1. Introduction
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, retail companies are actively seeking strategies to restore trade and increase turnover. While large retail companies have developed robust solutions to mitigate potential risks, challenges remain inherent in their supply chains. Many companies are finding it increasingly difficult to control costs associated with sourcing, labor, and transportation while supplier and consumer demand is surging.
In addition, the specialization of sales models has led to an increased need for effective inventory management. This means that the risk of running out of stock or having too much inventory becomes more prominent. Natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes and hurricanes add another layer of unpredictability to the entire supply chain, with the potential to disrupt operations, cause financial losses and in some cases even lead to bankruptcy.
Considering the multiple roles of environmental factors at home and abroad, this paper focuses on the ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) analysis methodology as a basis for studying hidden risks in supply chains. Taking Costco as an example, it aims to identify potential risks and explore supply chain management ideas by applying SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis. Specifically, the article aims to analyze the risks that large retailers may encounter in supply chain management, focusing on inventory-based supermarkets such as Costco or Freshippo, which operate under a similar sales model.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Review on Costco's Supply Chain
Based on analyses of current natural environment and social environment risks in the supply chain of retail industry by two companies, Smart Brief and Blue Ridge, it is widely acknowledged that retail industry are facing lots of significant challenges, such as long lead times, capacity constraints, the increasing demand for supplier collaboration, or new product management and satisfying the increasingly diverse requirements of public customers [1]. Jill E. Hobbs also made corresponding research on the food supply chain during the period of COVID-19 epidemic, and believed that the external environmental risks mainly caused by the epidemic would lead to unprecedented system impacts in logistics and distribution, and as the outbreak came to an end, Through this, entrepreneurs can learn a lot about how the food supply chain responds to the crisis and the strategies to deal with the crisis, which has implications for the warehouse supermarket Costco mentioned in this case analysis [2]. In addition, for Costco, Jesse Klein compared the supply chains of Costco and Walmart and believed that Costco should create its own supply chain characteristics, such as paying attention to environmental protection, in order to reduce the possible risks of the supply chain and attract more suppliers in this way. Even though the ever-changing supplier base is a challenge for Costco [3].
2.2. Review of ESG on Supply Chain
ESG ratings is an evaluation system for the sustainability of business operations and social values. It consists of three aspects E(environment), S(social) and G(governance), and urges enterprises to pay attention to ecological environment protection. So, according to the report of Trade Cloud One supply chain platform, ESG plays a significant role in the construction in the future enterprise supply chain. It not only impacts environment and society, but also influences the long-term financial success of the business. ESG can help companies to evaluate suppliers’ abilities so that they can ensure solid and reliable strategic partners [4]. Moreover, through the PwC Pulse Survey, COOs have insights about re-imagine the supply chain for transformation, growth, and value. They found that supplier risks is the second prominent and hard challenge, such as environmental pollution, management corruption or shortages of raw materials by ESG consideration [5]. Therefore, Costco made a climate action plan for a promise to customers on the official Costco report. As a ESG consideration, the report discussed in the document include human rights, diversity, equity and inclusion, life on land and underwater, water conservation and waste reduction. The manager of Costco wants to do some right thing for their members, employees, suppliers, communities where they do business, etc. So that they can attract more customers into market for purchasing and they can increase their profit [6].
3. Retail supply chain status and issues
3.1. Status of retail supply chain
At present, the international retail market because of the expansion of global trade scale, the demand for logistics and transport is also increasing. However, the efficiency of logistics has been severely affected by traffic congestion, delays in cargo ships and aircraft and rising transport costs. In particular, during the COVID-19 pandemic, global logistics systems were severely impacted, and shipping and shipping were restricted, resulting in many enterprises not having timely access to the required supplies. In addition, inadequate visibility into the supply chain is a challenge. Supply chain visibility refers to the ability to accurately track and monitor the entire process of products from raw material procurement to final delivery. However, in the traditional supply chain model, the flow of information is often blocked, resulting in difficulties in coordination and communication between the various links of the supply chain. This means that when problems arise, enterprises usually cannot respond in time, and then the operation of the entire industrial chain will be affected [1].
