1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
Driven by globalization, multinational retail enterprises have turned their attention to the Chinese market to seek new growth points. As the world's second-largest economy, China has a huge consumer market and shows a unique consumption trend and demand in the context of rapid economic growth. In recent years, with the improvement of residents' income levels and the upgrading of consumption structure, the Chinese market has an increasing demand for high-quality and personalized household products, which provides a broad space for the development of multinational retail enterprises such as IKEA. However, in the face of the complexity and variability of the Chinese market, multinational retail enterprises face many challenges in supply chain management. Therefore, given IKEA's important position in the global furniture retail market, it is of considerable practical significance to study how to optimize its supply chain management strategy in China and analyze how to deal with the unique economic environment for understanding and guiding multinational retail enterprises' operations in China.
1.2. Literature Review
The research on the supply chain management strategy of multinational retail enterprises in China has always been the focus of academic attention. Transnational retail enterprises are optimizing resource allocation worldwide to cope with the increasingly fierce market competition as globalization deepens. Enterprise operation revolves around supply chain management, which constantly enriches and develops its theoretical system. In the Chinese market, supply chain management research has made remarkable progress, and scholars have discussed supply chain management theory and practice from many angles.
First, the supply chain management theory has undergone a transformation from traditional logistics management to integrated supply chain management. Traditional logistics management focuses on the enterprise's logistics activities. In contrast, integrated supply chain management emphasizes the collaboration and integration between the upstream and downstream enterprises in the supply chain. In the Chinese market, scholars pay attention to the localization of supply chain management and discuss how to achieve effective supply chain management in the Chinese culture and market environment [1]. Secondly, the in-depth analysis of supply chain structure, process, and strategy reflects the progress of supply chain management research in the Chinese market. Through case studies, empirical analysis, and other methods, researchers discuss the role of supply chain management in improving the competitiveness of enterprises, reducing costs, and improving service quality. Research has focused on how multinational retail enterprises can effectively penetrate and control the Chinese market through supply chain management strategies [2]. In the study of IKEA's supply chain management, scholars focus on optimizing global resource allocation through supply chain integration. With its unique supply chain management model, IKEA has established an efficient supply chain system worldwide [3].
However, while the existing literature offers a valuable perspective on the supply chain management of multinational retail enterprises in China, research on how IKEA adjusts its supply chain strategy to adapt to local demand, improve response speed, and reduce operating costs is still lacking. Therefore, this study aims to fill this gap and, through a case analysis of IKEA's supply chain management practice in China, explore the effectiveness of its strategy and potential room for improvement.
1.3. Research Objectives
The goal of this study is to thoroughly examine IKEA's supply chain management strategy and identify ways to optimize it to meet the specific challenges of the Chinese market. The motivation for this research stems from the growing demand for localized supply chain management strategies by multinational retail enterprises in the context of globalization. This paper will present specific recommendations based on case studies and quantitative data analysis. The research framework is built around the core elements of supply chain management to provide a new theoretical perspective and practical guidance for the multinational retail enterprises in China.
2. A Basic Overview of IKEA in China
2.1. Company Background
IKEA, an internationally renowned furniture and household goods retailer, has experienced more than 30 years of steady development since its early 1990s involvement in the Chinese market. IKEA's China business development trajectory began with procurement activities, and in 1998, IKEA established its first store in Shanghai, marking its official entry into the Chinese retail market. Since then, IKEA has made remarkable achievements in the Chinese market with its unique business model and innovative design concept [4].
At present, IKEA's supply chain structure in China shows the advanced nature and complexity of its global supply chain management. IKEA implements a global sourcing strategy to maximize cost effectiveness through centralized and large-scale production. At the same time, IKEA also attaches importance to the flexibility and responsiveness of the supply chain to quickly adapt to changes in market dynamics and consumer needs. IKEA's focus on cost-effectiveness is also reflected in optimizing its supply chain processes. By adopting cost control measures such as flat packaging and modular design, IKEA not only achieves efficient storage and transportation of products, effectively reduces logistics and production costs, and improves customers' shopping experience [5]. IKEA's Asia Pacific Warehouse Business Development team has set its logistics business priorities for the next three years, including optimizing the logistics network, creating energy-efficient green warehouses, and strengthening warehouse automation and standardization. These strategic measures aim to further reduce logistics costs, improve supply chain efficiency, and promote green logistics development [6].
