1. Introduction
The luxury industry is an important part of China's foreign trade, and luxury goods have become a symbol of wealth and status in Chinese society, which is sought after by many people. From a global perspective, in 2023, Chinese mainland consumers are expected to account for about 22-24% of the total global luxury consumption, and the Chinese mainland market also accounts for about 16% of the total global luxury consumption, and the concentration of VIC customers is high. Despite the rapid development of China's luxury goods market, it has not yet recovered to the same period in 2019, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is still being felt [1]. In the post-epidemic era, how to seize opportunities, accurately position themselves, and quickly seize the Chinese market through reasonable marketing strategies has become an urgent problem for luxury companies to solve. As a leading enterprise in China's luxury market, LVMH Group's marketing strategy is worthy of reference. This paper uses the 4P model to analyze it from four aspects: product, price, channel and promotion. On this basis, the author puts forward some marketing suggestions for LVMH Group's future development in the Chinese market. Then it provides some references for China's luxury brands’ overseas expansion.
2. Current Development Status of the Luxury Goods Market
2.1. Current Status of the Luxury Market in China
China's luxury consumption market has shown rapid growth in recent decades, and has become the main driving force for the growth of the world's luxury market. According to Bain & Company's 2023 China Luxury Market Report, the luxury market in mainland China doubled in size from 2017 to 2021, but sales revenue saw a double-digit decline in 2022. Following the pandemic, the recovery of social and economic activities in early December 2022 helped the luxury market in mainland China rebound in 2023, with full-year sales revenue expected to grow by around 12% year-on-year (see Figure 1) [2].
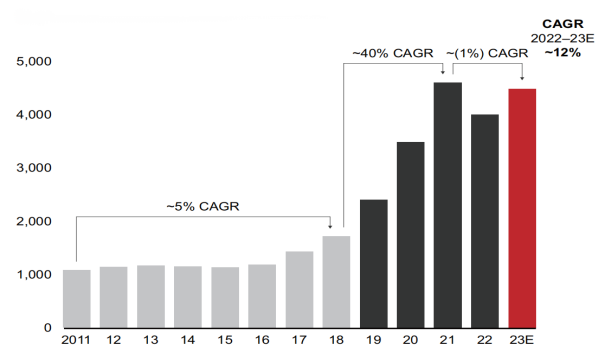
Figure 1: Sales Revenue of the Personal Luxury Goods Market in Mainland China [2].
In the post-pandemic era, the Chinese luxury market has developed new characteristics. With the growth of the digital economy, spending on digital marketing has increased significantly. In 2021, the online business of China's luxury market grew by 75%, with online channels accounting for 26% of total sales. From the perspective of consumer age structure, luxury consumers are becoming increasingly younger, with those under 30 contributing 47% of total spending. In terms of market geographic concentration, luxury consumption is gradually moving towards higher-tier cities, with the top 50 cities accounting for 75% of total consumption, a year-on-year increase of 10%. In terms of product structure, the penetration rate across all categories is increasing, with sales of handbags, jewelry, watches, and other items showing significant growth due to their strong value retention.
The rapidly developing Chinese luxury market has attracted investments from numerous brands and provided a favorable environment for the growth of domestic luxury brands. Over 90% of consumers express a preference for local cultural integration, and more than half are creatively supportive of this trend. However, the Chinese luxury industry is still in its developmental stage; the intellectual property identification system remains to be improved, and domestic brands have yet to gain strength, which reduces the market's credibility and consumer confidence in transactions.
2.2. Current Status of LVMH Group's Development in China
LVMH Group attaches great importance to the development of the Chinese market. From a geographical perspective, between 2022 and 2023, LVMH's various divisions opened 83 new stores in 20 cities across mainland China. As the economic center of the Southwest region, Chengdu saw the opening of 20 new stores, while the Yangtze River Delta cities of Shanghai and Nanjing ranked second and third with 13 and 7 new stores, respectively. 29% of LVMH’s stores are located in first-tier cities (Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen), while the remaining 71% are situated in non-first-tier cities. Notably, this expansion is mainly concentrated in 12 provincial capitals: Hefei, Xiamen, Guangzhou, Nanning, Guiyang, Zhengzhou, Wuhan, Nanjing, Jinan, Taiyuan, Chengdu, and Hangzhou. These statistics indicate that LVMH is strategically increasing its presence in China, going beyond its previous focus on economically developed cities and gradually expanding its operations into second-tier cities [3].
