1. Introduction
The full name of REITs is Real Estate Investment Trusts, that is, real estate investment trusts, also known as real estate trust funds and real estate trusts. REITs originated in the United States in 1960. It is a kind of securities that collects funds through the issuance of income trust certificates/shares, and the manager conducts real estate investment, operation and management, and distributes the comprehensive investment income to investors. For property owners, REITs are an effective financing method to revitalize stock and improve balance sheets. For investors, through the securitization of real estate and fundraising from many investors, REITs enable ordinary investors without huge capital to participate in the real estate market with a lower threshold, and obtain the real estate market transactions, rents and value-added. income. At the same time, investors can trade in the securities market without actually holding real estate targets, so the market liquidity is better than that of real estate. REITs are widely welcomed by investors around the world, and have extensive influence in major capital markets such as the United States, Japan, Singapore, Mainland China and Hong Kong.
In Mainland China public infrastructure REITs market: In 2020, the sudden outbreak of the new crown epidemic will have a huge impact on domestic economic development. In this context, the steady development of infrastructure construction has become the engine of sustained economic growth and recovery. In view of the limitations of the traditional infrastructure investment and financing model, my country has actively introduced public offering REITs as a way to carry out infrastructure construction. On August 6, the China Securities Regulatory Commission officially released the "Guidelines for Public Offering of Infrastructure Securities Investment Funds (Trial)", which means that my country's public offering of REITs pilots has officially started. In the current situation where the government and state-owned enterprises have very limited financial resources for investment, public offering REITs can take advantage of their advantages to revitalize and reorganize stock assets, relieve financial pressure, and make up for the funding needs of infrastructure construction, which is of great significance to promote infrastructure construction. Since 2020, in order to accelerate the development of the REITs market, my country has promulgated a number of relevant laws and regulations to improve market players and related mechanisms. Based on mature experience, it puts forward suggestions for the development of my country's infrastructure REITs. In June 2021, the first batch of 9 publicly offered infrastructure REITs will be listed on the Internet respectively.
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of REITs in China, offering insights into their historical development, current state, operating mechanisms, financial innovation, and future prospects. It aims to serve as a valuable resource for academics, investors, policymakers, and other stakeholders interested in the Chinese REIT market.
2. Current State of REITs
2.1. Current Market Size and Growth of REITs in China
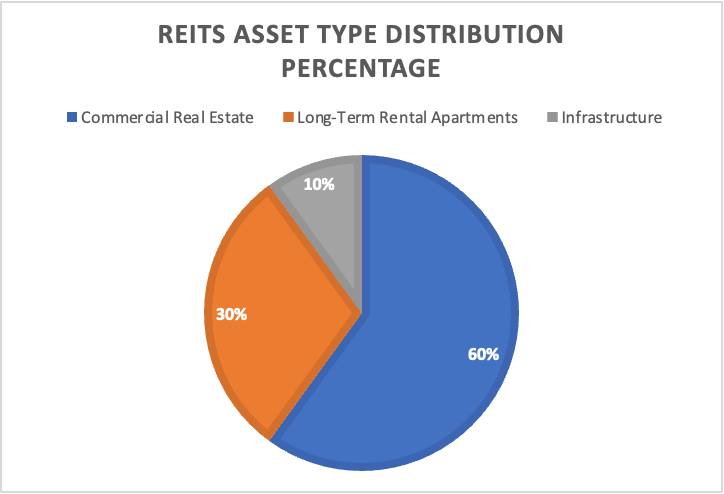
Figure 1: REITs ASSET TYPE DISTRIBUTION PERCENTAGE (Source: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/cn/Documents/real-estate/deloitte-cn-re-china-reits-development-report-zh-230714.pdf)
The Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) market has seen significant growth and diversification across various regions, including the United States, Singapore, Hong Kong, and Mainland China. In the United States, where REITs originated in 1960, there were 206 listed REITs as of December 2022, with a market value of $1.27 trillion, accounting for nearly 70% of the total REITs market value. The asset types include office, retail, infrastructure, hotels, apartments, medical real estate, campus real estate, forestry, data centers, etc., with long-term annualized returns higher than the S&P 500 index. Singapore marked the 20th anniversary of its first REIT in 2022, with 42 REITs listed and a total market value exceeding $74 billion, and an average dividend yield of 7.5%. Over 90% of Singapore's REITs have offshore assets, including 5 with underlying assets entirely from China. In Hong Kong, the market has grown nearly five times since 2005, with a total market value exceeding $20 billion and an average dividend yield of about 8.0%. The Hong Kong SAR government supports the development of REITs, subsidizing up to 70% of eligible costs for newly listed REITs. Mainland China saw the successful listing of the first batch of 9 public infrastructure REITs in Shanghai and Shenzhen in June 2021. Two years after the first issuance, there are 29 issued or approved public infrastructure REITs, with a total market value close to RMB 1,000 billion. The asset types include industrial parks (9), highways (8), affordable housing (4), warehousing and logistics (3), clean energy (3), ecological and environmental protection facilities (2). The development of REITs in China, including various international markets, reflects the global acceptance and influence of REITs, making them an attractive investment option for both property owners and investors.
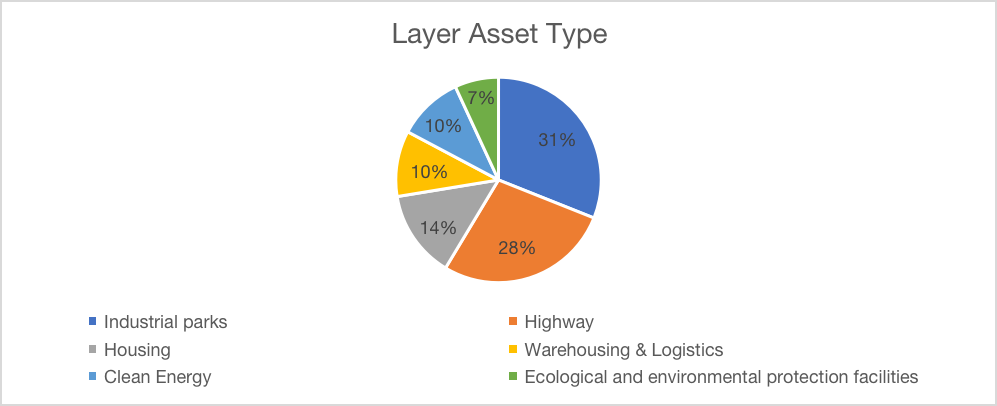
Figure 2: Layer Asset Type (Source: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/cn/Documents/real-estate/deloitte-cn-re-china-reits-development-report-zh-230714.pdf)
China's public infrastructure REITs market has experienced remarkable growth since its inception. In June 2021, the first batch of 9 public infrastructure REITs was successfully listed in Shanghai and Shenzhen, marking a significant milestone in the country's financial landscape. Within just two years after the first issuance, the market has expanded to include 29 issued or approved public infrastructure REITs, with a total market value close to RMB 1,000 billion. This rapid growth underscores the potential and attractiveness of REITs as an investment vehicle in China's burgeoning infrastructure sector.
