1. Introduction
As the wave of digitalization sweeps the world, enterprise digital transformation has become the core driving force for economic development, profoundly changing the operating model, market competitiveness and interaction mode of enterprises with the external environment [1]. For the capital market, enterprise digital transformation has not only reshaped the fundamentals of enterprises but also had a profound impact on investor sentiment through changes in information dissemination channels. As an important platform for information dissemination and investor communication, financial social media is instant, interactive, and extensive, allowing information about corporate digital transformation to spread rapidly, triggering fluctuations in investor sentiment [2]. However, when existing studies explore the impact of corporate digital transformation on investor sentiment, most focus on macroeconomic effects or single-dimensional information dissemination, ignoring the complex role of financial social media as a key information intermediary.
This study aims to deeply analyze the impact mechanism of corporate digital transformation on investor sentiment from the perspective of financial social media and reveal the complex dynamic relationship contained therein. Specific objectives include: constructing a quantitative indicator system of investor sentiment based on financial social media text data. The innovative contributions of this study are mainly reflected in the following aspects: firstly, it comprehensively and deeply explores the impact mechanism of enterprise digital transformation on investor sentiment from the perspective of financial social media for the first time. Second, it constructs a quantitative indicator system of investor sentiment based on financial social media text data, providing new methods and tools for subsequent research. Third, using social network analysis methods, it reveals the information dissemination characteristics in financial social media and the impact of investor interaction behavior on sentiment diffusion, enriching the research content in related fields.
2. Related work
In an era of rapidly developing social financial networks and exponentially increasing information propagation speed, enterprise digital transformation has become an important driving force to promote economic growth and reshape the industrial ecology. To investigate the influence mechanism of social sentiment on digital transformation in the manufacturing industry, Zhao et al. used a fixed-effects panel regression model to conduct an empirical analysis based on sample data of A-share listed companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen from 2016 to 2020 [3]. To analyse the characteristics of investor behaviour related to complex financial information, Hussain and Alaia's team developed an online questionnaire based on specific financial articles and applied multivariate statistical methods to conduct the study [4]. To investigate the driving effect of online public opinion on corporate digital transformation, Yang and Zhu's team combined multivariate public opinion data and constructed a deep learning-based public opinion index using data from A-share listed companies from 2007 to 2022 [5]. Liu et al. investigated the synergistic effects of stock price volatility and investor sentiment and developed an analytical framework based on social media text data and natural language processing techniques [6]. In a study on the impact of digital transformation on financial performance, Ji et al. divided the transformation path into a technological transformation path and a market transformation path, and 2,363 listed manufacturing companies from 2008 to 2018 companies [7]. Liu et al. investigated the impact of digital transformation in finance on financial performance using data from 2,566 A-share listed companies and analysed it using a panel regression model [8]. To assess the effectiveness of market risk monitoring, Zheng et al. constructed a focal model combining 2.5 million social media data and 24 months of market performance and conducted a mixed sentiment analysis [9]. In selecting a paradigm for digital transformation research, Paul et al. systematically reviewed research developments in key areas such as the Internet of Things and social media from an interdisciplinary perspective [10].
Most studies focus on analysing the impact of digital transformation on a single dimension, such as financial performance and market reaction, and have not yet established a systematic framework for studying the interaction between corporate digital transformation and investor sentiment in the financial social media environment. Therefore, this paper focuses on a specific scenario of financial social media to systematically identify the internal mechanism of correlation between corporate digital transformation and investor sentiment. The study focuses on the evolution of firm-level digital transformation paths and investor sentiment as an important market signal, and deepens the understanding of the relationship between firm behaviour and market feedback in the financial social media ecosystem by constructing a two-way interaction analysis model, which provides an innovative analytical paradigm for further research.
3. Relevant theoretical background
3.1. Financial social media information feedback mechanism
Social media facilitates the depth and breadth of investor participation in corporate governance. In the traditional media environment, high information collection costs and one-way communication modes limit investors' willingness to participate in corporate governance. However, financial social media significantly reduces investors ‘information processing costs and stimulates stakeholders’ enthusiasm to participate in governance by establishing multi-channel information access and one-click communication mechanisms [11]. Second, social media interaction reconfigures the corporate governance feedback mechanism. The two-way communication characteristics of financial social media break the feedback delay and content control barriers of traditional media and reshape the dynamic balance of corporate governance [12]. Third, financial social media has a profound impact on corporate digital transformation. Driven by digital transformation, financial social media have systematically improved the efficiency of corporate governance by reducing information processing costs, increasing investor engagement, and rebuilding feedback mechanisms. This change is not only a breakthrough to the limitations of the traditional media governance function, but also an inevitable requirement for high-quality development of enterprises in the era of digital economy.
