1. Introduction
In the traditional concept of many Chinese people, "tasting coffee" belongs to the spiritual and cultural aspects, and the warm atmosphere of cafes can bring good experience and perception to consumers. Talk about Chinese coffee brands, the most well-known one is Starbucks, which has always been considered the most popular brand. Starbucks Coffee Company was founded in 1971, headquartered in Seattle, Washington, USA. Starbucks' goal is to find and roast high-quality Coffee with good taste around the world. With more than 32,000 stores in 82 markets, Starbucks is the world's premier specialty coffee roaster and retailer. Starbucks puts coffee and its customers at the core and strives to live up to the following values. The first one is to create a culture of warmth and belonging that embraces and welcomes everyone. The second is to take positive action, to dare to challenge the status quo and break old rules in an innovative way in order to achieve the company's and its partners' common growth. The third is that Starbucks is dedicated, open, and respectful to each other at all times when they interact. The fourth one is to Starbucks does everything it can to be the best and responsible. From the humanistic perspective, Starbucks pursues outstanding performance.
Besides, data and information show that Starbucks coffee has different prices in different countries. According to this pricing situation, the research topic is the main factor that makes Starbucks coffee sales different in different countries. From the information in the internet, there is very little research on the factors that influence Starbucks prices in different countries. Most people just compare Starbucks price data in different countries and make a simple comparison. The research method is to find the price data of Starbucks in different countries and borrow some content from existing papers. The significance of the study is to understand the factors that contribute to Starbucks coffee price differences. Therefore, we can know the pricing secrets for different market conditions.
2. Universal Pricing Strategy
There are four pricing strategies of Starbucks: cognitive value pricing, product line pricing, reverse complementary and targeted promotion pricing. The four pricing strategies of Starbucks are also closely related to the factors that affect the price of coffee, so this paper will introduce the four pricing strategies of Starbucks.
2.1. Cognitive Value Pricing
Starbucks' business philosophy is to provide customers with world-class coffee and consumption experiences. To do so, Starbucks uses the best coffee beans from the world's major coffee regions and roasts them in Seattle. There are dozens of varieties based on coffee beans from various locations, different brewing technology, and the process to produce different tastes; the staff should be trained for about 3 months. Coffee knowledge and coffee drinking methods are held to high standards. In Starbucks, you can also buy coffee making equipment and related small items that are difficult to find in ordinary coffee shops, such as portable coffee machines, milk balls, seasonal water cups and other exquisite products. Starbucks has also done a lot to shape the coffee scene. The store design of all Starbucks stores comes from the professional design team at the headquarters. Starbucks' well-crafted Spaces have become the best third choice for many people, after their homes and workplaces, where they can order a cup of coffee and study while working. This good atmosphere brings consumers a great experience [1].
This makes Starbucks coffee the most professional, unique and popular product. Starbucks coffee has eternal excellent taste and excellent service quality. Brand equity is regarded by consumers as a symbol of "fashion, success and status", which also greatly improves the perceived value of products, so it naturally reduces consumers' sensitivity to prices. Most Starbucks customers are satisfied with the price of a medium cup of coffee, which can cost as much as 22 yuan, according to a survey by Starbucks in Shanghai. In fact, the brand premium may account for about half of the price. There is no doubt that perceived value pricing has created huge profit margins for Starbucks.
2.2. Product Line Pricing
Starbucks offers a dizzying array of beverage choices, as well as a wide range of fresh and delicious pastries. Cooperating the change of the season, and the demand of consumer of different country, different area, variety of its design and color still is renewing ceaselessly. The wide variety of Starbucks coffee fully reflects the image of the world's top coffee brand. At the same time, the pricing strategy of the product line is also conducive to attracting customers and expanding the audience, thereby increasing product sales and company profits. When Starbucks opened its first store in western China in September 2005, there were many different flavors of coffee on the market. Surprisingly, the lowest price for a cup of coffee is just 12 yuan. The most expensive coffee caramel macchiato is 32 yuan/cup, mocha is 23-30 yuan/cup, cappuccino is 19-26 yuan/cup, latte is 17 yuan/cup. When consumers compare the price of Starbucks coffee with their own price expectations and the prices of other brands of coffee, They may think that Starbucks coffee is not much more expensive than other brands of coffee, and some coffee is even cheaper than others, so they are more likely to accept the price of Starbucks coffee [2].
