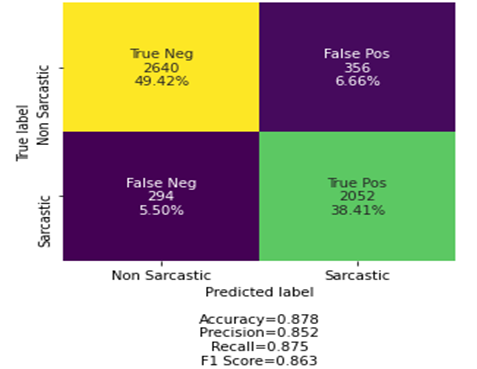
Sarcasm prediction is a text analysis task that aims to identify sarcastic and non-sarcastic statements in text. Sarcasm is a figure of speech that uses opposite or contradictory language to express a certain meaning or idea. Sarcasm is usually cryptic, vague, and suggestive, which makes sarcasm prediction a challenging task. In sarcasm prediction projects, techniques of natural language processing are usually leveraged to analyze and classify the text. The main challenge of this task lies in the fact that sarcasm usually has multiple manifestations and needs to consider the contextual and semantic information of the text. The prediction of sarcasm holds significant application value in natural language processing, such as social media analysis, public opinion monitoring, sentiment analysis and so on. In this paper, by controlling variables, the influence of adding the long short-term memory (LSTM) layer and changing the grid structure of the model on the accuracy of prediction results is explored. Moreover, accuracy of the LSTM prediction performance is compared with that of the bidirectional encoder representations from Transformers (BERT) model. At the same time, this paper analyzed and discussed the phenomenon that adding the number of LSTM model layers could not obtain higher prediction accuracy, and the accuracy gap of prediction results between LSTM model and BERT model, and finally obtained relevant conclusions.

 View pdf
View pdf


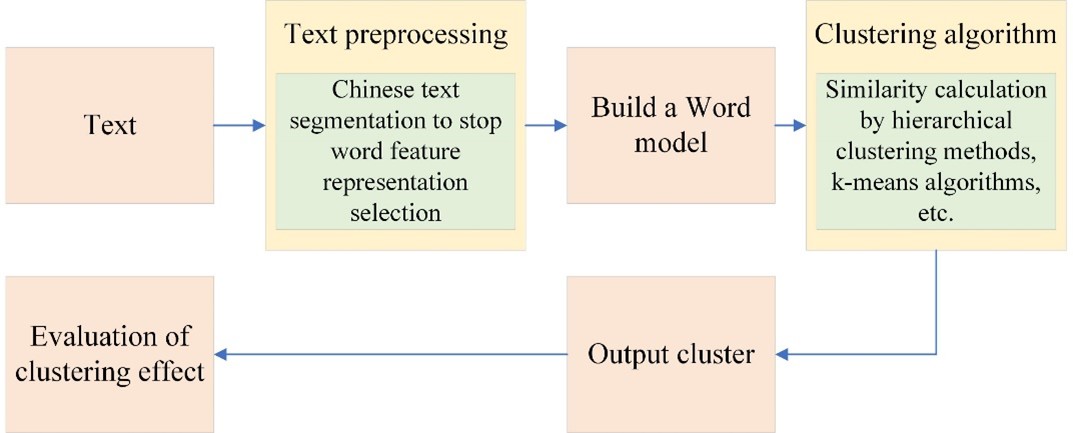
With the development of the Internet, information sharing is higher, and the amount of information that each user is exposed to is increasing. How to find the information peoples want from so much information is a very important question. The vast majority of these resources are related to textual information. The most intuitive manifestation of these problems is that when people usually use search engines, enter a piece of text, and search out the relevant website, if the algorithm is not good, the search results will be very unsatisfactory. Therefore, this paper studies the application of text similarity in text clustering in the Chinese context. First, the basic concept of text similarity is introduced. In addition, text clustering is explained/explained from three aspects: definition, application, and general processing process. Secondly, combined with the existing data, some mainstream clustering algorithms are comprehensively summarized. Then, combined with the above content, the similarity calculation method in text clustering is analyzed. Finally, the above methods are compared and analyzed according to the experimental results in the Python environment.

 View pdf
View pdf


Brain tumors pose a substantial health challenge globally. Their accurate detection and segmentation are crucial for effective treatment, and recent advancements in machine learning (ML) present a promising solution to these tasks. This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of traditional and modern ML algorithms for brain tumor detection and segmentation. It highlights the pivotal role of ML in advancing brain tumor analysis and how it can potentially mitigate the impact of malignant tumors. Traditional image processing techniques have shown their value but face limitations in dealing with the complexity of brain tumors. The integration of ML has substantially enhanced the capabilities of traditional detection techniques, with architectures such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) providing improved results. Moreover, brain tumor segmentation techniques have also seen significant enhancements, with the transition from conventional techniques like Region Growing and Watershed methods to state-of-the-art deep learning methods, such as U-Net. Despite these advancements, great challenges remain. Ongoing researches are necessary to further harness the potential of ML in brain tumor diagnosis and treatment. The findings of this review underscore the significance of ML in brain tumor analysis and its profound potential impact on patient outcomes and the overall landscape of cancer treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf




