1. Introduction
The robust growth of SMEs stems from the thorough execution of the innovation-driven development strategy, serving as a crucial vehicle for national innovation initiatives and significantly contributing to sustainable economic growth, industrial optimization, and job creation. In a competitive market landscape, the advancement of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is inextricably linked to robust financial backing. The challenges of securing affordable financing are persistent and unavoidable, underscoring the critical need for sustained financial support in this dynamic environment.[1] Driven by the application of digital technology, small and medium-sized enterprises gradually establish an equal relationship with financial institutions and the government in the financing system, at the same time, wider financing channels, shorter financing cycle, lower financing costs make digital financial services in the process of small and medium-sized enterprise credit financing is highly favored. "From a macro perspective, digital finance is a product of the deep integration of traditional finance and modern information technology, covering a wide range of areas such as payment, financing, investment and insurance. The essence of the technology sector is rooted in the application of digital innovations to enhance the efficiency and accessibility of financial services, lower transaction expenses, and promote greater inclusivity within the financial marketplace.[2] Digital finance uniquely leverages technological innovation over traditional finance, explored through three dimensions in this paper. First, it enhances efficiency; automation and intelligent technologies significantly reduce service processing times, improving efficiency by over 50%. Second, reduced dependency reduces service costs by 30%, allowing consumers to afford high-quality services. Finally, it expands service boundaries and financial inclusion, removing geographical restrictions and allowing rural residents to receive high-quality services, resulting in an 80% financial services penetration rate. These benefits demonstrate digital finance's importance in service quality, efficiency, and socio-economic inclusion. China's digital banking development from 2011-2020 shows a decline following tremendous expansion, yet it still grows well. The digital finance index has advanced due to digital finance sophistication.[2] Based on SMEs' issues and digital finance's benefits, this article explains how digital finance can accurately finance and strategically analyse SMEs. This study will use flowcharts and tables to discuss "information asymmetry," "elevated financing costs," and "limited financing options" using a comprehensive literature review. This paper summarises SME funding issues and solutions in depth to clarify the aim and make the technique viable. This study will address the academic void on digital finance's impact on SME financing, guide future research, and expand digital finance theory.
2. Financing Methods and Problems of SMEs
2.1. High Financing Cost
The financing expenses incurred by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in China are disproportionately elevated in comparison to those of larger corporations. Specifically, the primary financing avenue for SMEs—bank loans—reveals that the prevalent deficiencies in financial management systems within these enterprises contribute to chaotic financial records and diminished transparency. This often culminates in a heightened failure rate during the bank loan approval process. Furthermore, financial institutions may impose elevated repayment rates on SMEs seeking loans as a risk mitigation strategy, thereby exacerbating financing costs. Additionally, SMEs encounter obstacles such as suboptimal internal resource allocation and a lack of comprehensive talent. During the loan application process, the necessity to engage professionals for evaluation and advisory services further escalates financing expenses. Consequently, even with a constant loan amount, the per-unit financing cost increases.
