

Volume 196
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2025 Symposium: The 4th International Conference on Applied Economics and Policy Studies
Poisson distribution, a foundational discrete probability distribution, describes the probability of observing k independent events within a fixed temporal or spatial interval under conditions of constant mean occurrence rate (λ). Therefore, it can be used to address a variety of real-world challenges across diverse domains, particularly in the application of low-probability phenomena. This paper investigates the application of the Poisson distribution through rigorous theoretical analysis and case studies specifically spanning on two fields, which are healthcare resource allocation and communication network optimization. Although the Poisson distribution has inherent limitations in some phenomena, our study reveals that as long as the model is optimized based on statistical principles and specific domain contexts, this framework can effectively provide valuable and actionable insights to inform data-driven decision-making across diverse domains ranging from healthcare resource allocation to telecommunications network optimization in complex systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


Taking the era of emotional consumption as the background, this study deeply explores the emotional marketing strategy of the sports brand lululemon, focusing on how the brand conducts marketing through emotional resonance, community operation and DTC mode, aiming to reveal how the brand can transform emotional demand into actual consumption behavior through precise marketing strategies, and to analyze the effectiveness and limitations of these strategies in practical application. This study adopts the literature analysis method to organize and summarize the current relevant information, and combines online and offline case collection to comprehensively analyze the brand's marketing strategy and psychological drivers of consumer. The study results show that lululemon successfully realizes the interchange between consumer behavior and lifestyle identity through the above marketing model, and satisfies customers' needs for functional and emotional aspects. However, the brand is controversial in terms of product quality and cost-effectiveness and faces competition from emerging brands. In the future, enterprises should pay more attention to the balance between emotional and functional values and maintain their existing strengths and features to optimize their marketing strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


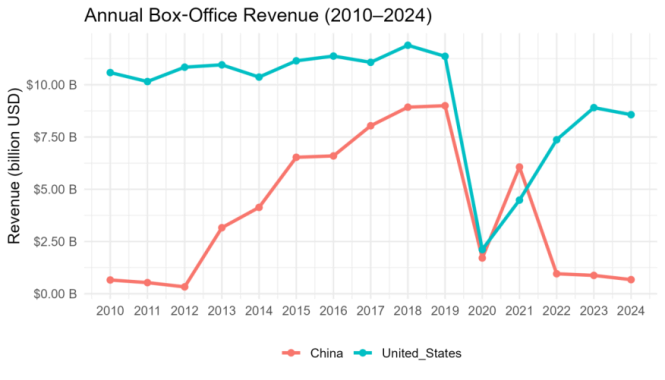
This paper investigates the impact of macroeconomic factors on the film industries of China and the United States from 2010 to 2024. The study explores how box-office revenues adjust to GDP growth and unemployment changes in the context of globalization, digital transformation, and recurring economic shocks, particularly the 2019–2020 global recession. The research applies harmonized annual data together with transparent descriptive methods to detect essential patterns in film industry performance throughout time. The analysis yields three major findings. First, cinema earnings show direct correlation with general economic conditions particularly during periods of unemployment increases. Second, the 2019–2020 economic downturn reduced average annual earnings by approximately one quarter in China and one-third in the United States. Third, the Chinese market experienced the same level of damage in 2020 but recovered at a faster pace because of supportive policies and market structure, which reduced long-term economic shock impacts. The research joins multiple studies which investigate how economic changes affect cultural consumption patterns and industry stability. Its findings demonstrates how cultural industries remain sensitive to economic conditions while showing that strategic planning and policy development play essential roles in achieving recovery and sustaining long-term growth.

