1.Introduction
Profitability is a key indicator of a company’s healthy and long-term viability, influencing its development trajectory and the decision-making processes of investors and stakeholders. For enterprises, profitability serves as a reflection of operational efficiency, competitive positioning, and financial sustainability. As a leading enterprise in China’s home appliance industry, Midea Group plays a critical role in shaping industry standards and trends. However, the intensification of market competition and changes in the industry environment demand an in-depth analysis of Midea Group's profitability and its influencing factors. Such analysis is crucial not only for Midea’s strategic planning but also for its ability to maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
This study aims to conduct an in-depth analysis of Midea Group's profitability by examining key financial indicators such as revenue generation, profit level, return on invested capital (ROCE), and return on equity (ROE). The study identifies critical factors affecting profitability by analyzing these indicators and evaluates how Midea Group can enhance its asset utilization efficiency. Additionally, this research provides targeted business suggestions for optimizing its business strategies and aligning with industry trends. Midea Group's profitability can provide references and inspiration for the profitability analysis of other home appliance enterprises and even enterprises in other industries and promote the development of enterprise profitability analysis theory.
The significance of this research extends to multiple stakeholders. For Midea Group, this research can help it accurately understand its profitability status, identify the key factors affecting profitability, and provide a basis for the enterprise to formulate strategic decisions. For investors, this research can provide a reference for them to evaluate the investment value of Midea Group. For creditors, this research can help them evaluate Midea Group's debt repayment ability. For the home appliance industry, this research can provide experience and inspiration for other enterprises in the industry. Ultimately, this study not only enriches the theoretical framework of profitability analysis but also bridges the gap between theory and practice by offering practical insights for businesses, investors, and industry stakeholders.
2.Literature Review
Although research on profitability analysis has been extensive, relatively few studies have focused on the home appliance industry, and even fewer have analyzed Midea Group in detail. This paper aims to fill this gap by investigating Midea Group’s profitability and reviewing the current state of research in this field through an analysis of relevant literature.
In China, research on the profitability of the home appliance industry has gradually increased, especially research on the Midea Group. Researchers often use quantitative methods, such as the DuPont analysis, to evaluate the financial performance of companies. For example, Shi Yanqing and Li Li, in their work "The Application of DuPont Analysis in the Financial Analysis of Listed Companies," highlighted that profitability could be thoroughly assessed by analyzing indicators such as return on net assets, return on total assets, and net profit margin [1]. Li Bin analyzed the profitability of listed companies in the pharmaceutical industry from the perspective of economies of scale and pointed out the relationship between enterprise scale and resource allocation efficiency [2]. Li Jingming and Fan Qinru also pointed out some problems in profitability research in "Profitability Analysis of Listed Companies: Taking Steel Enterprises as an Example," such as the lack of in-depth consideration of the impact of global economic trends on enterprise profitability in the macro environment [3].
Internationally, research on profitability is more extensive, and research methods are more diverse. Fama and Jensen pointed out that the proportion of independent directors is positively correlated with the company's profitability because independent directors can provide better company supervision [4]. Lev analyzed the role of intangible assets in driving profitability [5]. Chen, Joseph Lakonishok, and Sougiannis found that R&D expenditure is positively correlated with the company's future profitability, and the higher the R&D intensity, the better the profitability [6]. Emma Welch focused on the impact of ownership structure on the company's profitability [7].
Existing studies on profitability primarily focus on financial indicators such as ROE and ROA. However, few address the specific challenges of the Chinese home appliance industry or integrate qualitative factors like market competition. This study fills this gap by analyzing Midea Group's profitability within its industry context.
3.Methods
Figure 1: The Diagram of Methods for Analyzing 1
This study mainly uses the DuPont analysis model to analyze the profitability of Midea Group. The DuPont analysis model focuses on return on equity (ROE) as the core indicator, decomposing it into three main factors: net profit margin, total asset turnover, and equity multiplier. The formula is expressed as:
ROE = net profit margin × total asset turnover × equity multiplier
Through this decomposition, it can be seen whether the enterprise achieves a higher return on net assets by obtaining profits through efficient sales (net profit margin), efficient operation of assets (total asset turnover), or a reasonable capital structure (equity multiplier).
