1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
On June 28, 2018, China’s National Development and Reform Commission and the Ministry of Commerce issued the "Special Administrative Measures for Foreign Investment Access (Negative List) (2018 Edition)," which, except for prohibiting investments in retailing of tobacco leaves, cigarettes, re-dried tobacco leaves, and other tobacco products, does not include general retailing in the negative list. This signifies that foreign investment in retailing is granted the same market access qualifications and treatment as domestic Chinese companies. Since the official promulgation of the "Foreign Investment Law of the People's Republic of China" on January 1, 2020, which affirmed the principles of national treatment and most-favored-nation treatment, China's economic development has accelerated rapidly. The investment by multinational corporations in China has been increasing, reaching $142.931 billion in 2020 across various regions, a growth rate that aligns with the trend of economic globalization. This regulation also applies to the foreign-funded retail industry. As the openness of China's retail industry continues to increase, international retail giants such as Amazon, KFC, and Starbucks have begun to accelerate their market layouts in China.
Furthermore, the development of the e-commerce industry has not only changed traditional shopping methods but also catered to new consumer demands. The international financial crisis of 2008 affected the development of various industries, but China's e-commerce industry continued to grow at a high rate. During this period, the internet infrastructure matured, the number of Chinese netizens steadily increased, the payment system and security environment were progressively refined, and the logistics industry became more convenient.
The e-commerce industry is fiercely competitive, with capital competition intensifying. This has led multinational companies to realize that markets with different cultural backgrounds in each country or ethnicity vary greatly. Localization of marketing is an unavoidable issue for any company wishing to gain a foothold in the Chinese market. Through brand localization, multinational companies can offer products and services more aligned with local cultural values and consumer habits, which helps to enhance consumer identification and loyalty, establish competitive brand advantages in the local market, and reduce the risk of conflicts due to cultural differences. Therefore, researching and exploring effective brand localization strategies and implementation methods is crucial for multinational companies to improve their global market competitiveness and market share.
1.2. Research Significance
This paper focuses on the localized strategies using e-commerce as a tool and studies how companies can quickly develop in the Chinese market. It delves into the swift progression of firms in China, focusing on specific corporate case studies, to dissect the strategies multinational corporations have employed to adapt to the local market. By enriching the research with case studies of multinational retail companies, such as KFC, Starbucks, and Amazon, from challenges to recommendations, this research significantly contributes to the understanding of e-commerce localization strategies in China. It presents a treasure trove of experiences and insights, serving as a guide and a reference for multinational retail companies looking to thrive in the Chinese marketplace.
1.3. Research Method
The research methodology adopted in this paper begins with an extensive literature review, collecting, reading, and organizing a vast array of research findings on corporate strategy theories and their influencing factors. It integrates theories related to the operations of multinational companies with the product life cycle theory to analyze and compare how these companies can better satisfy domestic market demands and seize the immense opportunities in China's burgeoning consumer market. Additionally, the paper employs case study analyses, drawing from rich examples such as KFC, Starbucks, and Amazon, to ground the research in tangible evidence and bolster the credibility of the findings. This combined approach offers a comprehensive analysis of how multinational corporations can better meet domestic market needs and leverage the significant opportunities presented by the new consumer market in China.
2. Basic Theory
2.1. Core concepts
The retail industry is a vast sector that generates profit through the sale of goods or services. It encompasses a diverse range of product and service categories, making it one of the largest industries worldwide. This sector is marked by its ability to fulfill consumer needs and adapt to changing market demands [1].
Within this broad industry, Multinational corporations, also known as "International Firms" or "Multinational Enterprises," are defined by the United Nations Economic and Social Council as economic organizations that, based in their home country, engage in international production and business activities through foreign investment and by establishing subsidiaries or branches in various countries or regions around the world [2].