Given China's rapid economic growth, significant population increase, rising national income levels, and the strengthening of duty-free shopping policies in coastal regions like Guangdong and Hainan, LVMH is expected to expand its market share in China. Additionally, as mainland Chinese tourists contribute to a larger market share for Hong Kong and Macau, LVMH will be more confident about the Chinese market. With the continued rise in demand for luxury goods in China, an analysis of LVMH’s financial performance in the Chinese market over the past year indicates that the company will prioritize investment in this market. Therefore, the Chinese market is expected to further contribute to greater profits for the LVMH Group in the future.
3. Marketing Strategy Analysis Based on 4p Model
3.1. Product Strategy
As luxury goods become increasingly "symbolic", their uniqueness has become a key attraction for many consumers. To showcase uniqueness, it is essential to start with the product itself. Louis Vuitton, a brand under the LVMH Group, has taken the unique expression of its products to the extreme. The brand collaborates with artists like Takashi Murakami and Yayoi Kusama, blending its classic monogram pattern with the personal styles of these artists, thereby introducing new symbolic "signs" while retaining the original features of the traditional brand. This approach not only brings commercial benefits to the brand but also adds artistic value to the bags owned by consumers.
Furthermore, brands under the LVMH Group, such as Loewe and Dior, have launched various customization services across different product categories. Customers can personalize their bags by choosing leather types, colors, and even lining materials according to their preferences, catering to high-end consumers' desire to express their personal aesthetics and to own unique, one-of-a-kind products.
3.2. Price Strategy
LV implements a global price harmonization strategy to reduce price differences across regions. For example, in 2021 and 2022, LV raised the prices of certain products (such as the Speedy, Alma, and Capucines handbag series) worldwide, with price increases in the Chinese market being roughly the same as in other markets, around 5%-10%. Through this strategy, LV aims to reduce the incentives for purchasing through agents and cross-border shopping, encouraging consumers to buy locally and increasing customer loyalty in local markets. Additionally, LV has introduced different product lines in the Chinese market to attract various consumer segments, aiming to gain a larger market share and audience. For instance, entry-level handbags like the Pochette Accessoires and Mini Pochette are priced relatively low (approximately 6,000-8,000 RMB), appealing to younger consumers or first-time luxury buyers. In contrast, the more upscale Capucines series, made with more precious leather and handcrafted techniques, typically costs over 40,000 RMB, attracting high-end consumers who seek superior quality and unique designs. Finally, LV usually increases its prices several times a year to account for rising costs, exchange rate fluctuations, and inflation. According to statistics, some classic handbags (like the Speedy and Neverfull) have seen price increases of 8%-15%. This strategy keeps the price changes within a range acceptable to most consumers while helping the brand offset rising costs and maintain its exclusivity and high-end image.
3.3. Place Strategy
In recent years, the LVMH Group has been expanding its physical stores and scaling up its sales channels while also deeply collaborating with Chinese technology companies to enhance the luxury omnichannel consumer experience. On the offline front, LV has launched pop-up events in various locations, establishing a profound emotional connection with local markets and creating a novel shopping experience for customers. Online, about 30 prestigious brands under the LVMH Group have partnered with Tmall Luxury Pavilion, covering areas such as leather goods, beverages, jewelry, and cosmetics. Tmall leverages its digital innovation capabilities to enhance interactive experiences, such as the highly customizable digital store model "Luxury Stage", 3D product displays, virtual try-ons, and live streaming. Brands like Bulgari, Tiffany, and Chaumet were among the first to use "Luxury Stage" to create unique and innovative digital stores on Tmall Luxury Pavilion. On the platform, one-on-one private consultations between customers and shopping advisors can address queries and provide personalized recommendations. Tmall Luxury Pavilion can also drive high-end consumers to physical stores; for instance, Chaumet recently collaborated with Tmall 88VIP to offer exclusive offline jewelry experiences to select customers.
