1. Introduction
As the latest variant of the coronavirus, Omicron, is being investigated, the world drops into a new round of war between humans and the virus. The World Health Organization states that Omicron has a higher level of infection transmissibility than the variants found before, which will also lead to a serious symptom [1]. Due to the growth of the pandemic, the global market for e-commerce has been impacted a lot. According to statistics in Shopify, the expected value of the global e-commerce market is around $4.89 trillion totally in 2021, which shows there is a huge increase in e-commerce market share from 2019 to 2021, at 45.8% [2]. Therefore, how to develop the e-commerce market during the COVID pandemic has become a hot and controversial topic all over the world.
Douyin, also called Tiktok in western countries, is a social media platform designed by Byte Dance Ltd., China, and was successfully released in 2016, provided an innovative way for personal communication and interaction, which has generated and stored a large number of users so far [3]. The marketing strategies of Douyin are promising. After collecting a large number of users as a foundation, Byte Dance Ltd. established the e-commerce business group to be responsible for the tasks related to the e-commerce service [4]. The marketing tactics for Douyin are efficiently built by the decision-makers.
As the customer-based marketing strategy grows in the e-commerce industry in recent years, service quality and logistics management have been recognized as being much more important. To win the competition in the short video e-commerce industry, Byte Dance Ltd. has done a lot of operations to make it happen. Therefore, this article aims to collect the influential factors of consumer behavior transformation in Douyin e-commerce and the success factors that assist Douyin in becoming one of the most popular social media and e-commerce platforms, which will also provide some recommendations for the growth of other e-commerce platforms based on the discovery.
2. Conceptual Development
2.1. Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) Model
Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) Model is the conceptual model in consumer behavior, which indicates to be used for constructing the stimulus from online elements and lead to a consumer behavior response or change by cognitive or emotional transformation. This model was first proposed by Mehrabian and Russell and used in the field of psychology [5].
SOR Model shows the individuals will make a response on their behavior by receiving the stimuli from the environments with their five senses (vision, hearing, taste, touching, smelling). Individuals will make changes in their cognitive or emotional situations to generate the transformation of their behaviors.
This paper uses the SOR model as the theoretical frame of the influential factors to find out why consumers change their purchasing behaviors during the Omicron pandemic. Based on this model, there are also some hypotheses proposed, which will be tested later in the paper.
Hypothesis 1: The stimulus from the short video does not impact consumer behavior.
Hypothesis 2: The stimulus from the short video impacts consumer behavior.
2.2. Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM)
The Elaboration Likelihood Model was first proposed by Petty and Cacioppo, which is one of the most useful and critical persuasion models in the field of consumer behavior [6]. The Elaboration Likelihood Model shows a process of how a person will generate attitude changes based on persuasion, which has two different routes based on the level of elaboration, called the central route and the peripheral route [7]. The central route shows an individual needs to pay much effort into consideration about the issue and target behaviors, while the peripheral route indicates a low cognitive level and only needs the individual to accept or reject messages without much consideration [8]. The Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM) is based on the strength of ability, motivation, and opportunity, including the degree of mind change (Ability), the different operating procedures at the two ends of the elaboration continuum (Motivation), and the different processes of attitude change that occur at different points along the continuum (Opportunity) [9]. As Figure 1 shows, ability, motivation, and opportunity are three key factors that impact the formation of different routes in the elaboration likelihood model.
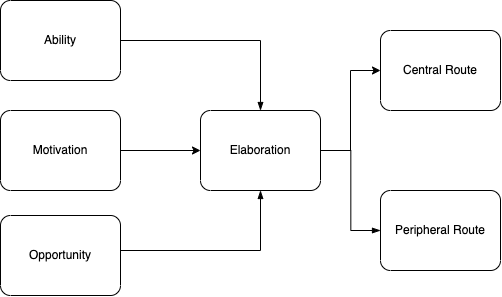
Figure 1: Elaboration likelyhood model [7].
Perceived Benefits. Consumers’ perceived benefits are related to their mindset [10]. The construct of perceived benefits is defined as beliefs about the positive outcomes associated with a behavior in response to a real or perceived threat. Consumers’ mindset and attitude are found to be closely related to their perception of benefits [11, 12].
Perceived Costs. The perceived cost of an activity is defined as the unit cost that a consumer thinks he incurs by undertaking a particular activity. A consumer's expenditure consists of direct price and non-price cost elements, which this paper assumes to be independent. High perceived costs have been found to forecast consumers’ purchasing aspirations [13].
