AI, the performance of employees, management decision-making, policy innovation, technological change
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the economy and technology, artificial intelligence technology is becoming more mature. It has penetrated all industries and it also encompasses a lot of potential, especially when it comes to employee performance. ‘But over the last decade things have moved on rapidly. Winter has given way to spring, and to a suite of new technologies, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, that are finally allowing AI to fulfil its business potential.’ [1].
Because all industries are booming and people are choosing more and more career paths, employee performance is also deepening its impact on society, implicating the productivity and economic growth of the whole society.
So I wanted to investigate how AI will affect employee performance in the future, which I think effectively considers not only the issue of innovation in company management, but also the impact of AI on the labour force and the economy. However, existing research lacks a comprehensive overview in this field, so I want to study and deepen my understanding of this field.
In this research, I made full use of both primary and secondary data. First, I discussed the relationship and impact of AI on employee performance, and how to make better use of this system and keep the system moving forward. In studying the obtained data, Primary and secondary data also play a different role, first discussed the relationship and impact of AI on employee performance, and how to make better use of this system and make the system continue to move forward. When studying the data obtained, the research used a mixture of qualitative and quantitative research methods. Some data from developed countries are analyzed to better understand the role of AI in improving employee performance. At the same time, in order to minimize the negative impact of AI on employee performance, this paper also analyzes and conceives some possible effective policy incentives, optimization and orientation plans of AI itself, etc., to promote employees to adapt to scientific and technological changes and make better use of AI to assist their work. In order to achieve the maximum effect of performance improvement, through the research on this topic, this paper hopes to provide a new perspective for AI to improve employee performance at present, make contributions to my research, and provide some good suggestions. Due to practical limitations, this paper cannot fully review how AI affects employee performance, but I will continue to do some research, such as expanding sample size, interdisciplinary combination and improving sample quality, and other measures to continue to make progress.
2. Literature review and summary
First, to clarify and define again the concepts of AI and employee performance. AI refers generally to the development of machines and autonomous agents able to perform tasks normally requiring human-level intelligence [1]. Employee performance is the employee's contribution to the organization.
In this article, To investigate this question that how will AI affect the performance of employees, I am going to start with a set of data to help us with our research. [2].This data shows that in 'The performance of companies using AI', the positive effect is significantly higher than the negative effect or no effect, In The section 'The performance of employees', the proportion of positive and negative effects is similar, In the column of "employment development", the negative effects are significantly higher than the positive effects. Analysis of this set of data shows that the positive and negative effects of AI on employee performance are equal, the impact on the company is mostly positive, while the impact on employment development is mostly negative. This set of data is very explorable for my research. Of course, there are some limitations to this data, as it comes from France and productivity and management structures vary from country to country.
Similarly, the positive impact of AI on employee performance is equal to the negative impact. There are many positive effects and negative effects, the positive effects were ‘AI technology can generate 3D virtual paths and programmable intelligence and enable machines to think intelligently in coordination with the simulation of many examples or data[3]. Thus, AI may perform better than humans using the deep learning model to analyze previous examples/data and simulate various situations based on big data. For example, the IBM Deep Blue first won against a world champion in the 1996 chess match by evaluating the function from past board game records. A significant advance is Google AlphaGo: this supercomputer completed self-learning through an artificial neural network (a deep machine learning method) to improve chess-playing capability and beat the top-ranked chess player in the world in 2017. AI has also penetrated many organizational processes [4]. Through the deep learning algorithm system, AI has developed strength in dealing with organizational decision-making processes that are uncertain, complex, and equivocal. Thus, AI technology can replace not only manual and routine tasks conventionally performed by humans, but also tasks that are based on human judgment and decisions in manufacturing and management processes.’ [5].
