1. Introduction
With the development of the times, China's healthcare industry has shown great potential. Artificial Intelligence (AI) healthcare, as an important part of the future healthcare industry, is driving the transformation of the healthcare industry. At the same time, private equity capital is highly active in the AI healthcare field. According to incomplete statistics from Zhiyao Bureau, in the first half of 2025, there were a total of 67 financing deals in the global AI+healthcare track, with a total amount of nearly 6 billion US dollars, and 17 financing deals exceeding 100 million US dollars, promoting the rapid development of the industry.
According to existing research, many biomedical companies in China generally face profitability difficulties in the early stages of entrepreneurship. Their development is highly dependent on policy promotion and government support [1]. In addition, in clinical applications, there are constantly emerging issues such as trust, regulation, and ethics regarding AI among patients and doctors. These issues make market regulation of the AI healthcare industry increasingly important [2]. Strict regulation has also generated high costs, bringing another challenge to the company's development. The demand for funding in the AI healthcare industry has led many companies to introduce private equity.
The existing literature has conducted in-depth research on the impact of introducing private equity on companies. Private equity can introduce capital to boost corporate profit growth, drive Initial Public Offering (IPO) processes, expand production lines, and help companies develop steadily [3]. In terms of governance, private equity investors strengthen the standardization of the internal governance structure and prevent operational risks by deeply participating in the decision-making process of the enterprise [4]. In terms of innovation, private equity can effectively promote corporate innovation, especially substantive innovation [5]. Compared to companies that have not introduced private equity investment, companies that have introduced private equity have more significant growth performance [6]. In addition to these positive effects, some scholars also believe that the introduction of private equity harms companies. For example, excessive involvement of private equity in a company may lead to strategic diversification and a decrease in business profitability [7]. Regardless of the viewpoint, existing research has fully demonstrated the crucial role of private capital in the development of enterprises. The participation of private equity funds can serve as a powerful market signal, completely replacing the impact of other signaling mechanisms such as board experience and network intermediaries on post IPO performance [8]. This indicates that the introduction of private equity funds will systematically change the decision-making weight and resource effectiveness within the company.
However, existing research is mostly focused on traditional industries, and there is still a gap in research on emerging and highly uncertain industries such as AI healthcare. At the same time, most studies focus on the economic performance after introducing private equity capital. There is a lack of detailed empirical research on the specific changes in corporate strategy.
Based on the above literature, this study aimed to supplement the theoretical gap of private equity in the field of AI healthcare. Also, this study hoped to provide decision-making references for AI healthcare entrepreneurs in practice, help private equity investors optimize post-investment management strategies, and provide microdata references for the formulation of relevant government policies.
This study adopted a longitudinal single case study method and selected Koya Medical Technology Co., Ltd (Koya Medical) as the research object. As a leading enterprise in the AI healthcare industry, Koya Medical has a large amount of data available for research and a relatively complete "Venture Capital (VC)- Private Equity (PE)" process. From 2019 to 2020, Koya Medical conducted multiple rounds of financing. After the D-round financing in December 2020, Koya Medical made strategic adjustments in multiple aspects and submitted its prospectus in 2021. This study conducted qualitative analysis on the collected data based on comparative analysis, presenting the changes in strategic focus, product development direction, recruitment of personnel, and IPO process of Koya Medical Company after introducing private equity.
2. Strategic focus: shifting from technological research and development to commercial implementation
The change in the focus of corporate strategy profoundly affects the changes in corporate strategic decision-making. After analyzing and organizing reports from various financial media and official websites, it can be concluded that before the introduction of private equity in 2020, Koya Medical's strategic focus was mainly on product research and development and obtaining product certification. After it was established in 2016, the company invested a large amount of manpower and funds in product research and development, and the overall business revolved around product research and technological upgrades. After conducting extensive product development, a number of clinical and registration personnel were recruited to be responsible for the clinical and regulatory certification of the products.
After the introduction of private equity in 2020, Koya Medical's strategic focus shifted to commercial development and market expansion. In addition to continuing to invest heavily in scientific research, the company began to focus on the application of its products in real clinical scenarios. Product research and development expanded to multiple fields and scenarios, and the product market developed from the domestic market to the foreign market.
In summary, after the introduction of private equity, the strategic focus of Koya Medical shifted from technology research and development to commercial implementation. This transformation profoundly influenced Koya Medical's strategic decision-making, resulting in significant changes in product development direction, recruitment of personnel, IPO process, and other aspects.
3. Product development direction: increase in application-oriented patents and accelerated market expansion
To objectively evaluate the changes in product development direction of Koya Medical, this study conducted a statistical analysis of the patents applied for by Koya Medical in recent years. The patents currently applied for by Koya Medical can be divided into two categories: technical products focused on core algorithms, models, and technologies, and applied products focused on specific medical application scenarios.