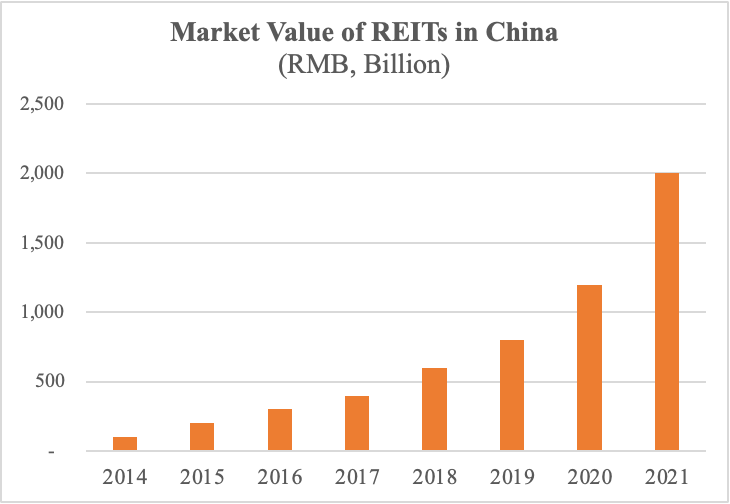
Figure 3: Market Value of REITs in China (Source: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/cn/Documents/real-estate/deloitte-cn-re-china-reits-development-report-zh-230714.pdf)
The development of public infrastructure REITs in China has been facilitated by supportive regulatory frameworks and government initiatives. The successful listing of the first batch of REITs has set the stage for further expansion and diversification, attracting both domestic and international investors. The average yield of these REITs has also been competitive, offering an appealing option for those seeking stable returns.
In conclusion, China's public infrastructure REITs market represents a dynamic and evolving segment of the country's financial ecosystem. The growth, diversity of assets, and regulatory support have positioned it as a key player in the global REITs landscape. Continued research, analysis, and strategic investment in this sector will be vital in realizing its full potential and contributing to China's broader economic development.[1]
2.2. Regulation and Legal Environment of REITs in China
The Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) in China have undergone significant evolution in recent years, with the regulatory and legal environment playing a pivotal role in shaping their trajectory. The Chinese government's proactive approach to fostering a conducive environment for REITs is evident in its various initiatives and policy adjustments.
Starting from 2014, the Chinese government began piloting REITs in select regions as a means to invigorate the real estate market. This move was seen as a strategic step to diversify investment channels, optimize the structure of the real estate market, and promote the healthy development of the capital market. The China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) emerged as the primary regulatory body overseeing the operations of REITs, ensuring that they adhere to the stipulated guidelines and maintain transparency in their dealings.
The legal framework governing REITs is primarily derived from the Securities Law, which lays down comprehensive guidelines regarding their issuance, trading, and information disclosure. Being trust products, REITs are also subject to the provisions of the Trust Law. This dual layer of legal oversight ensures that REITs operate within a well-defined boundary, safeguarding the interests of investors and maintaining market integrity.
Taxation policies related to REITs have also been a focal point of discussions and reforms. Typically, REITs are subject to a corporate income tax rate of 25%. However, there are instances where certain exemptions or reductions might apply, depending on the nature of the REIT and its underlying assets. Additionally, a value-added tax (VAT) at a rate of 6% is levied on REITs, further emphasizing the government's intent to streamline revenue collection from this burgeoning sector.[2]
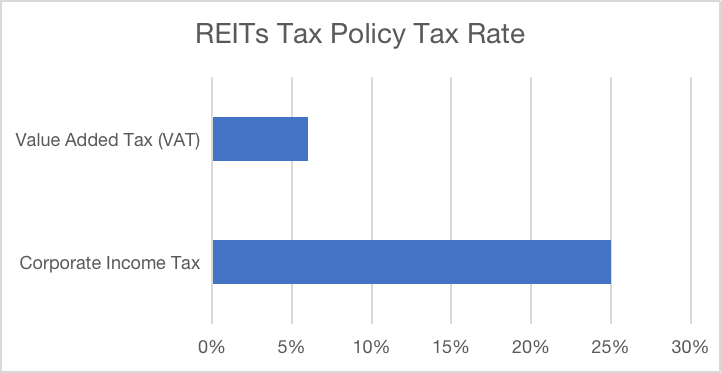
Figure 4: REITs Tax Policy Tax Rate (Source: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/cn/Documents/real-estate/deloitte-cn-re-china-reits-development-report-zh-230714.pdf)
One of the critical aspects of the REITs market in China is the qualification criteria set for their managers. To ensure the smooth operation and management of REITs, managers are expected to meet specific capital and experience thresholds. This not only ensures that REITs are managed by competent entities but also instills confidence among investors. Furthermore, there are stipulated investment restrictions for REITs, primarily focusing them on commercial real estate and long-term rental apartments
In terms of market data, by the end of 2021, the market size of REITs in China was estimated to be around RMB 2 trillion. The trading volume in 2020 alone touched approximately RMB 500 billion, underscoring the growing investor interest and market liquidity. The growth trajectory of REITs in China looks promising, with experts predicting a steady rise in the coming years, especially as regulations become more refined and the market matures.
However, like any evolving market, the REITs sector in China faces its share of challenges. The regulatory landscape, although improving, still has areas of ambiguity. The lack of a consistent regulatory approach and gaps in the execution of some policies can sometimes pose challenges. But, on the flip side, the rapid urbanization in China and the expanding middle class present enormous growth opportunities for REITs. The demand for diversified investment channels and quality real estate assets is on the rise, positioning REITs as a preferred choice for many investors.
Recent regulatory changes in 2021 further relaxed investment restrictions for REITs, allowing a broader range of assets, including infrastructure, to enter the market. This move is expected to significantly expand the scope and appeal of REITs, attracting more institutional and retail investors.