3.2. Major issues of the retail supply chain
3.2.1. Delivery Time
Smart Brief revealed in its 2022 survey that across all industries, 49% of respondents noted that they were unable to complete the time required to meet customer needs, compared to 24% of 2020 participants. On-time delivery should be one of the top priorities for all transport and logistics industries, but in the face of increasing demand, diverse customer needs, and the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak in 2020, the retail supply chain is increasingly struggling to meet delivery times.[1]
With the intensification of supply chain competition, the original quality and price competition has gradually become time-based competition, which means that retail enterprises need to strengthen the control of time to improve their market competitiveness with high efficiency and high quality.
3.2.2. Cost Pressure on Supply Chain
Whether it is the need for supplier collaboration or the demand of new customers and digital e-commerce, many companies are now more difficult to pass on the cost of goods sold, labor and transportation constraints across the supply chain, which in turn brings greater cost pressure to companies.
For consumers, the cost of purchasing goods is higher, especially in industries closely related to life, such as food retailing, which has a greater impact on consumers' profit margins. Besides, customers in different countries have different shopping habits, and the purchasing behavior of customers in different age groups is also different. How to consider all of them is a difficult problem to solve.
For suppliers, they need the complete transport tools and roads to ensure the quality and speed of the goods. How can products be shipped to distributors efficiently, reducing transportation costs and increasing profits, they are so important.
3.2.3. Inventory Management Problem
Due to the huge variety of commodities involved in the retail industry, whether it is domestic large retail enterprises, such as Freshippo, Yonghui supermarket etc., or foreign warehouse supermarkets, such as Costco, Walmart, are operating tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of commodities, which will inevitably bring huge challenges to the inventory management of retail enterprises. Then may occur in the supply chain out of stock or backlog phenomenon.
The report by Retail Systems Research (RSR) highlights that 60% of retailers struggle with inventory visibility, which creates challenges in accurately tracking inventory and meeting consumer demand [3]. Therefore, how to use limited resources to maximize inventory turnover is a serious test for all companies and supermarkets. This is not only a management problem but also it is a potential challenge for the most of enterprises.
3.2.4. Environmental Risk
The external influencing factors of the supply chain of retail enterprises include unpredictability and irresistible. The unpredictability is mainly reflected in the influencing factors of natural disasters, such as flood, fire, earthquake and so on. Many natural disasters, such as Fukushima earthquake and tsunami that struck Japan in 2011, may lead to the interruption of the entire supply chain, resulting in the shortage of raw materials or overstocking of upstream suppliers, the failure of normal operation of production lines, and the lack of purchase channels for downstream retailers leading to losses. The irresistibility is mainly reflected in two aspects: market economy and political environment. The stability of national social environment, economic environment and political environment is an important factor to ensure the complete operation of the supply chain. Once a problem occurs, it will inevitably affect the operation of the entire supply chain.
4. Unveiling the Risks: A Comprehensive Analysis of Costco's Supply Chain
4.1. Introduction of Costco
Founded in 1983 and located in Seattle, Washington, Costco is a member-based retail giant that operates a chain of warehouse supermarkets and has opened many branches in the Unit States, while also expanding its business internationally with warehouses in countries such as Canada, Mexico, the United Kingdom, Japan and Australia. The Costco Corporation follows a unique business model that emphasizes delivering quality products to customers in bulk at wholesale prices. On May 23, 2022, Costco was ranked 11th on the Fortune 500 list. In the fiscal year 2022, the company's total revenue was $227 billion, up 15.83% from the previous year, and its net profit was $5.915 billion, up 16.46% from the previous year. According to the Figure 1, the net sales of Costco increased significantly from 2019 to 2022, especially on the category of food and sundries. Based on the Figure 2 and Figure 3, 847 stores operate functionally worldwide by the end of fiscal year 2022. As of the end of August 2023, the Company operates 861 stores worldwide, mainly in North America, 591 in the United States and 107 in Canada.
