1. Introduction
On May 31, 2023, Dolls Kill's Los Angeles store was subject to looting and vandalism following a controversial social media post by Shoddy Lynn, the co-founder and Chief Creative Officer. The post endorsing law enforcement during the "Black Lives Matter" protests sparked widespread outrage and backlash against the company. Dolls Kill issued an apology that many felt did not adequately address the severity of the situation, resulting in skepticism and rejection [1]. Furthermore, accusations of promoting racism through the sale of t-shirts with designs like "Goth is White" have damaged the brand's reputation and demonstrated insensitivity towards the fight against racial injustice [2]. Additionally, Dolls Kill has faced allegations of unauthorized use of the artwork without proper compensation and criticism for supposedly glorifying rape culture and mental illness [3]. Despite these controversies, Dolls Kill remains a prominent player in the online retail fast fashion industry, recognized as one of the top firms in San Francisco by Inc. Magazine. However, it is important to acknowledge that these controversies have significantly impacted the brand's reputation and consumer perception [2]. Understanding the factors driving its success requires studying the influence of brand loyalty, customer satisfaction, and ethical considerations when purchasing from the company.
1.1. Brand loyalty and truth
According to Chaudhuri and Morris, brand loyalty comprises two crucial components: attitude and behavior [4]. Attitudinal commitment and repeat purchase behavior collaborate to shape customer loyalty, which underscores the importance of trust in the brand. Customers who exhibit brand loyalty are often willing to pay a premium due to their perception of unique value compared to alternatives [4]. Shoppers typically view their shopping and consumption experiences as personally relevant [5]. This distinctive value can originate from a higher level of trust in the brand's reliability or from a more positive emotional connection with the brand. Establishing trust fosters highly valued exchange relationships, ultimately leading to brand loyalty [4]. Since customer satisfaction is crucial for loyalty, as it is based on direct experiences, it is easily accessible and can impact behavioral intentions, regardless of other factors [5].
1.2. Brand ethic and Brand identity
An ethical brand is characterized by its commitment to conducting business in a manner that avoids causing harm and demonstrates principles of integrity, honesty, responsibility, accountability, and respect toward a broad range of stakeholders. [6]For a brand to be regarded as ethical, it must meet significant standards regarding the quality of its products, the quality of its services, and the perceived pricing.[6] Some scholars have argued that every brand should adhere to ethical standards, primarily because customers have easy access to information about the company's practices, which can significantly impact their purchasing decisions. [4&6]
Brand identity plays a crucial role in fostering brand loyalty, even when unethical events occur [7]. Customers with a strong brand identity may purposely overlook such events and rationalize them, considering themselves aligned with the brand and willing to support it [8]. This strong identification with the brand can lead customers to stand with Dolls Kill and maintain trust in the company, even in the face of heightened societal scrutiny towards its unethical actions.
1.3. Problem state
This study aimed to examine how brand loyalty and ethical standards impact customer perceptions and satisfaction levels within the controversial company Dolls Kill. Despite facing criticism, the research suggests that loyal customers tend to have positive experiences and attitudes toward the brand, leading to high satisfaction. These customers remain committed to the brand, even in the face of perceived unethical behavior.
2. Method
2.1. Data collection
This research exclusively analyzed customer reviews of "Dolls Kill" on Trustpilot from 2020 to the present. A total of 4671 comments were collected for analysis, focusing solely on the textual content without considering reviewer names, comment titles, or geographical locations. By examining both positive and negative viewpoints, we aimed to understand individuals' perspectives and gain insights into the overall perception of Dolls Kill. The analysis also aimed to assess customer satisfaction and identify keywords that could indicate loyalty toward the company. Data collection and analysis were conducted using tools like 'Octopus', 'Word-count', 'Excel', and 'Python'. 'Octopus' was used to gather comments from websites and organize them in an Excel sheet, capturing publication time, titles, and people's opinions. After filtering irrelevant and empty comments using Python, the resulting dataset comprised 4671 relevant comments. 'Wordcount' was then employed to identify the top 20 frequently mentioned keywords for further investigation.
2.2. Sampling
Out of a total of 4761 comments from the website from 2020 January to current, there are 4671 comments that can be used as the sample for this study.