In conclusion, the regulatory and legal environment for REITs in China is a dynamic one, reflecting the government's intent to balance market growth with investor protection. As the market continues to evolve, it will be crucial for regulators, investors, and other stakeholders to collaborate and ensure that China's REITs market realizes its full potential.[3]
Important policies for publicly offered infrastructure REITs from June 2021 (the first batch of listings) to May 2023:
Table 1: Important policies for publicly offered infrastructure REITs from June 2021 (the first batch of listings) to May 2023 (Source: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/cn/Documents/real-estate/deloitte-cn-re-china-reits-development-report-zh-230714.pdf)
Date | Issuing Department | Policy | Document Name |
May 2022 | State Council Office | About Further Activating Stock Assets to Expand Effective Investment Opinions | Further expanding the key areas, regions and enterprises focusing on the revitalization of stock assets; proposing to optimize and improve the way of revitalizing stock assets, including promoting the healthy development of real estate investment trusts (REITs) in the field of infrastructure and Public-Private Partnership projects; and requesting to increase the policy support for the revitalization of stock assets, including the implementation of the detailed support for the relevant tax policies for infrastructure REITs, etc. |
May 2022 | Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges | Publicly Raised Infrastructure Securities Investment Fund (REITs) Rules Application Guidelines No. 3 - New Purchase of Infrastructure Projects (Trial) | Regulates new acquisitions of infrastructure projects during the life of currently listed infrastructure funds and related expansion and disclosure matters |
May 2022 | China Securities Regulatory Commission | Notice on Regulating the Work of Issuing REITs in the Field of Infrastructure for Affordable Rental Housing Pilot | Emphasized the significance of issuing public infrastructure REITs for guaranteed rental housing and the implementation of the relevant requirements for the stable and healthy development of the real estate market; strictly regulated the use of recycled funds, etc. |
Jun 2022 | State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission | Notice on Matters Concerning the Transaction and Circulation of Enterprise State-owned Assets | Clearly revitalize the stock of assets through the issuance of infrastructure REITs, involving the transfer of state-owned property rights in accordance with the provisions of the non-public agreement reported to the state-owned assets supervision and management institutions at the same level for approval, etc. |
Jul 2022 | Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges | Publicly Raised Infrastructure Securities Investment Fund (REITs) Rules Application Guidelines No. 4 - Affordable Rental Housing (Trial) | Special guidelines on the conditions related to public infrastructure REITs using guaranteed rental housing projects as underlying assets, including the qualification of original equity holders and identification standards |
Jul 2022 | National Development and Reform Commission | Notice on Doing a Good Job in the Declaration and Recommendation of New Purchase Projects in the Field of Infrastructure Real Estate Investment Trust Funds (REITs) | Reasonably simplify the reporting requirements for newly purchased projects and further improve the reporting and recommendation procedures for newly purchased projects. |
Sep 2022 | National Development and Reform Commission | Notice on Doing a Good Job in Activating Stock Assets to Expand Effective Investment | Encourage localities to flexibly adopt a variety of ways to effectively revitalize different types of stock assets, and for infrastructure stock projects with relevant conditions, real estate investment trusts (REITs) in the field of infrastructure, government-social capital cooperation (PPP) and other ways to revitalize |
Oct 2022 | National Development and Reform Commission | Opinions of the National Development and Reform Commission on Further Improving the Policy Environment and Increasing Support for the Development of Private Investment | Supporting private investment projects to participate in pilot real estate investment trusts (REITs) in the infrastructure sector, etc. |
Nov 2022 | Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges | Notice on Regulating the Distribution of Income Related Matters of Publicly Raised Infrastructure Securities Investment Fund (REITs) | Reaffirms that infrastructure REITs should distribute income strictly at a rate of no less than 90% of the annual distributable amount of the consolidated fund, etc. |
Mar 2023 | National Development and Reform Commission | Notice on Further Doing a Good Job in the Pilot Work of Real Estate Investment Trust Funds (REITs) in the Field of Infrastructure | It further clarifies the general requirements of the infrastructure REITs pilot work, clarifies the procedures for reporting and recommending newly acquired projects, and emphasizes the strengthening of the organization, coordination and supervision of the infrastructure REITs pilot work, etc. |
3. Operating Mechanism of REITs in China
3.1. Operating Model of REITs
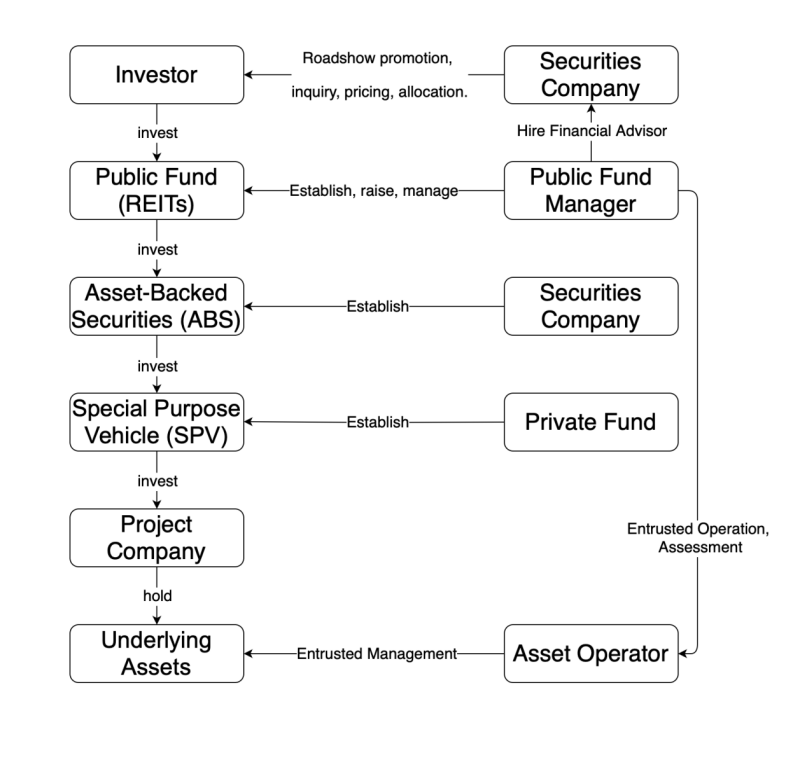
Figure 5: Operating Model of REITs (Source: https://www.investor.org.cn/learning_center/gmjytx/yjs/kj/jyxl_3474/202303/P020230320386915808486.pdf)
Description of the process related to China Infrastructure Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):
1. Securities Company Establishes ABS (Asset-Backed Securities): The securities company creates Asset-Backed Securities (ABS), a fixed-income product that finances by packaging an asset pool and selling it to investors.
2. ABS Invests in SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle): ABS invests funds in a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), a legal entity typically used to isolate assets and risks.
3. SPV Invests in Project Company: The SPV further invests funds in a project company, which is responsible for holding and managing underlying assets, such as infrastructure projects.
4. Investors Invest in REITs: Investors invest funds in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), an investment tool that allows investors to invest in a portfolio of real estate assets.
5. REITs Invest in ABS: REITs invest funds in the aforementioned ABS, thereby indirectly investing in underlying assets.
6. Role of Public Fund Manager: The public fund manager is responsible for establishing, raising, and managing REITs. The public fund manager hires financial advisors from the securities company to find investors to invest in REITs.
