1. Introduction
Up to the year 2021, the total value of the digital economy in China has reached 45.5 trillion yuan (equal to USD 7.1 trillion) and account for 40% of GDP, according to the white paper released by China’s State Council Information Office. There are also many people who have paid attention to the booming development of the digital economy and made original analysis, including but not limited to education, medical services, information technology, entertainment, and finance, but there are still many industries that have also been affected but not attracted widespread attention. So, this essay will study the impact of the development of China's digital economy on various industries and the world through literature analysis and reading. For example, the 5G technology that China first developed is more closely related to Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent or BAT than to external companies, which prefer to skip 5G and study 6G. Why? What are they worried about? The essay also explains the convenience that e-commerce and electronic payments bring to people's lives. Through this study, it is not difficult to find that in the future, the digital economy will become the mainstream of the world and an important factor in leading the world economy. However, we also need to be careful of the disadvantages brought by the digital economy, such as data leakage, which will have serious consequences.
2. Current Situation
2.1. Technical Support
5G technology and its production are the foundation of much of what powers China's digital economy. Considering that its network equipment, mobile phones, and internet access devices reach over 170 regions and countries, it is noteworthy that Huawei has grown to become the world's largest maker of telecommunications equipment by revenue.
Many Chinese companies have innovated new business models and use cases in the past decade. Chinese businesses reexamined their business models in light of 5G, revising their product portfolios, marketing strategies, and even the markets and regions they operate in. Giant internet firms Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent, or BAT as they are collectively known, are developing a complex, multi-sector digital ecosystem that has an impact on different parts of customers' life. In addition to being a potent technology in and of itself, 5G brought together and accelerated a number of other cutting-edge technologies, such as edge computing, artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the internet of things (loT). When combined with 5G, each of these technologies performs better and adds more value, assisting Chinese businesses to develop a "technology flywheel" and swiftly become a major force in global competition. In the meantime, though, worries about 5G development, ownership, and data protection have rocked the world's political scene, particularly between China and the US. Many governments including the US, UK, France, Australia have raised security concerns, accusing Chinese-backed 5G producers of having close ties to the Chinese government.
Despite the fact that many involved Chinese companies purport that their operations are independent of the Chinese government or its influence, the US government continues to apply more strict policies on technology, law, and trade to prevent this level of risk for its own country’s interests. 5G adoption is in its infancy globally, and in the foreseen future, it is easy to expect that 5G can be part of everyone’s life everywhere, just like it is for Chinese people now. In fact, both China and the United States have cited 5G standard-setting leadership as a crucial component to protecting their respective 5G implementations. The technical basis of China's digital economy is 5G technology because of the country's existing first-mover advantage in laying the platform for international regulations and standards.
2.2. E-Commerce
Only a decade ago, China accounted for less than 1 percent of worldwide e-commerce transactions, but that share is over 40% now [1]. A growing young middle class is hungry for life-changing technology. And this provides a strong foundation of requirements for digital business success. These young internet users have incredible enthusiasm for online transactions, which facilitate the rapid commercialization of digital technology. The COVID-19 pandemic has increased e-commerce in China as cautious consumers buy more products online to prevent exposure to the diseases, a trend that will last after the pandemic [2].
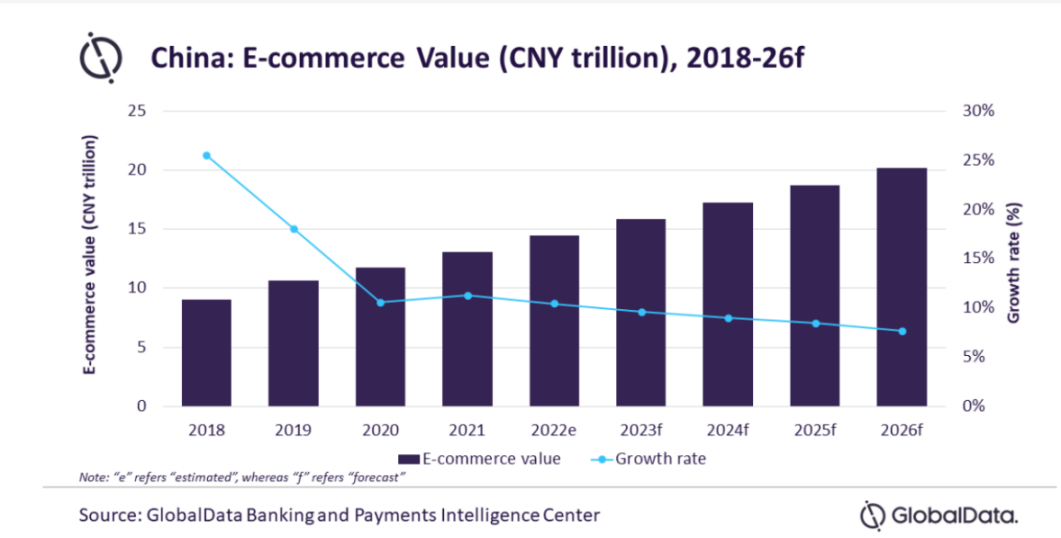
Figure 1: China’s E-commerce value in 2018(CNY).
