1. Introduction
With the increasing trend of global economic integration, Asian financial markets have been gaining ground in the global economy. According to the 32nd Global Financial Centers Index Report (GFCI 32), Singapore has overtaken Hong Kong, China (hereinafter referred to as Hong Kong) to become the new Asian financial center and ranked 3rd globally.This study aims to compare the similarities and differences between Hong Kong and Singapore in terms of their status as international financial centers. Through literature review and data analysis, we analyze factors such as the size of the financial markets, product innovation, and international cooperation in the two places, and explore the impact of these factors on the local economies [1]. As two major financial centers in Asia, Hong Kong and Singapore play an important role in the global financial system. However, the two places have developed their own unique financial market characteristics and their advantages due to their different national conditions, policy preferences and regional cooperation. Hong Kong has a significant advantage in terms of international financial market volume and trading activities, while Singapore has made remarkable progress in financial innovation and technology application [2].
The purpose of this thesis is to conduct a comparative study on the status of Hong Kong and Singapore as financial centers and their characteristics, and to explore their respective strengths and challenges in different aspects, with a view to providing some useful references and lessons for future financial market development and policy formulation.
2. Size and development of financial markets in Hong Kong and Singapore
2.1. Financial market size, market capitalization and trading volume
Both Singapore and Hong Kong are among the most important financial centers in Asia, and key indicators such as the size of their financial markets, market capitalization and trading volume are important in comparing their status as international financial centers.The stock markets of the two financial centers are shown in Figure 1.
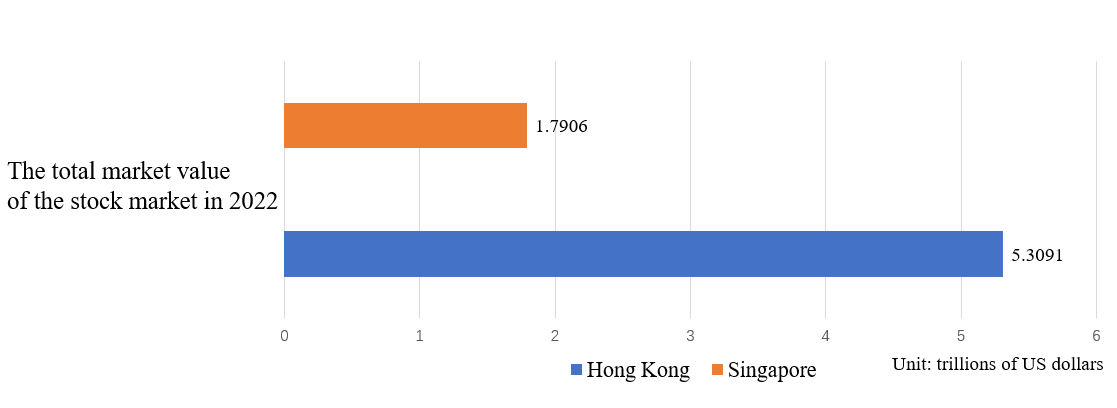
Figure 1: Stock markets in two major financial centers.
(Photo credit: Original)
In terms of the size of the financial market, Hong Kong has a relatively large financial market with a leading position in the world. According to the Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited, by the end of 2022, the total market capitalization of Hong Kong's stock market will be about HK$41.53 trillion, or about US$5.31 trillion. Singapore's financial market is also sizable. According to the Singapore Exchange, by the end of 2022, the total market capitalization of Singapore's stock market will be about S$2.41 trillion, or about US$1.79 trillion.
Hong Kong's stock market is huge and is one of the largest in the world. The Hong Kong Stock Exchange is one of the largest stock exchanges in Asia, with about 2,475 companies listed on its main board at the end of 2022. Singapore, on the other hand, has a relatively small stock market, but it is also one of the important stock exchanges in Asia. The Singapore Exchange (SGX) is the main stock exchange in Singapore, with about 758 listed companies as at the end of 2022.
In terms of trading volume indicators, Hong Kong is one of the most active stock markets in the world, with a sizable daily trading volume. According to the Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited, the average daily turnover of Hong Kong's stock market as of the end of 2022 is about HK$121.2 billion. In contrast Singapore's stock market has a relatively small trading volume, but is still active. According to the Singapore Exchange, by the end of 2022, the average daily turnover of Singapore's stock market will be about S$1.2 billion [3].
However, indicators such as financial market size, market capitalization and trading volume are only preliminary comparisons of the size of the financial markets of the two places. The actual differences are very complex and other factors, such as trading varieties, trading systems and market participants, need to be taken into account. The volume of transactions in the two international financial centers is shown in Figure 2. The number of companies listed on the Main Board of the two international financial centers is shown in Figure 3.
