

Volume 198
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
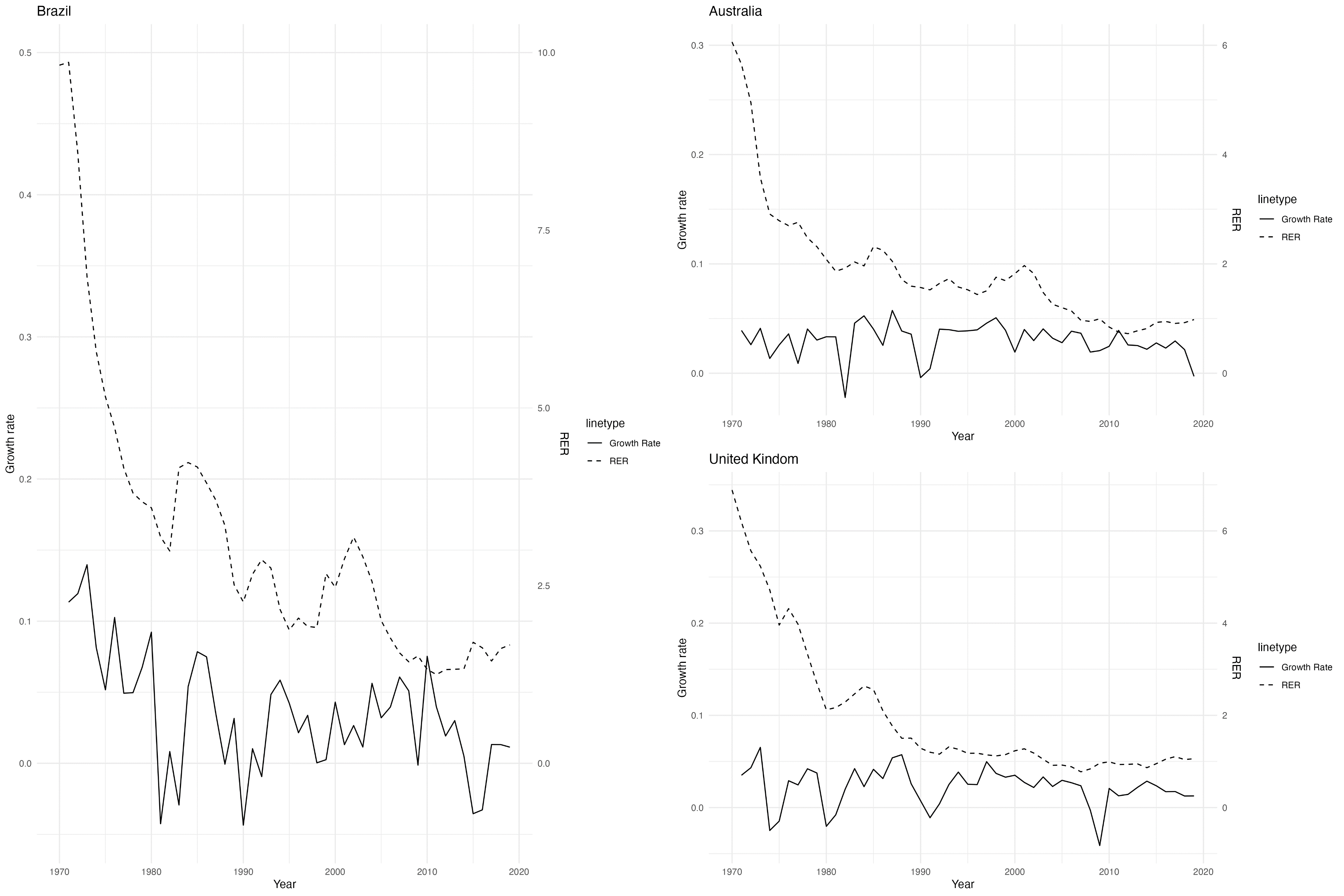
Current literature indicates that currency undervaluation has various effects on economic growth. This work testified the correlation between a low real exchange rate and economic growth, and also explores the mediating effects of intermediate variables such as foreign direct investment and net export. The research firstly calculates the undervaluation of the real exchange rate based on the Balassa-Samuelson effect. The data is used to construct an econometric model, which employed panel regression to analyze annual data from 156 countries from 1970 to 2019 to examine the impact of undervaluation on a country's economic growth. Secondly, a mediation analysis is conducted to unveil the specific mechanisms through which the independent variable influences the dependent variable. Besides, a three-order VAR (Vector Autoregression) model with four variables is established using the previously obtained undervaluation index to analyze the multi-dimensional dynamic relationship between different variables. The results passed the Granger Causality Test, indicating there might be a casual effect between these two variables. Results show that the impact of undervaluation on economic growth varies across different types of countries, and the dominant intermediate variables differ as well. This study may as well offer some insights for policymakers in formulating appropriate exchange rate policies to promote economic growth based on their country’s specific circumstances.

 View pdf
View pdf