2.2. Key Issues
As the world's leading furniture and household goods retailer, IKEA's supply chain management strategy in the Chinese market is characterized by the advancement and complexity of its global supply chain management, as well as the challenges it faces in localized operations. IKEA needs to respond to market dynamics and demand fluctuations, adjust inventory strategies timely, and ensure supply chain flexibility and response speed, especially when optimizing inventory levels and supplier relationship management. Resolving these challenges is decisive for IKEA's continued development in the Chinese market. Supply chain optimization can not only reduce operating costs and improve overall efficiency, but it can also enhance market adaptability and customer service quality, significantly improving enterprises' market competitiveness. By strategically managing the supply chain, IKEA can efficiently allocate resources, enhance supply chain transparency and collaboration efficiency, and promote long-term sustainable company development [2].
IKEA was chosen as the study case because of its leading position in the global home retail market and the universality and representative nature of IKEA's innovative practices and challenges in supply chain management. Under the background of global economic integration and increasingly fierce market competition, the importance of supply chain management has become growing prominent. An in-depth study of IKEA's supply chain management in the Chinese market can provide valuable strategic inspiration and reference for other multinational retail enterprises, as well as promote the continuous improvement and innovation of supply chain management [7]. Therefore, this study aims to analyze the key issues in supply chain management through the case of IKEA and propose corresponding optimization strategies to provide theoretical support and practical guidance for supply chain management in the same industry.
3. Supplier Relationship Management at IKEA
3.1. Problem Identification
IKEA, an internationally renowned furniture and household goods retail giant, plays a vital role in global supply chain management. In its Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) strategy, IKEA establishes long-term strategic partnerships with its suppliers that go beyond traditional buyer-seller relationships. Despite this, IKEA still faces multiple challenges in its supplier management practice, mainly involving vital links such as supplier negotiation, selection and evaluation, and performance monitoring.
IKEA's challenges in negotiating with suppliers are complex. The volatility of raw material prices, the complexity of global supply chains, and cultural differences all significantly impact the negotiation process. Due to the diversity of IKEA's product line and global sourcing strategy, it must consider multiple factors when negotiating with suppliers, such as currency fluctuations, transportation costs, and policies and regulations in different countries. In addition, IKEA must ensure that its suppliers strictly adhere to the company's social and environmental standards, which undoubtedly adds to the complexity of the negotiations. These challenges necessitate that IKEA maintain cost efficiency while considering supply chain sustainability and compliance, ensuring supply chain stability and long-term supplier cooperation potential [8].
IKEA also faces challenges in selecting and evaluating suppliers. Companies must develop strict criteria to identify suppliers that meet their quality, environmental, and social requirements. This process requires IKEA to conduct exhaustive supplier background checks and continuous assessments of the supplier's production processes, quality management systems, and environmental and social responsibility practices. Performance monitoring is a core component of SRM. IKEA needs to establish an effective mechanism to track supplier performance and make strategic adjustments based on performance data. This requires IKEA to have advanced data analysis capabilities and maintain open communication channels with suppliers to facilitate continuous improvement and problem-solving.
3.2. Strategy Analysis
IKEA's supplier management faces many challenges. In order to deal with these problems, IKEA has adopted a series of comprehensive strategies to optimize supplier relationship management. In the process of supplier selection and evaluation, IKEA has built a multi-dimensional evaluation system that not only looks at traditional factors such as price and quality but also covers critical indicators such as delivery time, social responsibility, and environmental impact [9]. This comprehensive evaluation mechanism enables IKEA to effectively identify suppliers that meet its high standards and build strong partnerships.
Furthermore, IKEA attaches significant importance to long-term cooperation with suppliers. It is committed to improving suppliers' production capacity and product quality through information sharing, technical exchange, and resource complementarity [3]. IKEA designs its training and technical support to assist suppliers in enhancing their production efficiency, cutting costs, and boosting their market competitiveness, resulting in mutual benefits for both the upstream and downstream of the supply chain.
IKEA implements a strict monitoring system to ensure that suppliers can continuously meet IKEA quality standards and service requirements by regularly reviewing their performance in product quality, delivery punctuality, cost control, and innovation ability [10]. In addition, IKEA has also introduced an incentive mechanism to reward suppliers with excellent performance to motivate them to improve their performance continuously and promote continuous improvement and optimization of the entire supply chain.