Have negative effects: ‘Alternatively, AI technology may not generate productivity gains immediately upon commissioning[6]. The potential time lag in the productivity effect of AI technology may be attributed to adjustment costs, complementary innovations, and organizational changes[7]. In practice, the adjustment and combination of AI and existing technologies may not be successful. AI technology is not a panacea that can be applied to all production processes and firms. For instance, some sudden occurrences of production process might be managed and judged better by experienced workers; the magnitude and level of AI technology introduced into the production process may not fit well with the existing manufacturing workforce and technologies. This is because the effective use of AI technology relies heavily on big data that must adapt to firm-specific human capital and manufacturing processes. Workers often have no incentives to learn them, being afraid of losing their jobs.’ [8]. In order to minimize the negative impact of these AI on employee performance, I think some effective measures can be implemented, maybe policy incentives, maybe some oriented programs. ‘While most executives won’t need to know the difference between convolutional and recurrent neural networks, you should have a general familiarity with the capabilities of today’s tools, a sense of where short-term advances are likely to occur, and a perspective on what’s further beyond the horizon. Tap your data-science and machine-learning experts for their knowledge, talk to some AI pioneers to get calibrated, and attend an AI conference or two to help you get the real facts; news outlets can be helpful.’ ‘ AI algorithms need assistance to unlock the valuable insights lurking in the data your systems generate. You can help by developing a comprehensive data strategy that focuses not only on the technology required to pool data from disparate systems but also on data availability and acquisition, data labeling, and data governance.’ ‘Keeping up with today’s AI technologies and use cases is not enough to remain competitive for the long haul. Engage your data-science staff or partner with outside experts to solve a high-impact use case with nascent techniques, such as the ones discussed in this article, that are poised for a breakthrough. Further, stay informed about what’s possible and what’s available.’ [9].
3. Methodology
On the basis of analyzing the impact of AI on employee performance, this study attempts to explore further the mechanism of AI's effect on employee performance and how to make this system better play the potential of AI. This study is mainly based on secondary data, supplemented by primary data, and some surveys are conducted.
The main targets of this study are companies in developed countries. In addition, There are a number of possible policies that could be used to overcome some of the potential challenges.
Secondary materials can help us understand the research problem from a more comprehensive and multi-perspective, broaden the channels of acquiring knowledge, and provide a lot of basic data and background, primary data can be collected according to the specific needs of the current primary data, with timeliness, evidence and vividness.
I use this data as a background to support my quantitative qualitative hybrid analysis, European Marketing Confederation. [10]. Take-up of artificial intelligence (AI) in marketing, sales, and service in Europe as of December 2023 [Graph].
The main advantage of second-hand data is that it is accurate and convenient. Due to the limited time in this paper, it mainly focuses on second-hand resources and data. The following is the development process of AI intelligence in recent years. However, it can be seen that the adoption of AI in most companies is growing rapidly.
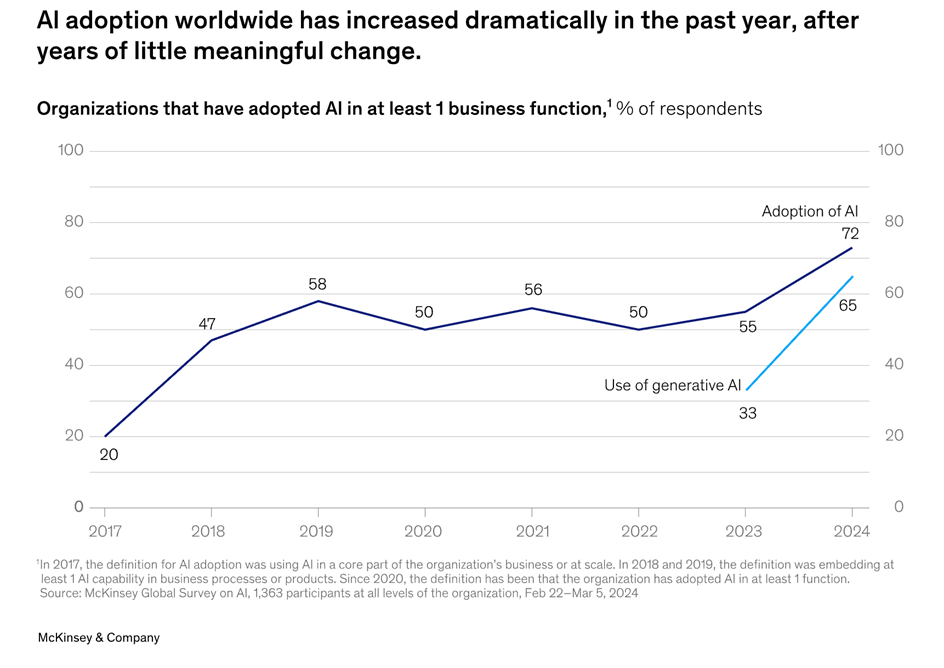
Figure 1: Growing trends in the adoption of artificial intelligence in various industries
"The chart illustrates the adoption of AI across industries in Europe, highlighting the significant growth trend of AI integration in enterprise operations."