The competitive landscape of retail has been undergoing significant transformation, especially with the advent of e-commerce. This shift has been accelerated by the rapid expansion of the mobile internet sector, leading to a substantial migration of retail operations to the online space. This transition has not only improved operational efficiency for retailers but also substantially lowered the costs associated with retail management.
In response to the evolving and expanding demands of consumers, both traditional and online retail businesses find themselves in a highly competitive environment. To maintain and enhance their market position, these businesses, including multinational corporations, are compelled to continuously innovate and improve the quality of their offerings. By leveraging the power of e-commerce and focusing on consumer-centric strategies, retailers aim to address consumer needs more effectively. This, in turn, contributes to increased operational efficiency and profitability, ensuring that they retain a competitive edge in the fast-paced retail market.
2.2. Western Market Marketing Theories
Classical economist Adam Smith posited in his seminal work "The Wealth of Nations" that the market economy is inherently not just "national" but "global" in scope [3]. Professor Raymond Vernon of Harvard University suggested that when a company's product or service reaches near saturation in a given country or region's market, the enterprise will seek to develop new markets. This pursuit leads to what is known as the product lifecycle theory, as shown in the Figure 1, which describes how companies vie for market share in their growth strategies [4]. Multinational corporations' global activities are driven by the quest for larger markets and the maximization of resource allocation.
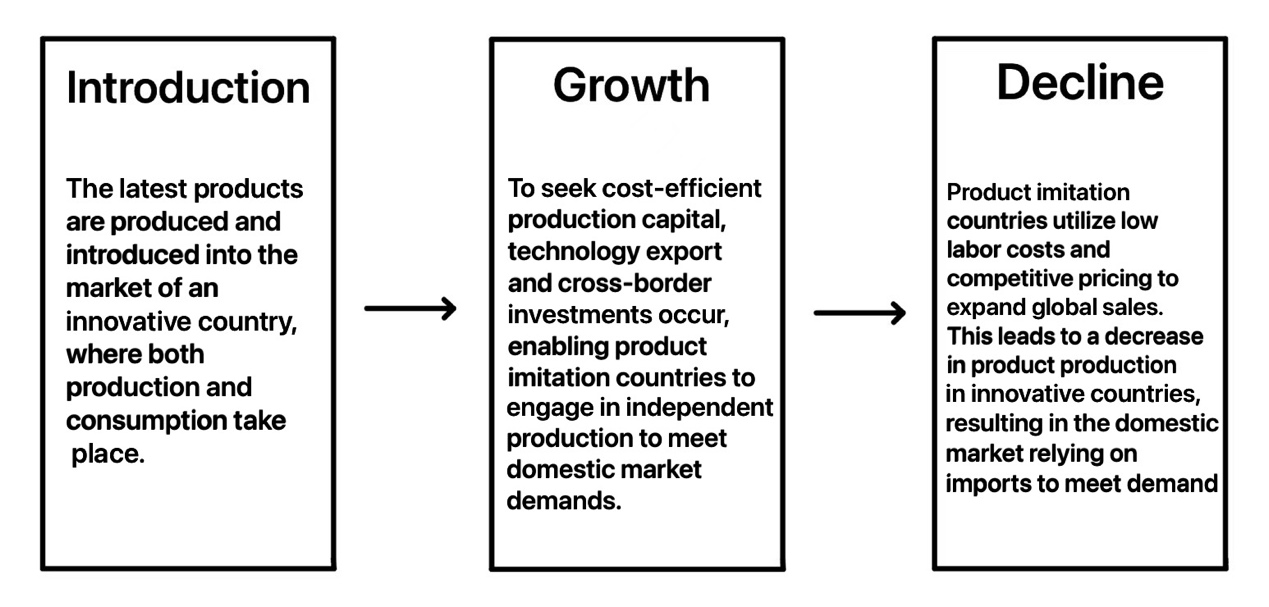
Figure 1: Vernon’s Product Lifecycle Theory
Globalization strategies view the world as a unified large market, operating under the premise that global markets possess homogeneity, allowing for the standardization of marketing processes and the formation of economies of scale [5]. However, differences between various countries or markets mean that multinational corporations cannot simply replicate a successful market experience and apply it globally without adjustments.