7. Private Funds May Establish SPV: Private funds may also establish an SPV for investment, similar to the process of ABS investing in an SPV.
8. Public Fund Manager Entrusts Operation and Assesses Asset Operator: The public fund manager entrusts the asset operator to manage the underlying assets and assesses them. The asset operator is entrusted to manage the underlying assets, ensuring effective operation and maximizing returns.
This process involves multiple entities and investment tools, aiming to invest and manage infrastructure assets through complex structured financing. Through tools like ABS, SPV, REITs, etc., the isolation of assets, diversification of risks, and efficient flow of funds can be achieved. The public fund manager plays a key role in the entire process, responsible for the establishment, raising, and management of REITs, as well as the entrustment and assessment of the asset operator.
Table 2: Operating Model of REITs' position (Source: https://www.investor.org.cn/learning_center/gmjytx/yjs/kj/jyxl_3474/202303/P020230320386915808486.pdf)
Name: | Product Creation → | Regulatory Approval → | Issue and Establishment → | Operation Management → | Capital Operation |
Public Fund | Product Design, Due Diligence | Facing Regulatory Reporting Projects | Product Establishment, Fundraising, Investment | Information Disclosure Project Operation, Delegated Operation and Assessment of Product-Level Operation Investor Communication | Additional Fundraising, Target Selection, Investor Communication |
Securities Company | Construct ABS (Asset-Backed Securities) structures |
| Financial Advisor, Roadshow Promotion, Inquiry, Pricing, Allocation | Transfer of Funds, Distribution | Financial Advisor, Roadshow Promotion, Inquiry, Pricing, Allocation |
Original Equity Holder/Operating Organization |
|
|
| Accept Entrusted Management |
|
Appraisal Agency | Asset Appraisal |
|
| Annual Assessment, Change Every 3 Years |
|
Accountant | Financial audit, cash flow forecasting. |
|
| Annual Audit |
|
Law Office | Legal Opinion. |
|
|
| Legal Opinion |
Bank | Product Custody/Trusteeship |
|
|
|
3.2. Structure of Infrastructure REITs
China Infrastructure REITs include transportation facilities such as warehousing and logistics, toll roads, municipal engineering such as water, electricity, heat, urban sewage and garbage treatment, solid waste and hazardous waste treatment and other pollution control projects. Encourage new infrastructure such as information networks, as well as national strategic emerging industry clusters, high-tech industrial parks, and characteristic industrial parks to carry out pilot projects. And here are 5 major industries:
Table 3: Five Major China Infrastructure REITs (Source: https://www.investor.org.cn/learning_center/gmjytx/yjs/kj/jyxl_3474/202303/P020230320386915808486.pdf)
Industry: | Example: |
Data center | data room, etc. |
Industrial parks and other infrastructure | new industrial cities, characteristic towns, incubators, etc. |
Municipal facilities | water, heat, electricity, gas, etc. |
Transport infrastructure | Toll roads, airports, ports, etc. |
Warehouse and Logistics | Logistics warehousing, cold storage, etc. |
And here are several projects analysises:
Toll Roads Analysis:
On June 21, 2021, China witnessed the listing of the first batch of publicly offered Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) with underlying assets in toll roads. Among these, significant projects included Guangzhou Guanghe REIT and Zhejiang Hanghui REIT, with fundraising scales of 9.114 billion yuan and 4.360 billion yuan, respectively. Subsequently, Huaxia Yuexiu Expressway REIT was listed on December 14, 2021, with a fundraising scale of 2.130 billion yuan.
Toll roads represent 3.40% of China's total road mileage, primarily comprising expressways. By the end of 2020, China had 161,000 kilometers of expressways, the largest network globally. Investment in highways has escalated from 623.1 billion yuan in 2006 to 2.19 trillion yuan in 2019, growing at an average annual compound rate of 10.15%. Expressway mileage, displaying the highest traffic level, has compounded at 9.62%. Toll roads, with their clear profit model, anti-cyclical ability, and relatively stable income, stand as high-quality underlying assets and a vital project source for public infrastructure REITs.
Industrial Park Analysis:
The first batch of publicly offered REITs with underlying assets in industrial parks were listed on June 21, 2021. These included Shekou Industrial Park REIT, Zhangjiang REIT, and Dongwu Suyuan REIT, with respective fundraising scales of 2.081 billion yuan, 1.495 billion yuan, and 3.493 billion yuan. Jianxin Zhongguancun REIT was subsequently listed on December 17, 2021, with a fundraising scale of 2.880 billion yuan.
Industrial parks in China typically involve substantial capital investment during the construction phase, and the payback cycle is prolonged. Hence, there exists a strong motivation to shorten the capital recovery cycle through REIT issuance. Furthermore, the growth in the scale of industrial parks and the clarity in the park asset income model provide excellent underlying assets for public infrastructure REITs. Park assets also offer good value-added potential, enhancing investment returns for public REITs investors.
Warehousing and Logistics Analysis:
On June 21, 2021, the listing of the first batch of publicly offered REITs included projects with underlying assets in warehousing and logistics, such as Hongtu Yantian Port REIT and Zhongjin Prolus REIT, with fundraising scales of 1.840 billion yuan and 5.835 billion yuan, respectively.
Warehousing and logistics REITs present a mature issuance model, with high investor acceptance and substantial market potential. They form an integral part of infrastructure REITs, offering high long-term returns and resilience under epidemic pressures. Demand analysis indicates that domestic warehousing and logistics enterprises primarily hold facilities in an asset-heavy mode, necessitating extensive spatial layout and large fund requirements. On the supply side, warehousing and logistics REITs are expected to exceed 200 billion yuan in China, with corresponding stock assets reaching approximately 450 billion yuan.