2.2. Single Financing Method Available
Financing methods for SMEs are mainly categorized into external financing and internal financing. The cost of internal financing is relatively low, but it is closely related to the enterprise's asset scale, operation status and profitability. In the early stage of enterprise development, internal financing alone cannot meet the capital required for operation, so external financing becomes an important way for enterprises to obtain capital. The ways of external financing for SMEs mainly include applying for loans from banks, issuing stocks or bonds, and making venture capital investments. Nevertheless, the inherent uncertainty and underdeveloped nature of SMEs' asset portfolios impose constraints on the issuance of rigorously audited capital goods. This, combined with the inadequate standardization of private lending practices and the sluggish progression of private investment, results in SMEs having access to a limited array of financing options.[3]
2.3. Asymmetry of Financing Information
When SMEs raise funds from commercial banks and other financial institutions, there is the problem of information asymmetry between SMEs and financial institutions, which hampers the further financing behavior of SMEs. When SMEs carry out external financing, they are limited by the financing amount, and they will submit financing reports to many financial institutions at the same time. However, due to the unstandardized internal management of SMEs, the information data on their production and operation and financial reports are seldom disclosed to the public. In the process of evaluating the financial reports of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and performing risk assessments, financial institutions, particularly commercial banks, often encounter significant challenges. They must invest considerable time in verifying and scrutinizing the documentation, which complicates the accurate assessment of SMEs' profitability, risk management capabilities, creditworthiness, and potential returns on future projects. This complexity ultimately hinders SMEs' ability to successfully navigate the qualification process for financing.[4]
3. Strategies for Digital Finance to Accurately Serve SME Financing
3.1. Increase Ways to Reduce the Cost of Enterprise Financing
3.1.1. Unsecured Loan Platform
Unsecured loan platforms represent a significant advancement in digital financial innovation, offering SMEs collateral-free borrowing through online channels. Firstly, these platforms present lower financing costs and streamlined processes compared to traditional financial institutions, which impose extensive assessment and regulatory requirements, thereby elevating costs for SMEs. By leveraging Internet technology, unsecured loan platforms facilitate direct connections between SMEs and investors, minimizing intermediaries and reducing expenses. Secondly, these platforms enhance competition, as SMEs previously reliant on a limited number of lenders now have access to diverse borrowing options, fostering competitive interest rates and further decreasing financing costs.[7]
3.1.2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, as a distributed and decentralized technology, has a significant impact on SME financing costs. Blockchain technology minimizes financing costs for SMEs by streamlining processes and eliminating intermediaries through smart contracts and decentralization. It also addresses information asymmetry by reducing the need for extensive documentation and financial reporting traditionally required by financial institutions. In contrast, blockchain technology makes the financing process more transparent and traceable through the open and transparent ledger and smart contract mechanism, which reduces the information asymmetry cost and improves the success rate of financing for SMEs, thus reducing the financing cost.[5]
3.2. Broaden the Financing Channels of SMEs