First, social media promotes the depth and breadth of investors' participation in corporate governance.
In the traditional media environment, high information collection costs and one-way communication models limit investors' willingness to participate in corporate governance. However, financial social media significantly reduces investors' information processing costs and stimulates stakeholders' enthusiasm for participating in governance by building a multi-channel information acquisition and one-click communication mechanism [11]. The decentralized nature of financial social media has weakened the herd mentality of users, and the message and comment area has become a public space for investors to express heterogeneous views. At the same time, the precise push mechanism of vertical public accounts has further strengthened users' sensitivity to specific topics, making them more proactive in collecting, forwarding and commenting on relevant information, forming an information network with professional depth. In the context of digital transformation, financial social media user groups have shown high knowledge density and strong interactivity. Their participation in corporate governance is no longer limited to passive information reception, but actively influences corporate decision-making through structured comments, data visualization interpretation, etc. This transformation enables investor sentiment to more accurately reflect the quality of corporate governance, thereby affecting the pricing efficiency of the capital market.
Second, social media interactivity reconstructs the corporate governance feedback mechanism.
The two-way communication characteristics of financial social media have broken the feedback delay and content control barriers of traditional media, and reshaped the dynamic balance of corporate governance [12]. Interactive tools such as likes, reposts, and comments enable companies to obtain instant feedback from investors on issues such as compensation policies and strategic decisions. This "instant governance" model effectively makes up for the lag defect of traditional media feedback mechanisms. The open platform nature of social media has caused companies to lose absolute control over information dissemination. Investors can jointly voice out pressure from online public opinion, forcing companies to adjust their governance strategies. This "external governance" force complements the internal governance mechanism and significantly improves the transparency and credibility of corporate governance.
Third, the profound impact of financial social media on enterprise digital transformation.
Driven by digital transformation, financial social media has systematically improved corporate governance effectiveness by reducing information processing costs, enhancing investor participation, and reconstructing feedback mechanisms. Compared with traditional media, the "preemptive" governance of investor sentiment can help companies predict market risks and optimize governance decisions by real-time monitoring of social media sentiment indexes. The supervisory pressure from social media has prompted companies to establish a salary incentive mechanism that is strongly linked to performance and curb opportunistic behavior of executives. As an important carrier of corporate digital transformation, financial social media not only optimizes the transmission path of investor sentiment but also promotes the paradigm shift of corporate governance system by building a "low-cost-high-efficiency" channel for investors to participate in governance and reshaping the "real-time-interactive" feedback mechanism of corporate governance. This change is not only a breakthrough in the limitations of traditional media governance functions but also an inevitable requirement for high-quality development of enterprises in the digital economy era.
3.2. Investor behavior spillover
From the perspective of financial social media, in the study of the impact of corporate digital transformation on investor sentiment, current research on investor behavior spillovers mainly focuses on three directions: the first is the spillover effect of investor behavior on price indicators; the second is the cross-market investor behavior spillover; and the third is the mediating role of investor behavior in other spillover relationships. In the chain of the impact of corporate digital transformation on investor sentiment, investor behavior does not exist in isolation, but as an important mediating variable, it connects the spillover relationship between corporate digital transformation and various economic phenomena. The digital transformation of enterprises changes the fundamentals of enterprises and market expectations by improving production efficiency, innovating products and services, and thus affecting investor sentiment [13-14]. Changes in investor sentiment will in turn affect the financing costs and capital structure of enterprises through their investment behavior, and ultimately affect the operation of the entire macroeconomic system. In this process, investor behavior plays an intermediary role of transmission and amplification, allowing the impact of corporate digital transformation to spill over across different levels and fields.