The above analyses collectively underscore the pivotal role of REITs in different sectors of China's infrastructure development. The insights drawn from toll roads, industrial parks, and warehousing and logistics sectors reflect the multifaceted opportunities and challenges in harnessing REITs for sustainable economic growth.[4]
3.3. Case Study of Huaxia China Communications Construction REIT
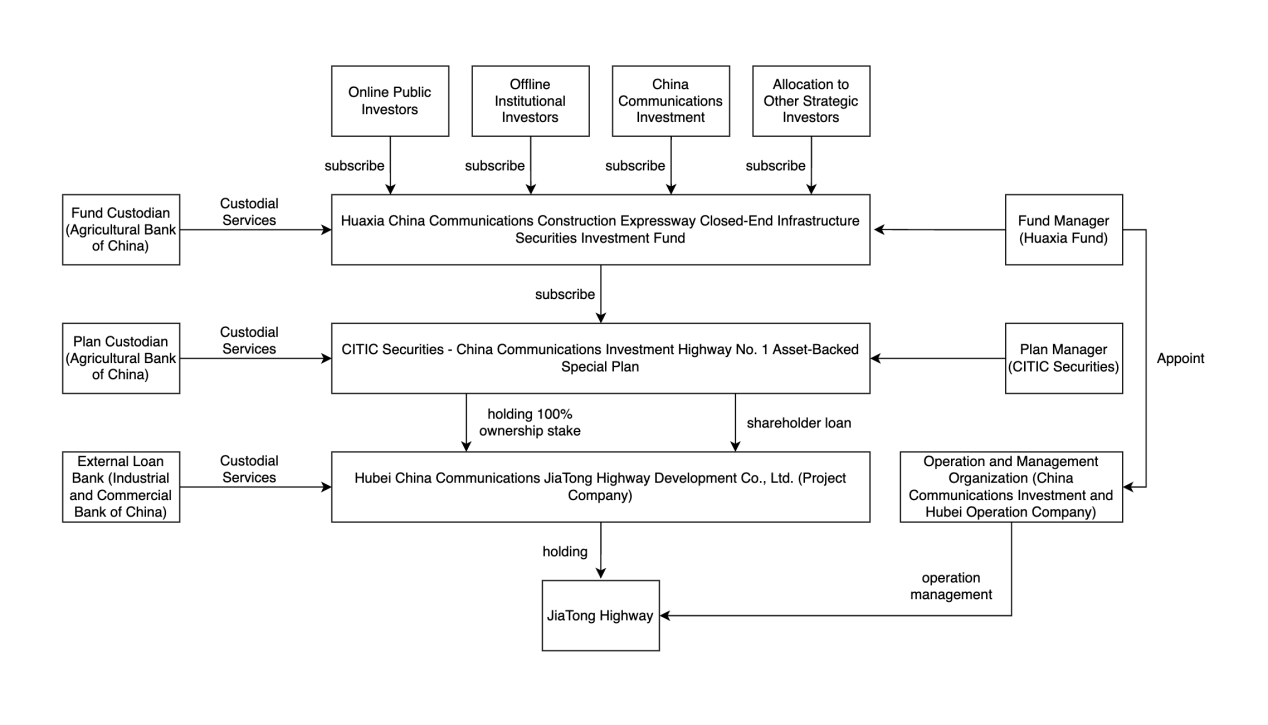
Figure 6: Financial structure diagram
Figure 6 illustrated the investment flow and custodial relationships for the Huaxia China Communications Construction Expressway Closed-End Infrastructure Securities Investment Fund and its associated entities.
Huaxia China Communications Construction REIT has a two-layer trading structure, comprising a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) and an Infrastructure Fund. Upon completion of the transaction, the Plan Manager (representing the SPV) will own 100% of the equity in the Project Company and will have corresponding creditor rights to the Project Company. The Fund Manager (representing the Infrastructure Fund) will hold all the shares of the SPV.
The fund manager of Huaxia China Communications Construction REIT is Huaxia Fund, and the plan manager is CITIC Securities. The project operation and management agencies are China Communications Investment and China Communications Investment Hubei Operation Company. The product's term lasts for 40 years from the date the fund contract takes effect. However, according to the "Concession Agreement for the JiaYu to TongCheng Section of the Wuhan to Shenzhen Expressway" for the underlying infrastructure project, the remaining concession operating right is approximately 24 years. After the expiration of the concession operating right, the government has the right to reclaim it without compensation. In subsequent situations where additional funds are not successfully raised, there is a risk of early termination of the fund.
4. Financial Innovation
4.1. Individual investors
For most investors, REITs are real estate investment tools with low threshold and high liquidity. Compared with traditional assets such as stocks, bonds and commodities, REITs, as the "fourth category of assets", provide investors with a new major asset allocation channel.
At the same time, REITs have low correlation with the stock market and bond market. Compared with bonds, they have higher yield, reduce the risk of price fluctuation compared with stocks, and can give investors stable and high dividend income. It is a medium risk and medium return financial instrument.
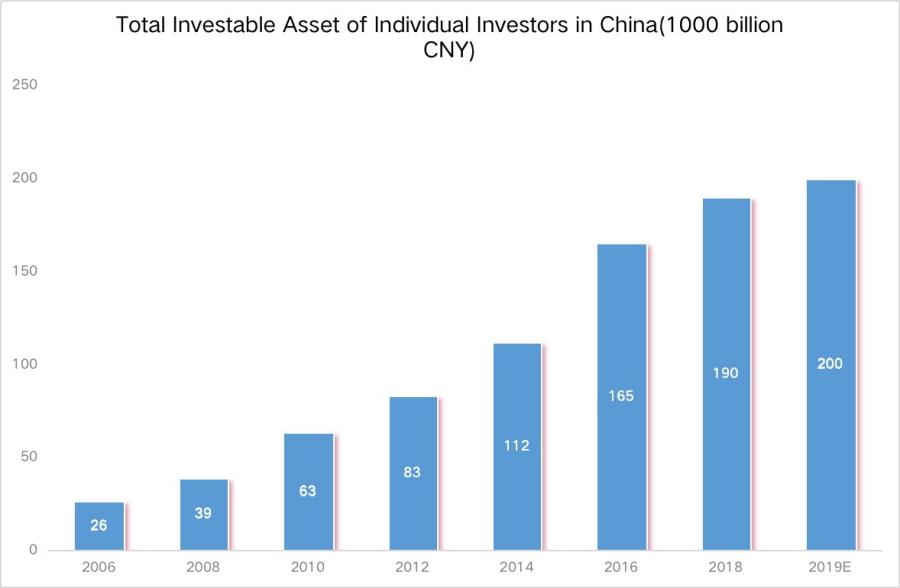
Figure 7: Total Investable Asset of Indivdual Investors in China (Source: CMS and Bain & Company)
Low investment threshold: case study: Let's take the first batch of public offering REITs as an example, the minimum threshold of off-site subscription is between 100 yuan and 1000 yuan, the minimum subscription threshold of public offering REITs listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange is 1000 yuan; the minimum subscription threshold of public offering REITs listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange is 1000 shares
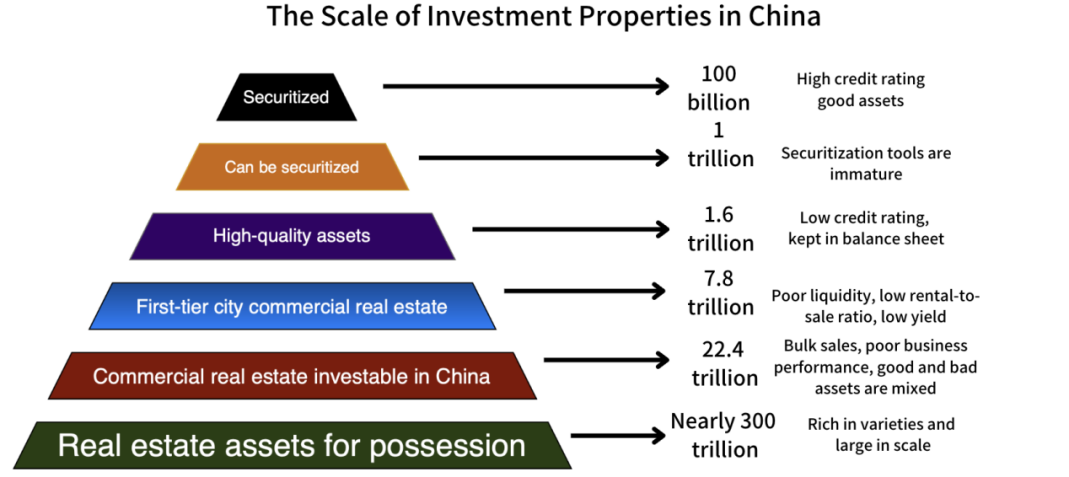
Figure 8: The Scale of Investment Properties in China (Source: GSUM)
At the same time, it can also diversify the investment risk of investors. Public offering REITs have a low correlation with the performance of major assets such as stocks and bonds, which is a differentiated supplement of traditional investment tools and helps investors realize the diversification of asset allocation. Spread the risk of different assets while the dividend proportion is high. Because REITs have a mandatory dividend system, according to regulatory requirements, the allocation of public offering REITs should not be less than once a year under the condition of meeting the distribution conditions, and more than 90% of the annual distribution amount of the infrastructure fund should be allocated to investors. This is about the interest on a bond, but higher than a bond. Good liquidity.