To further enhance the analysis, this study employs a comparative analysis model, benchmarking Midea Group’s profitability indicators against its key competitors, such as Gree Electric Appliances and Haier Smart Home. This comparison helps identify Midea Group’s competitive position within the industry and highlights its relative strengths and weaknesses in profitability.
This study combines quantitative and qualitative analysis methods. In terms of quantitative analysis, the financial statement data of Midea Group for many years are collected and sorted out, and various profitability indicators are calculated, such as the net profit margin, total asset turnover, equity multiplier, and return on net assets in the above DuPont analysis model. Through data comparison and trend analysis, the change in Midea Group's profitability is intuitively shown. Qualitative analysis focuses on analyzing factors such as the market environment in which the enterprise is located, the competitive situation in the industry, and the enterprise strategy, and exploring the potential impact of these factors on profitability indicators. For example, analyzing the impact of changes in market demand on the product sales of Midea Group and how enterprise strategy adjustments (such as diversification strategy, technological innovation strategy, etc.) affect various aspects of profitability.
4.Analysis of Midea Group's Profitability Indicators
4.1.Net Profit Margin
Net profit margin is one of the important indicators to measure the profitability of an enterprise. Midea Group's net profit margin shows a stable growth trend, and in the first half of 2024, the net profit margin reached a certain level, indicating that the company has a strong ability to convert sales revenue into net profit. This growth can be attributed to the company's efforts in cost control, product pricing strategy, and product structure optimization. By reducing production costs, reasonably formulating product prices, and increasing the sales proportion of high value-added products, the company can achieve a relatively high proportion of net profit after deducting various costs and expenses.
4.2.Return on Assets
Return on assets (ROA) reflects the enterprise's ability in utilizing its assets to generate profits. Midea Group's ROA is at a relatively reasonable level in the industry. This indicates that the company has a certain degree of efficiency in asset allocation and operation management. This performance is achieved through strategic investments in fixed assets, such as production equipment and storage facilities, coupled with the optimization of current asset management, including inventory and accounts receivable.
4.3.Return on Equity
Return on equity (ROE) reflects the return level of shareholders' equity. Midea Group's ROE is relatively high, indicating that the company has created good returns for shareholders. This is mainly due to the synergistic effect of the company's sales profitability, asset operation efficiency, and balanced capital structure. High net profit margin and asset turnover, as well as a moderate equity multiplier, enable shareholders' equity to obtain relatively high returns.
4.4.Total Return on Assets
Total return on assets (TROA) measures the comprehensive utilization effect of enterprise assets. Midea Group's TROA is at a relatively high level in the industry, showing the company's advantages in asset operation and profitability. The company realizes the full utilization of different types of assets in their respective business fields through a diversified business layout. For example, in the smart home business, production equipment, R&D facilities, and other assets create value through efficient production and innovation activities; in the logistics and distribution segment, transportation equipment, storage facilities, and other assets ensure the timely supply and sales of products, thereby improving the total return level of assets.
4.5.Operating Profit Margin
Operating profit margin reflects the profitability of an enterprise's operating activities. Midea Group's operating profit margin has steadily increased, indicating that the company has achieved certain results in operation management and cost control. The company has achieved this by implementing fine-grained management practices, optimizing internal processes, reducing unnecessary operating links, reducing operating costs, improving product quality and service levels, and increasing product added value.
5.Comparison of Midea Group's Profitability with Industry Indicators
This section compares Midea Group’s profitability with key competitors in the home appliance industry by analyzing various profitability indicators, including operating revenue, net profit, return on equity, and high-end market competitiveness. The comparison highlights Midea Group’s position relative to its peers, emphasizing its strengths and areas for improvement.
5.1.Operating Revenue
Midea Group's operating revenue is significantly higher than that of its main competitors, indicating its leading position in the market. In the first half of 2024, Midea Group achieved a total operating revenue of 218.1 billion yuan, 2.1 times Gree Electric Appliances’ 99.783 billion yuan. This advantage stems from Midea’s diversified business model, where air-conditioning revenue accounts for only 46.70% of total revenue, compared to Gree’s reliance on air-conditioning, which contributes 70.54% of its revenue. Midea’s diversified operations provide a balanced revenue stream and reduce risk, unlike Gree’s dependence on a single segment.