3.4. Promotion Strategy
In recent years, the domestic entertainment industry in China has developed rapidly, and the emergence of celebrities and internet influencers has sparked a wave of imitation. The LVMH Group has keenly recognized the importance of celebrity effects and has continuously signed top Chinese stars. For example, Liu Yifei and Zhou Xun have become ambassadors for Dior and Louis Vuitton, respectively, leveraging their influence and large fan base to build strong brand recognition and consumer loyalty for LVMH's major brands in China.
Additionally, LVMH promotes its products through brand foundation exhibitions and art exhibitions. For instance, LV held its first brand exhibition of 2020 in Wuhan, the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. This move served both as an expression of compassion and an effective public relations strategy [4]. The exhibition, which utilized contemporary art, was divided into seven display areas and showcased Louis Vuitton's brand story, classic creations, as well as some of its innovative designs and technological achievements. The choice of Wuhan as the exhibition venue was a tribute to the city at the heart of the pandemic and reflected Louis Vuitton’s humanitarian concern. Furthermore, through this exhibition, Louis Vuitton also conveyed its brand culture and expressed its ambition for the Chinese luxury market.
4. Problems Faced by LVMH Group in the Chinese Market
In 2024, due to the impact of geopolitical factors, the Chinese economy experienced significant fluctuations, and LVMH Group notably showed a slowdown in its growth within the Chinese luxury goods market. According to financial reports, in the first half of 2024, LVMH's sales in the Asian market (excluding Japan), with China leading, decreased by 10% compared to the previous year. In the second quarter, sales in this region fell by 14%, falling short of expectations. LVMH attributed the cooling of the Chinese sales market to a shift in Chinese consumers' shopping habits towards Japan [5]. Chinese high-end shoppers are redirecting some of their luxury purchases to overseas markets, while the local Chinese market faces issues such as reduced customer loyalty.
Additionally, LVMH faces ongoing competition from various challenges. In 2023, its long-time rivals Chanel and Hermes saw their sales in China continue to grow, reaching 19.7 billion and 13.4 billion yuan respectively, with year-on-year increases of 16% and 21% [6]. At the same time, domestic luxury brands such as Shang Xia have gradually emerged in the Chinese market, introducing products that align with Chinese aesthetic preferences and quickly capturing a portion of the market, intensifying the competition.
5. Improvement
5.1. Adjust China's Pricing Strategy
To attract local Chinese customers back, they must reconsider their pricing strategy to address cost increases due to inflation and other factors from the supply side, rather than passing these costs on to consumers through higher prices. LVMH has the ability to hold the majority stake in the Italian leather factory [7]. By acquiring some factories, production costs can be reduced accordingly, eliminating the need to significantly raise prices to cover costs. This approach can help draw back customers who have been spending abroad due to high prices.
5.2. Actively Adjust the Target Demographics
Despite facing challenges from multiple competitors, LVMH Group can implement a differentiated competition strategy. Since 2015, the demographic structure of China is undergoing great changes [8]. Against the backdrop of an aging population in China, the company should analyze the consumption pain points of different age groups, with a particular focus on those under 30 who are becoming the main drivers of luxury goods consumption. By identifying the unique needs of this demographic, LVMH can blend the brand's traditional image with local cultural characteristics to create unique and innovative luxury products that align with young people's aesthetic preferences.
6. Conclusion
LVMH Group's marketing strategy in China is quite successful. In terms of products, the artistic value of products is enriched through joint ventures and cooperation with independent designers. An exclusive customization department is set up to meet the individual requirements of different consumers for the products they purchase and highlight their own uniqueness; in terms of pricing, from a regional perspective, the principle of global unified pricing is adopted, and the prices of various products of the group are almost the same in various regions of the world, which stabilizes profits. And adopt a step-by-step pricing strategy, using high, medium and low-level products to attract consumers with different consumption abilities and enhance consumer loyalty; in terms of channel sales, LVMH actively tries to digitize luxury goods [9], takes advantage of the opportunities brought by the epidemic period to smooth online and offline channel sales methods, hold various activities to interact deeply with Chinese consumers, and integrate into the daily consumption scenes and consumption habits of Chinese consumers; finally, use popular celebrities to endorse and hold various brand art exhibitions to widely spread the brand value and concept of products.