Over the years, Chinese companies have established global platforms that connect sellers and buyers (B2B and B2C) from over 200 countries.
JD.com (1998), having well-established logistics and customers, was the first brand to offer same-day delivery to its users. The platform buys its inventory from brands and then operates its logistics in-house.
Tencent (1998), which created the most popular social media app called Wechat, embedded many retail stores within the platform to function as mini-websites and help convert product leads seamlessly into paying customers.
Taobao and Tmall, two well-known online stores, were offered by Alibaba in 1999. As a marketplace for consumer-to-consumer purchases, Taobao is comparable to eBay, but Tmall facilitates bussiness-to-consumer transactions between domestic and foreign enterprises.
The most recent arrival in e-commerce is Bytedance (2012). Its Tiktok app, which enables users to share brief videos, has grown to be the most well-liked amid the global lock down.
Some early investors in leading Chinsee e-commerce players are estimated to have earned returns of thousands of times their initial investment. Investors are enthusiastic and tend to have high expectations about the growth potential of China's startups.
2.3. Electronic Payment
At the end of the 20th century, e-commerce began to become a market trend, so in order to comply with this development, the electronic payment industry began to rise. Electronic payment refers to the transfer of funds through individuals, enterprises, and businesses on the Internet. It also has many types, such as electronic currency and electronic credit cards. Actually, electronic money is divided into electronic cash and electronic wallet while electronic cash is a kind of currency that flows as data on the network. It converts cash into numbers that can be used for payment and purchase. E-wallets have also become the majority of payments in this era of rapid internet data development. The WeChat coin purse, for example, is a type of e-wallet that can be used to make payments. What’s more, in the past 15 years, China's IC card, which is also known as a smart card, has made tremendous achievements, such as the expense card and telephone card, which have provided great convenience for people's social lives.
In 2006, the overall size of China's IC card market showed a rapid growth trend. The annual sales of enterprise cards exceeded 1.6 billion, the highest in all years, and increased by 55% compared with 1.08 billion in the previous year [3]. It is estimated that the global IC card shipments will be around 3 billion in the same period, and China accounts for more than half of them. It is indisputable that China will become the global IC card manufacturing center. By the end of 2019, China had 8.06 bank accounts per capita, up 11.63% year on year. Each person held 6.01 bank cards, a year-on-year increase of 10.48%. 89.90% of adults actively use accounts, an increase of 1.26 percentage points over the same period last year. This is the same as 83.37% in rural areas, an increase of 1.12 percentage points over the same period of the previous year.
2.4. Chinese Government Regulation
The Chinese government has always played a critical role in the digital economy revolution in China. It plays the part of an active supporter and gave the digital players space to experiment before enabling the official regulation. As the market matures, the government and individual businesses both becoming more proactive in shaping a healthier and regulated digital development. What’s more, China’s Cybersecurity Law (2017) came into effect. The Cyber security law is the first basic law in China which completely control cyberspace security management.
After soliciting public feedback, the Personal Information Protection Law (2021) becomes officially effective. This law establishes a legal foundation for Personal Information processing in China and increases each enterprise's legal responsibility for Personal Information protection.
The Data Security Law (2021) was created to control data processing operations, guarantee data security, encourage the development and use of data, protect the legitimate rights and interests of people and organizations, and uphold national sovereignty, security, and development interests.
Governance has become more centralized for the digital industry, which is also subject to mandatory oversight by Chinese authorities, following the introduction of sweeping regulations. Big tech companies, especially those focused on e-commerce, social media, fintech (electronic payments), are coming under greater scrutiny. Their business expansion, investment plans, especially initial public offerings, or expansion into other business areas in foreign markets are often subject to scrutiny.
3. The Impact on the Global Economy
3.1. Industrial Upgrading
While it is true that new technologies like the Internet, information, and communication have supported the creation and growth of the digital economy, the rapid growth of the digital economy has also created a demand for new technologies, which has encouraged their further development. 5G and even 6G technology, artificial intelligence, big data, cloud computing, and other technologies, for example, have been constantly innovated and developed. This has also led to the birth of many new industries around the world, such as the express industry, software development, and so on [4].
3.2. Initiative in Technology
Now China has mastered 5G technology, but because many countries are unwilling to buy this technology, they decided to bypass it and directly develop 6G networks. According to news from the Associated Press on July 27, Russian Deputy Minister of Digital Development, Communications and Mass Media Ivanov said that Russia has decided to invest 30 billion rubles in the research and development of 6G network technology. Of course, Russia is not the first country to announce the development of 6G. Japan, South Korea and the United Kingdom have also announced. In this case, if China takes the lead in developing 6G, only then can international standards suitable for Chinese companies and technologies be formed. As the basis of the digital economy, the development of 5G and even 6G has given China the initiative in the field of technology. Similarly, the development of the digital economy has also helped technological progress and promoted the improvement of 5G or 6G technology.