5.2.Net Profit
Midea Group also leads in net profit, reflecting stronger profitability. In the first half of 2024, Midea’s net profit attributable to the parent company was 20.8 billion yuan, compared to Gree Electric’s 14.136 billion yuan and Haier Smart Home’s 10.16 billion yuan. Midea’s 14% year-on-year growth in net profit surpassed Gree’s 11.54% growth but trailed Haier’s 18.09% growth, demonstrating that while Midea excels in scale, Haier outpaces in growth rate. Haier’s success can be attributed to its strong presence in the high-end market, while Midea benefits from a more balanced and diversified business model.
5.3.Comparison of Profitability Indicators
From indicators such as weighted average return on net assets, Midea Group is gradually catching up with and surpassing Gree Electric Appliances in terms of profitability. Midea Group has advantages in diversified operations, technological innovation, brand advantages, and global operations, which reduce the company's risks, improve competitiveness, and increase market share. Gree Electric Appliances has certain advantages in profit margins but is relatively weak in diversification, internationalization, growth ability, debt ratio, and cash flow.
For example, in terms of air-conditioning revenue, Midea Group's HVAC business revenue in the current quarter increased by nearly 10 billion yuan to 101.46 billion yuan, accounting for 46.52% of the company's total revenue, with a gross profit margin of 23.37%. Gree Electric Appliances' air-conditioning revenue in the first half of the year was 69.998 billion yuan, with a year-on-year growth of 1.82%, accounting for 70.54% of the total revenue, and a gross profit margin of 35.69%. In terms of gross profit margin, Gree air-conditioners are 12.32 percentage points higher than Midea's, but Midea Group has improved the overall gross profit margin level through product structure upgrading, brand building, and overseas market expansion.
In terms of B-end business, Midea Group's B-end business has a relatively high growth in the first half of the year. The financial report shows that the company's industrial technology revenue in the reporting period was 13.6 billion yuan, with a year-on-year growth of 12%; the building technology revenue was 14.8 billion yuan, with a year-on-year growth of 21%; the robotics and automation revenue was 15.2 billion yuan, with a year-on-year growth of 24%; and the revenue of the robotics, automation system, and other manufacturing industries in the period was 17.262 billion yuan, with a year-on-year growth of 26.07%. Gree Electric Appliances' diversification has always attracted attention. In the first half of the year, Gree Electric Appliances' air-conditioning income accounted for 70.54% of the total income, and the proportion decreased slightly, but it is still the main source of income. The industrial products and green energy businesses increased by 90% and 51.3% respectively, and the significant increase in performance was mainly due to the consolidation of Dun'an Environment.
In addition, Midea Group has taken various measures to control costs and effectively reduced them. By optimizing the production process, establishing long-term and stable cooperative relationships with suppliers, and optimizing the internal management structure, the net cash flow from operating activities has increased. Gree Electric Appliances also has certain achievements in cost control but is relatively lagging behind in upgrading its product structure and diversifying its development.
In summary, Midea Group is gradually catching up with and surpassing Gree Electric Appliances in terms of operating revenue, net profit, and profitability indicators, mainly due to its efforts in diversified operations, product structure upgrading, brand building, and cost control.
5.4.Competition in High-End Brands
Haier Smart Home holds a clear advantage in the high-end home appliance market, primarily due to its Casarte brand. Casarte leads in the premium segment with dominant market shares in high-end refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, achieving 40.3%, 83.5%, and 28.5% shares in respective high-end markets (10,000+ or 15,000+ yuan price range). This performance underscores Haier’s strategic focus on high-value products and premium branding.
While relatively weaker in the high-end segment, Midea Group has made strides in promoting its dual high-end brand strategy through COLMO and Toshiba, which enhances its competitiveness in premium markets. Simultaneously, Midea benefits from risk diversification through its broader business development in industrial technology, robotics, and smart home solutions, areas where Haier is less dominant.