The rapid advancement of digital technology has led to the emergence of numerous fintech and loan companies, which are increasingly favored by SMEs due to their higher loan amounts, simplified procedures, and more personalized financing services. This has expanded financing channels for SMEs. Recently, innovative financing models like supply chain finance have developed, where core enterprises provide essential funds to weaker downstream SMEs, thereby enhancing their creditworthiness and competitiveness, and alleviating financing barriers. At the same time, the development of the digital finance industry has also gradually broken down spatial constraints, increasing the possibilities for SMEs in remote areas to obtain financing, thus promoting the sustainable development of more SMEs (see Figure 1).[3]
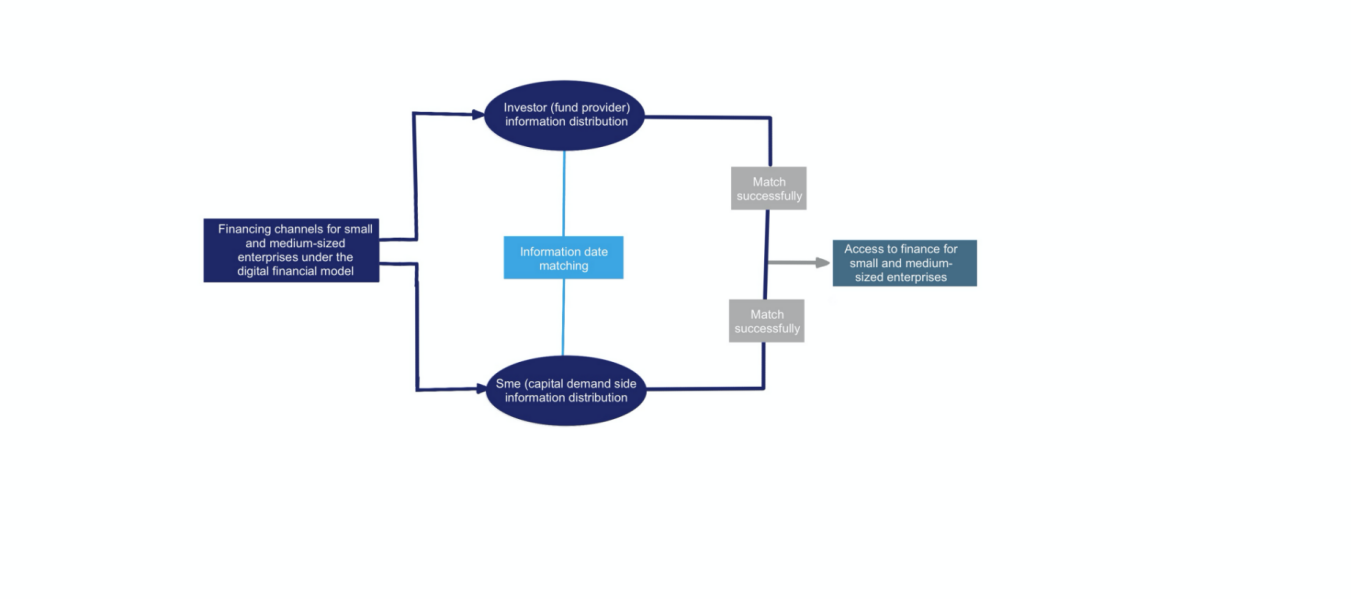
Figure 1: New ways of financing SMEs under the digital finance model
3.3. The Mechanism of Alleviating the Role of Information Asymmetry
The rise of digital finance effectively addresses enterprise information asymmetry. Beyond offering essential macro, industry, and company data, digital financial services empower SMEs by enhancing decision-making in investment, trading, and risk management through comprehensive content, platforms, and tools, including the integration of alternative and fundamental data. From an enterprise perspective, SMEs can access valuable R&D information at minimal cost. For consumers, SMEs can leverage their data and technological strengths to facilitate the search and purchase of specialized products, thereby stabilizing or increasing their market share. In summary, this paper proposes the mechanism of digital finance's role in incentivizing SME financing innovation by alleviating information asymmetry as shown in Figure 2.[6]
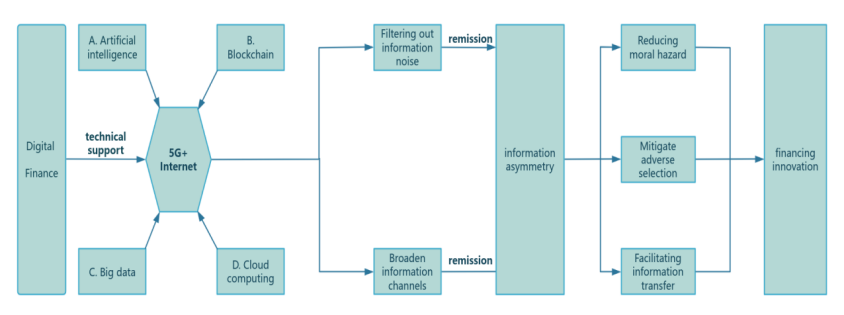
Figure 2: Mechanism of action to alleviate information asymmetry
4. Case Study
4.1. Theory
In the current digital age, the financial sector is undergoing significant transformation. Digital banks, like Baxin Bank, have carved out a niche in the financial ecosystem through innovative strategies and a pioneering spirit. Leveraging digital intelligence, they enhance financial service innovation and redefine financial inclusion, effectively serving the real economy. Inclusive finance seeks to deliver suitable financial services to all societal sectors in line with equal opportunity and sustainability principles. In contrast to traditional inclusive finance, digital inclusive finance employs technology to mitigate financial risks and reduce information asymmetry, efficiently catering to small, medium, and micro enterprises as well as low-income groups. Yuan believes that inclusive finance lowers the threshold of financial services, improves the efficiency of resource allocation, promotes technological innovation of small, medium and micro enterprises, supports the development of disadvantaged industries, and promotes the upgrading of industrial structure. [8, 9]
4.2. Background
Baxin Bank President Li Rudong explained the bank's role as the first autonomous legal entity direct marketing bank and how digital finance may improve inclusive finance. He advocated "finance as the foundation, technology as the application." Internet banks need this technology and data-driven approach. Over four years, Baxin Bank has invested 2.16 billion yuan in fintech. Baxin Bank's independent legal standing allows it to make more decisions in product development, operations, risk management, and talent organisation, enabling sustainable fintech investment. Most domestic direct selling banks are internal bank departments. Therefore, Baxin Bank uses a completely online direct-to-consumer model without branches or bank cards, bypassing the geographical limits of traditional branch banking and allowing flexible integration into diverse ecological circumstances.
