

Volume 206
Published on August 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2025 Symposium: Digital Transformation in Global Human Resource Management
Against the background of the accelerated internationalization process of enterprises and the extensive penetration of ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) concepts, this paper empirically examines the impact of ESG performance on enterprises' outward foreign direct investment (OFDI) behaviors and the mechanism of its action based on the panel data of Chinese enterprises in the period of 2009-2021. The results show that corporate ESG performance has a significant positive relationship with OFDI size, with OFDI size (natural logarithm) increasing by about 2.004 units on average for every 1-unit increase in ESG level, and that this positive effect is still robust after controlling for year fixed effects (coefficient 1.299, p< 0.05). Mechanism tests show that ESG performance indirectly promotes OFDI by alleviating financing constraints (KZ index): a 1-unit increase in ESG level is associated with a 1.117-unit decrease in the financing constraints index (p< 0.01), whereas for every 1-unit decrease in financing constraints, OFDI size increases by 0.155 units (p< 0.01), validating a partial mediating effect of financing constraints. In addition, firm size (positive), gearing ratio (negative) and management shareholding (short-term positive and long-term negative) are the key control factors affecting OFDI. The findings provide empirical support for firms to promote their internationalization strategies by enhancing ESG performance and alleviating financing constraints, and also provide a theoretical basis for policy makers to improve ESG guidance mechanisms to promote the high-quality development of corporate OFDI.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of China’s "dual-carbon" goals being integrated into the top-level design of ecological civilization construction, frequent corporate "greenwashing" behavior (i.e., selective or symbolic disclosure of environmental information to mislead stakeholders) has severely impeded the efficiency of green financial resource allocation and the digital transformation of the real economy. Existing studies predominantly focus on the unidirectional impact of ESG performance on capital, yet systematically neglect the critical question of whether patient capital (long-term value-oriented capital) can inversely constrain corporate "greenwashing." Using panel data from the Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share listed companies (2010–2022), this study constructs a two-way fixed-effects model, incorporating patient capital as an independent variable into the analytical framework of corporate environmental information quality for the first time. Textual analysis and panel threshold models are introduced to optimize measurement methods. The findings reveal that patient capital significantly inhibits greenwashing through three pathways: alleviating financing constraints, strengthening governance mechanisms, and promoting green technological innovation. This effect is more pronounced in heavily polluting industries and non-state-owned enterprises (non-SOEs). The study transcends the limitations of traditional ESG governance reliant on external ratings or policy intervention, revealing the market-endogenous constraint mechanism on greenwashing from the perspective of capital attributes. It provides novel insights for optimizing green financial instruments and guiding long-term capital to "vote with its feet."

 View pdf
View pdf


This study employs panel data from 117 Chinese cities (2011–2022) to investigate the impact of digital inclusive finance (DIF) on agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP) and the mediating role of rural e-commerce. Results show that DIF significantly enhances AGTFP by alleviating financing constraints, optimizing resource allocation, and promoting green technology adoption, with more pronounced effects in non-grain-producing regions and areas with scarce financial resources. Rural e-commerce, represented by the expansion of Taobao villages, serves as a key mediating pathway, facilitating the marketization of green agricultural products and digitalization of supply chains. Regional disparities are evident: eastern coastal regions achieve an annual AGTFP growth of 8.5% through technology-intensive models, while northeastern regions lag due to traditional factor lock-in effects. The study provides policy insights for advancing agricultural low-carbon transition by optimizing digital financial policies, including targeted DIF penetration, rural e-commerce infrastructure upgrading, and region-specific technology diffusion strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of global competition in the cultural industry, the innovation of cultural symbols has become the core path to enhance the market competitiveness of domestic animations films. This research takes "Nezha: The Demon Child's Rebellion in the Sea" as the research subject and comprehensively uses questionnaire analysis and online text analysis to study the innovation of cultural symbols in domestic animated films. Firstly, the core dimensions of cultural symbol innovation are analyzed through questionnaire surveys. Secondly, high-frequency words, semantic networks and sentiment analyses are conducted on online texts. This study aims to explore the influence of cultural symbol innovation on consumers' behavioral intentions and their emotional tendencies. Finally, targeted suggestions are put forward for the development of domestic animated films. The research finds that character design and ideological values are the core factors driving consumers' brand culture identification and recommendation willingness. This article aims to explore the impact of cultural symbol innovation on consumers' willingness, explore new paths for cultural symbol innovation, and promote the breakthrough and rise of domestic animated films in the global cultural market competition.

