1. Introduction
Operations management is a crucial component of any firm. It guarantees streamlined procedures, maximized resource utilization, and the accomplishment of established corporate objectives [1]. It involves coordinating the entire process from input to output to ensure an organization operates successfully and efficiently. Walmart is a global retailer that has grocery stores, supermarkets, hypermarkets, and discount stores in more than 19 countries. The company's operations management prioritizes retail service through an emphasis on efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The company's generic competitive strategy emphasizes low cost and low selling prices, with an operational focus that is considered vital [2]. Establishing operational performance objectives is essential to assess the efficacy and efficiency of Walmart's overall process. Walmart focuses on operational performance targets that aim to decrease costs and waste through enhancing productivity and optimizing resource planning and use. Embracing a cost leadership generic strategy involves supplying goods and services at cheaper rates than competitors, which can only be achieved by maintaining low costs throughout the entire process [3]. The company has successfully provided affordable products and improved client experiences by utilizing many elements of operations management, including supply chain, inventory, quality, and capacity management. This work employs literature review and literature analysis as methods for research. The paper examines the disparities in operational management and performance among organizations and the implementation of competitive strategies. The study highlighted the importance of operation management in Walmart's development process by emphasizing the significance of precise planning and performance. It offers a solid basis and guidance for companies facing uncertainty and various options in operational management going forward.
2. Quality Management
Quality management involves supervising the implementation of all tasks and procedures in a specific operation to reach and uphold the required level of perfection. The dimensions of quality, as stated in reference [1], can be assessed through performance, reliability, perception, durability, characteristics, conformance, and service. Recently, there has been a surge in product recalls due to quality issues. Due to Walmart's huge scale and the multitude of locations it oversees, ensuring uniform quality is a difficult task. Quality control is crucial for a company that is a major supplier of fruits, vegetables, and seafood to improve customer satisfaction and reduce expenses associated with issues of low quality that could result in product recalls. In 2010, the firm made the decision for all its stores to adhere to Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) regulations, which mandate suppliers to conduct audit inspections to guarantee product quality. However, this only covers a small part of the company's product range and procedures, highlighting the necessity for a more thorough quality management strategy.
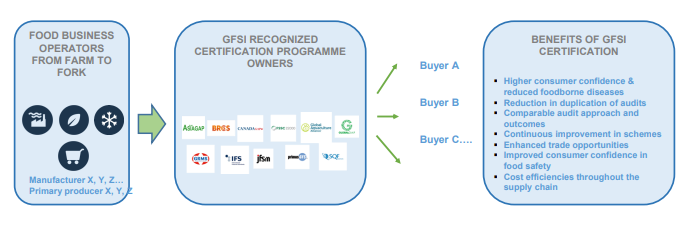
Figure 1: The GFSI model [4]
Walmart has divided its operations management into three tiers of quality standards to make thorough quality decisions. The lower categories represent the least quality standards, primarily associated with names like Great Value [5-6]. This quality standard primarily emphasizes providing clients with the highest value at the lowest possible cost. The middle tier ensures average market quality that is similar to most low-cost shops. This tier focuses on performance, allowing sales professionals to use items to boost sales figures. The highest quality standards involve expectations that above the average in the retail industry. However, this tier is only relevant to a small selection of Walmart's products, primarily from the Sam's Choice private label brand. Classifying quality standards into distinct tiers with varied quality expectations helps Walmart manage the quality-cost dynamics that affect customer perception of pricing and perceived value [5]. This quality management technique assists Walmart in upholding quality standards for various consumer segments while offering a diverse array of products at varying pricing levels.
Furthermore, Walmart's current performance is also attributed to its efficient utilization of total quality management (TQM) decision-making process. TQM focuses on ongoing enhancement, client contentment, and streamlined procedures across the complete supply chain and retail activities [7-9]. The organization works with its suppliers to follow established quality standards and ensure consistency in quality that aligns with company, industry, and consumer expectations, as demonstrated by moves like adopting the GFSI model. The organization also focuses on continuous improvement throughout its operations. Walmart implements testing and verification processes for its own brands and external brands offered in its stores to provide valuable feedback on areas that need improvement to satisfy quality standards (figure 2) [9]. Additionally, the organization provides extensive personnel training programs to enhance its capacity to fulfill customer requirements and maintain efficient quality control across all operational phases [10]. Therefore, Walmart's diverse Total Quality Management (TQM) strategy enhances its ability to continually provide value to customers.
