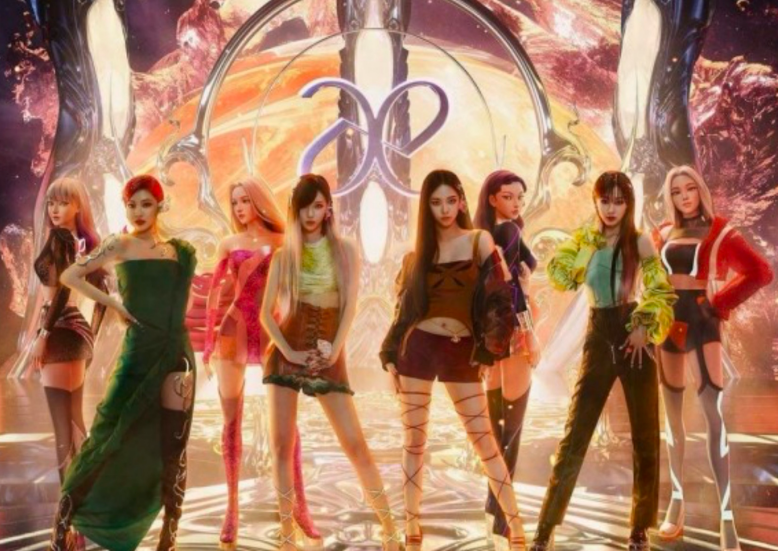1. Introduction
Metaverse, a combination of the prefix “meta” (implying transcending) and the word “universe”, describes a hypothetical synthetic environment linked to the physical world [1]. It is a special medium transferring people from reality to an imaginary world on a spiritual level, and it does not really exist in the real world. It is worth noting that the metaverse is not a concept that appeared recently. Early in 1992, Neal Stephenson created the word “metaverse” in his novel Snow Crash to define a virtual world where people can create their own 3-dimensional (3D) avatars and are able to buy or sell real estate [2]. However, the concept of the metaverse was widely known to the general public in 2021 [3]. At present, people can work, socialize, and organize or participate in various entertaining activities in the metaverse as they do in reality. The metaverse breaks the boundary between the real world and the virtual world, satisfies people’s spiritual needs, and generally becomes a future trend.
This paper is devoted to discussing three topics related to the metaverse. Firstly, the way that the metaverse is being applied in the entertainment industry today is included, and to make it easier for readers to understand, some practical examples are taken. Secondly, the commercial value of the metaverse is mentioned and analyzed. The metaverse is now being broadly promoted to the public and is extremely famous, which indicates that it has a stable market, and its market acceptance is relatively high. Finally, this paper predicts the future development trend of the metaverse based on its development history. This paper can help clearly show the future development of the metaverse in the field of digital culture, suggesting its contribution of great value as well as an irreplaceable position.
2. The Application of the Metaverse in the Entertainment Industry
In the past, some writers and directors inserted the concept of the metaverse into their works to illustrate their own understandings of it, and these works were highly discussed at that time. With the advancement of science and technology, the metaverse is now combined with many state-of-the-art technologies, including virtual reality (VR), a new technology utilized in many fields, especially games and medical science. VR also contains several types, such as Entry VR (EVR), Basic VR (BVR), Advanced VR (AVR), and Immersion VR (IVR) [4]. Diverse hardware leads them to own different functions, so users are able to select the proper one based on their user experience as well as prices. Probably, people from various walks of life recognize the metaverse differently but, overall, it can be understood as a virtual space where specific machines are manipulated to draw a fantasy world coming from humans’ minds, and the users can even participate in this virtual world to do something they can not do in their real life.
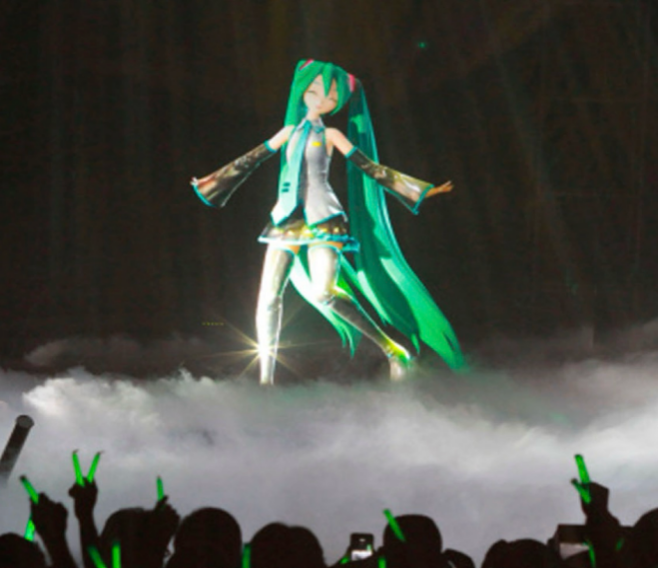
Combined with VR technology, the metaverse provided entertainment companies with a new idea to create a new generation of virtual idol groups. These virtual identities were later proved to be popular among the public, and they led a new era of science and technology. As an illustration, Hatsune Miku (see Fig. 1), the first virtual idol around the world, was launched by a Japanese corporation, Crypton Future Media, in 2004. Hatsune Miku means “the first sound from the future” in Japanese. It was primarily a software that adopted the singing synthesis technology named Vocaloid mainly for music creation [5]. With her sweet tone, Hatsune Miku has become a highly sought-after virtual idol and received a large number of fans, dominating the 2D world and becoming a top female star. Her fame is so big that almost every comic show has a cosplayer copying her appearance.