In-depth research on the impact of corporate digital transformation on investor sentiment from the perspective of financial social media, especially the key link of investor behavior spillover, has important theoretical and practical significance for understanding the operating mechanism of the financial market, optimizing corporate decision-making, and guiding investors to make rational investments. This not only helps to reveal the complex interaction between corporate behavior and market response in the financial social media environment but also provides a scientific basis for policymakers to formulate more effective regulatory policies and guiding measures to promote the stability and healthy development of the financial market.
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Experimental setup
In order to effectively control the factors that may interfere with the analysis of the impact of corporate digital transformation on investor sentiment, this paper constructs a multi-level analysis framework from the variable control dimension: First, the enterprise characteristic dimension variables, including the nature of corporate property rights (State), business scale (Size), and the degree and quality of implementation of digital transformation (Quality). Second, the investor dimension are variables, management shareholding incentives (Mshare), board size (Board), the degree of implementation of the independent director system (Indb), and market sentiment and macro environment (Market). Third, the technology and social dimension variables, include technology maturity, security (Maturity) media, as well as public opinion influence (Influence). The specific definition of each variable is detailed in Table 1.
Table 1: Variable definitions
Variable type | Variable | Variable symbol | Variable definition |
Dimension of enterprise characteristics | Property rights nature | \( State \) | State owned enterprises have a value of 1, while others have a value of 0 |
Scale | \( Size \) | Natural logarithm of total assets of the enterprise | |
Digital quality | \( Quality \) | The high level of enterprise digitalization is 1, otherwise it is 0 | |
Investor dimension | Stock holding incentives | \( Mshare \) | Natural logarithm of employee shareholding |
Board size | \( Board \) | Natural number of board members | |
The degree of implementation of the independent director system | \( Indb \) | When the chairman and general manager are assumed by one person, the value is 1. Otherwise, it is 0 | |
Market sentiment | \( Market \) | The market sentiment is high at 1 and low at 0 | |
Technological and social dimensions | Technology maturity | \( Maturity \) | Technology maturity is 1, otherwise it is 0 |
Media influence | \( Influence \) | Media influence is 1, otherwise it is 0 |
The table above creates a detailed analysis framework from various angles, which helps to effectively manage interference factors when studying how corporate digital transformation affects investor sentiment. By clarifying the specific definition of each variable, subsequent research can more accurately analyze the relationship between each factor and investor sentiment, and improve the reliability and validity of the research results. The descriptive statistical results of these variables are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics of variables
Variable | Mean value | Standard deviation | Minimum value | Maximum value |
\( State \) | 0.808 | 0.21 | 0.399 | 0.439 |
\( Size \) | 25.643 | 1.891 | 19.572 | 25.742 |
\( Quality \) | 0.808 | 0.2 | 0.569 | 0.1 |
\( Mshare \) | 26.937 | 6.506 | 0.199 | 28.564 |
\( Board \) | 1.766 | 1.985 | 1.975 | 1.696 |
\( Indb \) | 1.347 | 1.756 | 1.956 | 1.517 |
\( Market \) | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.459 | 0.05 |
\( Maturity \) | 0.09 | 0.948 | 0.609 | 0.968 |
\( Influence \) | 1.317 | 1.107 | 1.666 | 1.227 |
As shown in Table 2, most enterprises in the sample are state-owned enterprises (mean 0.808, standard deviation 0.21 for variable 'Ownership type'); the size of enterprises varies to some extent (mean 25.643, standard deviation 1.891 for variable 'Business size'); the degree of digitalisation of most enterprises is high (mean 0.808 for variable 'Digital quality', mean 0.808, standard deviation 0.2).
4.2. Statistics on emotional communication in financial social media
This paper focuses on the communication effect of articles and comments on the digital transformation of enterprises in a financial column under social media, and studies the data from September 2, 2020 to March 31, 2024. The study classifies the texts by statistically analyzing the emotions shown in 1,418 articles and comments, using the number of readings as an indicator of the popularity of information disclosure, and the number of likes and reposts as indicators of the accuracy of audience understanding. The descriptive statistical results of the main variables are shown in Figure 1.