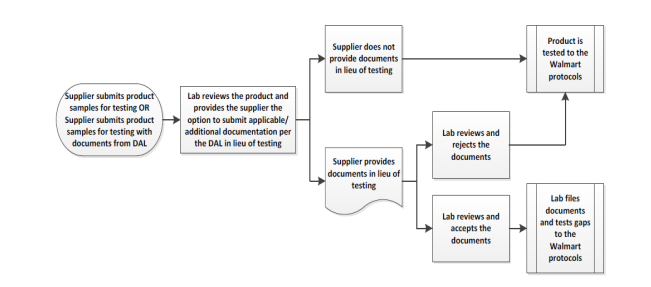
Figure 2: Walmart’s testing and verification process to ensure quality [9]
3. Inventory Analysis
Inventory management is crucial for Walmart's operations, particularly in achieving its goal of minimizing costs to support the company's cost leadership strategy. Efficient inventory management enhances the company's capacity to adapt to market developments by maintaining adequate stock levels to meet client demands without excess or shortage [1,7]. Walmart serves both customers who shop in-store and those who shop online. Therefore, the inventory analysis must take into account trends and demand issues among various consumer categories. The organization has used data-driven inventory management and forecasting to enhance accuracy in inventory planning as part of its extensive operations. The organization utilizes an AI-powered inventory management system to maintain the ideal products required by clients at a reduced cost [9]. Walmart uses historical data and predictive analytics to decide which items to stock, improving the overall shopping experience. This inventory management strategy involves using historical sales data and seasonality to forecast future demand, enabling the organization to predict and understand inventory needs [1]. Inventory forecasting at Walmart aids in comprehending the movement of items among its many operations, allowing for the maintenance of ideal inventory levels to optimize costs and improve customer satisfaction.
Walmart employs a vendor-managed inventory approach with just-in-time cross-docking for inventory analysis. Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) is a method where the buyer, like Walmart, shares inventory and demand information with the supplier to improve inventory management, rather than making judgments independently on order quantities [11], as shown in figure 3. By sharing real-time inventory data with important suppliers, Walmart reduces inventory overhead costs, improves forecasting, and aligns inventory with consumers' demand. However, the VMI method provides Walmart with little adaptability in response to abrupt shifts in demand patterns and market conditions. Furthermore, its performance depends on the reliability of suppliers. Walmart's just-in-time cross-docking system minimizes inventory levels to help cost-reduction objectives. This inventory system follows just-in-time principles by allowing the company to acquire necessary stock close to when it is needed, hence preventing the accumulation of excess inventory and reducing holding costs [1, 12]. Cross-docking is a logistic method that is part of Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management. It speeds up the transfer of goods from suppliers to consumers while keeping handling costs low.