There is a sizeable, actionable and profitable market for luxury goods in China [10]. LVMH's experience in supply chain collaboration and product innovation is very valuable to Chinese companies. Chinese luxury brands can first take advantage of the price advantage of local production to quickly seize the market in the early stages. Afterwards, they can use their familiarity with Chinese local culture and the current trend of people pursuing domestic brands to conduct in-depth product innovation and launch unique luxury products with Chinese cultural characteristics. They can also expand product categories, integrate manufacturing processes similar to China's intangible cultural heritage, surpass European and American luxury brands in quality, and create a representative luxury brand with Chinese characteristics.
References
[1]. Wang Y. X. (2022). Analysis on the development prospect of luxury industry and Chinese local luxury brands [J]. Modern Business, 17:9-12.
[2]. Bain & Company (2024). 2023 China Luxury Goods Market: A Year of Recovery and Transition. https://www.bain.cn/news_info.php?id=1805.
[3]. Sun J. (2024). Research on the Development of China's Luxury Goods Industry-based on LVMH [J]. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, 24: 2159-2165.
[4]. Jingwen Wang. (2022). Research on artistic marketing Strategies of luxury brands from the perspective of consumer culture [D]. Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.26932/d.cnki.gbjfc.2022.000079.
[5]. Yinan Liu. (2021). The transformation and effect analysis of luxury brand image communication strategy in the post-epidemic era: A case study of Louis Vuitton's "Seeing LV" fashion exhibition in Wuhan [J]. Time-honored Brand Marketing, 04: 10-12.
[6]. Xiujuan Guo, Junhua Zhang. (2024). Louis Vuitton can't sell? [N]. Beijing Business Daily.
[7]. Mimosa Spencer. (2024). Chanel to open more stores in China even as growth shifts abroad. https://www.reuters.com/business/retail-consumer/chanel-open-more-stores-china-even-growth-shifts-abroad-2024-05-21/.
[8]. Justine C. (2020). Analyse SWOT-Louis Vuitton. Publications Études & Analyses.
[9]. Wei L. (2022). Research on the Current Situation and Development Direction of China's Luxury Goods Industry Under the Regular Epidemic-Taking LVMH as an Example [C]//2022 2nd International Conference on Economic Development and Business Culture. Atlantis Press, 2022: 917-922.
[10]. Sivakumar S. (2012). Luxury China: market opportunities and potential [J]. South Asian Journal of Global Business Research, 1(2): 314-317.
Cite this article
Zhu,Z. (2024). Study of LVMH's Marketing Strategy in the Chinese Market — Based on the 4P Model. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,131,14-19.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wang Y. X. (2022). Analysis on the development prospect of luxury industry and Chinese local luxury brands [J]. Modern Business, 17:9-12.
[2]. Bain & Company (2024). 2023 China Luxury Goods Market: A Year of Recovery and Transition. https://www.bain.cn/news_info.php?id=1805.
[3]. Sun J. (2024). Research on the Development of China's Luxury Goods Industry-based on LVMH [J]. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, 24: 2159-2165.
[4]. Jingwen Wang. (2022). Research on artistic marketing Strategies of luxury brands from the perspective of consumer culture [D]. Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.26932/d.cnki.gbjfc.2022.000079.
[5]. Yinan Liu. (2021). The transformation and effect analysis of luxury brand image communication strategy in the post-epidemic era: A case study of Louis Vuitton's "Seeing LV" fashion exhibition in Wuhan [J]. Time-honored Brand Marketing, 04: 10-12.
[6]. Xiujuan Guo, Junhua Zhang. (2024). Louis Vuitton can't sell? [N]. Beijing Business Daily.
[7]. Mimosa Spencer. (2024). Chanel to open more stores in China even as growth shifts abroad. https://www.reuters.com/business/retail-consumer/chanel-open-more-stores-china-even-growth-shifts-abroad-2024-05-21/.
[8]. Justine C. (2020). Analyse SWOT-Louis Vuitton. Publications Études & Analyses.
[9]. Wei L. (2022). Research on the Current Situation and Development Direction of China's Luxury Goods Industry Under the Regular Epidemic-Taking LVMH as an Example [C]//2022 2nd International Conference on Economic Development and Business Culture. Atlantis Press, 2022: 917-922.
[10]. Sivakumar S. (2012). Luxury China: market opportunities and potential [J]. South Asian Journal of Global Business Research, 1(2): 314-317.