 View pdf
View pdf


As ESG disclosure frameworks become increasingly standardized across jurisdictions, a growing policy concern is whether individual investors can actually interpret and act upon the information presented. This issue is particularly acute in emerging markets like China, where sustainability reports remain lengthy, jargon-heavy, and difficult to process for non-professional audiences. This study examines whether improving the linguistic readability of ESG disclosures affects investment-related perceptions and intentions among individual investors. We implement a between-subjects experiment involving 232 Chinese participants, randomly exposed to either a high-readability or low-readability version of an ESG text excerpt. Findings reveal that clearer wording significantly enhances perceived informativeness, moral alignment, and investment intention. Notably, while prior literature suggests that cognitive and affective mechanisms should mediate such effects, we observe a direct impact of readability on intention without sequential mediation. The results offer both theoretical insights into investor cognition under linguistic constraints and practical implications for regulatory bodies seeking to reform ESG communication standards through plain-language mandates.

 View pdf
View pdf


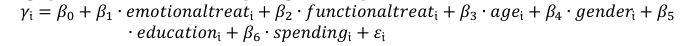
This study investigates the impact of different advertising appeals on consumer behavior by comparing emotional, functional, and neutral advertisements. Utilizing an experimental design, 475 participants were randomly assigned to view one of three types of advertisements for a fictional smartphone, with their purchase intention and decision time measured through questionnaires. The results indicate that emotional advertisements significantly enhance purchase intention (β = 1.871, p < 0.01) compared to functional and neutral advertisements, supporting behavioral theories that position emotion as a critical driver of consumer choice. In contrast, functional advertisements reduce decision time (β = -0.210, p < 0.05), likely due to their clear, feature-focused information facilitating quicker evaluation. These findings align with the dual-process model of decision-making, where emotional appeals evoke affective responses, and functional appeals satisfy cognitive efficiency. The study provides actionable insights for marketers, suggesting that emotional strategies are more effective in boosting purchase intention, while functional approaches optimize decision processes. Limitations include sample imbalance and cultural specificity (data collected in China), which may affect the generalizability of the results. Future research should explore cross-cultural differences and diverse product categories to further validate these findings. Overall, this study underscores the importance of tailoring advertising strategies based on consumer psychology and product types.

 View pdf
View pdf


It is common for investors’ irrational decisions, driven by their “herd behavior,” to influence the stock prices of companies in the electric vehicle (EV) industry. However, investors are usually regarded as rational decision makers, and few scholars have considered this kind of irrational behavior. Thus, the effect of “herd behavior” remains unknown. This study, using two representative companies, Tesla and BYD, as case studies, aims to determine the impact of the “herd behavior” of investors on EV companies’ stock prices. The Cross-Sectional Absolute Deviation (CSAD) model and descriptive analysis are applied in order to sort out events that lead to the “herd behavior” of investors and figure out the trend of changes in stock prices following these significant events. The research findings indicate that although the emergence of herd behavior among investors does not directly cause greater volatility in stock prices over a longer period, it does lead to significant fluctuations in stock prices two days after major events of the EV company. This research fills the gap in the existing research concerning the impact of investor “herd behavior” on the stock prices of electric vehicle companies by using a more systematic method.

 View pdf
View pdf


Consequently, venture capital investment is characterized by elevated risk and substantial returns, predominantly channeling resources into nascent enterprises and projects with pioneering concepts and significant growth prospects. Features of VC investing include high risk: The risk is high as the investment target is usually at an early stage and faces many uncertainties. High returns: Once the investment is successful, it can reap huge returns.Innovativeness: Focus on enterprises with innovative ideas and technologies.Long-term investment: It usually takes a long time to realize returns. The VC investment process generally consists of the following stages: Project Screening: Look for potential investment projects. Due diligence: Conduct an in-depth understanding and evaluation of the project.Investment decision: Decide whether to invest or not.Post-investment management: provide support and oversight. The main roles of VC investment are to promote innovation and provide financial support to innovative enterprises. Driving economic growth: Helping businesses grow and create jobs. Resource integration: Provide a variety of resources and experiences. However, there are some challenges to VC investing: High risk: There is a high probability that the investment will fail. Information asymmetry: It is difficult for investors to have a comprehensive understanding of the project.

 View pdf
View pdf