Investment in REITs. Different from direct investment in physical real estate, real estate can be regarded as an illiquid asset, and a long investment cycle needs to go through a series of procedures. If the goods involved, may be as long as months, it is difficult to deal immediately. By investing in REITS, investors can sell REITs in the securities market like stocks, funds and ETFs. Most of the REITs take the form similar to public funds, and REITs cut property assets into standardized units. Investors can be more convenient transfer of investment shares, very convenient and efficient. Improve the liquidity of the asset portfolio and reduce the investment risk.
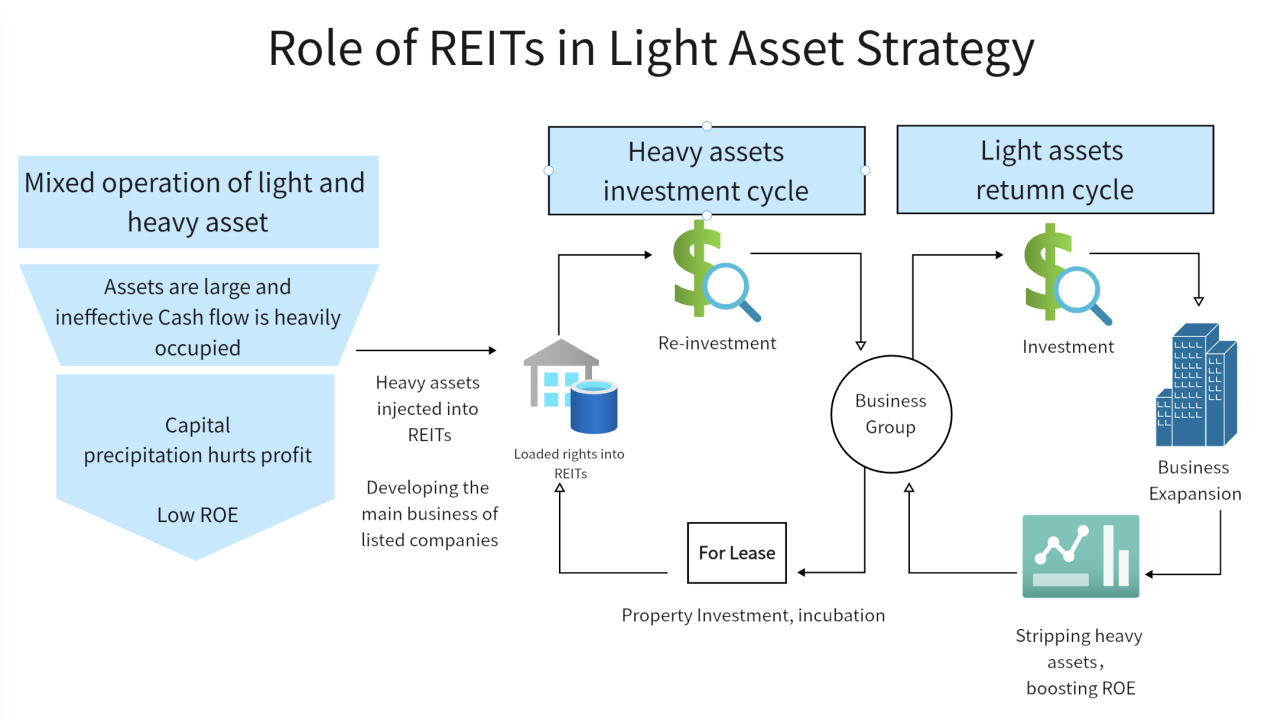
Figure 9: Role of REITs in Light Asset Strategy (Source: https://ink.library.smu.edu.sg/etd_coll/270)
4.2. Government
Infrastructure REITs can directly drive the regional consumption upgrading. It helps to expand government demand. It is conducive to the construction of an effective isolation mechanism, prevent funds from flowing into the commercial housing development field in disguise, and ensure the steady and long-term development of consumption infrastructure REITs. We will focus on improving consumption, quality and capacity expansion. The dominant force of domestic demand in the regional economy will be directly stimulated with the support of the infrastructure REIT. And infrastructure REITs play a role in driving effective regional investment. In the short term, infrastructure REITs is conducive to stable growth, while in the long term, it will help defuse financial risks and provide supplementary funds for the government to support new infrastructure and develop new economy. Promoting effective investment with infrastructure REITs is also a common practice around the world. More than half of the world's economies launch REITS in times of economic crisis or economic downturn and slow growth, in order to stimulate market vitality and thus improve the economic situation.