"As an Internet bank with a state-owned background, Baxin Bank has always practiced two major missions since its inception: the development of digital transformation in the banking industry and the development of financial technology innovation." Baxin Bank is more like a technology-driven digital bank.
4.3. Discussion
4.3.1. Intelligent Technology Boosts the Development of Digital Banking
In terms of digital banking development practice, Baxin Bank, based on AI, big data, cloud computing and other technologies, spreads its business across the country through the Internet, better reaches the customer groups with typical inclusive characteristics that are difficult to be covered by traditional banks, forms a differentiated development model, better practices digital inclusive finance and effectively serves the real economy.
Baxin Bank, a pioneer in China's fintech cloud adoption, excels in AI, blockchain, cloud computing, big data, and federated learning. Twice a People's Bank of China "supervisory sandbox" pilot, it embodies cloudization, intelligence, agility, and security. Li Rudong states, "Finance is foundational; technology is instrumental." As an AI-driven digital inclusive bank, Baxin Bank leverages AI and data capabilities, using APIs to deliver personalized, intelligent, and accessible financial services, enhancing affordability for SMEs and underserved groups.
4.3.2. Launching Specific Products for Core Customer Groups
Using "financial management for the people," Baxin Bank targets long-tail customers like white-collar workers, metropolitan blue-collar workers, and small-town teens. Li Rudong prioritises integrating services within the Internet's ecological framework to deliver flexible, high-value, and customised financial solutions beyond deposits and loans. To do this, the bank offers "100 car loans," "100 business loans," "Supply Loans" and "Breeding Loans." Li Rudong would concentrate loan resources for inclusive small and micro companies, rural revitalisation, and green sectors, delivering secure, digital, and convenient financial services through innovative financial technology.
In line with the wave of digitalization and the advantages of fintech, Baxin Bank continues to focus on the exploration and innovation of the digital finance track.
4.3.3. Continuous Exploration and Innovation
Internet bank Baxin Bank improves financial technology to respond to digital transformation. The internet economy is changing banking models, and Baxin Bank prioritises young users. AIYA offers accessible financial services through pleasant, immersive encounters. As a result, Baxin Bank has had significant success: in 2020, the Canadian Pension Fund invested, raising its valuation to over 12.6 billion yuan; by 2021, total assets reached 79.406 billion yuan (up 19.46% year-on-year), total liabilities were 72.601 billion (up 21.20%), and user scale surpassed 69 million households.
Net operating income of RMB 2.998 billion, up 74.05% year-on-year; net profit of RMB 263 million, with both profit before provision and provision coverage ratio significantly improved; non-performing loan ratio and new non-performing generation rate significantly decreased; approved to issue RMB 2 billion of Tier 2 capital bonds, and once again obtained AAA main long-term credit rating.[10]
5. Conclusion
This paper analyzes the ways and strategies of accurate service SME financing according to digital finance. Overall digital finance has a positive impact on SME financing. Through the unsecured loan platform, blockchain technology and other digital financial innovation tools and platforms for SMEs to reduce the cost, provide more financing channels, to alleviate the dilemma of enterprise information asymmetry to provide a significant effect of the solution.
By directly connecting SMEs and investors, the unsecured loan platform reduces the cost of intermediary links in financing, reduces appraisal costs and handling fees, and improves the efficiency and convenience of financing. Blockchain Through features such as smart contracts, distributed ledgers and transparency, blockchain technology provides
SMEs a more secure, efficient and cost-effective way of financing. In addition, it also effectively filters information noise for SMEs, broadens information access channels, and alleviates the problem of information asymmetry. Meanwhile, government involvement also plays a key role in the development of SMEs. In the next research, the management and support aspects of digital financial innovation by relevant government departments can be analyzed and studied and related strategies can be made.