In addition, the survey results also show that enterprises are now using AI in more areas of their business. Half of respondents said their organizations have adopted AI in two or more business functions, up from less than a third in 2023. [11]
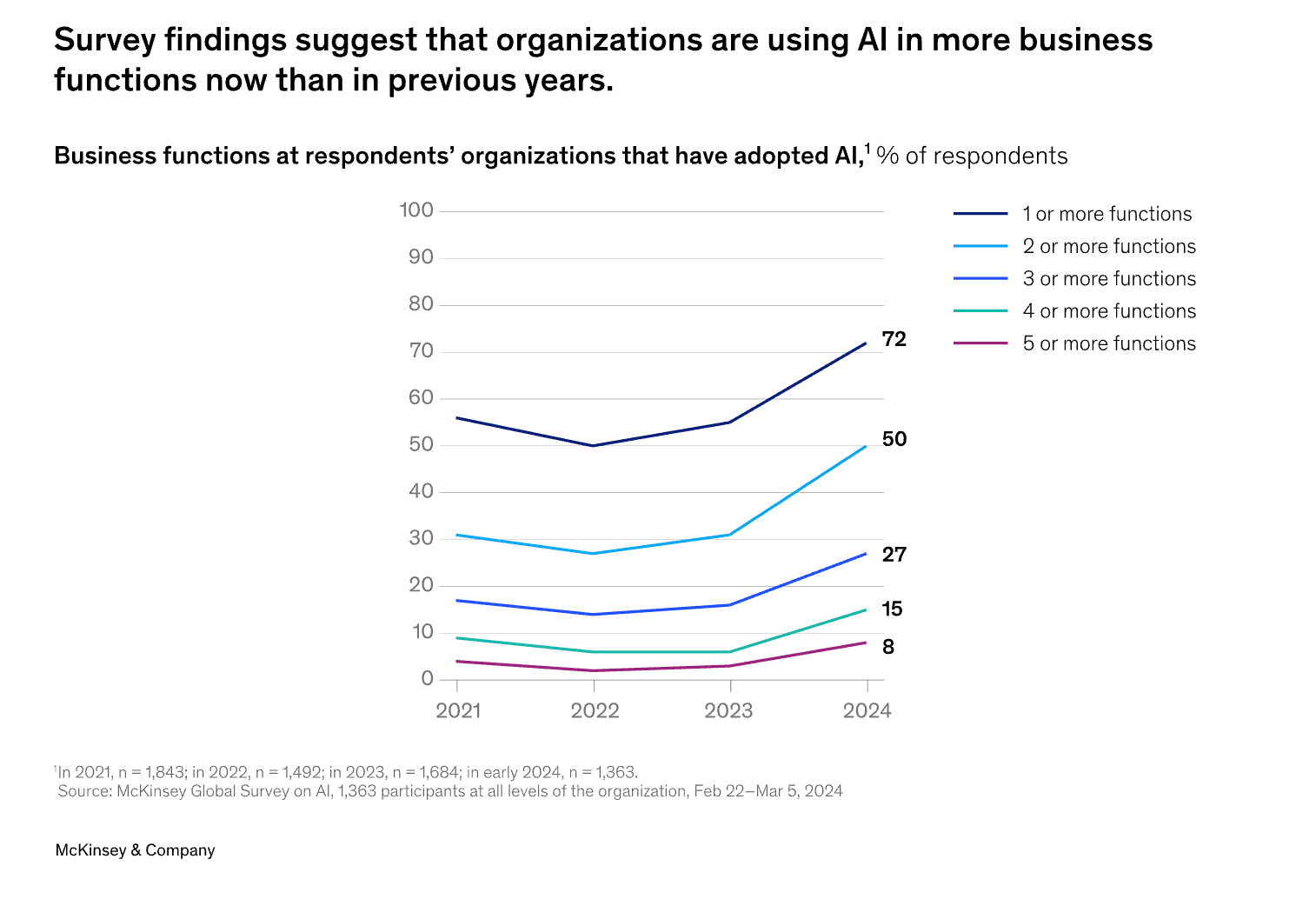
Figure 2: Changes in the application of AI to other business functions
"The chart reflects the changing trends in the application of AI in non-core business functions by enterprises in 2023, based on survey data from the surveyed enterprises."