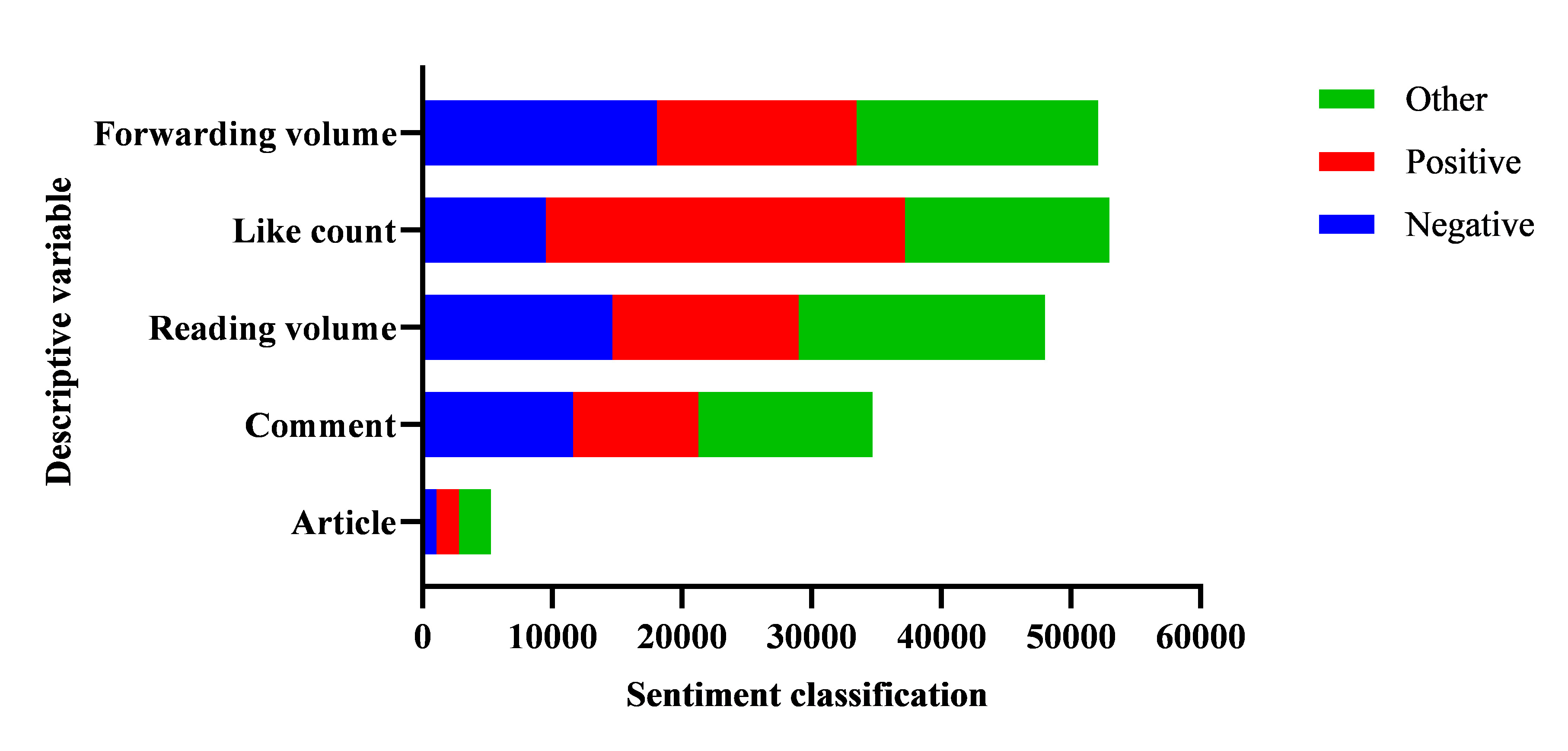
Figure 1: Statistics on sentiment communication on financial social media
According to Figure 1, the number of negative comments far exceeds that of articles, the number of articles with positive emotions is less than that of comments, and the number of comments with other emotions is also higher than that of articles. The emotions of comments are more diverse and negative ones are prominent. In terms of the popularity of information disclosure (reading volume), there is little difference between texts with different emotions, and emotions have limited impact on reading volume. In terms of audience understanding accuracy, the number of likes for articles with positive emotions far exceeds that for negative and others, and the number of likes for comments with negative emotions is relatively low; in terms of forwarding volume, there is no obvious difference between articles and comments with different emotions. That is, articles with positive emotions are more likely to get likes, and the impact of comment emotions on forwarding volume is not significant, and the correlation between reading volume and emotions is low.
