

Volume 221
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2025 Symposium: Global Trends in Green Financial Innovation and Technology
Green finance has steadily grown to be a significant factor influencing the modification of corporate capital structures in recent years as investors have become more aware of ESG and global climate rules have gotten more stringent. However, how exactly green financing affects corporate capital structures remains a key issue of concern in both academia and practice. Motivated by this, this paper aims to explore the impact of green financing on corporate capital structures. Combining literature review and case analysis, this paper selects Apple Inc. and ExxonMobil as typical cases and reveals, through comparative analysis, the differentiated impacts of green financing on different types of enterprises. The results show that green financing has a debt redistribution effect: it can extend debt maturities, reduce financing costs, and decrease reliance on equity financing. At the equity structure level, green financing attracts long-term investors by enhancing a company’s “green reputation,” thereby stabilizing shareholder structures and lowering the cost of equity capital. In terms of capital costs, the “greenium” effect of green bonds and the accumulation of a long-term green reputation significantly optimize the weighted average cost of capital (WACC). In sum, green financing not only improves the stability of corporate capital structures but also enhances corporate value and sustainable development capacity.

 View pdf
View pdf


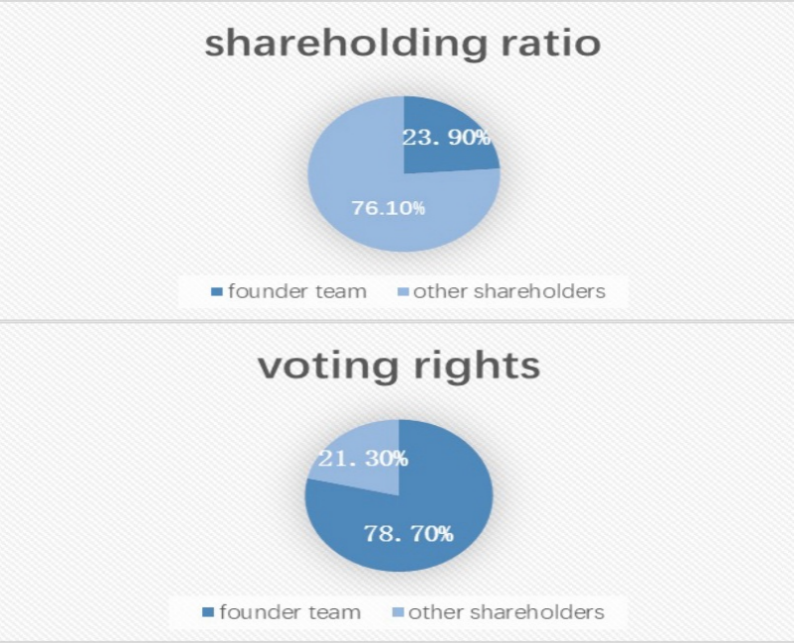
The financial fraud case of Luckin Coffee stands as one of the most iconic fraud incidents in the history of Chinese companies listing in the United States. Its complete journey from swiftly achieving listing, experiencing delisting, to ultimately relisting has exposed three core loopholes: governance imbalance, information distortion, and accounting manipulation. The power struggle between the founding team and capital parties rendered the internal control mechanism ineffective, creating room for such practices as inflating orders and forging transactions. In terms of information disclosure, it evaded supervision by fabricating supply chain transactions through related parties, exaggerating store revenue data, and taking advantage of the information asymmetry of the U.S. stock market regarding emerging business formats. For accounting manipulation, it exploited the accounting loopholes in the complex franchise model to include false revenues in financial statements. It has also sounded an alarm for the global capital market. This article focuses on governance failures, inaccurate disclosures and fraudulent means, analyzing the institutional incentives and specific operational methods behind its fraudulent behavior. At the same time, it interprets the core path of self-rescue through governance reconstruction and technology application, thereby providing practical references for enterprises in financial compliance management and market supervision.

 View pdf
View pdf