In the early 20th century, large multinational corporations continually expanded their overseas operations, making a series of macroeconomic decisions focused on increasing market share and influence. To facilitate the rapid integration of subsidiaries into local economies and societies, these corporations implemented localized marketing strategies. Localization is a process by which multinational companies, in the course of their global strategic development, adapt their products, services, or management to align with the cultural contexts of their target markets [6]. The localization strategy involves a company viewing itself as a member of the target market, actively adapting to the local culture to secure more significant development opportunities.
In summary, the evolution of multinational corporations reflects a balance between the pursuit of global standardization and the need for local adaptation. This dual strategy of global standardization and local adaptation is vital for multinational corporations to sustain growth and remain competitive in an ever-more interconnected world economy.
3. Case Study
3.1. KFC
Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC), an emblematic brand of the American fast-food sector, stands as the globe's second-largest chain in the industry and the preeminent purveyor of fried chicken. Established in 1952 by its founding figure, Colonel Harland Sanders, the franchise specializes in an array of high-calorie offerings, including its signature fried chicken, alongside burgers, fries, rice dishes, tarts, sodas, and more. KFC's marketing catchphrases, are "Life is so much more" and "Indulge yourself in KFC" [7].
KFC's foray into the Chinese market is a paragon of American fast-food success abroad. Since launching its inaugural outlet in Beijing in 1987, the brand has burgeoned across China, now boasting above 9,000 locations — nearly double the footprint of its competitor McDonald's. China has burgeoned into KFC's largest global market, accounting for more than a quarter of its worldwide sales. Employing a shrewd strategy of cultural assimilation, the brand has catered to the local palate by crafting specialty items tailored for Chinese consumers, and leveraging its significant brand clout to captivate the Chinese dining audience. This approach has not only fostered a robust brand presence but also woven KFC into the fabric of China's culinary landscape.
3.1.1. Online Platform
In response to the burgeoning development of mobile payment and internet technologies in China, KFC has embraced this trend by combining digital coupons with its smartphone applications, launching the KFC App and a WeChat mini-program, which are continuously optimized for greater convenience.
To promote these digital marketing tools, KFC has introduced a series of promotional activities, broadly categorized into three types: First, new users who download the app and register are welcomed with free coffee and complimentary delivery on their first order. Second, KFC has launched "Crazy Thursday" offers during off-peak weekdays to drive engagement on Chinese social media platforms. Lastly, promotional campaigns are conducted to commemorate significant company milestones, such as allowing users to purchase select items at 1987 prices in celebration of KFC's 30th anniversary in China.
In China, most consumers have adapted to shopping in the form of takeout, to align with the new digitalization trend in China's food industry, KFC has incorporated a loyalty system and food delivery services into its mobile app, enabling customers to accumulate points for coupons and physical rewards. KFC has expanded its reach and delivery efficiency through partnerships with delivery platforms like Meituan and Eleme.
Currently, KFC boasts over 160 million registered users, with over 65% of orders made via smartphones. The company employs around 50,000 couriers, and online sales contribute to 20% of its total revenue [8]. Additionally, the KFC app includes a scan-to-order feature that allows dine-in customers to select their meals before entering the restaurant, thus avoiding lines during peak times.