3.3. Results Analysis
IKEA has implemented a series of supplier management strategies that have had a significant positive impact, including improving product quality and supply stability, improving customer satisfaction, effectively controlling costs, and reducing the risk of supply chain disruptions. However, although the strategy adopted has improved the efficiency and responsiveness of the supply chain to a certain extent, there are still several problems and deficiencies.
First, IKEA's over-reliance on certain vital suppliers may lead to increased vulnerability in the supply chain. Any production disruptions or other problems experienced by these suppliers will seriously affect IKEA's supply stability. In addition, the complexity of global supplier management requires IKEA to have efficient coordination and communication skills, and IKEA's current practice in this area is not yet ideal. Communication barriers and lack of execution led to the unsatisfactory implementation of the supply chain cooperation plan, which affected the supply chain's synergies and limited IKEA's ability to respond quickly to market changes.
Secondly, in terms of internal coordination, there needs to be better communication between the purchasing department and the replenishment department within IKEA, which leads to repetitive and inefficient order processing. This lack of internal coordination increases operating costs and affects customer satisfaction, as well as a company's market responsiveness. In addition, the ability of suppliers to use the data provided by Ikea for analysis and decision support needs to be improved. Suppliers' inability to analyze data limits their initiative and innovation in the supply chain, which in turn affects the entire supply chain's competitiveness.
Finally, the challenges encountered in implementing IKEA's supplier management strategy also reflect the problems in the promotion and execution of its supply chain cooperation plan. Some vendors lack sufficient support and recognition for partnership programs, which may be due to incompatibility with their existing operating models or a lack of understanding of the long-term value of partnership programs. This lack of support is particularly evident at the management and executive levels, leading to resistance to implementing supply chain cooperation programs.
4. Inventory Management at IKEA
IKEA, the world's leading furniture and household goods retailer, has an inventory management strategy that plays a pivotal role in maintaining business efficiency and reducing costs. Not only does the optimization of inventory levels contribute to cost control, but it also influences IKEA's ability to respond quickly and adapt to market changes. Excessive inventory may increase capital occupation and warehousing costs, while insufficient inventory may miss sales opportunities and affect customer satisfaction. As a result, in order to further explore how IKEA improves operational efficiency and market adaptability through inventory management strategies, this chapter first analyses the impact of the JIT strategy implemented by IKEA and batch procurement on inventory cost and turnover rate, and then discusses the changes in shelf inventory ratio, demand forecasting accuracy rate, and discount sales ratio. Finally, the challenges and room for improvement in IKEA's logistics warehouse management are evaluated.
4.1. Strategy Analysis
In order to meet the challenge of optimizing inventory levels in the Chinese market, IKEA has adopted a series of strategies, the most critical of which is the implementation of a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management strategy and a "cost per touch" strategy.
First, IKEA has established close cooperation with suppliers through the JIT strategy to achieve a timely supply of raw materials and semi-finished products. The core of this strategy is to reduce inventory carrying costs while maintaining the supply chain's flexibility and responsiveness. Through accurate demand forecasting and supply chain coordination, IKEA can reduce inventory overstocking and improve inventory turnover, effectively responding to market demand fluctuations [11]. In addition, IKEA has adopted the strategy of mass procurement and mass production, taking advantage of economies of scale and negotiating reasonable production and delivery times with suppliers to ensure a timely supply of products and meet market demand changes.
Second, IKEA has adopted a "cost per touch" strategy, which is a unique approach to supply chain management that aims to reduce costs and improve efficiency by reducing the number of times products are moved through the supply chain. Through a well-designed warehouse management system, IKEA achieves efficient inventory control and cost optimization. The implementation of this strategy relies on close cooperation between IKEA and third-party logistics, which emphasizes the importance of efficient management and cost control, thus enhancing IKEA's competitiveness in the market [12].
IKEA's warehouse management strategy also reflects its emphasis on cost-effectiveness. IKEA's in-store logistics managers are responsible for monitoring all warehousing processes, including delivery, sorting, and proper placement of goods. The IKEA store's unique layout combines the display area and the warehouse, allowing customers to view products directly in the display area and pick them up in the warehouse by product number, reducing the middle link and cost per touch [13]. In addition, IKEA has divided the design of its warehouses into automated and manual facilities for fast-selling and slow-selling items, respectively, as a strategy to reduce handling costs and ensure the smooth flow of high-demand products.