2.3. Reverse Complementary Pricing
According to the general pricing logic, in a restaurant or similar establishment, the main specialty food is often cheap, but the related other food is very expensive, this is a typical complementary pricing strategy. The low price of the main product is conducive to expanding the sales of the product, thereby driving the sales of the ancillary products, and the enterprise can obtain higher profit returns from the ancillary products. By this logic, cafes should charge high margins for snacks like cupcakes, while coffee itself is a cheap commodity. But Starbucks is doing the opposite [3].
At Starbucks, a variety of fresh and delicious pastries are quietly interpreting the coffee category. These foods are perfect for tasting while drinking coffee, creating the perfect texture with the coffee. The advantage of Starbucks' unusual reverse complementary pricing lies in the fact that it has already made a fat profit on coffee, while allowing customers to taste and experience delicious desserts. It's a win-win strategy to get customers to buy coffee and desserts.
2.4. Targeted Promotional Pricing
Promotional pricing is when a company temporarily lowers the price of a product below the normal price, sometimes even below cost, in order to create an impulse and sense of urgency among consumers to buy. In addition to the usual price reductions, like a 15-day $5 cash coupon, Starbucks places a special emphasis on the experience and word-of-mouth of its regular customers. Starbucks in January 2006 introduced a "VIP club", the members of the welfare is in addition to fixed news information via email, you can also send messages by mobile phones, or you can download games on the Internet, once pass you can get coupons, many consumers will put forward this message to other friends, such not only can be their own profit, It also helps Starbucks get free publicity, which is a win-win measure. Starbucks in Shanghai has also pioneered electronic invoicing. The bottom of the electronic invoice is designed as a coupon, and the back is a coffee room, which introduces the characteristics of various coffees [4].
3. Factors Influencing the Price of Coffee
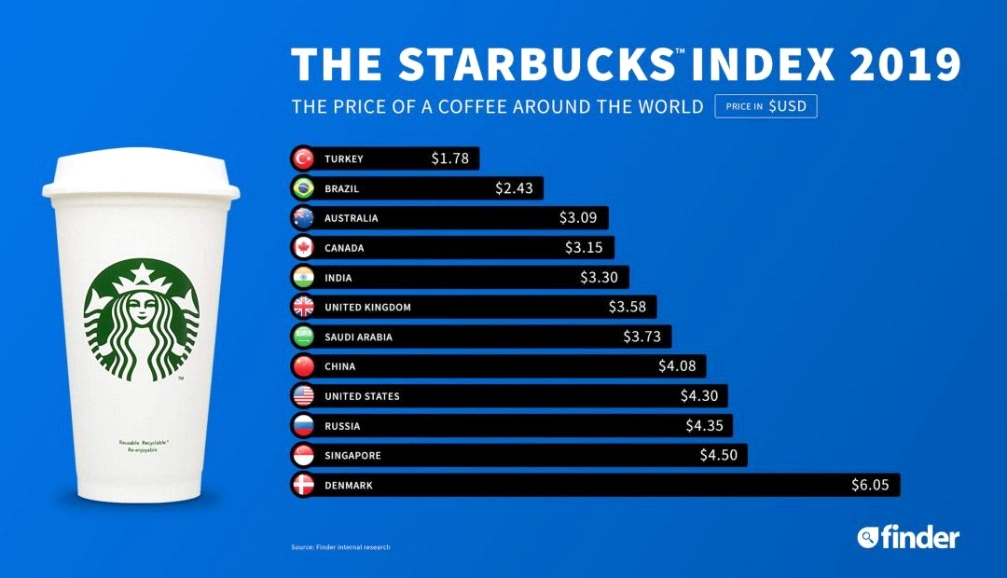
Figure 1: The price of a tall Starbucks latte in the different countries in 2019.
This ranking shows the countries in the study where coffee prices rank from lowest to highest: Turkey, Brazil, the United States, China, and Denmark. The lowest price is in Turkey and the highest price is in Denmark. Next, this paper will combine the characteristics of these five countries and the pricing strategy of Starbucks to analyze the factors that affect the different prices of Starbucks in different countries.