Through the combination of quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis, some data collection and questionnaire survey also provide strong support for the research. The first is some data on the impact of AI on company performance and its impact on employees, as well as first-hand data collected through face-to-face consultations and inquiries
It can be seen from these materials and data that AI has a very good effect on the performance of companies and employees, and it is gradually integrated into finance, management, manufacturing, infrastructure and other aspects with the development of the times, and constantly intervenes in people's production, life and work. It can quickly help us to complete some advanced calculations that the human brain can not quickly complete, to help us make more intelligent and objective decisions compared to their own, it also indirectly affects employee performance through a series of models at different social levels, but people do not use AI in all aspects of the assistance, in many cases, the use of people's own initiative and creativity will bring us a different harvest, AI The impact of AI on employee performance doesn't stop there, it goes deeper and deeper. Turning to the findings of some of the enquiries and interviews, the interview (see Appendix 2 ) revealed that we all have our own capacity to think about AI, and we all have a 'pros and cons' attitude towards it. But it seems that managers will have some concerns about the use of AI.
These are some of the results of my research methodology, in addition to my thoughts on some possible policies to overcome the adverse effects of AI on employee performance. We should of course use AI wisely, but sometimes we can both fall into the 'AI trap', sometimes the intelligence level of AI is relatively limited, sometimes AI may reduce human employment. Sometimes employees may rely too much on AI and reduce human initiative. Therefore, in response to the above analysis of research methods, I think about some good policies that I believe can mitigate the negative impact of AI on employee performance. Some staff to guide policy, For example, encourage employees to put forward innovative ideas or questions, which can not only cultivate people's initiative and creativity, but also weaken the adverse impact of AI mechanization, effectively improve employee performance and company productivity, but also cultivate an atmosphere of social innovation.
In the process of designing the research process for the research project, the impact of AI on employee performance was limited. It is manifested in three aspects: insufficient representativeness of samples, lack of timeliness of data, and unverifiable subjectivity of qualitative data. In order to avoid the existing problems and predict the problems that may occur in the actual implementation process, the following preventive measures are proposed to be included in future studies.
This study will further expand the sample size, increase the sample data horizontally and vertically, expand the age of the sample group, and divide the sample data into different regions, ages, genders and occupations to improve the diversity and representativeness of the sample. For example, the main group of this study is young grass-roots workers, so next time, in order to conduct a more accurate and comprehensive study on the overall impact, the study will adopt a unified questionnaire sampling of different age groups for analysis, so as to improve the diversity and representativeness of samples.
In the later stage of the study, the research data will be updated regularly to solve the problem of lack of timeliness of the data. Analyze the specific impact of AI by continuously tracking the performance of investigators.
In the subsequent research, more analytical tools and methods will be introduced, and the construction of the theoretical framework will be constantly improved to solve the subjective problems of qualitative data processing that are common in the quantitative analysis of surveys. Explain and analyze the reasons more objectively. Improve the objectivity and consistency of quantitative data interpretation.
4. Results
Finally, I think I have gained a lot from this research. First, it has become an innovation for me in this field. Second, I have deeply understood the relationship between AI and employee performance, and the research try to continue to explore how to use this system to better utilize AI as an auxiliary tool and give full play to its potential. From these two sets of data, it can be seen that both the adoption of artificial intelligence and the adoption of generative artificial intelligence are constantly improving, especially the adoption of generative artificial intelligence increased by 42 percent year-on-year. For these two sets of data, it is not difficult to see that the adoption of artificial intelligence for the company is constantly increasing, which has a necessary impact on employee performance and company operation. (According to the above chart, the proportion of artificial intelligence adoption increased from 55 percent to 72 percent, and generative artificial intelligence increased from 33 percent to 75 percent). From these two sets of data, it can be analyzed that the application of artificial intelligence in the company continues to grow. In the research method, my constant inquiry, reading and analysis of secondary materials made me understand different perspectives and opinions on how AI affects employee performance, which taught me a more comprehensive and dialectical understanding of the world, the survey also studied businesses and economies in the developed world. In the research method, my in-depth study of primary data, interviews and some consultations also made me grow a lot, and I was able to obtain some answers to my research questions in a more real and unique way. When I surveyed and analyzed the data, Appendix 1 presents that the evidence showed that companies were using AI at a high rate, and employees were using AI at a high rate, but in management, it didn't seem that AI was influencing people's decisions overall. More and more businesses are using AI tools to streamline operations, enhance decision-making processes, and increase overall efficiency.