4.2. Results Analysis
Implementing inventory management strategies has significantly improved IKEA's global inventory turnover efficiency, as well as effectively reducing inventory holding costs.
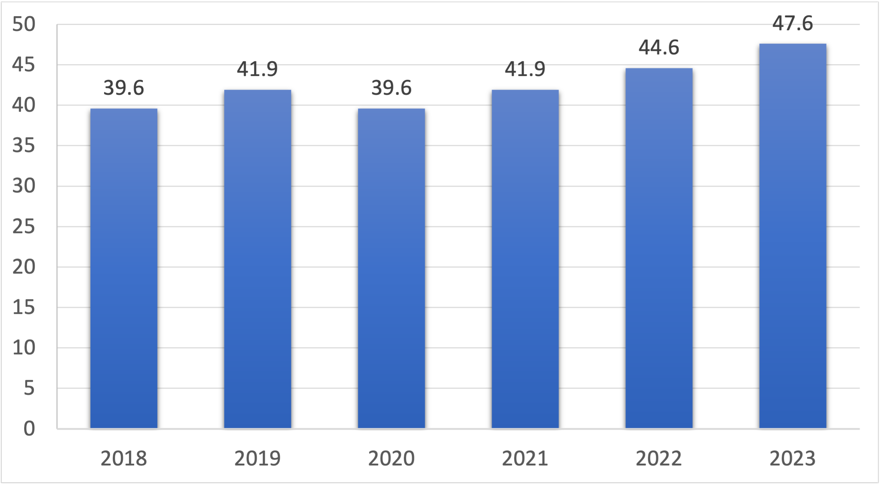
Figure 1: Global sales of IKEA in 2018-2023 in billions of euros (Photo credit: Original)
Figure 1 provides a visualization of IKEA's total sales, which surged from approximately €39.6 billion in 2018 to nearly €47.6 billion in 2023. Global retail sales have shown a steady growth trend since 2018, reflecting the positive impact of inventory management strategies on sales performance. Therefore, an increase in sales will inevitably lead to a rise in the absolute value of inventory, even with greatly optimized inventory management [14].
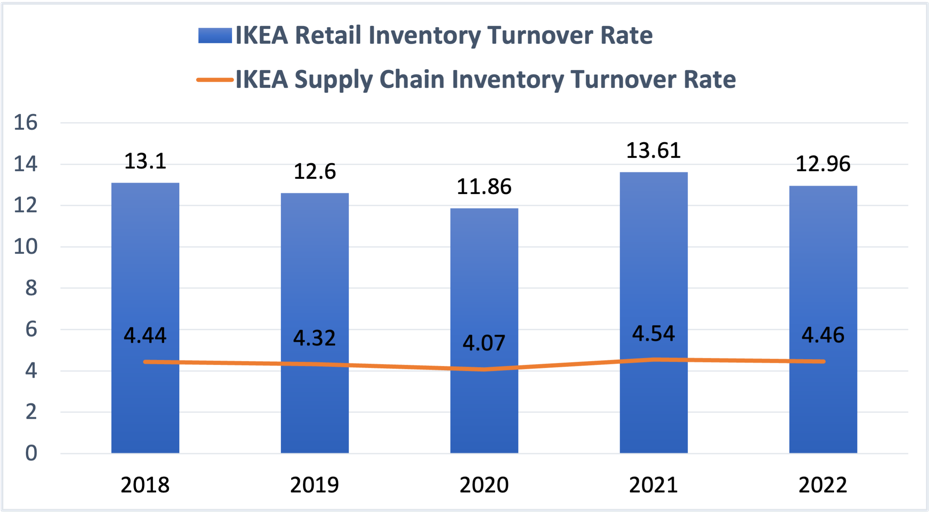
Figure 2: Inventory turnover of IKEA in 2018-2022 (Photo credit: Original)
At the same time, Figure 2 shows the changes in IKEA's retail and supply chain inventory turnover over the past few years. IKEA's website does not provide specific figures for 2023, so this paper can only analyze this study based on data from previous years and general trends. The figure reveals that IKEA's inventory turnover rate remained stable, hovering around 13, from 2018 to 2022, and even experienced a slight decrease, demonstrating its strong liquidity and effective implementation of its inventory management strategy [15]. Simultaneously, IKEA has sped up its response to market changes, effectively controlled inventory levels, and enhanced the accuracy of demand forecasting by reducing the lead time of its overseas purchase orders from an average of about 50 days in 2018 to about 30 days in 2022.