6.Research Findings on the Current Situation and Problems of Midea Group's Profitability
6.1.Current Situation
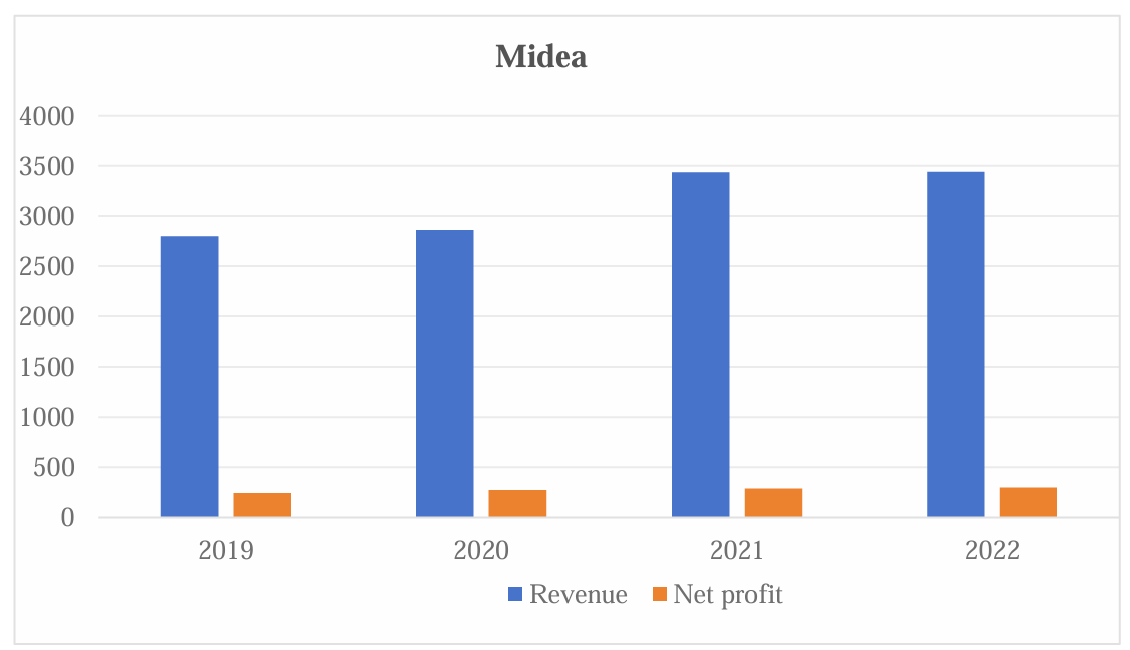
Figure 2: Midea Group Revenue and Net Profit 2019-2022
Midea Group demonstrates relatively high profitability, as indicated in its strong net profit margin over recent years. The company’s ability to maintain relatively stable profitability highlights its advantages in market competition and the market demand and sales performance of its products.
6.2.Existing Problems
Despite its strong profitability, Midea Group faces several challenges that limit its financial performance and long-term growth potential. Its return on shareholders' equity (ROE) is relatively low. In the past three years, Midea Group's current assets have increased year by year, resulting in a decline in the current asset turnover rate [8]. This may indicate that Midea Group still has room for improvement in capital operation and capital structure. Improving the return on shareholders' equity is one of the keys to achieving sustainable development and requires further research and measures.
Although Midea Group has achieved certain results in asset utilization efficiency, there are still some problems. For example, the asset turnover rate may not be high enough. Midea Group's asset turnover rate needs to be improved, which indicates that there is still room for improvement in the company's asset utilization efficiency. Some of the company's fixed assets and current assets may be idle or inefficient. Improving asset utilization efficiency will help increase productivity and reduce costs, further improving profitability. The improvement in asset utilization efficiency will accelerate the turnover of total assets and ultimately increase the company's return on net assets [9].
With the intensification of competition in the Chinese home appliance market, Midea Group is facing increasingly fierce competitive pressure. The continuous influx of competitors and changes in consumer demand pose challenges to Midea Group's profitability. Therefore, Midea Group needs to continuously strengthen its market research and innovation capabilities to maintain its competitive advantage and improve profitability.