To sum up, AI with great potential to enrich and assist our lives, this widespread use of AI demonstrates its critical role in transforming the way businesses operate and the performance of their employees. Some people think that artificial intelligence will be more than human ability, but also very likely to replace some manufacturing and management of human role, some people think that AI may promote human mechanization, in the face of some unexpected situations AI can not make better judgment than an experienced worker. So the impact of AI on employee performance is an indirect system, which has advantages and disadvantages, and the real choice depends on how we choose. Therefore, for this situation, we can promote people's better improvement and correct use of AI in the form of some policies, but also through the improvement of their own ideas. This widespread use of AI shows that it plays a key role in transforming the way businesses operate and employee performance. The findings suggest that in order to better harness the potential of AI while mitigating its negative impact on employee performance, companies can implement some guiding policies, such as encouraging employees to come up with innovative ideas or questions and fostering their initiative and creativity These measures not only help mitigate the negative impact of AI mechanization on employees, but also effectively improve employee performance and enterprise productivity. In my interviews and some surveys, the results show that employees are indeed good and bad in dealing with AI problems, and sometimes people's self-control is a little poor. It is obvious that AI channels play little role in management. The results of the study show that while AI can significantly improve employee and business productivity, the percentage of AI adoption increased from 55 percent to 72 percent, and the percentage of generative AI increased from 33 percent to 75 percent, and it is not difficult to see that the percentage of companies using AI intelligence is constantly increasing. But the interaction between humans and AI is complex. The data shows that employees' over-reliance on AI may inadvertently inhibit their creativity and innovation. Going forward, I plan to further analyze the data, explore from more dimensions, and continue to expand the sample size and improve the quality of the data. My goal is to achieve more impactful research results, reveal more potential problems, and propose effective solutions to promote harmonious and efficient collaboration between humans and AI.
5. Discussion
This study also confirmed that the results were consistent with the expected literature collection results. My research must also have some limitations, such as insufficient sample size, which cannot better summarize the impact of AI and employee performance. For this problem, the research will further expand the sample size, improve the quality of the sample while expanding the sample size, and accurately locate and analyze the views of employees and some management on this issue. Secondly, I think my research may lack some more comprehensive perspectives and perspective analysis. The research will try to improve my personal ability and try some more innovative methods, such as interdisciplinary analysis, personal trial analysis and comprehensive questionnaire analysis. In addition to focusing on the impact of AI on employee performance, I also explored some of the policies that might leverage this mechanism between AI and employee performance, and how can we better deal with this system.
6. Conclusions
With the rapid development of economy and science and technology, artificial intelligence technology has a long history and has achieved breakthroughs again and again. It has had an important impact on improving production efficiency and quality of life, and artificial intelligence also provides more sensible guidance for building the future of artificial intelligence technology As a member of society, we should also work hard to jointly study and discuss some ethical issues and challenges in the development of artificial intelligence index, and promote the development of artificial intelligence in the direction of more advantages than disadvantages.
In summary, in this paper, the research try to explore the question of how AI affects employee performance, conduct in-depth understanding and research on this issue, and consider some possible policies to deal with it. Research shows that the proper application of AI can not only improve the individual performance of employees, but also help employees adapt to technological change and bring out the maximum potential of both AI and employees through innovative incentives and teamwork. At the management level, enterprise managers can also adopt diversified strategies and help employees effectively adapt to technological changes and the AI era through some independent and active policies. At the same time, with the continuous development of AI technology, future research should continue to pay attention to the complex relationship between AI and employees, continue to innovate our response mechanism to cope with the system, and explore a more balanced, comprehensive and high-quality management model, so that the management can better use AI technology to improve employee performance.
References
[1]. Agrawal, A., Gans, J., & Goldfarb, A. (2018). Prediction, judgment, and complexity: a theory of decision-making and artificial intelligence. In The economics of artificial intelligence: An agenda (pp. 89-110). University of Chicago Press.