IKEA's shelf stock rate has also increased from about 90% in 2018 to more than 95% in 2022, reducing out-of-stock stores and sales losses. In terms of demand forecasting accuracy, IKEA improved from about 75% in 2018 to more than 85% in 2022, demonstrating the maturity of its technology and strategy in demand forecasting and inventory management. The rate of markdown sales also dropped significantly from about 10% in 2018 to about 2% in 2022, indicating that IKEA is more accurately matching market demand when purchasing, reducing inventory overstocking and markdown sales caused by inaccurate forecasts.
These strategies enhance IKEA's ability to adapt to market changes, significantly improving customer satisfaction and the shopping experience by ensuring a timely supply of products and efficient logistics distribution. Through close cooperation with suppliers and an efficient inventory management system, IKEA can respond quickly to fluctuations in market demand and adjust procurement and production strategies promptly, thus maintaining its leading position in the fierce market competition.
Although IKEA has adopted a series of strategies in inventory management and achieved certain results, there are still some problems and deficiencies, which are particularly obvious in the operation of logistics warehouses. In IKEA's logistics warehouse, there are obvious deficiencies in the efficiency of material sending and receiving, which directly affects the efficiency of overall inventory management. Specifically, IKEA's logistics warehouse relies too much on paper documents in the process of data and information transmission, which reduces operational efficiency, leads to inventory overstocking, and increases the risk of obsolete products. In addition, inventory accuracy suffers, and the cost and complexity of inventory management increase.
By further analyzing the current situation of IKEA logistics warehouse management, it can be found that the main problems include low accuracy of warehouse information, the significant influence of human factors on operation efficiency, the complexity of inventory operations caused by manual labor intensive, and untimely and inaccurate statistics and calculations. The existence of these problems not only highlights the space for IKEA to optimize further and improve its inventory management but also reflects the challenges IKEA will continue to face in adapting to the digital transformation process. With the fierce competition in the warehousing and logistics industry, IKEA urgently needs to improve operational efficiency and cost control through technological innovation and process optimization to maintain its competitive advantage. IKEA must focus on and solve these problems, which serve as warnings.
5. Suggestions and Future Outlook
For the supply chain management of IKEA, this paper puts forward some suggestions to strengthen local collaboration, improve the supply chain's efficiency and resilience, and provide a reference for other multinational retail enterprises. Furthermore, this study proposes specific suggestions for optimizing supply chain management with advanced technology to serve as a reference and inspiration for other enterprises.
5.1. Strengthening Local Collaboration
First, increasing local suppliers' participation is the key to IKEA's supply chain competitiveness in the Chinese market. IKEA can diversify and optimize its supply chain by deepening cooperation with local suppliers. According to previous research, multinational enterprises face the dual challenges of globalization and localization in the global supply chain operation, which requires businesses to seek balance in supply chain management. In practice, IKEA adopts the multi-country production and global sales model, which not only distributes supply chain risks but also improves response-ability to local market changes [2]. Therefore, IKEA should strengthen its partnership with local suppliers through joint research and development, technical exchange, and market information sharing to enhance the flexibility and innovation of the supply chain.
Secondly, in the globalization and localization business environment, adjusting the supply chain to meet local needs is necessary for IKEA's sustainable development in the Chinese market. Ikea must better understand Chinese consumers' buying behavior and preferences to meet market demand through localized supply chain strategies. As previous scholars have pointed out, IKEA has begun to consider the specific needs of Chinese consumers in product design and store layout. This paper proposes two specific recommendations based on these findings: First, IKEA should build a comprehensive and sophisticated market intelligence system that collects and analyzes key data such as consumers' purchase history, preference changes, and feedback opinions in real time. Using advanced data analysis technology, IKEA can gain insight into the specific needs and trends of Chinese consumers, achieve precise adjustments in the supply chain, and ensure that product development and inventory management can promptly respond to consumer expectations. Second, IKEA should incorporate Chinese elements into its product design and, through close cooperation with local designers, create products that both conform to the IKEA brand concept and have Chinese cultural characteristics. This integration can attract consumers who are interested in the integration of traditional Chinese culture and modern design, improve the localized image of the IKEA brand, and increase market competitiveness [7]. By implementing these strategies, IKEA will be able to meet Chinese consumers' needs better, improve customer satisfaction, and maintain a leading position in the fierce market competition.