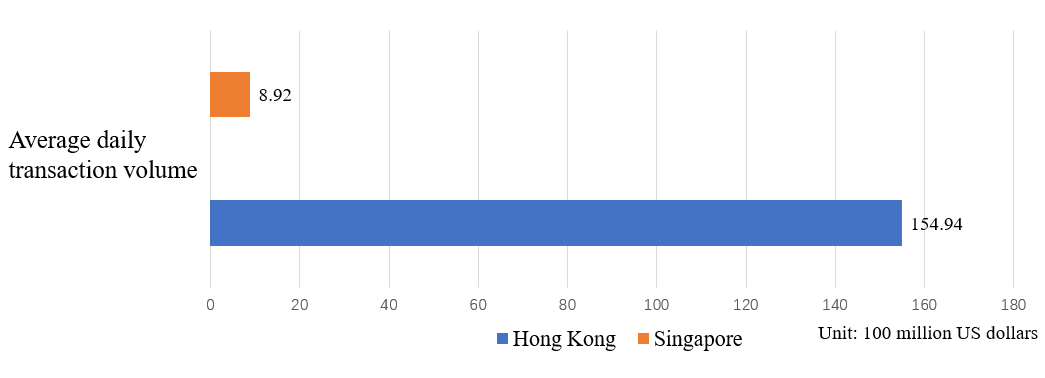
Figure 2: Trading volume in the two major international financial centers.
(Photo credit: Original)
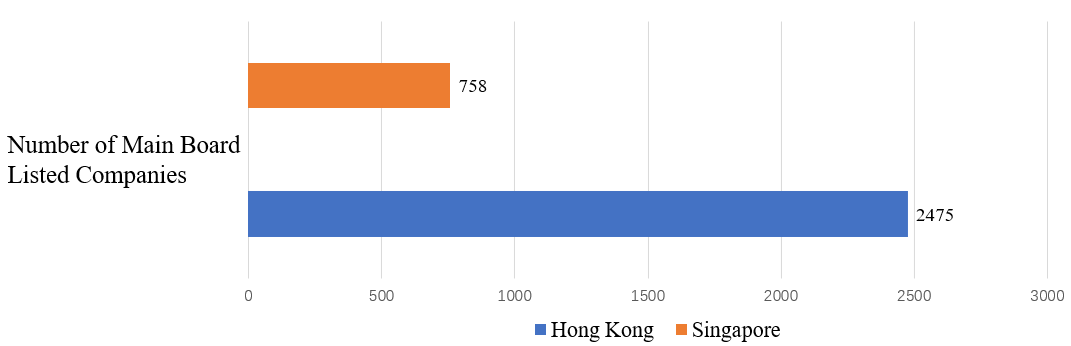
Figure 3: Number of Main Board Listed Companies in the Two International Financial Centers.
(Photo credit: Original)
2.2. History of the development of financial markets and main business areas
The financial markets of both Hong Kong and Singapore have a rich history of development and diversified business areas.
The development of Hong Kong's financial market began in the 19th century, influenced by its status as a British colony. At the beginning of the 20th century, Hong Kong became one of the major financial centers in Asia and gradually established a sound financial system and regulatory regime. After World War II, Hong Kong's financial position in East Asia was further enhanced and it became an important bridge connecting the financial markets of the East and the West [4].
The main business areas of Hong Kong's financial market:
(1) Stock market: Hong Kong's stock market is one of the largest and most active in Asia. The Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited operates the Main Board and Growth Enterprise Market, attracting many international and local enterprises to raise capital through listing.
(2) Securities market: Hong Kong's securities market offers a diversified range of investment instruments such as stocks, bonds and derivatives. Hong Kong's bond market also offers high liquidity and a wide range of issuances.
Singapore has a shorter history of financial market development, but has made remarkable achievements. In the 1960s, the Singaporean government actively promoted the development of the financial services industry and established the Monetary Authority (MAS) to regulate and promote the development of the financial market [5]. Through active policy support and financial innovation, Singapore's financial market has gradually emerged as one of the most important financial centers in Southeast Asia.
The main business areas of Singapore's financial market:
(1) Stock Market: Singapore Exchange (SGX) is the main stock exchange in Singapore, providing a reliable and highly liquid stock market. The Singapore stock market mainly consists of the Main Board market and the Innovation Board market, which attracts many international and local companies to go public.
(2) Financial Derivatives: Singapore's financial derivatives market has a high degree of liquidity and a sophisticated risk management system, providing a diverse range of financial derivatives products such as stock index futures, commodity futures and interest rate derivatives.
The financial markets of Hong Kong and Singapore are unique in terms of their development history and major business areas.
As one of the most important financial centers in Southeast Asia, one of the important insurance centers in Asia and an important private wealth management center in Asia, Singapore's major business areas also include insurance business, capital market and wealth management.
2.3. Financial market characteristics and global reach
As the two major financial centers in Asia, Hong Kong and Singapore possess unique market characteristics and considerable global influence [6].