|
|
Figure 1: The hologram of the virtual idol Hatsune Miku performing in front of fans [6]. | Figure 2: AESPA human and digital “ae” members standing side by side [7]. |
Similarly, SM entertainment company, a huge and well-known Korean corporation, launched a female K-pop group named AESPA, including 4 metaverse members and 4 real-world members (see Fig. 2). Their albums center on the concept of the metaverse and bring it into the eyes of the global audience. Each human group member matches with a specific artificial intelligence image, who has a unique appearance and superpower. In addition, Naevis, another virtual character SM designed, is an additional member of the group AESPA. She does not participate in any album making, however, she worked on almost all the comeback music videos of AESPA. Her presence was extremely profitable for the company, making the album more creative and attracting a lot of attention. Overall, a large amount of money and effort are invested in AESPA, the first metaverse girl group in the K-pop universe, and, in turn, the group has also obtained great success in the global entertainment industry [8]. One of their albums breaks the top historical sales record in China, becoming a veritable sales champion.
3. The Commercial Value of the Metaverse
With the development of science and technology as well as the rapid change of people's lifestyles, the metaverse has gradually integrated into the entertainment, educational, medical, and other fields in a variety of forms. US research company Gartner predicts that by 2026, 25% of the global population will spend at least one hour per day in the metaverse. This includes many aspects of daily life, such as education, work, and leisure activities [9]. As a result, people will gradually become dependent on this technology. Many capitalists also see the development potential of the metaverse, so more and more technical teams begin to be built by companies. At the same time, more in-depth research is conducted on the metaverse as well. The metaverse has been given great commercial value and has now become an essential part of people's lives.
For example, collaboration with metaverse characters has become a very popular marketing model in business. Co-branding is a commercial behavior in which a company combines its brand with a cross-domain brand to form a composite brand. Usually, it is a win-win strategy for both of the companies, as customers will be attracted to try new things, and sometimes, merchants will give buyers some freebies related to the cross-domain brand, which can also draw more customers to buy their goods, thus getting high incomes [10].
Nowadays, co-branding products are very popular, and many companies build cooperation with 2D/3D character roles, in order to seize the attention of consumers and stimulate their desire to buy products. KFC’s collaboration with Hallkyuu!! can be taken as an instance. Hallkyuu!! is a teenage comic strip created by Japanese cartoonist Haruichi Furukate. As early as 2012, when it was first published, it was sought after by many young people. KFC is a global chain of fast food brands. With low prices and good taste, it has become a leader in the fast food industry. However, no matter how good the product is, there is a risk of it being replaced by other products or being eliminated from society. Nowadays, fast food brands are emerging in an endless stream. In order to stand out in the fierce competition, major brands need to promote consumption by continuous innovation, so customers will be willing to pay for their products continuously. KFC’s launching of exclusive Haikyuu!! merchandise and themed stores have succeeded in attracting the attention of comic fans by satisfying their curiosity and stimulating their desire to buy KFC products.
4. The Future Development of the Metaverse
Even though the related technology is relatively advanced now, building a complete metaverse still faces a large number of challenges. At present, the Internet has entered into every aspect of human life, and it has passed on a lot of useful information to netizens. As a new concept, the metaverse has brought many questions to people about the future, such as whether AI will really replace human beings in the future and whether humans will have a distinctive AI image of their own in a parallel universe. This greatly stimulates people's curiosity about the future world, which encourages many researchers to delve further into its secrets. The creation of the metaverse is a major step forward in the history of world science and technology, and it marks the birth of avatars for the great benefit of many companies. These avatars may be idols for star-struck fans, soulmates for lonely people, or role models for the strong, and they are bringing positive energy to the audience in a whole new way. However, the metaverse can also pose a threat to humans since digital technology such as AI is mainly the result of data and calculation formulas that can be used by others with a bad intention, and, sometimes, the unknown conjecture can make people be afraid of technology. Nevertheless, there is no need to worry too much since the rapid development of science and technology is an inevitable trend, and it will make a great contribution to society.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, this paper introduces the definition of the metaverse, studies its application in the entertainment industry by taking the virtual singer Hatsune Miku from Japan and the virtual girl group AESPA from Korea as illustrations, and explores the commercial value of the metaverse as well as its future development. It can be summarized that the metaverse has great potential in the entertainment industry and carries significant commercial value. For capitalists, the metaverse is a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity, and a mature market business model is needed. For individuals, the metaverse can bring convenience and happiness so that people are highly efficient and able to release their pressure from real-life study and work. However, it is essential to realize that the metaverse is originally an artificial imaginary world where everything is idealized, therefore, users should not rely too much on it. In the future, research can be conducted to study more values the metaverse creates for humans, including the real interactions with the virtual identities in the metaverse.