Figure 1: Net sales of Costco worldwide in 2019 and 2022, by merchandise category (In million U.S. dollars) [7]. Source: Company annual reports (2019, 2020, 2021, 2022).
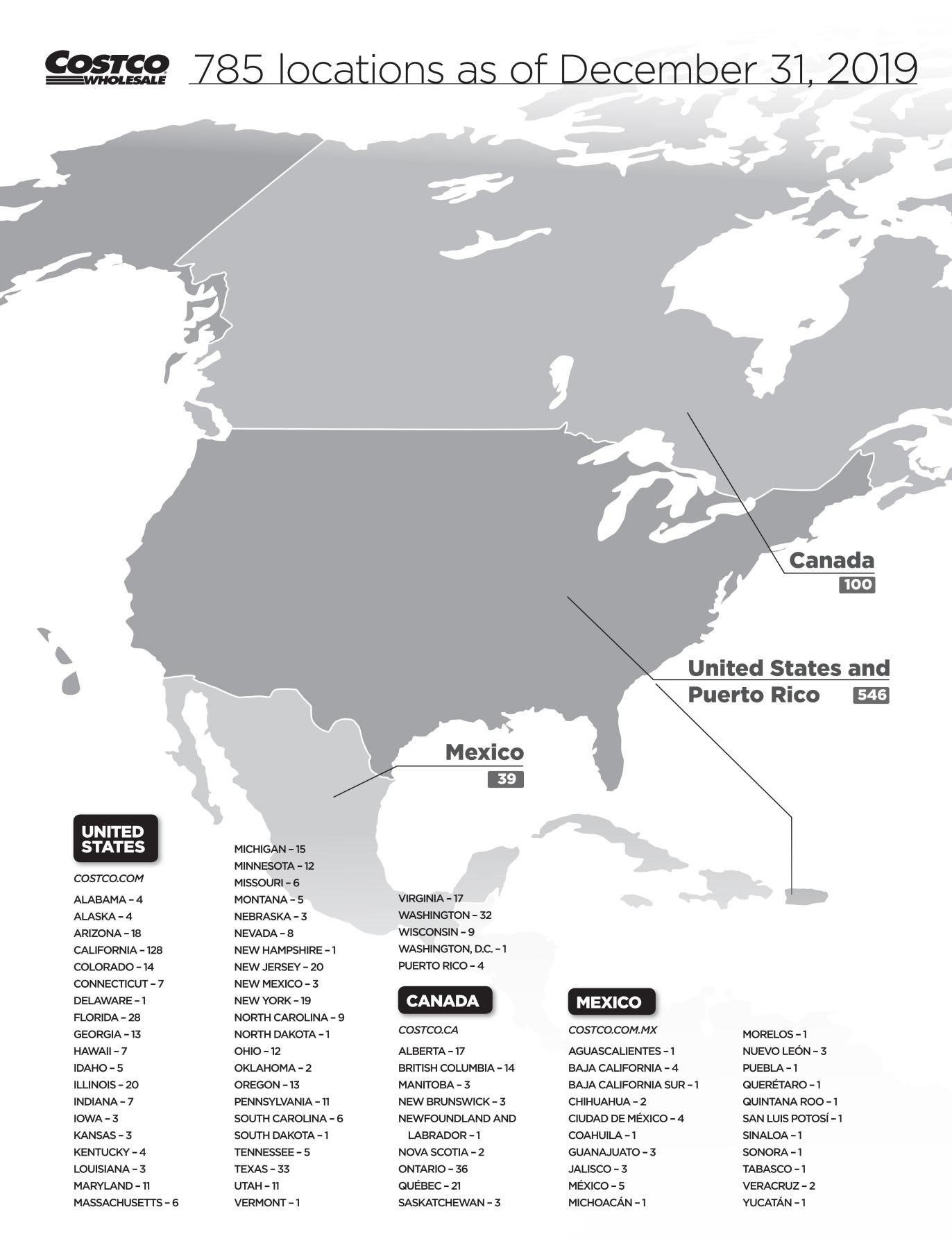
Figure 2: Distribution of Costco stores in North America. Source: Company official website, Company annual report (2022) [8].