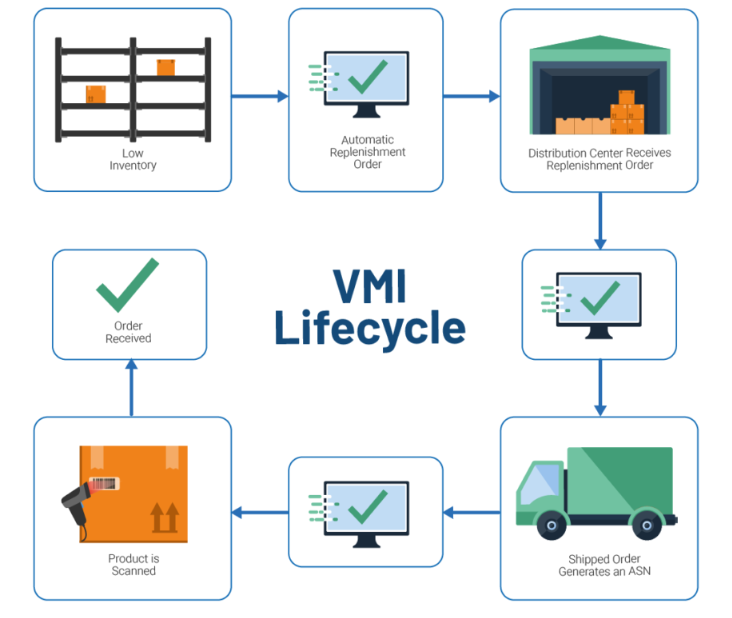
Figure 3: VMI inventory management model [11]
4. Capacity Management
Capacity refers to the greatest quantity of products or units that a facility may retain at a specific time without exceeding its allotted space limit. Capacity management involves managing fluctuations in demand and supply [1]. The basic objective of capacity management is to synchronize an organization's resources (supply side) with service delivery needs and expectations (demand side) while upholding a balance between cost and efficiency. Forecasting demand is a fundamental component of Walmart's capacity management. Accurately predicting consumer demand is crucial for Walmart's capacity management as it enables the corporation to allocate resources effectively to satisfy customer expectations and market demands [13]. It is crucial for Walmart's operational performance goals as it aids in balancing the supply and demand sides of operations. It prevents inefficient resource allocation, which can lead to higher expenses, lower service quality, or resource limitations. Capacity management guides Walmart's choices about facility design and layout to optimize space and resource usage. The organization can optimize its operations and resource use by comprehending capacity to reduce bottlenecks and maintain a smooth workflow, leading to desired outputs.
Understanding the possibility of demand changes in the retail sector, Walmart needs to utilize both level capacity and chase capacity planning strategies to enhance capacity management. Chase capacity planning involves modifying production capacity to align with changes in demand [14]. Walmart optimizes its workforce based on fluctuations in demand through their chase capacity approach. The corporation hires part-time personnel during holidays to meet the higher customer demand [15].
Additional tactics including cross-docking facilities, just-in-time inventory, promotion planning, and e-commerce flexibility support the execution of the chase capacity strategy. Conversely, Walmart employs level capacity planning when demand remains constant, maintaining a fixed capacity regardless of demand fluctuations [14]. Walmart prioritizes maintaining a consistent workforce of mainly full-time employees and emphasizes efficiency in all areas of its business. The chasing method to capacity management increases resource utilization but may result in substantial costs when modifying output rates and labor levels.
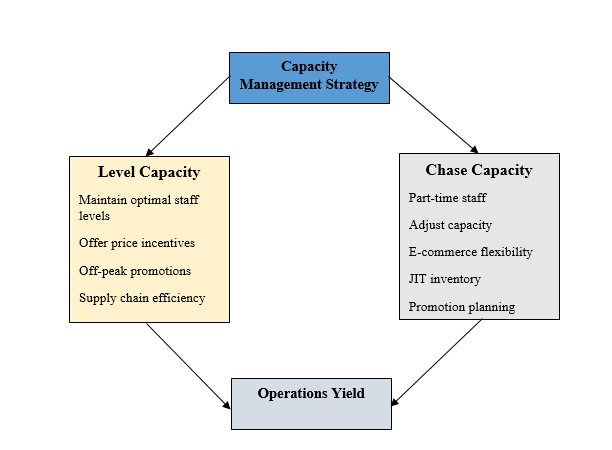
Figure 4: Walmart level and chase capacity strategies
5. ITO and 4Vs Analysis
The ITO model elucidates the process by which activities and resources are converted to enhance value and generate outputs that contribute to the organization achieving its operational performance goals [1]. Walmart's Information Technology Outsourcing effectively places the main elements of its business. The company's key inputs consist of labor, raw materials for producing private-label brand products, technology, adequate capital, and broad supplier networks due to its integrated brick-and-mortar and e-commerce platform [16]. The company's wide supplier network supports its vendor-managed inventory approach and enables it to get products at reduced costs, resulting in lower pricing throughout the supply chain. Walmart utilizes its extensive network of shops, fulfillment centers, and online platforms to transform these resources into valuable results.