The study then uses the number of readings as an indicator to measure the popularity of information disclosure, the number of likes and reposts as indicators to measure the accuracy of audience understanding, and constructs a comprehensive indicator to measure the speed of emotional communication. The comprehensive indicator of emotional communication speed is defined as:
\( V=α×Reading+β×Likes+γ×Retweets \) (1)
In formula (1), α, β, and γ are weight coefficients. To simplify the analysis, assuming that the weights of the three are equal, that is, \( α=β=γ=\frac{1}{3} \) . The study then compares the time limits of the spread of two emotions under the most recent 10 articles on the social media. This is illustrated in Figure 2.
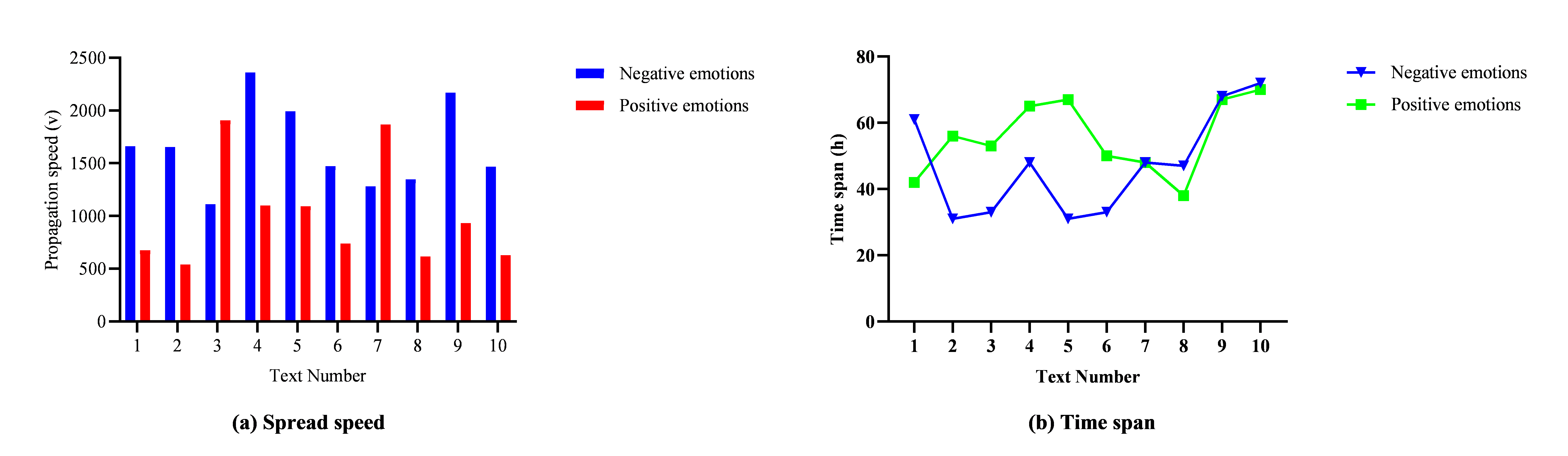
Figure 2: The spread of two emotions on this social media
As shown in Figure 1 (a), in terms of the time limit of emotional transmission, for negative emotions, the time limits of transmission of each article vary greatly, and the time limits of negative emotions in most articles are higher than those in positive emotions. This indicates that negative emotions tend to persist longer on this social media platform, while positive emotions sometimes spread more rapidly As shown in Figure 1 (b), the time spans of transmission of negative and positive emotions in articles are quite different, which proves that the emotional tendencies of most articles do not have a two-level differentiation trend.