 View pdf
View pdf


Based on environmental and international trade data from 40 countries, this study constructs a Policy Synergy Index for environmental regulations and international trade rules. Using regression models, it examines the synergistic impact of these regulations on corporate innovation. Findings reveal a measurable synergistic effect, primarily manifested as a linear relationship between the synergy index and patent output. From a governmental perspective, the paper proposes: (1) establishing an international coordination mechanism through multilateral platforms like the WTO to advance mutual recognition of carbon tariffs, green technology standards, and environmental goods lists, thereby reducing corporate dual compliance costs; (2) implementing innovation-oriented policies that dynamically link the Environment-Trade Synergy Index with tax incentives, while creating a cross-border green technology transfer fund to accelerate innovation diffusion. Tiered policy tools should target developed countries (technical standard mutual recognition), emerging economies (compliance capacity building), and least-developed countries (green assistance). Progress should be monitored through a globally unified accounting system for synergy indices. Governments must pre-assess policy international compatibility, while enterprises should strengthen full-chain compliance management, ultimately achieving dual wins in green trade expansion and global carbon emission reduction.

 View pdf
View pdf


The evaluation of real estate investment environment constitutes a critical research domain for investment decision-making and regional economic development. This paper systematically reviews the progress in real estate investment environment assessment, with particular emphasis on the application of diverse statistical methodologies. Through comprehensive literature analysis, we identify that existing evaluation systems primarily construct indicator frameworks across five dimensions: macroeconomic conditions, policy regulations, market supply-demand dynamics, infrastructure, and social environment, employing quantitative techniques including factor analysis, regression modeling, and spatial econometrics. The comparative analysis examines the applicability, advantages, and limitations of various statistical models, with special focus on panel data models and machine learning applications in dynamic assessment. The findings demonstrate that the evolution from static analysis to dynamic prediction in real estate investment evaluation has been significantly enhanced through methodological innovations in statistics. The paper concludes by identifying current limitations in data quality and model interpretability, while proposing directions for future research.

 View pdf
View pdf


Currently, the Chinese bond market continues to expand in size, with corporate bonds emerging as a crucial channel for direct financing in the real economy. This study focus on the bond issurance of listed companies in China. It can be concluded that significant progress has been made in product innovation, as well as structural adjustments across regions and industries. Bond financing demonstrates multiple advantages in terms of cost, maturity, and pricing mechanisms. However, the development of the corporate bond market for listed companies faces several challenges, including higher financing costs for private enterprises, a regulatory system that requires strengthening, and the need for further expansion of issuance scale. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a two-pronged approach: first, institutional reforms, specifically the deepening of the registration-based system and the enhancement of pricing mechanisms, and second, a recommendation that enterprises transform their financing concepts and embrace innovative financing approaches. This research also indicates that although China's corporate bond market exhibits an upward development trend, existing problems still require attention and improvement.