The corporation may efficiently use technology to boost its data-driven strategy in managing demand changes by streamlining supply chain management and optimizing inventory and capacity management processes. The outputs include products and services available in retail locations and online platforms, financial outcomes, and any other human outcomes resulting from activity within the firm [16]. Therefore, Walmart's success with its ITO model stems from its emphasis on achieving cost-effective operations and improving customer experience and happiness.
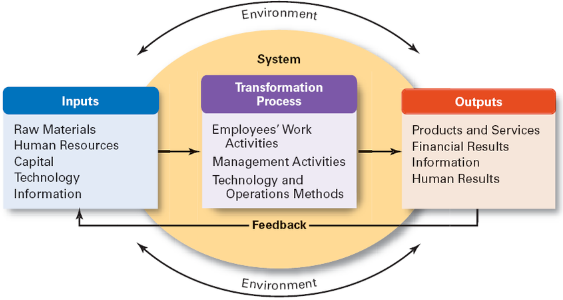
Figure 5: A representation of Walmart’s ITO model [16]
Walmart distinguishes itself from its retail competitors in the operations management realm by excelling in the 4Vs. Walmart's operations are defined by four dimensions: volume, variance, diversity, and visibility [1]. Operating in more than 19 countries, Walmart handles large volumes of products daily, which is a key strength in the retail sector. Walmart's enormous volume allows for the production and sourcing of goods and services on a large scale, resulting in cost savings and economies of scale. Variety refers to the range of products or services provided by a business [1]. Walmart's diverse product variety enhances its capacity to serve various consumer demographics. Variations pertain to the unpredictability and volatility in demand. Walmart use demand forecasting and inventory management methods like vendor-model inventory to handle fluctuations in demand. Visibility refers to the level of transparency in operations. The company's vendor-managed inventory system involves sharing real-time data with important suppliers to improve supply chain visibility, leading to cost savings and better resource use.
6. Conclusion
Walmart efficiently handles its operations by utilizing elements of operations management, including inventory, quality, and capacity management. The analysis shows that the company's vendor-managed inventory system and just-in-time cross-docking support its operations performance targets by reducing operational costs. VMI's main drawbacks are its limited capacity to adapt to rapid changes in demand and its dependence on the reliability of suppliers. It is advised that Walmart enhance engagement with suppliers by exchanging inventory data and demand insights. This is crucial for enhancing responsiveness and inventory planning. Additionally, Walmart's tiered quality standards establish quality expectations for various product categories. It is necessary to establish process improvement teams with cross-functional roles to promote synergy throughout the whole supply chain process. The organization can enhance quality standards by utilizing techniques like Six Sigma to minimize defects and eradicate inefficiencies. The company's decision to balance level and chase capacity planning has improved its ability to maximize resource usage in response to fluctuating demand levels. The organization should consider the 4Vs when deciding on a strategy for the retail industry, since it is a dynamic sector that need a harmonious blend of operational components to ensure effectiveness and cost savings.
References
[1]. Slack, N., Brandon-Jones, R., & Johnston, R. (2019). Operations Management. Pearson UK.
[2]. Tanwar, R. (2013). Porter’s generic competitive strategies. Journal of business and management, 15(1), 11-17.
[3]. Nilufer, N. (2020). Critical assessment on business strategy from aviation to retail industry during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Walmart Case. International Journal of Business Ecosystem & Strategy (2687-2293), 2(2), 8-14.
[4]. World Trade Organization. (2020), GFSI- Global Food Safety Initiative. WTO.
[5]. Xie, Y., & Cooke, F. L. (2019). Quality and cost? The evolution of Walmart's business strategy and human resource policies and practices in China and their impact (1996–2017). Human Resource Management, 58(5), 521-541.
[6]. World Trade Organization. (2020), GFSI- Global Food Safety Initiative. WTO.
[7]. Johnston, R., Shulver, M., Slack, N., & Clark, G. (2020). Service Operations Management: Improving Service Delivery (5th Ed.). Pearson Education.