According to Figure 1, before the introduction of private equity in 2020, Koya Medical mainly applied for technical products, with very few applied products. After the introduction of private equity in 2020, the number of applied products significantly increased, with the most significant change in 2021. The significant increase in the number of application-oriented patent applications reflected the company's research and development direction shifting towards product landing and commercialization, focusing on the investment in specific clinical scenarios to achieve faster commercial returns. A separate analysis of patents after 2020 reveals that, in addition to a significant increase in the number of applied products, patents have rapidly expanded horizontally since 2020. They covered multiple disease fields and clinical scenarios, making the market expand and develop. At the same time, the application for international patents after 2020 also indicated that Koya Medical began to expand internationally, providing certain guarantees for the exit of private equity.
4. Recruitment of personnel: sales personnel increased significantly, and the commercial team was established on a large scale
As an emerging technology-based company, Koya Medical had a high demand for product research and development in the early stages of its establishment, so recruitment positions were highly concentrated in research and development technology positions. At the same time, a large-scale clinical registration team was established to provide guarantees for clinical trials and product certification. In 2020, Koya Medical completed several major rounds of financing and experienced significant changes in its workforce. According to the prospectus data, in 2020, the workforce of Koya Medical doubled from 150 to 300, with 65% of the increase in talent coming from the sales team and 35% from the research and development team.
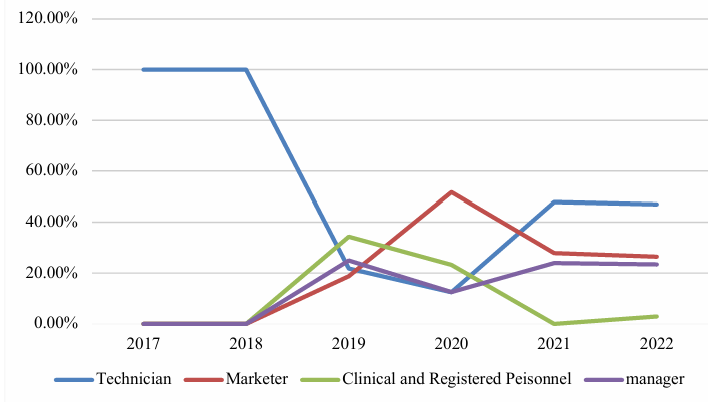
According to the data in Figure 2, from 2017 to 2019, the main recruitment positions for Koya Medical were technicians. In 2020, the recruitment positions for marketers accounted for the highest percentage of the total recruitment positions, and maintained a high level, indicating that the introduction of private equity in 2020 shifted the strategic focus of Koya Medical to sales and marketing. By establishing a large-scale sales and marketing team, it ensured the commercialization of various certified products. After 2020, although technicians returned to the focus of recruitment, sales positions remain high. The company continued to explore commercialization while ensuring technology research and development, becoming important evidence of the influence of private equity on the recruitment of personnel.
5. IPO process: IPO process significantly accelerates
Before Koya Medical secured private equity investment in January 2020, its "Deep Pulse Score" had obtained China's first Class III Artificial Intelligence Medical Device Certificate. Meanwhile, the product had also secured triple certifications from China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the EU Conformité Européenne (CE) . The certification obtained from the 'Deep Pulse Score' allowed it to be sold and used in hospitals. In the same year, Koya Medical recruited a large number of sales and marketing personnel, forming a large-scale commercial team. The certification of "Deep Pulse Score" and the establishment of the business team laid a certain foundation for the Initial Public Offering (IPO) of Koya Medical.
In 2020, Koya Medical conducted five rounds of financing, with the largest Series D financing in December. In the D-round financing, there are many well-known investment companies, including China International Capital Corporation (CICC) Capital. The addition of CICC Capital provided a strong endorsement for the development of Koya Medical, which can attract many external investments. At the same time, as one of the top investment banks and financial institutions in China, CICC's rich investment experience and talents can bring new strength to the development of Koya Medical and play a significant role in promoting the company's IPO process.
On March 16, 2021, Koya Medical officially submitted its prospectus to the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, intending to be listed on the Hong Kong Main Board, becoming the first medical imaging AI company to enter the IPO stage. From the completion of the D-round financing in December 2020 to the submission of the prospectus in March 2021, Koya Medical provided strong evidence of the impact of private equity on the company through its rapid IPO process. It can be seen that private equity played a significant role in promoting the IPO process of enterprises with a certain degree of commercialization, and was an efficient catalyst for the IPO process of enterprises.
6. Discussion
This study suggested that the introduction of private equity enabled companies to make overall strategic decisions centered around commercialization. The reason for this phenomenon is partly due to the need for private equity to increase value and successfully exit within a certain period of time. IPO, as a classic exit method that allows private equity investors to obtain high returns, has been relatively active in the Chinese market in recent years [9]. This goal requires the company to form a business team and produce a series of commercially valuable products to achieve profit growth. Private equity firms can also provide the company with rich management experience and talent, helping the company to undergo commercial transformation and accelerate its IPO process. On the other hand, after introducing private equity, the company will not only obtain sufficient funds, but also gain rich management experience and a good business reputation brought by private equity institutions. Meanwhile, private equity can effectively improve the risk-taking level of enterprises [10]. In this situation, in order to achieve sustainable and better development, the company will choose to accelerate commercialization in order to obtain higher returns and opportunities for the company to go public.