 View pdf
View pdf


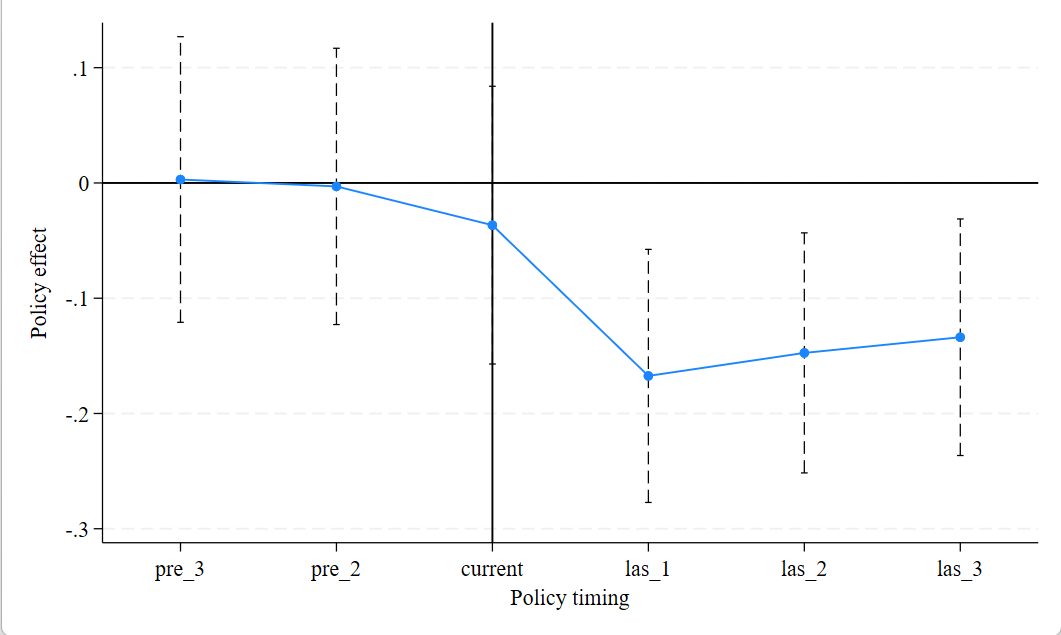
Greenwashing behavior leads to environmental and economic inefficiencies, seriously hindering sustainable economic development. The introduction of the VAT carry-forward tax refund policy in China in 2018 offers the possibility of reducing the overall level of greenwashing in the market. This paper uses the data of non-financial listed companies on the A-share market from 2012 to 2022 as samples, and employs a difference-in-differences model to study the impact of the VAT carry-forward tax refund policy on the greenwashing behavior of Chinese enterprises. A mediating model is also established to explore the influencing mechanism. The conclusion is that the implementation of the VAT carry-forward tax refund policy, by promoting green innovation among enterprises, has to some extent curbed their greenwashing behavior. Enterprises that are state-owned, located in the central and western regions, and have a higher capital intensity are more affected by this policy, and the inhibitory effect on their greenwashing behavior is more pronounced.

 View pdf
View pdf


Enterprise foreign direct investment (FDI) is closely linked to cultural ties between nations, and how to improve the efficiency of OFDI in the context of huge cultural differences has become an urgent problem for enterprises. Based on panel data from Chinese enterprises between 2013 and 2023, this study empirically investigates the impact mechanism of cross-cultural communication on OFDI. It is found that cultural communication significantly promotes corporate OFDI by enhancing host country’s cultural awareness and policy support, and this effect is more significant in cities with higher scientific and technological level and foreign investment concentration areas. Heterogeneity analyses show that the effect of cultural diffusion is stronger in SOEs and non-SOEs, revealing the importance of institutional advantages and governance structure. This study not only provides empirical evidence for the synergy between cultural communication and economic cooperation in the construction of the “Belt and Road”, but also makes suggestions for optimising enterprises’ overseas investment strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of the rapid development of the capital market and increasingly fierce corporate competition, earnings engagement, working as an important means for enterprises to adjust financial information, has attracted much attention regarding its rationality and potential risks. Enterprises influence financial statements through earnings management to achieve certain effects, which may mislead investors’ decisions and disrupt the efficiency of resource allocation in the capital market. Therefore, in-depth research on it is of great practical significance. This study focuses on real earnings management and accrual-based earnings management in corporate financial management. By comparing and analyzing their operational mechanisms, specific measures, differential characteristics, and industry application scenarios, it aims to reveal the motives, means, and governance paths of earnings management. The study finds that real earnings management adjusts earnings through constructing real transactions, such as production manipulation and related party transactions, which directly affect corporate cash flows and business activities. While accrual-based earnings management adjusts profits by virtue of accounting policy choices, which act more on financial statement data. These two types of earnings management show differentiated characteristics and applications in the manufacturing industry and service industry. In view of their respective disadvantages, this paper puts forward adjustment measures such as improving accounting standards, strengthening internal governance, and enhancing audit quality, so as to provide references for enterprises to standardize financial operations and optimize regulatory policies.

 View pdf
View pdf