[8]. Permana, A., Purba, H. H., & Rizkiyah, N. D. (2021). A systematic literature review of Total Quality Management (TQM) implementation in the organization. International Journal of Production Management and Engineering, 9(1), 25-36.
[9]. Musani, P. (2023). Decking the aisles with data: How Walmart's AI-powered inventory system brightens the holidays. Walmart Global Tech.
[10]. Thomson, G. S. (2010). High-Performance organizations: The Wal-Mart Stores Inc. Case Study. Case Study (March 27, 2010).
[11]. Govindan, K. (2013). Vendor-managed inventory: a review based on dimensions. International Journal of Production Research, 51(13), 3808-3835.
[12]. Lin, R. (2019). The importance of successful inventory management to enterprises: A case study of Wal-Mart. In 2019 International Conference on Management, Finance and Social Sciences Research (MFSSR 2019). London: Francis Academic Press.
[13]. Lei, L., DeCandia, L., Oppenheim, R., & Zhao, Y. (2017). Managing supply chain operations. World Scientific Publishing Co.
[14]. Jacobs, F. R., & Chase, R. B. (2018). Operations and supply chain management. McGraw-Hill.
[15]. Stebbins, J. (2022). Walmart plans to hire 40,000 workers for the holiday season. CNBC.
[16]. Chaudhry, A. A., Khan, K. S., & Hassan, A. (2015). Can HRM affirmed as a system? Applying general systems theory (GST) on human resource management. Journal of Management and Research (JMR),. 2 (2), 2-17.
Cite this article
Tang,C. (2024). The Investigation and Research on Operation Management. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,85,30-35.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Slack, N., Brandon-Jones, R., & Johnston, R. (2019). Operations Management. Pearson UK.
[2]. Tanwar, R. (2013). Porter’s generic competitive strategies. Journal of business and management, 15(1), 11-17.
[3]. Nilufer, N. (2020). Critical assessment on business strategy from aviation to retail industry during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Walmart Case. International Journal of Business Ecosystem & Strategy (2687-2293), 2(2), 8-14.
[4]. World Trade Organization. (2020), GFSI- Global Food Safety Initiative. WTO.
[5]. Xie, Y., & Cooke, F. L. (2019). Quality and cost? The evolution of Walmart's business strategy and human resource policies and practices in China and their impact (1996–2017). Human Resource Management, 58(5), 521-541.
[6]. World Trade Organization. (2020), GFSI- Global Food Safety Initiative. WTO.
[7]. Johnston, R., Shulver, M., Slack, N., & Clark, G. (2020). Service Operations Management: Improving Service Delivery (5th Ed.). Pearson Education.
[8]. Permana, A., Purba, H. H., & Rizkiyah, N. D. (2021). A systematic literature review of Total Quality Management (TQM) implementation in the organization. International Journal of Production Management and Engineering, 9(1), 25-36.
[9]. Musani, P. (2023). Decking the aisles with data: How Walmart's AI-powered inventory system brightens the holidays. Walmart Global Tech.
[10]. Thomson, G. S. (2010). High-Performance organizations: The Wal-Mart Stores Inc. Case Study. Case Study (March 27, 2010).
[11]. Govindan, K. (2013). Vendor-managed inventory: a review based on dimensions. International Journal of Production Research, 51(13), 3808-3835.
[12]. Lin, R. (2019). The importance of successful inventory management to enterprises: A case study of Wal-Mart. In 2019 International Conference on Management, Finance and Social Sciences Research (MFSSR 2019). London: Francis Academic Press.
[13]. Lei, L., DeCandia, L., Oppenheim, R., & Zhao, Y. (2017). Managing supply chain operations. World Scientific Publishing Co.
[14]. Jacobs, F. R., & Chase, R. B. (2018). Operations and supply chain management. McGraw-Hill.
[15]. Stebbins, J. (2022). Walmart plans to hire 40,000 workers for the holiday season. CNBC.
[16]. Chaudhry, A. A., Khan, K. S., & Hassan, A. (2015). Can HRM affirmed as a system? Applying general systems theory (GST) on human resource management. Journal of Management and Research (JMR),. 2 (2), 2-17.