Table 1: Top 20 Keyword Table
Positive Words | Count | Negative words | Count |
Great service | 842 | Wrong item | 138 |
Love company | 630 | Wrong size | 122 |
Helpful | 387 | return | 118 |
Quick respond | 225 | Wrong address | 99 |
Fast | 214 | Issue service | 63 |
Recommend | 194 | Wrong shipping | 49 |
Love Cloth | 127 | Lost transit | 43 |
Package lost | 42 | ||
Bad experience | 29 | ||
Missing item | 26 | ||
Issue shipping | 25 | ||
Issue store | 23 | ||
Total | 2619 | Total | 777 |
2.3. Measure
Analyzing the top 20 keywords mentioned allows us to gain a comprehensive understanding of public opinion about the company. Categorizing these keywords into positive and negative helps us identify areas of support and concern. By examining the associated sentiments, we can determine the prevailing overall sentiment among commenters, providing valuable insights into customer preferences and public perception. Analysis of Table 1 findings starting in 2020 reveals noteworthy results. Positive keywords like 'great service,' 'love company,' 'helpful,' 'quick response,' 'fast,' 'recommend,' and 'love cloth' appeared 2619 times, indicating high customer satisfaction in various aspects such as service quality and product appreciation. Conversely, negative keywords like 'wrong size,' 'wrong address,' 'wrong item,' 'lost transit,' 'package lost,' 'issue service,' 'bad experience,' 'missing item,' 'return,' 'issue shipping,' 'wrong shipping,' and 'issue store' were mentioned 777 times, highlighting challenges faced by customers including shipping issues, order inaccuracies, and overall customer service problems.
2.4. Result and Analysis
Customers provide more feedback on negative experiences or encountered issues, while positive experiences may be expressed using fewer varied phrases. This information is valuable for Dolls Kill to improve its services, enhance customer satisfaction, and promptly address any concerns, fostering a more positive overall perception. Negative words account for 22.9% of all words, while positive words make up 77.1%. In terms of categories, negative keywords represent 65%, while positive keywords account for 35%. Dolls Kill receives a high rating on Trustpilot, with negative review keywords accounting for 65% of the top 20 keywords. However, most customers have had positive experiences, particularly in terms of service. Positive comments outweigh the negatives, indicating customers generally have positive sentiments towards the company. Negative experiences result in a wider range of negative keyword categories but receive fewer comments in comparison.
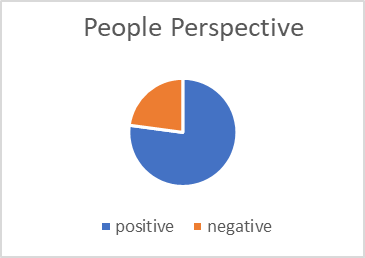
Figure 1: Percentage of Top 20 Words Count
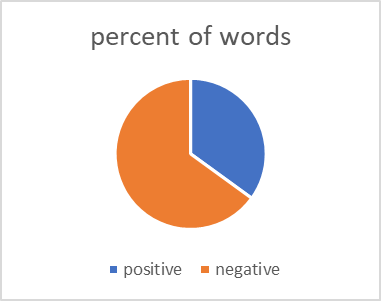
Figure 2: Percentage of Top 20 Words categories
3. Discussion
The research offers valuable insights into how the company is perceived overall. Despite facing challenges, most comments express a positive perspective, indicating customer satisfaction. However, the lower number of negative comments suggests that the company should pay attention to and address any complaints or issues raised by customers.
3.1. Brand loyalty and satisfaction level
The significance of brand loyalty is evident in the prominence of the keyword 'love company' among the top 20 most frequently used words. The frequent use of the word "love" indicates a high level of satisfaction that customers experience when engaging with Dolls Kill. The positive sentiment towards the shopping experience strengthens brand loyalty. Emotional connection and love for a brand are vital for driving loyalty, marketing success, and increased customer engagement. This enables Dolls Kill to establish robust and profitable customer relationships [4]. Data indicates Dolls Kill has substantial brand loyalty, influencing customer behavior and fostering repeat purchases and emotional commitment. These factors significantly impact sales-related brand outcomes and contribute to the brand's ability to command premium prices compared to market competitors [4]. Dolls Kill's strong brand loyalty highlights its success in building lasting connections with customers. Consistent with a study by Suh Jung-Chae and team, it was found that: Customer satisfaction's impact on brand loyalty and attitudes varies with product involvement. In low-involvement cases, customer satisfaction has a stronger influence, while corporate image and attitudes toward advertisements have a greater effect in high-involvement situations [5]. Hence, the satisfaction level is significant for brand loyalty, which affects customers’ punching behavior.
3.2. Limitation
This research exclusively relies on Trustpilot data, specifically analyzing 4671 review comments from 2020 onwards. Also, Data analysis may be limited by the software used.