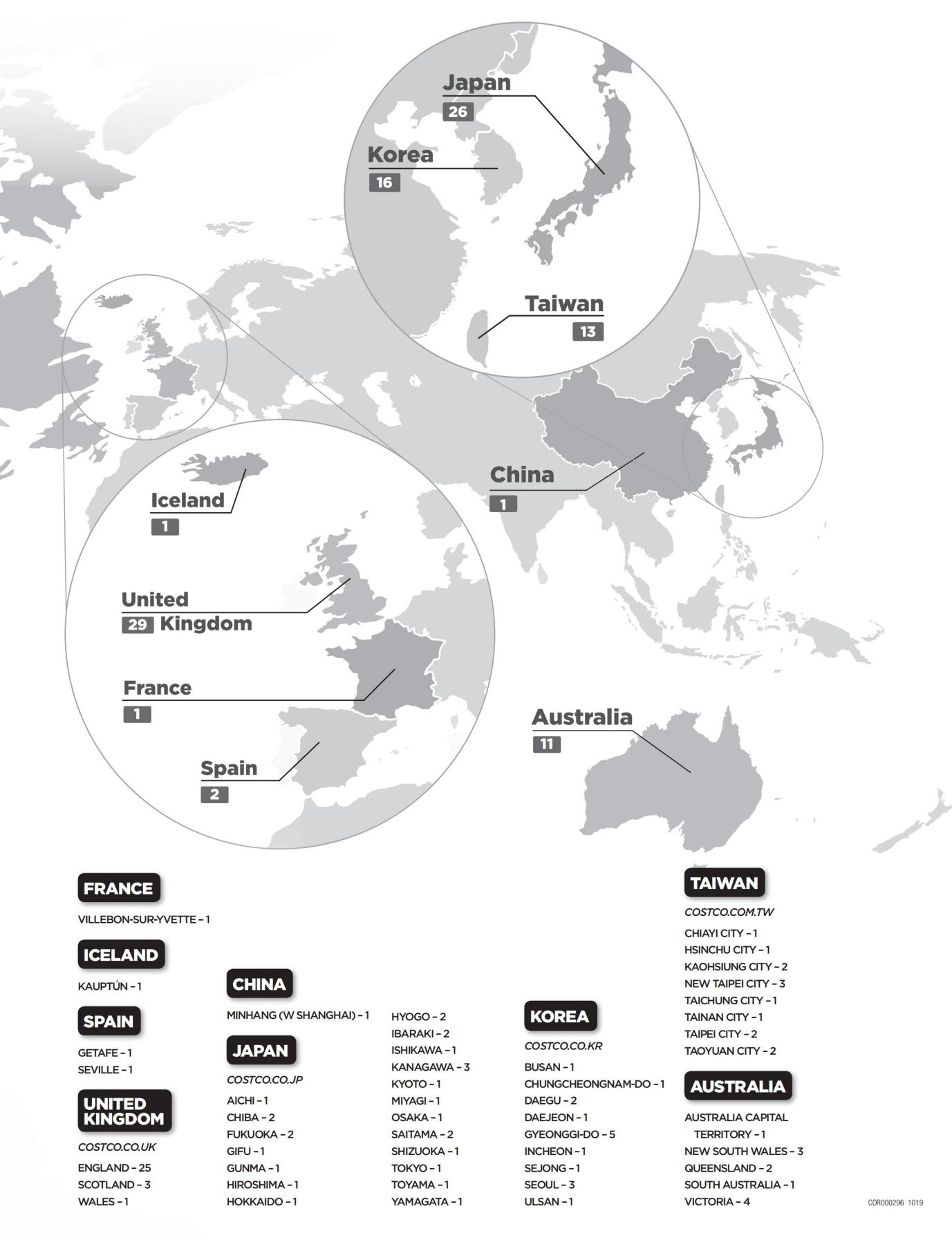
Figure 3: Distribution of Costco stores worldwide except North America. Source: Company official website, Company annual report (2022) [8].