Hong Kong's financial market is highly internationalized and open, with large stock and foreign exchange markets and a rapidly developing offshore RMB market. Hong Kong has a robust financial system, diversified financial products and services, sound regulation, rule of law environment and high transparency. Hong Kong is one of the world's major international financial centers, and its RMB offshore market, stock market and foreign exchange market have an important position in the world. Hong Kong's stable international financial environment and close ties with financial markets around the world play an important role in the global financial system and regional economic stability.
Singapore's financial market has a rich capital market, insurance business and wealth management business, and remarkable achievements in financial technology innovation.
Taken together, Hong Kong and Singapore, as Asian financial centers, each have unique market characteristics and global influence. Hong Kong, with its internationalization, openness and RMB offshore market, plays a pivotal role in the global financial system; while Singapore, with its mature capital market, insurance business and fintech innovation, plays an important role as a financial center in Southeast Asia.
3. Innovation in Financial Products and Services in Hong Kong and Singapore
As the two major financial centers in Asia, Hong Kong and Singapore have demonstrated unique characteristics in terms of innovation in financial products and services [7].
As an international and open financial center, Hong Kong's innovation in financial products and services is mainly reflected in asset management and offshore business. Hong Kong's asset management industry has been actively expanding its investment scope, promoting diversification of asset allocation and deepening of risk management. It has also developed the offshore RMB market and become an important trading and clearing base, providing more channels and convenience for global investors. In addition, Hong Kong has played an important role in bond market innovation by launching various types of bonds and financial derivative products to provide investors with more choices.
Hong Kong and Singapore have demonstrated different characteristics and development paths in terms of innovation in financial products and services. Drivers of innovation and supportive government policies have enabled the two financial centers to continuously promote financial innovation, upgrade their financial services, and adapt to market demands and challenges in the global financial environment. These innovations are significant to the development and global influence of the financial industries in Hong Kong and Singapore.
4. International cooperation and competition
Hong Kong and Singapore have demonstrated active international cooperation and competitiveness in the field of international finance. There are some differences in the mode and extent of cooperation between the two places with international financial institutions and other countries, but both play an important role in international financial cooperation and competition.
As an important international financial center in Asia, Hong Kong maintains close cooperation with global financial institutions. Hong Kong has attracted a large number of foreign and multinational financial institutions to set up branches or headquarters, making Hong Kong an important operation center for many international financial institutions.
The roles and influence of the two places in the international financial system are not only reflected in cooperation, but also in competition. Hong Kong and Singapore compete fiercely for the status of a regional financial center, striving to attract international financial institutions and investors. This competition has prompted the two places to continuously enhance their financial services and innovation capabilities and strengthen their regulatory norms, while at the same time promoting the vitality and competitiveness of their financial markets [8].
To summarize, both Hong Kong and Singapore possess an important position and role in international financial cooperation and competition. Both places have strengthened the internationalization and openness of their financial markets through cooperation with international financial institutions and other countries. In the international financial system, the two places play an important role in promoting the development of the Asian and global financial markets, and have enhanced their competitiveness and influence in the face of fierce competition.
5. Regulatory and legal environment
Both Hong Kong and Singapore have established relatively sound frameworks for their financial regulatory and legal environments, although there are some differences in their specific regulatory regimes, laws and regulations. The regulatory systems in both places are relatively mature and offer a high level of stability and transparency.
Hong Kong's financial regulatory system is overseen by regulatory bodies such as the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) and the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC). Hong Kong has a comprehensive system of financial laws and regulations covering a wide range of areas such as asset management, securities markets and derivatives. At the same time, Hong Kong's financial regulators also actively work in tandem with international norms, such as the Basel Accord, to strengthen the risk management and regulatory requirements of the local financial market.
Both Hong Kong and Singapore have demonstrated a high level of financial regulation and legal environment. The regulatory systems in the two places are relatively mature with good effectiveness, stability and transparency. The regulatory environment has a significant impact on maintaining financial stability, protecting investors' rights and enhancing the status of financial centers. This stable and transparent regulatory environment is an important factor in attracting international financial institutions and investors [9].
6. Geopolitical and regional economic environment
As important financial centers in Asia, Hong Kong and Singapore are situated in geopolitical environments and regional economic contexts that have a significant impact on their development. As a special administrative region of China, Hong Kong is closely linked to China's political and economic systems and is also subject to extensive international attention. In recent years, Hong Kong's geopolitical risks have been increasing due to its volatile political environment and social divisions. In contrast, Singapore is relatively geopolitically stable, and its government attaches great importance to its governance capacity and international image, and is committed to building an independent, neutral and open international image.