Perceived Values. Perceived value is a customer's perception of a product or service's merit or desirability to them, especially in comparison to a competitor's product. Perceived value can also be referred as the customers’ trade-off of the perceived benefits and perceived costs in their mindset [14]. In the scope of economics, consumers always try to maximize the utility of their belongings, which includes not only their money but also their non-monetary goods. Therefore, perceived value has been verified to positively impact consumer behaviors [14].
Based on these concepts, perceived benefits, perceived costs, and perceived value are worthy of study if they are the factors that impact the strength of ability, motivation, and opportunity, which finally affect the elaboration likelihood model. Therefore, H3 and H4 is shown as follows.
Hypothesis 3: The purchasing decisions are not based on the perceived benefits, perceived costs, and perceived values.
Hypothesis 4: The purchasing decisions are based on perceived benefits, perceived costs, and perceived values.
2.3. Consumer Decision-Making Process
The consumer decision-making process is the sets of stages that show the formation of purchasing behaviors during customers’ consumption, which includes six stages across the whole process [15]. The first stage is called need recognition, where the consumers generate a “need and want gap”. After recognizing it, consumers will collect all the necessary information of each factor that would be helpful for decision-making. Then, consumers will ensure there is a subset of alternatives to make the final decision. After the final decision is made, consumers will make a purchase. Finally, after purchasing, the fifth stage is called post-purchase. Consumers will be able to evaluate their feelings or emotions for post-purchase and generate comments about their purchasing experiences.
Hypothesis 5: The customer value during the post-purchase stage does not impact customer loyalty.
Hypothesis 6: The customer value during the post-purchase stage impacts customer loyalty.
3. Research Methodology
This research aims to examine the reasons for consumer behavior transformation and determine the relationship between customer value and consumer behavior transformation. The data was collected via an online questionnaire. To maintain the universality of the research objects, all research participants are from China and come from a variety of demographic backgrounds (e.g., ages, genders, occupations, etc.). The research distributes 456 pieces of the questionnaire and collects 388 pieces, the response rate is 85.08%. Based on the answers, the participants are mostly 18 to 39 years old, and women make up a large portion. The participants in the research are asked 26 questions. Among the questions, the questionnaire first determines the basic demographic information of participants and whether they are using Douyin or not. If the participants are not Douyin users, the questionnaire will be terminated. Then, the questions determine the period of participants’ use of Douyin. After that, the questions determine if the users are also consumers of the Douyin e-commerce platform. If the participants are not Douyin e-commerce consumers, the questionnaire will also be terminated.
3.1. Data Analysis and Results
The data is examined by a reliability and validity test to ensure the research is statistically significant. The reliability test of this research is the Cronbach \( α \) test, and the validity test is KMO and Bartlett test.
3.1.1. Reliability
Based on the results of the reliability test, the Cronbach \( α \) is 0.997, which shows the research is reliable and can be used for future research.
3.1.2. Validity
Based on the results of the validity test, the KMO value is 0.990, which shows that the information included in the data set can be extracted.
3.1.3. Research based on SOR Model
As for the research based on the SOR model, Pearson correlation is used. There are two variables in the correlation test, which are “Have you ever watched any videos about e-commerce from Douyin before?” and “Have you ever purchased through Douyin e-commerce platform?” In the following table, this paper sets “Have you ever watched any videos about e-commerce from Douyin Before?” as X1 and “Have you ever purchased through Douyin e-commerce platform?” as X2.
Table 1: Pearson correlation.
X2 | ||
X1 | Pearson Coefficient | 0.914** |
p-value | 0.000 | |
p<0.05 ** p<0.01 | ||
The data results show that the Pearson coefficient is 0.914, which means there is a strong positive correlation between x1 and x2. Therefore, the author rejects H1. Then, this paper can conclude that the result is statistically significant and that the stimulus from the short videos can impact consumers’ behavior positively.
3.2. Research Based on Elaborative Likelihood Model (ELM)
Due to the multiple factors that may impact consumer behavior, this paper examines the typical factors that are always effective during consumer purchasing experiences. First, the author uses linear regression to analyze the data. In the dataset, there are three independent variables, “The trust in the quality of goods” (X3), “The likability of video creators and the host of live commerce” (X4), and “the inconvenience of order inquiries” (X5). Let the dependent variable “consumer purchasing aspiration” (E).