7.Suggestions
7.1.Improving the Return on Shareholders' Equity
Midea Group optimizes the capital structure, rationally allocates the proportion of debt and equity, reduces financial costs, and improves the return on shareholders' equity. They might also strengthen capital operation and profit management by actively carrying out mergers and acquisitions and capital market operations, optimizing capital allocation and utilization, and improving the return on shareholders' equity. Enterprise profit levels can be increased by raising sales prices and reducing costs, thereby improving the return on shareholders' equity. It is also possible to optimize sales expenses by reducing expenditures in the product sales process and improve the return on shareholders' equity by improving capital utilization efficiency [10].
7.2.Improving Asset Utilization Efficiency
Midea Group should optimize the production process and supply chain management, improve production efficiency, reduce resource waste, and increase the asset turnover rate; Improve product quality and production efficiency through scientific and technological innovation to further improve asset utilization efficiency; Optimize and dispose of unnecessary or inefficient assets to improve asset utilization; and introduce new overseas market operation concepts, adjust the existing price system according to the actual situation of domestic and foreign markets, and improve the flexibility of product price setting.
7.3.Coping with Market Competition Pressure
Midea Group should continue to conduct market research, deeply understand the needs and preferences of consumers, and timely adjust product strategies. Through big data analysis and consumer behavior research, more accurately predict market trends and develop new products that better meet market demands. The brand is an important asset of an enterprise. Midea Group should strengthen the shaping and dissemination of brand image through multi-channel marketing activities such as social media, advertising, and public relations activities. At the same time, provides high-quality after-sales service and customer experience to enhance consumers' trust and loyalty to the brand. Technological innovation is the key to enhancing product competitiveness. Midea Group should increase R&D investment, encourage innovative thinking, and continuously launch products with innovative functions and designs. They may cooperate with scientific research institutions and universities to introduce the latest scientific research achievements.
7.4.Expanding Sales Channels and Improving Profitability
Utilize the brand influence and product advantages to actively expand overseas markets and improve the company's international competitiveness. As a leading enterprise in the home appliance industry, Midea Group has significant advantages in product quality and technological innovation. By promoting its high-quality home appliance products such as HVAC and consumer electronics in overseas markets, Midea Group can establish a good brand image and enhance brand awareness and reputation. For example, Midea Group can strengthen cooperation with overseas distributors, expand sales channels, and improve the coverage of products in overseas markets. At the same time, Midea Group can also participate in international home appliance exhibitions and other activities to showcase its latest products and technologies and attract the attention of overseas customers.
Strengthen brand building in overseas markets. Brand is an important asset for enterprises to compete in overseas markets. Midea Group can convey the brand value and concept to overseas consumers through various means such as advertising and public relations activities to improve consumers' loyalty to the brand. For example, Midea Group can carry out brand promotion activities on overseas social media platforms, interact with overseas consumers, understand their needs and feedback, and continuously improve products and services.
8.Conclusion
Midea Group's profitability exhibits multi-dimensional characteristics, and various indicators perform well and have industry competitiveness. The stable growth of the net profit margin reflects the remarkable effectiveness of its cost control and product pricing strategies; the return on assets is at a reasonable level, indicating high efficiency in asset allocation and operation management; the high return on equity benefits from the synergy of sales, asset operation, and capital structure; the high total return on assets is attributed to the diversified business layout that facilitates the comprehensive utilization of assets; the steadily increasing operating profit margin is largely due to management optimization and cost control.
Compared with its peers, Midea Group demonstrates unique advantages. Its operating revenue exceeds that of Gree Electric Appliances, and its business is more balanced with a lower proportion of air-conditioning revenue; its net profit is higher than that of Gree Electric Appliances and grows faster; in terms of profitability indicators such as the weighted average return on net assets, it is gradually catching up with and surpassing Gree Electric Appliances, performing outstandingly in diversified operations, technological innovation, and other aspects. Compared with Haier Smart Home, it leads in net profit scale, while Haier Smart Home's Casarte brand holds a prominent position in the high-end market, and Midea Group is known for its diversified business development and scale advantages.
Despite these achievements, Midea faces challenges such as relatively low return on net assets, inefficiencies in asset utilization, and increasing competitive pressure from market rivals. To address these issues, Midea Group should optimize its capital structure, strengthen asset utilization, and enhance market research and innovation to maintain its competitive edge. Expanding overseas markets and building its brand internationally will also be crucial for long-term growth.