4. Conclusion
To maintain a favorable image and ensure ongoing customer satisfaction, it is crucial for the company to build on positive sentiment and address any customer concerns or issues. Analyzing data from review websites, the research shows that intense satisfaction and affinity among customers lead to high brand loyalty. However, the absence of ethical practices in the "Top 20 Keywords" suggests customers may not prioritize the company's unethical practices.
References
[1]. Pappa, M. (2022, July 6). Why are people protesting dolls kill? Controversy explained. The Current Online. https://thecurrent-online.com/controversy/dolls-kill-controversies/15607/
[2]. Tost, M. (2020, June 5). Dolls kill called out for supporting police amid nationwide BLM protesting. Your EDM. https://www.youredm.com/2020/06/04/dolls-kill-called-out-for-supporting-police-amid-nationwide-blm-protesting/
[3]. Team, Y. (2023, May 3). 3 worst dolls kill controversies: Why they are problematic. Your Sustainable Guide. https://yoursustainableguide.com/is-dolls-kill-bad/
[4]. Chaudhuri, A., & Holbrook, M. B. (2001). The chain of effects from Brand Trust and brand affect to brand performance: The Role of Brand Loyalty. Journal of Marketing, 65(2), 81–93. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkg.65.2.81.18255
[5]. Suh, Jung-Chae; Youjae, Y. (2006). When brand attitudes affect the customer satisfaction-loyalty relation: The moderating role of product involvement. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 16(2), 145–155. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327663jcp1602_5
[6]. Iglesias, O., Markovic, S., Singh, J. J., & Sierra, V. (2017). Do customer perceptions of Corporate Services Brand Ethicality Improve brand equity? considering the roles of Brand Heritage, Brand Image, and Recognition benefits. Journal of Business Ethics, 154(2), 441–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-017-3455-0
[7]. Syed Alwi, S. F., Muhammad Ali, S., & Nguyen, B. (2017). The importance of ethics in branding: Mediating effects of ethical branding on company reputation and brand loyalty. Business Ethics Quarterly, 27(3), 393–422. https://doi.org/10.1017/beq.2017.20
[8]. Dalman, M. D., Buche, M. W., & Min, J. (2017). The differential influence of identification on ethical judgment: The Role of Brand Love. Journal of Business Ethics, 158(3), 875–891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-017-3774-1
Cite this article
Meng,Z. (2024). The Influence of Brand Loyalty and Ethical Practices on Company Growth: A Study on Dolls Kill's Customers’ Satisfaction in the USA Using Trustpilot Review Comments. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,73,319-323.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Pappa, M. (2022, July 6). Why are people protesting dolls kill? Controversy explained. The Current Online. https://thecurrent-online.com/controversy/dolls-kill-controversies/15607/
[2]. Tost, M. (2020, June 5). Dolls kill called out for supporting police amid nationwide BLM protesting. Your EDM. https://www.youredm.com/2020/06/04/dolls-kill-called-out-for-supporting-police-amid-nationwide-blm-protesting/
[3]. Team, Y. (2023, May 3). 3 worst dolls kill controversies: Why they are problematic. Your Sustainable Guide. https://yoursustainableguide.com/is-dolls-kill-bad/
[4]. Chaudhuri, A., & Holbrook, M. B. (2001). The chain of effects from Brand Trust and brand affect to brand performance: The Role of Brand Loyalty. Journal of Marketing, 65(2), 81–93. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkg.65.2.81.18255
[5]. Suh, Jung-Chae; Youjae, Y. (2006). When brand attitudes affect the customer satisfaction-loyalty relation: The moderating role of product involvement. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 16(2), 145–155. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327663jcp1602_5
[6]. Iglesias, O., Markovic, S., Singh, J. J., & Sierra, V. (2017). Do customer perceptions of Corporate Services Brand Ethicality Improve brand equity? considering the roles of Brand Heritage, Brand Image, and Recognition benefits. Journal of Business Ethics, 154(2), 441–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-017-3455-0
[7]. Syed Alwi, S. F., Muhammad Ali, S., & Nguyen, B. (2017). The importance of ethics in branding: Mediating effects of ethical branding on company reputation and brand loyalty. Business Ethics Quarterly, 27(3), 393–422. https://doi.org/10.1017/beq.2017.20
[8]. Dalman, M. D., Buche, M. W., & Min, J. (2017). The differential influence of identification on ethical judgment: The Role of Brand Love. Journal of Business Ethics, 158(3), 875–891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-017-3774-1