The geopolitical environment and regional economic context of Hong Kong and Singapore have far-reaching implications for their development. Government policy support and international image affect financial center status and international competitiveness. At the same time, the relationship and cooperation between the two places and their neighboring regions also provide important support for regional economic integration and common development. With the acceleration of globalization and the deepening of regional cooperation, Hong Kong and Singapore, as key financial centers in Asia, will continue to play an important role in the geopolitical and economic environment.
7. Conclusion
Hong Kong has a significant advantage in terms of international financial market volume and trading activities, and is one of the top financial centers in the world. As an important hub for global capital rotation, Hong Kong has an actively traded foreign exchange market and a large securities market. Hong Kong's asset management industry also has an important position, attracting many of the world's top private equity and hedge funds. The depth and breadth of Hong Kong's financial market gives it an important advantage in attracting international institutions and capital flows.
Singapore has made significant progress in financial innovation and technology adoption, making it a leading city in fintech. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) actively promotes fintech innovation by providing policy guidance, financial support and regulatory sandboxes. Singapore's FinTech innovation has made outstanding achievements in payment, blockchain and artificial intelligence, attracting many international technology companies and innovative enterprises.
Financial cooperation between Hong Kong and Mainland China was closer, while Singapore emphasized more on financial cooperation with other Asian countries. Hong Kong, under the framework of "one country, two systems", is an important bridge between the Mainland and the global financial market, carrying the internationalization of the RMB, the opening up of capital projects and other important tasks. As a financial center in Southeast Asia, Singapore has close financial cooperation with its neighboring countries and is an important promoter of regional financial cooperation and economic integration.
Hong Kong and Singapore have their own strengths and challenges in terms of financial market volume, financial innovation and technology application, regulatory regimes and financial cooperation with neighboring regions. The two places will continue to develop and enhance their financial market positions through competition and cooperation.
References
[1]. Aggarwal, R., & Goodell, J. W. (2010). Financial markets and the role of government in theKorean miracle. journal of Asian Economics, 21(2), 140-149.
[2]. Wu, B. X., Zhan, G. S. (2018). A comparison of Hong Kong and Singapore financial centers. Journal of Economic Research, (31) 4, 86-87.
[3]. Aizenman, J., Chinn, M. D., & Ito, H. (2010). The emerging global financial architecture: tracing and evaluating new patterns of the trilemma's configurations. journal of international money and Journal of International Money and Finance, 29(4), 615-641.
[4]. Berger, A. A., & Huntington, H. G. (2005). The world's business cultures: and how to unlock them. Kogan Page Publishers.
[5]. Chan, K., & Hameed, A. (2006). Stock price synchronicity and analyst coverage in emerging markets. journal of financial economics, 80(1), 115-147.
[6]. Bob Chin (2016). International financial center competition: a comparison of Hong Kong and Singapore. International Economic Review, (42) 6, 67-78.
[7]. Pan, Chunmei (2014). Comparative analysis of the financial center status of Hong Kong and Singapore. Research on Financial and Economic Issues, (28)2, 45-54.
[8]. Huang, R. D., & Ito, T. (2012). Monetary policy and asset prices revisited. journal of financial economics, 106(3), 398-417.
[9]. Chen, X. C., Lin, Y. H. (2012). A comparative study of Hong Kong and Singapore international financial centers. Finance China, (10), 39-45.
Cite this article
Zeng,Z. (2024). Comparative Research of the Two International Financial Centers of Hong Kong and Singapore. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,85,47-53.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Aggarwal, R., & Goodell, J. W. (2010). Financial markets and the role of government in theKorean miracle. journal of Asian Economics, 21(2), 140-149.
[2]. Wu, B. X., Zhan, G. S. (2018). A comparison of Hong Kong and Singapore financial centers. Journal of Economic Research, (31) 4, 86-87.
[3]. Aizenman, J., Chinn, M. D., & Ito, H. (2010). The emerging global financial architecture: tracing and evaluating new patterns of the trilemma's configurations. journal of international money and Journal of International Money and Finance, 29(4), 615-641.
[4]. Berger, A. A., & Huntington, H. G. (2005). The world's business cultures: and how to unlock them. Kogan Page Publishers.
[5]. Chan, K., & Hameed, A. (2006). Stock price synchronicity and analyst coverage in emerging markets. journal of financial economics, 80(1), 115-147.
[6]. Bob Chin (2016). International financial center competition: a comparison of Hong Kong and Singapore. International Economic Review, (42) 6, 67-78.
[7]. Pan, Chunmei (2014). Comparative analysis of the financial center status of Hong Kong and Singapore. Research on Financial and Economic Issues, (28)2, 45-54.
[8]. Huang, R. D., & Ito, T. (2012). Monetary policy and asset prices revisited. journal of financial economics, 106(3), 398-417.
[9]. Chen, X. C., Lin, Y. H. (2012). A comparative study of Hong Kong and Singapore international financial centers. Finance China, (10), 39-45.