Table 2: Liner regression.
B | t | p | VIF | R ² | Adjusted R ² | F | |
\( {b_{0}} \) | 2.719 | 63.935 | 0.000** | - | 0.932 | 0.931 | F =1750.182, p=0.000 |
X3 | 0.761 | 11.272 | 0.000** | 8.097 | |||
X4 | 0.603 | 8.625 | 0.000** | 7.237 | |||
X5 | 0.504 | 6.725 | 0.000** | 8.253 |
The linear regression function is:
\( E=2.719+0.761{X_{3}}+0.603{X_{4}}+0.504{X_{5}} \) (1)
The value of R2 is 0.932, which means that X3, X4, and X5 are the three independent variables that lead to the change in consumer purchasing aspirations. Due to the autocorrelation, this paper also uses ridge regression to examine the possibility of multicollinearity.
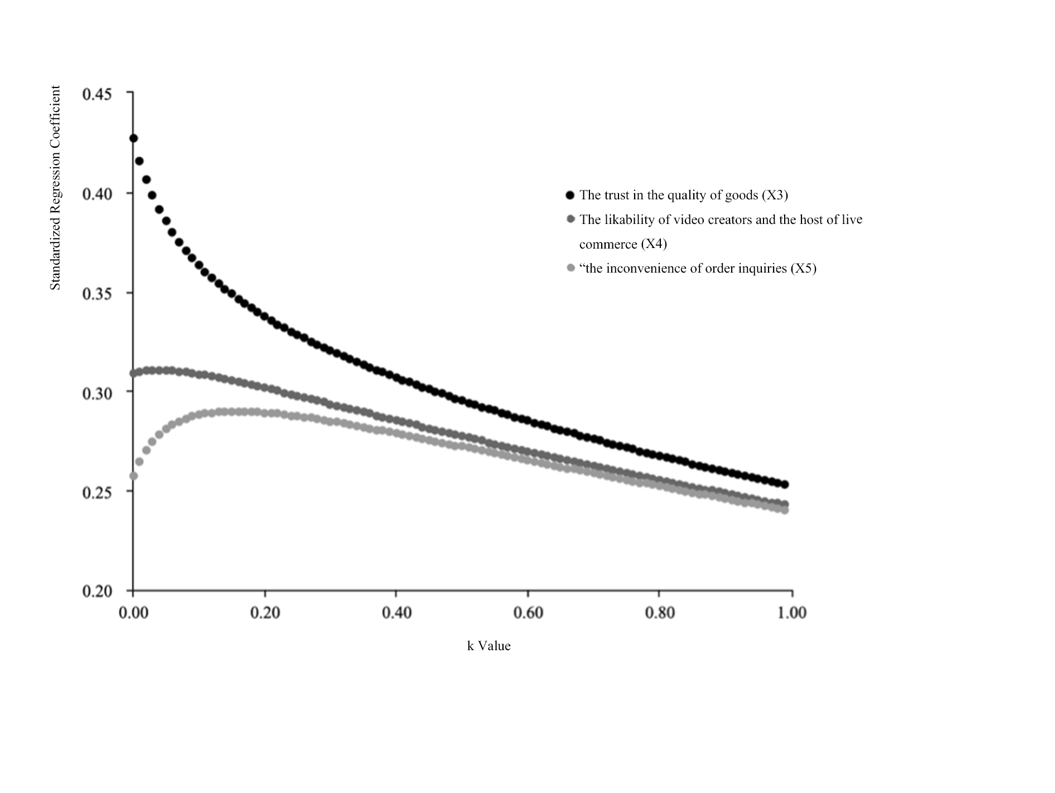
Figure 2: Ridge regression.
Based on Figure 2, the author sets k as 0.99. Then, the new linear regression function is:
\( E=2.678+0.450{X_{3}}+0.474{X_{4}}+0.471{X_{5}}+ε \) (2)
where E means the aspiration; X3, X4 are positive variables, which can be regarded as perceived benefits, while X5 is a negative variable, which can be regarded as perceived costs; \( ε \) is the error. Based on the results, R2 is 0.868, which means X3, X4 and X5 can explain 86.8 percent of changes in consumer purchasing aspirations. Also, X3, X4, and X5 all positively impact consumer purchasing aspirations. Therefore, the paper can reject H3 and concludes that “The trust in the quality of goods” (X3), “The likability of video creators and the host of live commerce” (X4), and “the inconvenience of order inquiries” (X5) impact the purchasing aspiration.