4.3. Investor sentiment survey
The study selects 108 investors with different investment experience, risk preferences and fields as interview subjects to ensure sample diversity and representativeness. The research team designs a detailed interview outline covering basic information, cognition, investment tendency, expected impact and other dimensions. In the hope of revealing the considerations that investors tend to take under the influence of social media, the experimental results are shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Proportion of investors’ investment preferences under the influence of social media
Consideration factors | Specific content | Investor preference ratio |
Reliability of social media information | Reliable and trustworthy | 45% |
Complexity requires caution | 35% | |
Most of them are not trustworthy | 20% | |
The impact of social media information on investment decisions | Significant impact and adjustment of plans | 30% |
Has an impact but requires comprehensive judgment | 50% | |
The impact is relatively small, mainly based on self analysis | 20% | |
Cognition and investment intention of enterprise digital transformation | Very familiar and strongly willing | 25% |
Have a certain understanding and willingness | 45% | |
Less understanding and lower willingness | 30% | |
Expected investment returns | Expected higher returns | 50% |
Expected to have certain returns but uncertain | 35% | |
Expectations are not very optimistic | 15% |
Through the analysis of the data in Table 3, it can be seen that in terms of the reliability of social media information, 45% of investors believe that it is reliable and trustworthy; in terms of the impact on investment decisions, 50% believe that it has an impact but needs to be comprehensively judged. In terms of the recognition of corporate digital transformation and investment willingness, 45% have a certain understanding and willingness. In terms of expected investment returns, 50% expect higher returns. The experimental results show that most investors have a positive attitude towards corporate digital transformation and are willing to increase investment, but investment decisions are jointly influenced by multiple factors such as technology maturity, market acceptance, corporate strategic planning and policy environment.
5. Conclusion
This study conducts an in-depth discussion of the impact of corporate digital transformation on investor sentiment from the perspective of financial social media. The study finds that financial social media, as a core platform for information dissemination and communication, significantly amplifies the impact of corporate digital transformation information on investor sentiment, and investor behavior shows a significant spillover effect on price indicators. Positive emotions drive stock prices up and improve returns, while negative emotions lead to the opposite result. At the same time, investor behavior has significant spillover across markets. The investor sentiment fluctuations caused by the digital transformation of enterprises in one market will quickly spread to other markets, triggering a chain reaction. In addition, investor behavior plays an important mediating role in a variety of spillover relationships, connecting different levels such as enterprise digital transformation and macroeconomic operation. These findings show that in the financial social media environment, corporate digital transformation is no longer an isolated corporate behavior, but has a broad and far-reaching impact on the financial market and even the macroeconomic system by influencing investor sentiment and behavior. However, this study also has certain limitations. For example, the limitations of the data sample may affect the universality of the research results to a certain extent, and the accuracy of the measurement of investor sentiment and behavior needs to be further improved. Based on the above findings and discussions, it is recommended that future research further expand the data source, adopt more accurate measurement methods, and deeply explore the internal mechanism and influencing factors of investor behavior spillover.
References
[1]. Wang Y, He P. Enterprise digital transformation, financial information disclosure and innovation efficiency[J]. Finance Research Letters, 2024, 59(1): 104707-104713.
[2]. Kalinin O, Gonchar V, Abliazova N, et al. Enhancing Economic Security through Digital Transformation in Investment Processes: Theoretical Perspectives and Methodological Approaches Integrating Environmental Sustainability[J]. Natural and Engineering Sciences, 2024, 9(1): 26-45.
[3]. Zhao X, Huang Q, Xing Y, et al. The motivating effect of positive social emotions on digital transformation of manufacturing enterprises–evidence from financial news and public opinion[J]. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 2024, 1(1): 1-15.
[4]. Hussain S M, Alaya A. Investor response to financial news in the digital transformation era: the impact of accounting disclosures and herding behavior as indirect effect[J]. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 2024, 22(2): 254-273.
[5]. Yang M J, Zhu N. Online public opinion attention, digital transformation, and green investment: A deep learning model based on artificial intelligence[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 371(1): 123294.
[6]. Liu Q, Lee W S, Huang M, et al. Synergy between stock prices and investor sentiment in social media[J]. Borsa Istanbul Review, 2023, 23(1): 76-92.
[7]. Ji H, Miao Z, Wan J, et al. Digital transformation and financial performance: The moderating role of entrepreneurs’ social capital[J]. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 2024, 36(8): 1978-1995.
[8]. Liu J, Zhou K, Zhang Y, et al. The effect of financial digital transformation on financial performance: the intermediary effect of information symmetry and operating costs[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(6): 5059-5061.
[9]. Zheng S, Zhang Y, Chen Y. Leveraging Financial Sentiment Analysis for Detecting Abnormal Stock Market Volatility: An Evidence-Based Approach from Social Media Data[J]. Academia Nexus Journal, 2024, 3(3): 11-21.