4.2. ESG of Costco’s Supply Chain
4.2.1. ESG: Environmental (E)
In terms of environment, Costco's unique business model requires a strong ability to take overall control of the upgraded supply chain, minimizing the cost of goods supplied to attract new customers. So, Costco employs an operational strategy of ultra-low inventory units, scale procurement and strict selection, with only about 3,700 Stock Keeping Units. SKUs is the minimum available unit for holding inventory control, which can help indicate the amount of inventory stored, which have a larger inventory size and scale effect, and therefore have greater bargaining power when purchasing goods with suppliers, thereby winning lower prices for consumers.
4.2.2. ESG: Social (S)
The products Costco chooses are all the brands of the same kind of products with good performance and low price. Costco has already made a layer of screening for consumers. Because there are only 2 or 3 brands per category, another positive effect of the low inventory unit strategy is the compression of inventory cycles. Costco has only 33 days of inventory turnover, well below that of Wal-Mart of 43 in 2022 [9]. This means Costco can get goods to supermarket shelves more quickly for people to buy, and we can also see it doesn’t have much changed from previous years. It is believed that this model has had a positive impact on society.
4.2.3. ESG: Corporate governance (G)
Costco's distinctive business model necessitates effective global governance to streamline its upgraded supply chain and minimize the cost of goods supplied to its members. The company's governance strategies have proven superior, particularly in managing its unique warehousing and wholesale supermarket model.
According to China's Donghai Securities, earlier this year, Costco adopted a direct collaboration approach with upstream suppliers for trading and shipping goods. This model has resulted in reduced logistics costs, simplified goods circulation links, significantly enhanced product turnover efficiency, and a notable decrease in traditional multi-level logistics expenses.
4.3. SWOT of Costco's Supply Chain
Because of its long history, Costco's supply chain in the United States has matured, and the maturity of the supply chain also makes Costco close to the cost of low-cost, good quality goods and many other advantages, in the United States market share. But because it entered the Chinese mainland later than other warehouse supermarkets, it still needs to use SWOT to judge the risks that Costco's supply chain might receive in China.
4.3.1. Strength
Costco has a long history of opening stores and a mature history of supply chain construction, which can greatly reduce the transportation cost of goods. Despite the low sales price, but still many customers to spend, to maintain high sales growth and help improve operational efficiency. Achieve greater operational efficiency by reducing variable costs.[10]
4.3.2. Weakness
Costco sells its goods primarily through a membership model of warehousing and retailing, which encourages customers to shop at Costco stores but also shows a greater reliance on supply chains. Take the Covid-19 Pandemic as an example, the serious logistics lag caused by the epidemic directly leads to a serious shortage of all kinds of materials, affecting customers' shopping experience and causing profit decline.
In addition, because the same type of retailers also have a mature and complete supply chain, once Costco has a weakness in goods and services. Customers may go to other retailers with more goods and services, such as Wal-Mart.
4.3.3. Opportunities
Costco has an opportunity to enter emerging markets as there is still plenty of room for retail sales at home and abroad, and young people often go to supermarkets on weekends to buy a lot of food because they are too busy.
At the same time, as technology develops, Costco has the opportunity to expand the reach of its e-commerce sites, such as in the US, Canada, the UK, Australia, Mexico, Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, Spain and Iceland, and to improve the supply chain to increase the variety of goods and services that Costco stores offer to more diverse consumers.
4.3.4. Threats
In 2016, Freshippo, as the first new retailer in China, opened its first store in Shanghai, which not only means the further development of domestic warehousing supermarkets, but also means that the emerging warehousing member store brand retail company will threaten Costco's domestic market share, and indirectly affect Costco's supply chain construction in the early stage of entering the Chinese market. [11]
In addition, there are a growing number of new warehousing member stores in overseas markets, such as Walmart, Sam's Club and other retail companies with mature supply chains, whose sophisticated marketing capabilities also threaten Costco.
