

Volume 197
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
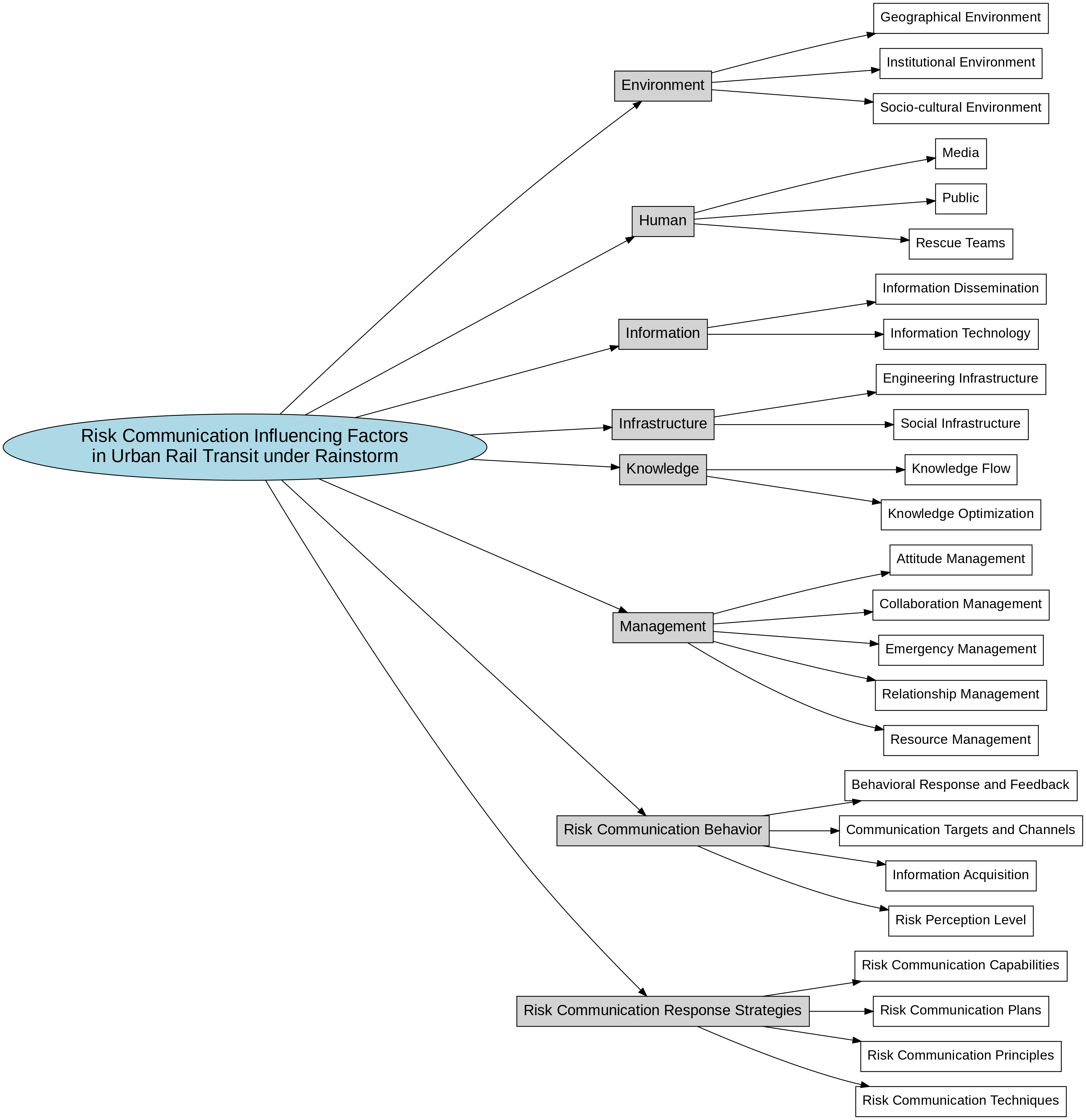
Against the backdrop of escalating climate change, the effectiveness of risk communication for urban rail transit systems under extreme weather events such as rainstorms has emerged as a critical issue in urban resilience building. Focusing on the risk communication challenges faced by urban rail transit in rainstorm scenarios, this study systematically extracts eight categories of core factors through a three-level coding process based on grounded theory. Building on this, the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is employed to quantitatively assess the importance of each influencing factor. The theoretical model developed in this research not only enriches the research framework in related fields but also provides a theoretical foundation and practical guidance for optimizing risk communication mechanisms in urban rail transit under extreme climatic conditions.

 View pdf
View pdf