3.3. The Gap Between Rich and Poor
Driven by the digital economy, digital has become the most powerful tool for wealth creation, further concentrating social wealth and widening the gap between the rich and the poor. During the two years of COVID-19, people were restricted from going out, so some people who engaged in the service industry and the white-collar workers faced unemployment, which meant that they could not get wages, so they became poorer. On the contrary, the rich use the internet and digital to create wealth; for example, Tesla's boss, Elon Musk, became the richest man in the world in less than a year, with personal wealth of more than 300 billion dollars [5].
3.4. Monopoly
Due to the rapid development of the digital economy and the fact that it has become a global trend, some relevant enterprises have become giants. On March 31, 2021, 8 of the top 10 enterprises on the "2021 Top 100 Global Enterprises with Market Value" list were digital enterprises, including Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Alphabet (the parent company of Google), Facebook, Tencent, Tesla and Alibaba. In November 2021, the market value of Apple in the United States reached 2.34 trillion dollars, equivalent to twice the annual GDP of a country in Australia [6]. Such a powerful enterprise will make it difficult for emerging enterprises to enter the market and expand, which is not conducive to market competition and may lead to price increases.
3.5. Data Leakage
Data leakage has always been a problem that disturbs the world. Since the amount of data on the network is huge and easily stolen, the leakage and improper use of data may cause harm to society. For example, Yahoo's disclosure in 2013 affected 3 billion accounts [7]. Hackers stole the names, birth dates, phone numbers, passwords, security questions, and email addresses used to reset passwords for Yahoo users.
4. Conclusion
The rapid development of e-commerce and electronic payments in China has also led to the development of various industries, which shows the importance of the digital economy. This rapid development has also brought other effects to the world, such as industrial development, technological innovation, monopolies, data leakage, and the widening gap between rich and poor.
The essay also has some limitations as it only studies China, a developing country, and the impact of the development of the digital economy on the world. It is expected that future research can be extended to different economies, such as those in the third world and developed countries.
References
[1]. McKinsey Global Institute 2017 “Digital China powering the economy to global competitiveness”. https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/china/digital-china-powering-the-economy-to-global-competitiveness
[2]. Pei Changhong, Ni Jiangfei, Li Yue. Political Economics Analysis of Digital Economy. Finance and Trade Economics, 2018, 39(09): 5-22. DOI: 10.19795/j.cnki.cn11-1166/f.2018.09 .001.
[3]. Xie Ping, Liu Haier. ICT, Mobile Payment and Electronic Money. Financial Research, 2013, No.400(10):1-14.
[4]. Jing Wenjun, Sun Baowen. Digital economy promotes high-quality economic development: a theoretical analysis framework. Economist, 2019, No.242(02): 66-73. DOI: 10.16158/j.cnki.51- 1312/f.2019.02.008.
[5]. Musk's return to the world's richest man is still four days away, 2023. https://www.jiemian.com/article/8885994.html
[6]. Apple's market value soared by trillion yuan overnight, the largest increase in the market value of the United States in a single day, 2022. https://3g.163.com/dy/article/HLT6K0QA0552XG61.html
[7]. Jin Yuanpu. Investigation and analysis report on personal privacy data leakage in the era of big data. Journal of Tsinghua University (Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2021, 36(01): 191-201+206. DOI: 10.13613/j. cnki.qhdz.003016.
Cite this article
Liu,J. (2023). Research on the Current Situation and Impact of China's "Digital Economy". Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,20,332-337.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. McKinsey Global Institute 2017 “Digital China powering the economy to global competitiveness”. https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/china/digital-china-powering-the-economy-to-global-competitiveness
[2]. Pei Changhong, Ni Jiangfei, Li Yue. Political Economics Analysis of Digital Economy. Finance and Trade Economics, 2018, 39(09): 5-22. DOI: 10.19795/j.cnki.cn11-1166/f.2018.09 .001.
[3]. Xie Ping, Liu Haier. ICT, Mobile Payment and Electronic Money. Financial Research, 2013, No.400(10):1-14.
[4]. Jing Wenjun, Sun Baowen. Digital economy promotes high-quality economic development: a theoretical analysis framework. Economist, 2019, No.242(02): 66-73. DOI: 10.16158/j.cnki.51- 1312/f.2019.02.008.
[5]. Musk's return to the world's richest man is still four days away, 2023. https://www.jiemian.com/article/8885994.html
[6]. Apple's market value soared by trillion yuan overnight, the largest increase in the market value of the United States in a single day, 2022. https://3g.163.com/dy/article/HLT6K0QA0552XG61.html
[7]. Jin Yuanpu. Investigation and analysis report on personal privacy data leakage in the era of big data. Journal of Tsinghua University (Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2021, 36(01): 191-201+206. DOI: 10.13613/j. cnki.qhdz.003016.