7. Conclusion
According to this study, after introducing private equity, the strategic focus of AI healthcare companies will shift from technology research and development to commercial implementation, with an increase in the development of applied products, accelerated market expansion, and large-scale construction of commercial teams, ultimately leading to a significant acceleration of the IPO process. For entrepreneurs and managers in the AI healthcare industry, they should fully consider the company's actual development situation, clarify the company's development direction after introducing private equity, make reasonable decisions based on the company's assets and personnel situation,; For private equity investors, they should actively engage in post investment management of the company, not only providing management and business experience, but also timely assessing the company's development status and market conditions, finding suitable IPO opportunities, and helping the company complete its listing. For government policy makers, they can increase funding support for the AI healthcare industry to assist in its long-term healthy development. This study has certain limitations. Firstly, the study adopts a single case study method, which lacks universality. Secondly, this study is entirely based on the analysis and research of publicly available company data, and has not researched some deep-seated private data. Finally, this study did not consider other factors that may affect company decision-making. Therefore, in future research, it is hoped to conduct multi-case comparative analysis, collect data from multiple companies for horizontal comparative research, deeply mine relevant data for long-term tracking, and attempt to explore the impact of different influencing factors on company strategic decision-making.
References
[1]. Liu, J. J. (2023) Analysis and Risk Control of Biomedical and Health Industry Investment. Technology and Economic Market 3, 10-12.
[2]. Mo, L. (2025) AI in Healthcare Becomes a New Blue Ocean for Global Investment. Financial Times 8, 36-44.
[3]. Wang, X. N. & Yan, L. (2025) Research on the Motivation and Post-Investment Performance of Introducing Private Equity Investment. Journal of Hubei University of Economics (Humanities and Social Sciences), 22, 55-58.
[4]. Zhang, Y. L. (2024) The Role of Private Equity Investment in the Financing of Technology-Based Enterprises. International Business Accounting 21, 88-91.
[5]. Nuchao, L., Ying, W. & Li, H. (2023) Does Private Equity Investment Influence Enterprise Innovation Strategy?. Finance Research Letters, 58, 104-159.
[6]. Huang, J. (2023) Research on the Impact of Private Equity Investment on Corporate Value and Performance. China Circulation Economy 5, 93-96.
[7]. Wu, J. Z. & Jiang, S. (2018) Private Equity Participation, Corporate Social Responsibility, and Profitability: Evidence From the NEEQ Market. Journal of Chongqing Technology and Business University (Social Sciences Edition), 35, 40-48.
[8]. Charles, K., Luciano, R., Andrea, M. et al. (2023) The Tradeoff Between Private Equity Sponsorship, Board Centrality, and Experience as Credible Signals for IPO Performance. Management and Organization Review, 19, 462-497.
[9]. Xu, H. H. (2024) Discussion on the Current Situation and Development Direction of Private Equity Investment Exit Mechanisms in China. Financial Community 35, 69-71.
[10]. Yang, S. & Du, Y. (2025) Private Equity and the Risk-Taking of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Finance Research Letters, 85, 108-194.
Cite this article
Yu,N. (2025). The Impact of Private Equity Investment on Strategic Decision-Making in Artificial Intelligence Healthcare Companies: A Case Study of Keya Medical. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,242,13-18.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-BPS 2026 Symposium: Sustainability Transitions and Regional Economic Restructuring in New Contexts
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Liu, J. J. (2023) Analysis and Risk Control of Biomedical and Health Industry Investment. Technology and Economic Market 3, 10-12.
[2]. Mo, L. (2025) AI in Healthcare Becomes a New Blue Ocean for Global Investment. Financial Times 8, 36-44.
[3]. Wang, X. N. & Yan, L. (2025) Research on the Motivation and Post-Investment Performance of Introducing Private Equity Investment. Journal of Hubei University of Economics (Humanities and Social Sciences), 22, 55-58.
[4]. Zhang, Y. L. (2024) The Role of Private Equity Investment in the Financing of Technology-Based Enterprises. International Business Accounting 21, 88-91.
[5]. Nuchao, L., Ying, W. & Li, H. (2023) Does Private Equity Investment Influence Enterprise Innovation Strategy?. Finance Research Letters, 58, 104-159.
[6]. Huang, J. (2023) Research on the Impact of Private Equity Investment on Corporate Value and Performance. China Circulation Economy 5, 93-96.
[7]. Wu, J. Z. & Jiang, S. (2018) Private Equity Participation, Corporate Social Responsibility, and Profitability: Evidence From the NEEQ Market. Journal of Chongqing Technology and Business University (Social Sciences Edition), 35, 40-48.
[8]. Charles, K., Luciano, R., Andrea, M. et al. (2023) The Tradeoff Between Private Equity Sponsorship, Board Centrality, and Experience as Credible Signals for IPO Performance. Management and Organization Review, 19, 462-497.
[9]. Xu, H. H. (2024) Discussion on the Current Situation and Development Direction of Private Equity Investment Exit Mechanisms in China. Financial Community 35, 69-71.
[10]. Yang, S. & Du, Y. (2025) Private Equity and the Risk-Taking of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Finance Research Letters, 85, 108-194.