[2]. IFOP. (November 7, 2018). In the world of work, would you say that Artificial Intelligence will have rather positive or negative impacts in the upcoming years? [Graph]. In Statista. Retrieved October 17, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/960424/employees-opinion-impact-artificial-intelligence-work-world-france/.
[3]. Goldfarb, A., & Trefler, D. (2018). AI and international trade (No. w24254). National Bureau of Economic Research.
[4]. Jarrahi, M. H. (2018). Artificial intelligence and the future of work: Human-AI symbiosis in organizational decision making. Business Horizons, 61(4), 577-586.
[5]. Yang, C. H. (2022). How artificial intelligence technology affects productivity and employment: firm-level evidence from Taiwan. Research Policy, 51(6), 104536.
[6]. Jovanovic, B., & Rousseau, P. L. (2005). General purpose technologies. In Handbook of economic growth (Vol. 1, pp. 1181-1224). Elsevier.
[7]. Brynjolfsson, E., Rock, D., & Syverson, C. (2019). Artificial intelligence and the modern productivity paradox. The economics of artificial intelligence: An agenda, 23, 23-57.
[8]. Chui, M., Manyika, J., Miremadi, M., Henke, N., Chung, R., Nel, P., & Malhotra, S. (2018). Notes from the AI frontier: Insights from hundreds of use cases. McKinsey Global Institute, 2, 267.
[9]. Scott, A. C., Solórzano, J. R., Moyer, J. D., & Hughes, B. B. (2022). International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Int. Artif. Intell. & Mach. Learn., 2(1), 1-37.
[10]. European Marketing Confederation. (February 5, 2024). Take-up of artificial intelligence (AI) in marketing, sales, and service in Europe as of December 2023 [Graph]. In Statista. Retrieved October 18, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1478530/take-up-ai-marketing-europe/.
[11]. McKinsey & Company. (2024). The state of AI. Retrieved October 18, 2024, from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai
Cite this article
Liu,Y. (2025). How Will Artificial Intelligence Affect the Performance of Employees. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,166,27-35.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Agrawal, A., Gans, J., & Goldfarb, A. (2018). Prediction, judgment, and complexity: a theory of decision-making and artificial intelligence. In The economics of artificial intelligence: An agenda (pp. 89-110). University of Chicago Press.
[2]. IFOP. (November 7, 2018). In the world of work, would you say that Artificial Intelligence will have rather positive or negative impacts in the upcoming years? [Graph]. In Statista. Retrieved October 17, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/960424/employees-opinion-impact-artificial-intelligence-work-world-france/.
[3]. Goldfarb, A., & Trefler, D. (2018). AI and international trade (No. w24254). National Bureau of Economic Research.
[4]. Jarrahi, M. H. (2018). Artificial intelligence and the future of work: Human-AI symbiosis in organizational decision making. Business Horizons, 61(4), 577-586.
[5]. Yang, C. H. (2022). How artificial intelligence technology affects productivity and employment: firm-level evidence from Taiwan. Research Policy, 51(6), 104536.
[6]. Jovanovic, B., & Rousseau, P. L. (2005). General purpose technologies. In Handbook of economic growth (Vol. 1, pp. 1181-1224). Elsevier.
[7]. Brynjolfsson, E., Rock, D., & Syverson, C. (2019). Artificial intelligence and the modern productivity paradox. The economics of artificial intelligence: An agenda, 23, 23-57.
[8]. Chui, M., Manyika, J., Miremadi, M., Henke, N., Chung, R., Nel, P., & Malhotra, S. (2018). Notes from the AI frontier: Insights from hundreds of use cases. McKinsey Global Institute, 2, 267.
[9]. Scott, A. C., Solórzano, J. R., Moyer, J. D., & Hughes, B. B. (2022). International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Int. Artif. Intell. & Mach. Learn., 2(1), 1-37.
[10]. European Marketing Confederation. (February 5, 2024). Take-up of artificial intelligence (AI) in marketing, sales, and service in Europe as of December 2023 [Graph]. In Statista. Retrieved October 18, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1478530/take-up-ai-marketing-europe/.
[11]. McKinsey & Company. (2024). The state of AI. Retrieved October 18, 2024, from https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai