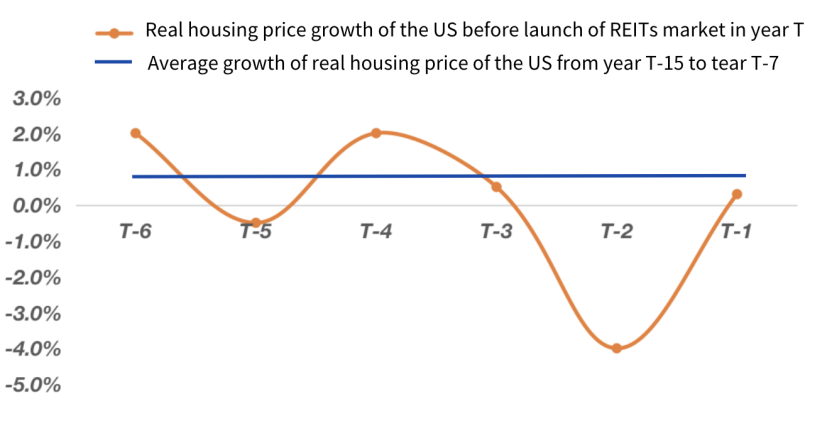
Figure 10: Role of REITs in Light Asset Strategy (Source: https://ink.library.smu.edu.sg/etd_coll/270)
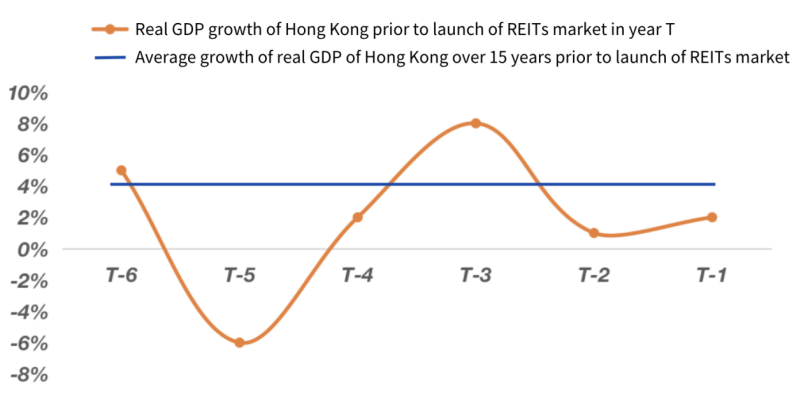
Figure 11: Role of REITs in Light Asset Strategy (Source: https://ink.library.smu.edu.sg/etd_coll/270)
On the other hand, with the improvement of relevant systems and policies, the investment model of infrastructure REITs backed by local government credit will be corrected, so as to realize the deleveraging of infrastructure investment, reduce the financial pressure of the government and prevent systemic financial risks.
The function of REITs in Real Estate Securitization:
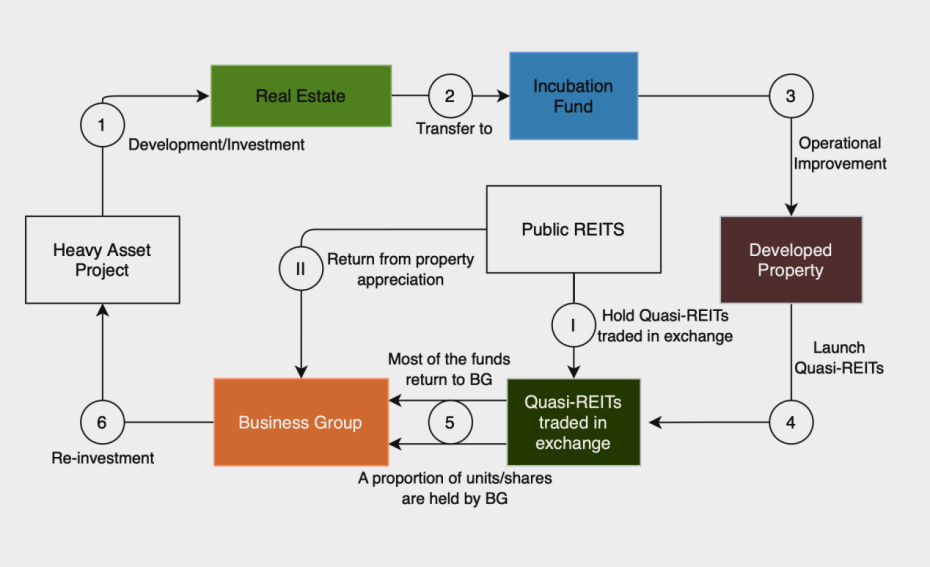
Figure 12: The function of REITs in Real Estate Securitization (Source: https://ink.library.smu.edu.sg/etd_coll/270)
4.3. Developer
Infrastructure REITs in China offer developers a revolutionary path to financing and growth. By converting real estate assets into tradable securities, developers can tap into new capital streams, optimize their capital structure, and mitigate risks associated with real estate development. The ability to unlock value tied in physical real estate enhances liquidity and allows developers to reinvest in new projects or reduce existing debt. Furthermore, the diversification that REITs provide enables developers to share exposure to market fluctuations and regulatory changes, fostering a more resilient business model.
For developers, participation in the REIT market also enhances market credibility and aligns with broader societal goals. Adhering to the regulatory requirements of REITs demonstrates transparency and governance, improving relationships with investors and stakeholders. Additionally, involvement in infrastructure REITs allows developers to contribute to socially significant projects, such as transportation and urban development, showcasing their commitment to sustainable growth. By embracing REITs, developers are positioning themselves at the forefront of an evolving market, unlocking opportunities for innovation and long-term success in China's competitive environment.
5. Conclusion and Recommendation
The emergence of infrastructure REITs, for investors, can revitalize and restructure illiquid under lying assets and also provide investors with stable income. For governments and enterprises, it can relieve the pressure of their debts and increase the enthusiasm of infrastructure construction. For the capital market, it cannot only diversify financial products and diversify financial risks, but also provide momentum for China's high‐quality economic development and promote the formation of a dual‐circulation pattern.
5.1. Problems and challenges of China Infrastructure REITs
5.1.1. The management model and structure of Infrastructure REITs need to be optimized
Publicly offered infrastructure REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) use an external management model, where an externally hired public fund manager handles all responsibilities, including fund management and property management. Previously, public offering fund managers mainly managed financial assets and lacked experience in infrastructure or real estate investment.
The complex structure of "public fund + asset-backed securities (ABS)" in public infrastructure REITs involves multiple relationships and responsibilities, leading to higher management and tax costs, greater moral hazard, and potential conflicts of interest.
To optimize this, the following measures can be considered:
1. Establishing an independent public offering infrastructure REITs team to enhance team building and talent reserves.
2. Expanding the range of entities that can act as fund managers, including those with experience in infrastructure or real estate investment.
3. Considering piloting corporate REITs or simplifying the existing structure, allowing the fund to directly hold underlying projects, provided that relevant laws and regulations are met.[5]
5.1.2. REITs supporting tax regulations and financial accounting issues need to be more clarified
In January 2022, the Ministry of Finance and the State Administration of Taxation issued Announcement No. 3 to support tax laws for publicly offered infrastructure REITs. This clarified three main issues for original stakeholders in reorganizing equity structures and provided support for the issuance of these REITs. However, there are still areas that need further clarification, such as the scope of application, special tax treatment conditions, and treatment of other taxes like value-added tax. Overseas practices like the U.S. and Singapore offer special tax exemptions and incentives for REITs, and perfecting related laws will help avoid efficiency problems and promote market development. Financial issues concerning REITs, such as the accounting treatment of funds invested by other shareholders, also need to be further clarified by relevant authorities.
5.1.3. The rules for newly purchased infrastructure projects and fundraising expansion need to be optimized
In May 2022, Guidelines No. 3 were introduced, setting the rules for new infrastructure projects and fund expansion. By June 2023, the first expansion of four publicly offered infrastructure REITs was completed, exceeding 5 billion yuan, marking a significant step in the development of public offering infrastructure REITs. This expansion has improved the relevant systems and mobilized the enthusiasm of stakeholders, ensuring steady growth. However, there are areas for further optimization. First, Guideline No. 3's requirement that new projects be of the "same type" as existing ones needs clarification, as focusing on the same asset type may limit diversification and hinder the management of multiple asset types. Second, the reporting and review process for new projects, mirroring the initial offering, may have long-term negative effects by complicating the expansion process and dampening enthusiasm. Third, consensus is still needed on pricing and valuation methods for newly purchased projects and fund expansion, requiring further market testing and agreement.
5.2. Future prospect of China Infrastructure REITs
5.2.1. Including consumer infrastructure in the underlying assets of public infrastructure REITs is significant
In March 2023, Document No. 236 marked a significant new era for publicly offered REITs in my country by including consumer infrastructure in the underlying assets and supporting the issuance by various commercial entities. This move aligns with the international REITs market, where commercial real estate is a key asset. Despite nearly 50 trillion yuan in commercial real estate, my country has long lacked an effective exit mechanism, suppressing its value and accumulating risks. The expansion to consumer infrastructure opens a new equity exit channel, aiding in value discovery and risk release. Additionally, this expansion aligns with recent shifts in the real estate industry, focusing on modernization and consumer experience, and supports the macro policy of stimulating domestic demand. It will assist developers in achieving product iteration while reducing leverage. Finally, the expansion will benefit private equity funds and transformed development companies, promoting professional management and a virtuous cycle in the real estate market.
5.2.2. Attracting more diverse original stakeholders will promote the healthy development of the public infrastructure REITs market
In October 2022, China's National Development and Reform Commission introduced Fa Gai Investment [2022] No. 1652, supporting private investment in infrastructure real estate investment trust funds (REITs). This policy ensures equal treatment for enterprises of all ownership types and accelerates investment in specific private projects. The China Securities Regulatory Commission's chairman, Yi Huiman, emphasized the expansion of REITs in the infrastructure sector, including affordable rental housing and private enterprise pilot projects. The inclusion of industrial parks, warehousing, logistics facilities, and talent apartments in the publicly offered infrastructure REITs pilot program has been enhanced by foreign and private capital, leading the industry in investment efficiency and asset management. By the end of May 2023, 24 of the 27 public offering infrastructure REITs were owned by state-owned enterprises. The support from the relevant commissions is expected to boost non-state-owned assets' participation, promoting a more diversified and healthy development of the public infrastructure REITs market.
5.2.3. Public infrastructure REITs and real estate private equity funds constitute a complete underlying asset investment closed loop together
After two years of development, publicly offered infrastructure REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) have become a prominent channel for infrastructure and real estate investment exits, with high issuance requirements and a need for at least 5 years of incubation. In February 2023, China initiated pilot programs for real estate private equity investment funds, introducing guidelines and a new product called "Real Estate Private Equity Investment Fund." This allowed for different management types and optimized investment conditions in various real estate sectors. By April 2023, six experienced institutions were chosen for the pilot program, enhancing the early asset selection and long-term financial support for public infrastructure REITs. This pilot program has diversified the investment options in Pre-REITs, satisfying various market risk preferences, and creating a comprehensive public infrastructure REITs investment loop. The future market is expected to see more instances of Pre-REITs like Huaan Zhangjiang Everbright REITs nurturing assets and exiting through public infrastructure REITs.
References
[1]. Wang, X. H. (2020) ‘Study on the Potential Market Size and Development Significance of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) in China’, Modern Management, 10(3), pp, 446-458, Available at:
[2]. Guanghua School of Management of Peking University (2017) ‘Research on the Market Scale of China's Real Estate Investment Trust Fund', Available at: https://www.gsm.pku.edu.cn/2.pdf (Accessed at: 20 July 20, 2021)
[3]. Zhang, F. X. (2020) ‘Analysis on the Opportunities and Challenges of the Development of Infrastructure Public Funding REITs’, Economic Outlook the Bohai Sea, 12(3), pp144-146, Available at: http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=71 03909487(Accessed at: 15 July 20, 2021)
[4]. Guanghua School of Management of Peking University (2017) ‘White Paper on the Development of Public REITs in China’, Available at: https://www.gsm.pku.edu.cn/1.pdf (Accessed at: 15 July 20, 2021) https://www.hanspub.org/journal/PaperInformation .aspx?paperID=36124(Accessed at: 15 July, 2021), doi: 10.12677/MM.2020.103055
[5]. Liow, K.H. and Yuting, H. (2018), “South East Asia”, The Routledge REITs Research Handbook, Routledge, Abingdon.
Cite this article
Peng,Z.;Hao,Y.;Liu,S.;He,J.;You,Y. (2024). "Analyzing Infrastructure REITs in China: Development, Regulations, and Financial Innovation". Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,97,298-314.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wang, X. H. (2020) ‘Study on the Potential Market Size and Development Significance of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) in China’, Modern Management, 10(3), pp, 446-458, Available at:
[2]. Guanghua School of Management of Peking University (2017) ‘Research on the Market Scale of China's Real Estate Investment Trust Fund', Available at: https://www.gsm.pku.edu.cn/2.pdf (Accessed at: 20 July 20, 2021)
[3]. Zhang, F. X. (2020) ‘Analysis on the Opportunities and Challenges of the Development of Infrastructure Public Funding REITs’, Economic Outlook the Bohai Sea, 12(3), pp144-146, Available at: http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=71 03909487(Accessed at: 15 July 20, 2021)
[4]. Guanghua School of Management of Peking University (2017) ‘White Paper on the Development of Public REITs in China’, Available at: https://www.gsm.pku.edu.cn/1.pdf (Accessed at: 15 July 20, 2021) https://www.hanspub.org/journal/PaperInformation .aspx?paperID=36124(Accessed at: 15 July, 2021), doi: 10.12677/MM.2020.103055
[5]. Liow, K.H. and Yuting, H. (2018), “South East Asia”, The Routledge REITs Research Handbook, Routledge, Abingdon.