[10]. Paul J, Ueno A, Dennis C, et al. Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary perspective and future research agenda[J]. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 2024, 48(2): 13015-13017.
[11]. Wu Y, Li H, Luo R, et al. How digital transformation helps enterprises achieve high-quality development? Empirical evidence from Chinese listed companies[J]. European Journal of Innovation Management, 2024, 27(8): 2753-2779.
[12]. Sun Z, Wang W, Wang W, et al. How does digital transformation affect corporate social responsibility performance? From the dual perspective of internal drive and external governance[J]. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 2024, 31(2): 1156-1176.
[13]. Chowdhury E K, Humaira U. Transformation of investor attitude towards financial markets: A perspective on the Russia–Ukraine conflict[J]. International Social Science Journal, 2024, 74(252): 561-583.
[14]. Zareie M, Attig N, El Ghoul S, et al. Firm digital transformation and corporate performance: The moderating effect of organizational capital[J]. Finance Research Letters, 2024, 61(1): 105032-105037.
Cite this article
Guo,Y. (2025). The Impact of Corporate Digital Transformation on Investor Sentiment: A Perspective from Financial Social Media. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,184,20-28.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICMRED 2025 Symposium: Effective Communication as a Powerful Management Tool
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wang Y, He P. Enterprise digital transformation, financial information disclosure and innovation efficiency[J]. Finance Research Letters, 2024, 59(1): 104707-104713.
[2]. Kalinin O, Gonchar V, Abliazova N, et al. Enhancing Economic Security through Digital Transformation in Investment Processes: Theoretical Perspectives and Methodological Approaches Integrating Environmental Sustainability[J]. Natural and Engineering Sciences, 2024, 9(1): 26-45.
[3]. Zhao X, Huang Q, Xing Y, et al. The motivating effect of positive social emotions on digital transformation of manufacturing enterprises–evidence from financial news and public opinion[J]. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 2024, 1(1): 1-15.
[4]. Hussain S M, Alaya A. Investor response to financial news in the digital transformation era: the impact of accounting disclosures and herding behavior as indirect effect[J]. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 2024, 22(2): 254-273.
[5]. Yang M J, Zhu N. Online public opinion attention, digital transformation, and green investment: A deep learning model based on artificial intelligence[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 371(1): 123294.
[6]. Liu Q, Lee W S, Huang M, et al. Synergy between stock prices and investor sentiment in social media[J]. Borsa Istanbul Review, 2023, 23(1): 76-92.
[7]. Ji H, Miao Z, Wan J, et al. Digital transformation and financial performance: The moderating role of entrepreneurs’ social capital[J]. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 2024, 36(8): 1978-1995.
[8]. Liu J, Zhou K, Zhang Y, et al. The effect of financial digital transformation on financial performance: the intermediary effect of information symmetry and operating costs[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(6): 5059-5061.
[9]. Zheng S, Zhang Y, Chen Y. Leveraging Financial Sentiment Analysis for Detecting Abnormal Stock Market Volatility: An Evidence-Based Approach from Social Media Data[J]. Academia Nexus Journal, 2024, 3(3): 11-21.
[10]. Paul J, Ueno A, Dennis C, et al. Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary perspective and future research agenda[J]. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 2024, 48(2): 13015-13017.
[11]. Wu Y, Li H, Luo R, et al. How digital transformation helps enterprises achieve high-quality development? Empirical evidence from Chinese listed companies[J]. European Journal of Innovation Management, 2024, 27(8): 2753-2779.
[12]. Sun Z, Wang W, Wang W, et al. How does digital transformation affect corporate social responsibility performance? From the dual perspective of internal drive and external governance[J]. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 2024, 31(2): 1156-1176.
[13]. Chowdhury E K, Humaira U. Transformation of investor attitude towards financial markets: A perspective on the Russia–Ukraine conflict[J]. International Social Science Journal, 2024, 74(252): 561-583.
[14]. Zareie M, Attig N, El Ghoul S, et al. Firm digital transformation and corporate performance: The moderating effect of organizational capital[J]. Finance Research Letters, 2024, 61(1): 105032-105037.