References
[1]. Chen, H. (2021). Empirical research on digital inclusive finance alleviating financing constraints of small and medium-sized enterprises . Hangzhou: Zhejiang University.
[2]. Zhang, Y. & Lu, M. (2024). Research on the effect mechanism of digital finance on the improvement of financial new quality productivity. Social Sciences of Henan (05),74-84.
[3]. Jia, W. (2024). Research on the Financing Strategy of Small and medium-sized Enterprises under the background of digital finance. Business Watch (06),93-97.
[4]. Wu, Z. & CAI, J. (2024). Research on the Financing Strategy of Small and medium-sized Enterprises from the perspective of digital finance. China Management Informatization (12), 91-93.
[5]. Zhang, X. (2024). Research on the Impact of digital financial innovation on the financing cost of small and medium-sized enterprises. Financial Literary World (01),4-6.
[6]. Chen, Y., Shen, L., Wu, L. & Zhou, M. (2024). Research on the mechanism and path of digital finance enabling financing innovation of small and medium-sized enterprises. Expo economy (05), 161-164. The doi: 10.19995 / j.carol carroll nki/F7.2024.05.161 CN10-1617.
[7]. Lihao, Z. (2017). Research on Financing of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises in China Based on P2P Net Loan Platform. Science Innovation, 5(4), 386-391.
[8]. Liang, M. (2020). Research on the impact of Chinese digital inclusive finance on industrial structure upgrade—based on spatial Dubin model. Open Journal of Statistics, 10(5), 863-871.
[9]. Yuan, H.D. (2018) Research on the Impact of China’s Inclusive Finance Develop- ment on the Upgrading of Industrial Structure. Shandong University of Technolo- gy, Zibo.
[10]. Li, R. (2022, March 25). Interview with Li Rudong, president of Baixin Bank: Adhering to innovation and becoming a "light cavalry" in the digital transformation of the banking industry. AI Bank. https://www.aibank.com/bsdt/xwdt/275709.shtml
Cite this article
Zhao,J. (2025). Analysis on the Ways and Strategies of Digital Finance to Accurately Serve the Financing of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,156,174-180.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Chen, H. (2021). Empirical research on digital inclusive finance alleviating financing constraints of small and medium-sized enterprises . Hangzhou: Zhejiang University.
[2]. Zhang, Y. & Lu, M. (2024). Research on the effect mechanism of digital finance on the improvement of financial new quality productivity. Social Sciences of Henan (05),74-84.
[3]. Jia, W. (2024). Research on the Financing Strategy of Small and medium-sized Enterprises under the background of digital finance. Business Watch (06),93-97.
[4]. Wu, Z. & CAI, J. (2024). Research on the Financing Strategy of Small and medium-sized Enterprises from the perspective of digital finance. China Management Informatization (12), 91-93.
[5]. Zhang, X. (2024). Research on the Impact of digital financial innovation on the financing cost of small and medium-sized enterprises. Financial Literary World (01),4-6.
[6]. Chen, Y., Shen, L., Wu, L. & Zhou, M. (2024). Research on the mechanism and path of digital finance enabling financing innovation of small and medium-sized enterprises. Expo economy (05), 161-164. The doi: 10.19995 / j.carol carroll nki/F7.2024.05.161 CN10-1617.
[7]. Lihao, Z. (2017). Research on Financing of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises in China Based on P2P Net Loan Platform. Science Innovation, 5(4), 386-391.
[8]. Liang, M. (2020). Research on the impact of Chinese digital inclusive finance on industrial structure upgrade—based on spatial Dubin model. Open Journal of Statistics, 10(5), 863-871.
[9]. Yuan, H.D. (2018) Research on the Impact of China’s Inclusive Finance Develop- ment on the Upgrading of Industrial Structure. Shandong University of Technolo- gy, Zibo.
[10]. Li, R. (2022, March 25). Interview with Li Rudong, president of Baixin Bank: Adhering to innovation and becoming a "light cavalry" in the digital transformation of the banking industry. AI Bank. https://www.aibank.com/bsdt/xwdt/275709.shtml