5. Conclusion
As the global economy recovers from the aftermath of the Covid-19 Pandemic, warehouse stores have also made sense of the advantages of ease of shopping, which is a key customer resource for new retail models.
Future Development of Retail Supply Chain
With the development of retail supply chain, it is necessary to take corresponding measures against environmental risks in order to deal with unexpected problems. In addition, consumers have more and more requirements for the quality and personalization of goods, and the importance of retail supply chain is more and more prominent. At the same time, retailers also need innovative marketing strategies and customized products to meet consumer demand.
Secondly, with the continuous progress of science and technology, retail supply chain will usher in more opportunities and challenges. For example, the application of artificial intelligence, big data, Internet of Things, and other technologies will help improve the efficiency and accuracy of retail supply chains. At the same time, these technologies will bring more risks and challenges, such as data security and privacy protection. According to the research findings, digital intelligent supply chain can bring a prominent positive promoting effect on the innovation and development of the retail industry. But there are some significant differences in the effect on the innovation and development of listed retail enterprises in different sectors.[12] So, how to deal with theses opportunities and challenges? Whether the company should change its current supply chain operation model? These all need to be considered by management.
In addition, with the continuous development of the global economy and trade liberalization, retail supply chains will be more international. Retailers need to adapt to the cultural, legal, and business environment of different markets to ensure the quality of goods and timely arrival of consumers. At the same time, retailers need to think about how to meet the challenges of globalization and digitization, especially how to strengthen the supply chain resilience, reduce the concentration of suppliers and customers through the advantages of ESG. By diversifying business risks, we can ease financing constraints and promote enterprise innovation.[13]
At last, optimization of supply chain sustainability also need to be achieved. If companies can deepen their understanding of the relationship between investment and ownership types and sustainable supply chain practices, and separately examine the motivations behind long-term investors prioritizing sustainable practices and investors with short-term perspectives lowering environmental, social, and corporate governance factors.[14]
Therefore, for the current retail industry, there are still many potential risks in the supply chain. How to properly manage the supply chain is the key point to help the long-term development of enterprises to improving in the future.
References
[1]. The state of the Supply Chain Industry (2022), Blue Ridge and Smart Brief, http://www.smartbrief.com/about/content-marketing
[2]. Jill E. Hobbs. (2020). Food supply chains during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue Canadienne agroeconomic (2). doi:10.1111/cjag.12237
[3]. Retail Systems Research. (2022). Costco and Walmart: A tale of two supply chains. https:/www rsrresearch.com/research/the-state-of-the-supply-chain.
[4]. ESG consideration report. (2023). ESG in Supply Chain Management: The Future of Corporate Responsibility. https://www.tradecloud1.com/en/esg-in-supply-chain-management-the-future-of-corporate-responsibility/
[5]. The use of ESG report. (2022) ESG in supply chains: Early integration can bolster your business. https://www.pwc.com/us/en/services/consulting/business-transformation/digital-supply-chain-2022-trends/esg-supply-chain.html
[6]. Environmental Supply Chain Report. https://mobilecontent.costco.com/live/resource/img/static-us-landing-pages/5aClimate-Action-Plan
[7]. Merchandise Category Chart Report (2022). https://investor.costco.com/company-profile/default.aspx
[8]. Securities research report. (2023) https://www.longone.com.cn/
[9]. COSTCO WHOLESALE CORP.(NASDAQ:COST) (2023) https://cn.stock-analysis-on.net/NASDAQ/%E5%85%AC%E5%8F%B8/Costco-Wholesale-Corp
[10]. Neeraj Kumar,Mohit Tyagi & Anish Sachdeva.(2023).A sustainable framework development and assessment for enhancing the environmental performance of cold supply chain. Management of Environmental Quality(4),1077-1110.