3.1. Cost
Starbucks uses cognitive value pricing, which is one of its pricing strategies, so there will be high economic levels of Starbucks stores in some countries that will carefully create a high-end grade of atmospheric environment and bring customers a good feel and experience so that products greatly improve their perceived value and the sensitivity of the consumer to price is reduced. However, such a practice incurs high labor, rent, and other costs for Starbucks, so the price of coffee is naturally raised to ensure profit. However, people in less developed countries do not have the economic ability to have such a sophisticated coffee buying experience, so Starbucks will not spend a lot of money on the stores in these countries, and the price of coffee in these countries will naturally be lower.
It is not difficult to draw from the graph, the price seems expensive countries for developed countries, the local price level and income level had higher than in other countries, Starbucks its cost high price includes a range of factors, such as infrastructure, labor, raw materials, currency, shop rent, etc., so when you drink Starbucks coffee, actually not just coffee drink, it also includes the entire store, cups, advertisements, and even the entire brand. Rent accounts for the largest portion of coffee pricing (26%), followed by profit (18%), store operating expenses (15%), raw materials (13%), and labor (9%). In Switzerland, the waiters at Starbucks are well paid, so it's understandable that the coffee is the most expensive. Among the six countries in the study, the three countries with higher prices are all developed countries, and the rent, the cost of production materials and the salary of employees are all higher, so the total cost is higher. To ensure profit, the price of coffee will naturally be higher at last. The three countries with lower coffee prices are all less developed countries. The overall economic level of these three countries is low, so they have low rent costs, labor costs and other costs, so the overall cost is low, and the price of coffee will naturally be lower at last.
Many people believe that Starbucks' coffee is excellent, but Starbucks is only good at consistent quality control and management; it is cheap with coffee beans, but Starbucks is still sought after by the masses of Chinese because it sells not only coffee, but also the experience of a coffee shop; the purpose of the Starbucks environment is to make you relax and sit for a long time. If you often go to Starbucks, you can also carefully observe the conversations of the service staff. In fact, they are all designed, from friendly greetings, smooth ordering, product recommendation, retelling the customer's order, and drawing a friendly smile on the cup. Starbucks is good at "atmosphere" management, which is exactly what consumers want. However, these created environmental atmosphere requires a large cost, for example, employees need to go through a long time of training, the store needs to be selected in relatively high-end buildings, so the rent will naturally be higher, and for example, the purchase of some high-end in-store decorations or chairs also needs to spend a certain cost. Therefore, the total cost is still relatively high. In order to maintain stable profitability, the price of coffee must be increased, but when customers experience good service, they will think that the coffee is worth paying more price [5].
3.2. Market Requirement
The degree of consumer preference for coffee is different, but the market demand is different. People in different countries or different cities have different degrees of preference for coffee. Countries with a high preference for coffee will have a large demand for coffee, so they are prone to shortages and higher coffee prices. Countries with a large coffee market are likely to be in short supply, so the price of coffee will be higher.
The top 10 countries in the world for annual coffee consumption per capita in 2022 were Luxembourg, Finland, Denmark, Norway, Switzerland, Sweden, Germany, Austria, Canada and Slovenia, according to official data. We can see from the rankings that Denmark's coffee consumption is very large, but before a few years, the annual coffee consumption statistics showed that Denmark basically ranked in the top three. This shows that the Danish people's preferences in coffee are very high, so the coffee demand in the Danish market is very large, so it's easy to have a tight situation and the price of coffee is on the high side.
Taking the US as an example, the 2020 US Coffee Market Report estimates the size of the US coffeehouse market to reach approximately $47.5 billion, growing by 3.3% over the past 12 months. Notably, Starbucks and Dunkin accounted for 80% of new store openings in the U.S. over the past year. In addition to a 3.3 per cent increase in the number of cafe outlets, total coffee sales rose 4.3 per cent.