This study provides valuable insights for Midea Group to refine its strategies, investors to assess its investment value, creditors to evaluate its financial stability, and peers in the home appliance industry to enhance profitability. Looking ahead, Midea should prioritize technological innovation, monitor industry trends, and continuously improve management and resource allocation to ensure sustainable development.
References
[1]. Shi Yanqing, Li Li. The Application of DuPont Analysis in the Financial Analysis of Listed Companies[J]. Value Engineering, 2010, (06): 26 - 27. Reference 61
[2]. Li Bin. Analysis of the Influencing Factors of the Profitability of Listed Companies in the Pharmaceutical Industry[J]. Technical Economics and Management Research, 2013(06): 67 - 71.
[3]. Li Jingming, Fan Qinru. Profitability Analysis of Listed Companies: Taking Steel Enterprises as an Example[J]. Accounting Communications, 2015(23): 44 - 47.
[4]. Johnson L D, Pazderka B. Firm Value and Investment in R&D[J]. Managerial and Decision Economics, 1993(14).
[5]. Lev B. R&D and Capital Market[J]. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 1999, 11(4): 21 - 35.
[6]. Chan, Lakonishok J, Sougiannis. The Stock Market Valuation of R&D Expenditures[J]. Journal of Finance, 2001, 56(06): 2431 - 2456.
[7]. Emma Welch. The Relationship between Ownership Structure and Performance in Listed Australian Companies[J]. Australian Journal of Management, 2002, 28(03): 287 - 306.
[8]. Wang Siyu. Profitability Analysis of Home Appliance Enterprises: A Comparison of the Profitability of Midea and Haier[J]. Guangxi Quality Supervision Guide Journal, 2020, (07): 104 - 105.
[9]. Wei Xixi, Li Yunxiang, Bi Lilou. Profitability Analysis of H Company[J]. Marketing World, 2021, (Z5): 37 - 39.
[10]. Yan Qu, Wang Fan. Profitability Analysis of Listed Companies in China: Taking Midea Group Co., Ltd. as an Example[J]. Investment and Entrepreneurship, 2023, 34(05): 122 - 124.
Cite this article
Wei,Y. (2025). Profitability Analysis in the Chinese Home Appliance Industry: A Case Study of Midea Group. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,174,151-159.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Shi Yanqing, Li Li. The Application of DuPont Analysis in the Financial Analysis of Listed Companies[J]. Value Engineering, 2010, (06): 26 - 27. Reference 61
[2]. Li Bin. Analysis of the Influencing Factors of the Profitability of Listed Companies in the Pharmaceutical Industry[J]. Technical Economics and Management Research, 2013(06): 67 - 71.
[3]. Li Jingming, Fan Qinru. Profitability Analysis of Listed Companies: Taking Steel Enterprises as an Example[J]. Accounting Communications, 2015(23): 44 - 47.
[4]. Johnson L D, Pazderka B. Firm Value and Investment in R&D[J]. Managerial and Decision Economics, 1993(14).
[5]. Lev B. R&D and Capital Market[J]. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 1999, 11(4): 21 - 35.
[6]. Chan, Lakonishok J, Sougiannis. The Stock Market Valuation of R&D Expenditures[J]. Journal of Finance, 2001, 56(06): 2431 - 2456.
[7]. Emma Welch. The Relationship between Ownership Structure and Performance in Listed Australian Companies[J]. Australian Journal of Management, 2002, 28(03): 287 - 306.
[8]. Wang Siyu. Profitability Analysis of Home Appliance Enterprises: A Comparison of the Profitability of Midea and Haier[J]. Guangxi Quality Supervision Guide Journal, 2020, (07): 104 - 105.
[9]. Wei Xixi, Li Yunxiang, Bi Lilou. Profitability Analysis of H Company[J]. Marketing World, 2021, (Z5): 37 - 39.
[10]. Yan Qu, Wang Fan. Profitability Analysis of Listed Companies in China: Taking Midea Group Co., Ltd. as an Example[J]. Investment and Entrepreneurship, 2023, 34(05): 122 - 124.