3.1.2. Social Media
KFC's "Crazy Thursday" promotion, launched in 2018, still stirs weekly buzz four years later. This event, with narratives ranging from lyrical to suspenseful and sensational, always circles back to the playful prompt, "Today is KFC Crazy Thursday, who's inviting me?" Featured across social media platforms like Xiaohongshu, TikTok, Weibo, public accounts, Douban, and Zhihu, it's a vital part of KFC's brand-building strategy, offering a humorous interlude to the workweek and fostering an emotional connection with consumers. KFC's "Crazy Thursday Literary Festival" further engages fans, enhancing the brand's reach and outperforming McDonald's. With nearly triple the Weibo followers of McDonald's and a more active fanbase, the campaign's Weibo topic has hit 1.8 billion views, with discussions over 4 million. These figures grow with each Thursday, underscoring KFC's integral role in the weekly routine of many young people. In an era where digital marketing demands innovative tactics to engage the youth, KFC capitalizes on trending topics to release themed products, like the World Cup-inspired "KFC #Soul Supper#," capturing a youthful demographic with timely, culturally relevant marketing [9].
3.1.3. Localized Advertising
KFC's localized advertising in China cleverly mirrors the cultural essence, utilizing traditional motifs and family values to resonate with consumers. An example is how KFC commercials on TV and video apps link the "Family Bucket" to the Chinese value of togetherness during reunions. This subtly conveys KFC's message of love and warmth, aligning with the Chinese emphasis on family gatherings. It connects with the Chinese emphasis on togetherness, while holiday-specific ads and late-night snack promotions like the "Night Owl Skewer Bucket" reflect local tastes and customs. These strategies enhance brand affinity and recognition within the Chinese market [9].
By intertwining its brand image with elements of Chinese art and poetry, KFC creates a unique cultural relevance. This approach, exemplified by integrating lines from "Qin Yuan Chun - Snow" into their messaging, has contributed to KFC's strong market presence. The brand's deep cultural integration through advertising not only appeals to consumers but also lays a foundation for KFC's long-term growth in China [10].
3.2. Starbucks
Starbucks, founded in Seattle in 1971, is a global coffee giant with a diverse product range including coffee, tea, and Frappuccino. Capitalizing on the digital boom, it opens approximately 600 stores each year. The brand is set to grow its presence in urban areas and gain market share, propelled by young consumers' habits of mingling over coffee and the middle class's embrace of coffee as an experience. In China, Starbucks faces the challenge of adapting to a culture with a deep-rooted tradition of tea drinking. The company has committed to high-quality coffee, innovative product launches, and the exploration of breakfast and beverage segments, merging American and Chinese cultural elements. Starbucks' strategy to create a 'third place' with a unique atmosphere and product range has enabled it to scale up, safeguard its brand, and boost profits [11].
3.2.1. Mobile Payment and Starbucks Card
Starbucks has innovated with the Starbucks Card, an advanced rewards and loyalty system, that allows customers to effortlessly manage their balances and points through mobile payments within the Starbucks App. This feature not only fosters customer interactions but also deepens emotional connections in an era increasingly dominated by digital relationships. The Starbucks Card, doubling as a thoughtful social gift, features a variety of thematic designs such as the elegant birthday series or the mythical mermaid series, perfect for a range of social occasions. This diversity in design helps to forge strong emotional ties among customers, elevating the concept of gifting within the Starbucks ecosystem.
3.2.2. Digital Services and Speed
Starbucks' "Starbucks Now" service enables customers to order swiftly through the App, providing options for in-store pickup or delivery that significantly enhance convenience and efficiency. Expanding its reach, Starbucks ensures that whether in bustling business districts or cozy residential areas, customers can enjoy the meticulously crafted "Star Delivery" express service. Moreover, the ability to customize ingredients and toppings within the App caters to personal tastes and dietary preferences, taking the personalization of the Starbucks experience to new heights.
3.2.3. E-commerce and Partnerships
Starbucks has forged strong partnerships with China's leading e-commerce platforms such as Alibaba, Meituan, and Alipay, facilitating accessible online ordering, exclusive membership services, and the dissemination of targeted marketing campaigns. Collaborations with Hema Fresh not only enable Starbucks to provide more efficient delivery during peak hours but also increase brand visibility and market penetration. Additionally, Starbucks leverages WeChat Official Accounts and the App to regularly release the latest brand news, promotional offers, and festive campaigns, thereby attracting and retaining customer interest.
3.2.4. User Experience and Market Growth
Starbucks leverages big data and precise marketing tools to continuously refine service processes and user experiences. With a well-trained professional delivery team and specially designed packaging, Starbucks ensures a high standard of product quality and service delivery. The innovation in digital services has not only enriched the consumer dining scene but has also opened up new avenues for market growth, allowing Starbucks' products and services to reach a broader customer base while strengthening the emotional brand connection. This positions Starbucks for sustained growth in the Chinese market.
The strategic integration of Starbucks' online and offline operations has not only successfully expanded the brand's influence and market share in China but has also carved out new growth opportunities and competitive advantages through its digital transformation strategy.
3.3. Amazon
Amazon (specifically referring to its headquarters in the United States) is one of the earliest companies to engage in e-commerce on the internet. Its headquarters is located in Seattle, USA, and it is currently the largest company in the United States. In 2015, Amazon's global cross-border e-commerce Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) was $20 billion, and it exceeded $28 billion in 2019. By 2025, the global cross-border e-commerce transaction volume is expected to reach $45 trillion, with Amazon's cross-border e-commerce market share expected to reach 16.3% [12].
3.3.1. Concepts and Marketing Strategies
"Customer obsession" is a prominent corporate culture of Amazon, and it forms the foundation for the company's macro development strategies and policies. Amazon empowers its customer service representatives with high authority to ensure customer satisfaction. For example, customer service representatives have the autonomy to compensate dissatisfied customers with coupons. Amazon believes that if customer service representatives lack the necessary authority to effectively and promptly resolve customer complaints, the customers' optimal experience will be compromised while they wait for instructions and final solutions. Additionally, Amazon has implemented a system called "Press the Button." If more than two customers lodge complaints about the same issue with a particular product, Amazon will immediately remove the product from its platform, regardless of its popularity. After entering the Chinese market, Amazon introduced a 60-day no-questions-asked return and exchange policy with lenient standards. Amazon understands that consumers value product quality and a flawless customer experience. The excellent customer experience provided to Chinese consumers not only helps win their trust but also signifies Amazon's confidence in its own services.
In terms of marketing strategy, Amazon China adheres to the "Everyday Low Price" strategy and rarely engages in promotional advertising. Amazon has a tradition of not advertising even in the United States. The company aims to attract consumers through word-of-mouth and by delivering the best customer experience. When Amazon entered China as the world's largest e-commerce company, it followed its established model from the United States. However, there are slight differences. Amazon China did invest in some advertising, such as registering the short domain name "Z.CN" when mobile internet was not yet well-developed and placing some advertisements on portal websites. The offline market remained significant. Due to a lack of sufficient marketing and promotion, Amazon has maintained a low-key image and is less known to the general public. In China, advertising has a significant impact on consumers. People have formed brand associations through powerful advertising and customer experiences. For example, Jingdong's "211 Guaranteed Delivery" and the annual "6.18" promotion have become ingrained in people's minds. Tmall's multi-billion-dollar marketing campaigns have created the enduring "Double Eleven" and "Double Twelve" shopping festivals, which are celebrated by Chinese consumers. This describes Amazon's marketing strategy, which focuses less on advertising and follows a similar approach to consumer behavior in the United States.
3.3.2. Limitations
China and the United States differ significantly in terms of systems, culture, and economic markets. Therefore, directly applying solutions implemented in the United States to the Chinese context would inevitably result in numerous problems. After Amazon acquired Joyo.com, it failed to retain the elite team or integrate the market experience gained in the United States with their understanding of the Chinese market, thus missing the opportunity to create a development path that combined Eastern and Western approaches. Instead, Amazon simply transplanted American culture and created a management team completely controlled by the United States. However, due to a lack of understanding of the national conditions, inadequate grasp of retail formats, and insufficient knowledge of Chinese consumers, Amazon's development in China has been relatively sluggish.
Amazon China, with its strong Western culture, conducted significant promotions similar to major Western department stores during the week following Thanksgiving, commonly known as "Black Friday." However, the timing of the "Black Friday" shopping festival was synchronized with that in the United States, without considering the time difference. The cultural differences between Amazon's headquarters and China played a significant role. The headquarters believed that promotions did not align with long-term interests and disliked pursuing short-term gains. Additionally, they lacked an understanding of marketing strategies tailored to the local culture. As a result, Amazon pushed itself to the fringes of the Chinese market [13].
4. Conclusion
4.1. Research Findings
This study conducted a case study on the implementation of localization strategies by multinational retail companies in the Chinese market, and the analysis revealed that localization strategies have a significant impact on the success of multinational retail companies in the Chinese market. By understanding and respecting Chinese cultural values, consumer habits, and market demands, multinational retail companies can better position their brand image and provide products and services that meet the needs of local consumers, thus establishing a close connection with Chinese consumers.
E-commerce is an important tool for implementing localization strategies. By leveraging mobile payment and diverse Internet and media technologies, multinational retail companies can offer more convenient and personalized shopping experiences, establishing closer interactions and connections with Chinese consumers. Successful localization strategies require comprehensive market research and in-depth understanding. Multinational retail companies need to deeply study the characteristics of the Chinese market, competitive environment, and consumer behavior to develop targeted marketing strategies and product positioning.
However, there are also drawbacks to marketing through e-commerce. This series of sales models brings inconvenience to those who are unfamiliar with the Internet or unable to use electronic payments. These individuals not only cannot be reached by advertisements but also encounter difficulties when placing orders. Therefore, businesses that primarily rely on e-commerce as their marketing method may lose a portion of their customer base. Additionally, the retail industry is highly competitive, and innovative sales methods adopted by companies may gradually be adopted or even surpassed by other competitors, reducing the competitive advantage. Therefore, companies need to constantly innovate and identify new marketing methods to maintain their advantage.
4.2. Implications and Effects
This study provides practical experiences and insights by analyzing case studies, showcasing the experiences and practices of successful implementation of localization strategies by multinational retail companies, as well as some inadequate implementation experiences. It serves as a reference for other companies in their localization process in the Chinese market. Through localization strategies, multinational retail companies can better meet the needs of Chinese consumers, establish competitive advantages, and improve their market share and brand awareness in the Chinese market. Furthermore, it promotes cultural exchanges between China and foreign countries. Localization strategies require multinational retail companies to have a deep understanding of Chinese culture, respect and integrate into the local society, which contributes to promoting cultural exchange and understanding between China and foreign countries.
4.3. Future Expectations
It is hoped that multinational retail companies can further enhance their understanding and knowledge of the Chinese market, delve into the needs and preferences of Chinese consumers, continuously optimize localization strategies, and provide products and services that are more in line with the Chinese market. It is hoped that this research can provide guidance and insights for multinational retail companies in implementing localization strategies in other developing countries, promoting sustainable development and mutually beneficial outcomes in the global market. Future research is expected to further explore and deepen the application of localization strategies in different industries and markets, providing more experiences and wisdom for companies to succeed in the globalization process.
References
[1]. Xinming, Y., Hongkui, L. (2022) Factor Resource Misallocation, Supply Efficiency, and the Construction of a National Unified Big Market. Paper presented at Qiushi Academic Journal International Conference.
[2]. Martin, E. (2019) Global marketing translation and localization for Frenchüspeaking countries. Paper presented at World Englishes International Conference.
[3]. Bei, J. (2016) On the Era of Economic Globalization 3.0 - Also on the Interconnectivity Concept of "One Belt One Road". Paper presented at China Industrial Economics International Conference.
[4]. Vernon, V. (2016) Implementing Domain-Driven Design. Paper presented at International Conference on Electronic Industry.
[5]. Yuan, Z., Lizhong, T. (2020) Comparative Study of Global Marketing and Local Marketing. Paper presented at China Business & Trade International Conference.
[6]. Hao, Z. (2015) Reflections on the Localization Strategy of Multinational Companies in China. Paper presented at China Business and Trade International Conference.
[7]. Qiaowei, S., Xiao, P. (2014) McDonald's and KFC in China: Competitors or Companions? Paper presented at Marketing Science International Conference.
[8]. Financial Times. (2019) Yum China's delivery and menu shake-up boost fast food sales. Paper presented at International Conference on Business and Economics.
[9]. Min, H. (2022) The Influence of Content and Form of Internet Celebrity Products on Consumer Purchase Intention: The Moderating Role of Aesthetic Expectations. Paper presented at Business and Economic Research International Conference.
[10]. Wei, W. (2014) Research on Localization Marketing Strategies of Multinational Food and Beverage Companies in China. Paper presented at Capital University of Economics and Business International Conference.
[11]. Wenrong, Z., Jiang, Y. (2022) Starbucks' Marketing Strategy in China in the Era of New Retail and Digital Economy. Paper presented at Modern Marketing (Bi-Monthly) International Conference.
[12]. Xiaofang, L. (2023) Analysis of Cross-border E-commerce Product Selection Strategy Based on the Amazon Platform. Paper presented at Logistics Technology International Conference.
[13]. Wenjie, Z. (2019) Research on the Localization Marketing Strategy of Amazon (China). Paper presented at Zhejiang Gongshang University International Conference.
Cite this article
Zhao,X. (2024). Localization of Retail Multinational Companies' E-commerce Marketing Strategies in China. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,87,187-195.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Xinming, Y., Hongkui, L. (2022) Factor Resource Misallocation, Supply Efficiency, and the Construction of a National Unified Big Market. Paper presented at Qiushi Academic Journal International Conference.
[2]. Martin, E. (2019) Global marketing translation and localization for Frenchüspeaking countries. Paper presented at World Englishes International Conference.
[3]. Bei, J. (2016) On the Era of Economic Globalization 3.0 - Also on the Interconnectivity Concept of "One Belt One Road". Paper presented at China Industrial Economics International Conference.
[4]. Vernon, V. (2016) Implementing Domain-Driven Design. Paper presented at International Conference on Electronic Industry.
[5]. Yuan, Z., Lizhong, T. (2020) Comparative Study of Global Marketing and Local Marketing. Paper presented at China Business & Trade International Conference.
[6]. Hao, Z. (2015) Reflections on the Localization Strategy of Multinational Companies in China. Paper presented at China Business and Trade International Conference.
[7]. Qiaowei, S., Xiao, P. (2014) McDonald's and KFC in China: Competitors or Companions? Paper presented at Marketing Science International Conference.
[8]. Financial Times. (2019) Yum China's delivery and menu shake-up boost fast food sales. Paper presented at International Conference on Business and Economics.
[9]. Min, H. (2022) The Influence of Content and Form of Internet Celebrity Products on Consumer Purchase Intention: The Moderating Role of Aesthetic Expectations. Paper presented at Business and Economic Research International Conference.
[10]. Wei, W. (2014) Research on Localization Marketing Strategies of Multinational Food and Beverage Companies in China. Paper presented at Capital University of Economics and Business International Conference.
[11]. Wenrong, Z., Jiang, Y. (2022) Starbucks' Marketing Strategy in China in the Era of New Retail and Digital Economy. Paper presented at Modern Marketing (Bi-Monthly) International Conference.
[12]. Xiaofang, L. (2023) Analysis of Cross-border E-commerce Product Selection Strategy Based on the Amazon Platform. Paper presented at Logistics Technology International Conference.
[13]. Wenjie, Z. (2019) Research on the Localization Marketing Strategy of Amazon (China). Paper presented at Zhejiang Gongshang University International Conference.