Finally, increasing cooperation with the government is the key to IKEA's sustainable development in the Chinese market. IKEA should actively respond to the policy orientation of the Chinese government, such as green supply chain construction, sustainable development goals, etc., and establish a positive cooperative relationship with the government. Previous scholars have mentioned in their research that IKEA pays attention to environmental protection and social responsibility in supplier management, which coincide with the government's sustainable development policy [6]. IKEA should continue to strengthen communication and cooperation with the government, improve its social image by participating in public projects and supporting local economic development, and at the same time obtain policy support and market access advantages.
5.2. Optimizing Through Technology
First and foremost, IKEA has introduced advanced information technologies in China's supply chain management, such as the Internet of Things, extensive data analysis, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. The application of these technologies has greatly improved the supply chain's transparency and response speed. By tracking product flows, stock levels, and market demand in real time, IKEA can predict demand more accurately, reducing the risk of overstocking and out-of-stock. For example, IKEA uses RFID technology to monitor the entire process of goods from production and storage to distribution, optimizing inventory management and reducing logistics costs.
Second, data analytics is critical to IKEA's supply chain management. Through in-depth analysis of historical sales data, consumer behavior, and market trends, IKEA can identify potential market opportunities and risks and thus develop more precise purchasing and production plans [11]. In addition, data analysis helps IKEA make more scientific decisions in product design, pricing strategy, and promotion activities, improving market competitiveness.
Information technology's optimization function is particularly significant in each supply chain link. In the procurement process, IKEA uses the online platform and electronic procurement system to achieve efficient communication and collaboration with suppliers, shortening the procurement cycle and improving procurement efficiency. In production, IKEA has improved production efficiency and product quality by introducing automated and intelligent production lines. In the logistics and distribution link, IKEA utilizes an advanced logistics management system and distribution network to enable real-time monitoring and optimization of the logistics process, ensuring rapid and accurate product distribution.
6. Conclusion
This study has drawn a series of meaningful findings through the in-depth analysis of IKEA's supply chain management strategy in the Chinese market. The study found that IKEA's success in the Chinese market is largely attributable to its fine control of supply chain management, especially in inventory optimization and supplier relationship management strategies. However, IKEA still faces challenges in responding to changes in market dynamics and consumer demand, which requires its supply chain management strategy to be more flexible and responsive. The conclusions of this study echo the theories mentioned in the literature review and further emphasize the core role of supply chain management in enhancing the competitiveness of enterprises.
This study contributes to the supply chain management theory of multinational retail enterprises by providing an empirical case study showing how supply chain management strategies adapt to a specific market environment and highlighting the importance of supply chain optimization in improving the performance of enterprises in the Chinese market. In addition, the study fills the gaps in the existing literature on IKEA's supply chain management practices in China, providing valuable insights and practical guidance for the academic community and industry.
However, there are some limitations to this study. Due to the limitations of data sources and the study's scope, it could not fully cover all of IKEA's supply chain activities in China. Future research could further explore how IKEA can leverage emerging technologies such as big data and artificial intelligence to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of its supply chain management. Furthermore, future research could focus on how IKEA addresses emerging consumer trends and competitive challenges in the Chinese market through supply chain management.
References
[1]. Zhao, Z, C. (2022). Research on Localization Operation Strategy of Multinational Retail Enterprises in China. Tianjin University of Commerce.
[2]. Lin, B., & Xu, J, J. (2022). Global Supply Chain Operation Model Analysis. Logistics Technology, 4, 120-122.
[3]. Zhao, C, P., Xu, X, J. & Gong, Y. (2020). Study on the Learning Mechanism of Multinational Enterprise Supply Chain Based on Complex Network Game. Supply Chain Management, 05, 39-58.
[4]. Zheng, Y, X. (2023). President, Global Supply, Inter-IKEA: Innovation in China is Accelerating. Economic Observer, 018.
[5]. Mao, S, M. (2023). Study on Cost Control of IKEA's Supply Chain. Bohai Sea Economic Outlook, 10, 89-91.