References
[1]. Cheng, R., Wu, N., Chen, S. and Han, B. (2022). Will Metaverse Be NextG Internet? Vision, Hype, and Reality. In IEEE Network, 36(5), 197-204. doi: 10.1109/MNET.117.2200055.
[2]. Lyu, F. J. (2022). Taking "virtual idol" as an example to discuss the boundary of virtual identity. Tianjin Academy of Fine Arts. doi:10.27361/d.cnki.gtmsy.2022.000067.
[3]. Sun, Z.Y. (2022). Diffraction of AESPA girl group programs under the metaverse horizon. (Shaanxi Normal University).
[4]. Bakkar, K. I. (1999). Development of a virtual reality milling machine for knowledge learning and skill training (Doctoral dissertation, Dublin City University).
[5]. Their, R. (2016). The Hatsune Miku phenomenon: More than a virtual J-pop diva. J. Popular Cult, 49, 1107-1124.
[6]. Jørgensen, S. M. H., Vitting-Seerup, S. and Wallevik, K. (2017). Hatsune Miku: an uncertain image. Digital Creativity, 28(4), 318-331.
[7]. Nuranda, D. R. and Purwaningtyas, M. P. F. (2023). Between Human and Virtual Idol: Fans Reception Analysis of Digital Alter Ego Concept. Komunikator, 15(1), 31-40.
[8]. Jeong, M. and Kim, S. (2023). What makes 'aespa', the first metaverse girl group in the K-pop universe, succeed in the global entertainment industry?. In 32nd European Conference of the International Telecommunications Society (ITS). Madrid, Spain, 19th - 20th June 2023.
[9]. Walk-Morris, T. (2022). Gartner: A quarter of consumers will use the metaverse daily by 2026. RETAILDIVE. https://www.retaildive.com/news/gartner-a-quarter-of-consumers-will-use-the-metaverse-daily-by-2026/618474/#:~:text=As%20companies%20invest%20heavily%20into%20the%20metaverse%2C%20a,attend%20school%2C%20socialize%20or%20consume%20entertainment%20by%202026.
[10]. Washburn, J. H., Till, B. D. and Priluck, R. (2000). Co-branding: Brand equity and trial effects. Journal of consumer marketing, 17(7), 591-604.
Cite this article
Fang,Z. (2024). The Application of the Metaverse in the Entertainment Industry and Its Commercial Value. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,84,116-119.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Cheng, R., Wu, N., Chen, S. and Han, B. (2022). Will Metaverse Be NextG Internet? Vision, Hype, and Reality. In IEEE Network, 36(5), 197-204. doi: 10.1109/MNET.117.2200055.
[2]. Lyu, F. J. (2022). Taking "virtual idol" as an example to discuss the boundary of virtual identity. Tianjin Academy of Fine Arts. doi:10.27361/d.cnki.gtmsy.2022.000067.
[3]. Sun, Z.Y. (2022). Diffraction of AESPA girl group programs under the metaverse horizon. (Shaanxi Normal University).
[4]. Bakkar, K. I. (1999). Development of a virtual reality milling machine for knowledge learning and skill training (Doctoral dissertation, Dublin City University).
[5]. Their, R. (2016). The Hatsune Miku phenomenon: More than a virtual J-pop diva. J. Popular Cult, 49, 1107-1124.
[6]. Jørgensen, S. M. H., Vitting-Seerup, S. and Wallevik, K. (2017). Hatsune Miku: an uncertain image. Digital Creativity, 28(4), 318-331.
[7]. Nuranda, D. R. and Purwaningtyas, M. P. F. (2023). Between Human and Virtual Idol: Fans Reception Analysis of Digital Alter Ego Concept. Komunikator, 15(1), 31-40.
[8]. Jeong, M. and Kim, S. (2023). What makes 'aespa', the first metaverse girl group in the K-pop universe, succeed in the global entertainment industry?. In 32nd European Conference of the International Telecommunications Society (ITS). Madrid, Spain, 19th - 20th June 2023.
[9]. Walk-Morris, T. (2022). Gartner: A quarter of consumers will use the metaverse daily by 2026. RETAILDIVE. https://www.retaildive.com/news/gartner-a-quarter-of-consumers-will-use-the-metaverse-daily-by-2026/618474/#:~:text=As%20companies%20invest%20heavily%20into%20the%20metaverse%2C%20a,attend%20school%2C%20socialize%20or%20consume%20entertainment%20by%202026.
[10]. Washburn, J. H., Till, B. D. and Priluck, R. (2000). Co-branding: Brand equity and trial effects. Journal of consumer marketing, 17(7), 591-604.