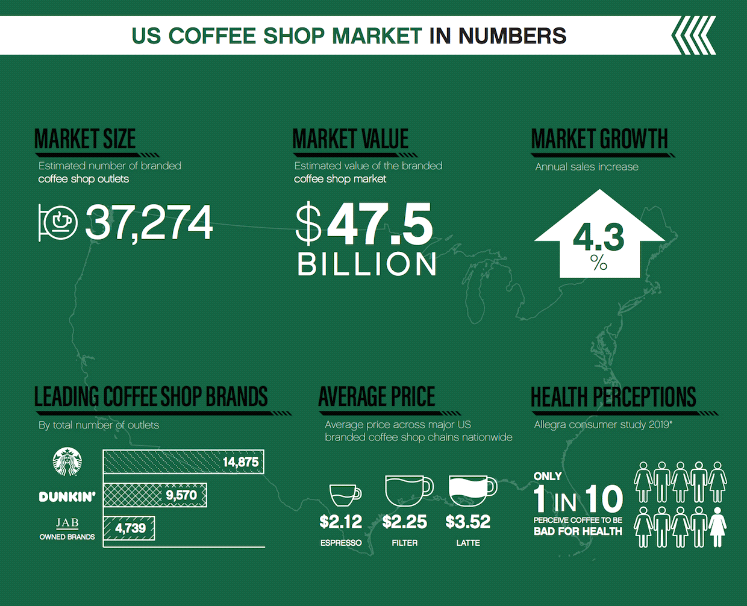
Figure 2: The US coffee shop market in numbers.
As can be seen from the picture on the left, the coffee market in the United States is large and growing. We can see that the market demand for coffee in the United States is also very high, so the price of coffee is relatively high.
3.3. Geographic Position
The most important raw material for coffee is the coffee bean, and different countries have different distances from where the beans are grown. Countries closer to where the beans are grown have geographical advantages. Starbucks can directly pick and grind coffee beans in China to make coffee, which reduces the transportation cost of coffee beans, which also greatly reduces the cost of Starbucks, so the price of coffee will be lower.
Coffee beans are generally grown in South America, Asia and Africa. Because Europe lacks coffee bean origins, the price of coffee in Europe is generally higher. In Denmark, for example, local Starbucks stores need to buy coffee beans from other continents, which incurs high transportation costs. As a result, the cost of Starbucks increases, and the coffee price is naturally higher.
Brazil, the research object, is a big coffee producer. For more than 100 years, Brazil, a big country in South America, has been the world's undisputed largest coffee producer and known as the "coffee kingdom". It is famous for its high quality and strong taste of caffeine, so it is also the world's largest exporter of coffee. Brazil is located in tropical and subtropical areas, the unique geographical environment and climate conditions are very suitable for planting coffee trees, coupled with the cheap labor force, Brazil's coffee planting industry has rapidly prospered. In the 19th century, coffee cultivation in Brazil was almost all over the country, and reached its peak in the 1920s, accounting for 80% of the world's total coffee. Later, with the widespread cultivation of other countries, the proportion decreased, but the current coffee cultivation in Brazil is still 27,000 square kilometers. Starbucks stores in Brazil can grind coffee directly from locally grown beans, eliminating shipping costs and keeping prices low.
3.4. Competitor
Starbucks has different numbers of competitors in different countries. Starbucks also has different pricing strategies for its competitors in different countries.
For example, Starbucks' rivals in China are becoming more and more strong, and the former industry leader Starbucks is facing great challenges. First up is Luckin Coffee. Luckin sold out its "raw coconut latte" for a while, but later launched a series of new products that gained traction. Today, with a valuation of $60 billion and Nai Xue's tea successfully listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, it is also a force to be reckoned with. Chinese convenience store brand Convenience Bee has also opened an in-store beverage store called "Sleepless Sea". Official data shows that the "shop-within-store" model of Sleepless Sea Beverage Station has reached 102 stores in the Beijing market after four months. The price of "Never Sleeping Sea" boutique coffee is about 15 yuan, in addition to fruit tea, milk tea and ice products, the price advantage is obvious. As far as the Beijing market is concerned, Never Sleeping Sea also has an advantage in the number of stores. Add Tims, the Canadian national coffee brand, and COSTA coffee, which costs about the same as Starbucks, and Starbucks has plenty of competitors [6].