[6]. Shen, R. (2021). Focus on Low-carbon Green Construction of Smart Supply Chain. Storage and Transportation, 12, 59.
[7]. Chen, X, Y. (2021). Practice and Enlightenment of Green Supply Chain Management in IKEA. Logistics Engineering and Management, 04, 54-57.
[8]. Zhang, X, X. (2021). Supplier Management Optimization Strategy of IKEA. Modern Trade Industry, 02, 57-58.
[9]. Pan, X, H. (2020). IKEA's Logistics Center Construction and Operation in China. Logistics Technology and Application, 07, 84-87.
[10]. Wang, X, H. (2005). Retail Internationalization: Motivation, Pattern and Behavior Research. Dongbei University of Finance and Economics.
[11]. Zhao, Y. (2023). Research on IKEA's Marketing Strategy in China under the Background of Digital Economy. Heilongjiang University.
[12]. Wang, X, F. (2023). Research on Financial Performance Evaluation of IKEA under the New Retail Business Model. Harbin University of Commerce.
[13]. Li, H, Y. (2022). Research on Location Selection of IKEA (China) Logistics Distribution Center. China University of Mining and Technology.
[14]. Gong, Y., Xu, X., Zhao, C., & Schoenherr, T. (2024). Multi-Tier Supply Chain Learning Networks: A Simulation Study Based on the Experience-Weighted Attraction (EWA) Model. Sustainability, 16, 10, 4085.
[15]. Gong, Y., Jiang, Y., & Jia, F. (2023). Multiple Multi-tier Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Social System Theory Perspective. International Journal of Production Research, 61, 14, 4684-4701.
Cite this article
Jia,J. (2024). Research on Supply Chain Management Strategies of Multinational Retailers in China Based on IKEA. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,140,138-147.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2024 Workshop: Finance's Role in the Just Transition
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhao, Z, C. (2022). Research on Localization Operation Strategy of Multinational Retail Enterprises in China. Tianjin University of Commerce.
[2]. Lin, B., & Xu, J, J. (2022). Global Supply Chain Operation Model Analysis. Logistics Technology, 4, 120-122.
[3]. Zhao, C, P., Xu, X, J. & Gong, Y. (2020). Study on the Learning Mechanism of Multinational Enterprise Supply Chain Based on Complex Network Game. Supply Chain Management, 05, 39-58.
[4]. Zheng, Y, X. (2023). President, Global Supply, Inter-IKEA: Innovation in China is Accelerating. Economic Observer, 018.
[5]. Mao, S, M. (2023). Study on Cost Control of IKEA's Supply Chain. Bohai Sea Economic Outlook, 10, 89-91.
[6]. Shen, R. (2021). Focus on Low-carbon Green Construction of Smart Supply Chain. Storage and Transportation, 12, 59.
[7]. Chen, X, Y. (2021). Practice and Enlightenment of Green Supply Chain Management in IKEA. Logistics Engineering and Management, 04, 54-57.
[8]. Zhang, X, X. (2021). Supplier Management Optimization Strategy of IKEA. Modern Trade Industry, 02, 57-58.
[9]. Pan, X, H. (2020). IKEA's Logistics Center Construction and Operation in China. Logistics Technology and Application, 07, 84-87.
[10]. Wang, X, H. (2005). Retail Internationalization: Motivation, Pattern and Behavior Research. Dongbei University of Finance and Economics.
[11]. Zhao, Y. (2023). Research on IKEA's Marketing Strategy in China under the Background of Digital Economy. Heilongjiang University.
[12]. Wang, X, F. (2023). Research on Financial Performance Evaluation of IKEA under the New Retail Business Model. Harbin University of Commerce.
[13]. Li, H, Y. (2022). Research on Location Selection of IKEA (China) Logistics Distribution Center. China University of Mining and Technology.
[14]. Gong, Y., Xu, X., Zhao, C., & Schoenherr, T. (2024). Multi-Tier Supply Chain Learning Networks: A Simulation Study Based on the Experience-Weighted Attraction (EWA) Model. Sustainability, 16, 10, 4085.
[15]. Gong, Y., Jiang, Y., & Jia, F. (2023). Multiple Multi-tier Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Social System Theory Perspective. International Journal of Production Research, 61, 14, 4684-4701.