[11]. Jiang Shuyu. The impact of digital intelligent supply chain on the innovation and development of retail industry: Based on the empirical analysis of listed retail enterprises [J]. Business Economics Research,2022(19):21-24.
[12]. Zhong, Boyuan,Shen, Houcai,Zhang, Jianqiang & Gao, Xing.(2022).Agency or wholesale? retail selling format in the presence of new manufacturer introduction. Electronic Commerce Research(prepublish),1-35.
[13]. Li Yongjian & Luo Wenyi. (2023). ESG how to promote enterprise innovation and development, based on the analysis of the supply chain resilience. Supply chain management (07), 81-96. The doi: 10.19868 / j.carol carroll nki gylgl. 2023.07.008.(2021).Smart Foodservice Warehouse Stores to Rebrand as US Foods Chef'store. Food and Beverage Close - Up.
[14]. Liliana Rivera,Norma Ortiz,Gabriel Moreno & Iliana Páez Gabriunas.(2023).The Effect of Company Ownership on the Environmental Practices in the Supply Chain: An Empirical Approach. Sustainability(16).
Cite this article
Liu,Z. (2024). On Supply Chain Risk in Retail Industry—Taking Costco as an Example. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,92,209-217.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. The state of the Supply Chain Industry (2022), Blue Ridge and Smart Brief, http://www.smartbrief.com/about/content-marketing
[2]. Jill E. Hobbs. (2020). Food supply chains during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue Canadienne agroeconomic (2). doi:10.1111/cjag.12237
[3]. Retail Systems Research. (2022). Costco and Walmart: A tale of two supply chains. https:/www rsrresearch.com/research/the-state-of-the-supply-chain.
[4]. ESG consideration report. (2023). ESG in Supply Chain Management: The Future of Corporate Responsibility. https://www.tradecloud1.com/en/esg-in-supply-chain-management-the-future-of-corporate-responsibility/
[5]. The use of ESG report. (2022) ESG in supply chains: Early integration can bolster your business. https://www.pwc.com/us/en/services/consulting/business-transformation/digital-supply-chain-2022-trends/esg-supply-chain.html
[6]. Environmental Supply Chain Report. https://mobilecontent.costco.com/live/resource/img/static-us-landing-pages/5aClimate-Action-Plan
[7]. Merchandise Category Chart Report (2022). https://investor.costco.com/company-profile/default.aspx
[8]. Securities research report. (2023) https://www.longone.com.cn/
[9]. COSTCO WHOLESALE CORP.(NASDAQ:COST) (2023) https://cn.stock-analysis-on.net/NASDAQ/%E5%85%AC%E5%8F%B8/Costco-Wholesale-Corp
[10]. Neeraj Kumar,Mohit Tyagi & Anish Sachdeva.(2023).A sustainable framework development and assessment for enhancing the environmental performance of cold supply chain. Management of Environmental Quality(4),1077-1110.
[11]. Jiang Shuyu. The impact of digital intelligent supply chain on the innovation and development of retail industry: Based on the empirical analysis of listed retail enterprises [J]. Business Economics Research,2022(19):21-24.
[12]. Zhong, Boyuan,Shen, Houcai,Zhang, Jianqiang & Gao, Xing.(2022).Agency or wholesale? retail selling format in the presence of new manufacturer introduction. Electronic Commerce Research(prepublish),1-35.
[13]. Li Yongjian & Luo Wenyi. (2023). ESG how to promote enterprise innovation and development, based on the analysis of the supply chain resilience. Supply chain management (07), 81-96. The doi: 10.19868 / j.carol carroll nki gylgl. 2023.07.008.(2021).Smart Foodservice Warehouse Stores to Rebrand as US Foods Chef'store. Food and Beverage Close - Up.
[14]. Liliana Rivera,Norma Ortiz,Gabriel Moreno & Iliana Páez Gabriunas.(2023).The Effect of Company Ownership on the Environmental Practices in the Supply Chain: An Empirical Approach. Sustainability(16).