In view of this, Starbucks adopts targeted promotional pricing. Starbucks temporarily adjusts the price of products below the normal price, sometimes even below the cost, in order to create a sense of enthusiasm and urgency to buy coffee, and it can attract more customers to buy coffee drinks in the store. In addition to these, Starbucks also gives out coupons at certain times such as a 15-day cash coupon. Starbucks also attaches great importance to regular customers and word-of-mouth effect. It often provides some benefits to regular customers to maintain their brand loyalty, and it can avoid consumers being attracted by other brands.
According to the latest figures, Turkey has 520 Starbucks stores, the second highest number in Europe, far higher than any other European country. There are not many other coffee chains in Turkey compared to traditional European consumers, and Starbucks has few dangerous competitors in the Turkish market, so the company has been able to gain traction quickly. And developing countries such as Turkey, less developed domestic economic level, people's income is not high so might not be able to buy very expensive coffee drinks, so, Starbucks also adjusted the price in Turkey, coffee at a lower price, so can better seize the Turkey market, let the people there can afford to buy the product.
4. Conclusion
Based on the different situations of the five countries we studied and the four main pricing strategies of Starbucks, the research came up with the final findings: cost, market demand, location and competitors are the factors that affect the pricing of Starbucks in different countries. Of course, there may be other factors at play, but there are too many of them to list. This research still has some shortcomings that can be improved. For example, the analysis should combine the four pricing strategies of Starbucks more closely and logically with the factors that affect the pricing of Starbucks in different countries. For another example, we should analyze the coffee market of these five countries, which is conducive to a deeper study of the pricing factors of Starbucks.
References
[1]. Haskova, Katerina. "Starbucks marketing analysis." CRIS-Bulletin of the Centre for Research and Interdisciplinary Study 1 (2015): 11-29. Available from: http://archive.sciendo.com/.
[2]. Lingley, Rebecca. "Marketing Strategy and Alliances Analysis of Starbucks Corporation." (2009). Available from: https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/ .
[3]. Nair, Rajesh Kumar, et al. "The effect of Starbucks marketing campaigns on consumer buying behaviour." Asia Pacific Journal of Management and Education (APJME) 4.1 (2021): 72-81. Available from: https://doi.org/10.32535/apjme.v4i1.1052.
[4]. Subramaniam, Tevyashini V. "Impact of social media on digital marketing: starbucks marketing strategy on Twitter." Case study 2 (2020): 1-7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/13527266.2016.1138139.
[5]. Tsai, Pei-Hsuan, et al. "Exploring the effect of Starbucks' green marketing on consumers' purchase decisions from consumers’ perspective." Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 56 (2020): 102162. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102162 .
[6]. KUMAR, Nirmalya, and Sheetal BHARDWAJ. "Starbucks China: facing luckin, the local disruptor." (2019): 1-27. Available from: https://ink.library.edu.sg .
Cite this article
Zhang,K. (2023). Factors Affecting the Pricing of Starbucks in Different Countries. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,12,211-217.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Haskova, Katerina. "Starbucks marketing analysis." CRIS-Bulletin of the Centre for Research and Interdisciplinary Study 1 (2015): 11-29. Available from: http://archive.sciendo.com/.
[2]. Lingley, Rebecca. "Marketing Strategy and Alliances Analysis of Starbucks Corporation." (2009). Available from: https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/ .
[3]. Nair, Rajesh Kumar, et al. "The effect of Starbucks marketing campaigns on consumer buying behaviour." Asia Pacific Journal of Management and Education (APJME) 4.1 (2021): 72-81. Available from: https://doi.org/10.32535/apjme.v4i1.1052.
[4]. Subramaniam, Tevyashini V. "Impact of social media on digital marketing: starbucks marketing strategy on Twitter." Case study 2 (2020): 1-7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/13527266.2016.1138139.
[5]. Tsai, Pei-Hsuan, et al. "Exploring the effect of Starbucks' green marketing on consumers' purchase decisions from consumers’ perspective." Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 56 (2020): 102162. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102162 .
[6]. KUMAR, Nirmalya, and Sheetal BHARDWAJ. "Starbucks China: facing luckin, the local disruptor." (2019): 1-27. Available from: https://ink.library.edu.sg .