3.3. Research Based on Consumer Decision Making Process
This research aims to find the relationship between the post-purchase stage and customer loyalty on the Douyin e-commerce platform. This paper uses logistic regression in this research. First, the author coded the results of consumer purchasing into two portions, 0 to 2 is regarded as 0 (low aspiration), 3-5 is regarded as 1 (high aspiration).
Table 3: Data coding.
Degree of Aspiration | Coding |
0-2 | 0 |
3-5 | 1 |
Three independent variables are examined here, including “The feelings of the unexpected return process in Douyin e-commerce platform” (X6), “The purchasing experience in Douyin e-commerce platform” (X7), and “The total assessment of the recommended goods in Douyin e-commerce platform” (X8).
Table 4: Logistic regression.
Independent Variables | Coefficient | z-value | p-value | Odds Ratio | OR 95% CI |
X6 | 0.104 | 0.324 | 0.746 | 1.110 | 0.591 ~ 2.082 |
X7 | 0.261 | 0.577 | 0.564 | 1.298 | 0.535 ~ 3.151 |
X8 | 1.071 | 2.086 | 0.037 | 2.919 | 1.067 ~ 7.984 |
b0 | -1.864 | -1.872 | 0.061 | 0.155 | 0.022 ~ 1.091 |
Then, the logistic regression function is:
\( Logit(P)=\frac{ln{{p_{i}}}}{1-{p_{i}}}= -1.864+0.104{X_{6}}+0.261{X_{7}}+1.071{X_{8}}+ε \ \ \ (3) \)
In the equation, this paper can find that the p-value of X8 is 0.037, which is less than 0.05. Therefore, X8 can positively impact consumer purchasing aspiration, at a level of the odds ratio of 2.919. Generally speaking, the consumer purchasing aspiration can increase 2.919 times more than before when the total assessment of the recommended goods in the Douyin e-commerce platform increases by one unit. However, this paper can also find that there is no significant p-value to show that the unexpected return process in the Douyin e-commerce platform can lead to a loss of loyal customers. Then, this paper cannot reject H5 (the customer value during the post-purchase stage does not impact customer loyalty).
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
As for the research in the SOR model, the goal of it is to examine if the consumers will purchase the products in Douyin e-commerce after they watch the short videos in the Douyin application. Based on the results, the paper can find that the correlation coefficient is 0.914, which indicates a strong positive relationship between these two variables. Then, this paper can reject H1 and conclude that there is a positive relationship between watching short videos and purchasing from Douyin e-commerce.
Moving to the next research based on Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM), this research is to figure out if the purchasing decisions are based on perceived value or not. As we all know, it is common that consumers will easily choose to buy some daily necessaries but need much time to decide of buying a car or a house. The reason why it happens is due to the difference in involvement levels. High involvement will need consumers to take much time and consider the purchasing choice; in contrast, low involvement is much easier for consumers to finish their decision-making process. Based on the results, R2 is 0.868, which means X3, X4, and X5 can explain 86.8 percent of changes in consumer purchasing aspirations. Also, X3, X4, and X5 all positively impact consumer purchasing aspirations. Also, the coefficient of X4 is the highest among the three independent variables, which means “the likability of video creators and the host of live commerce” can impact consumer behavior a lot. Generally speaking, the more a user likes video creators or hosts of live commerce, the higher possibility that the user will buy the product they recommend, even though there may be some perceived costs included.
In terms of the research based on the consumer decision-making process, the aim of it is to determine the relationship between the post-purchase stage and customer loyalty on the Douyin e-commerce platform. The results show that the consumer purchasing aspiration can increase by 2.919 times than before when the total assessment of the recommended goods in the Douyin e-commerce platform increased by one unit. This paper can also find that there is no significant p-value to show that the unexpected return process in the Douyin e-commerce platform can lead to a loss of loyal customers. Then, the paper cannot reject H5.
All in all, hypotheses (H1, H3, and H5) are successfully examined. The results determine some of the critical factors that lead to consumer behavior transformation.
4.2. Theoretical Contributions
This paper aims to study the main factors that impact the formation of the elaboration likelihood model and how those factors will affect the consumers’ purchasing decision-making processes. Theoretically, this paper contributes to the study of the elaboration likelihood model in the scope of a short video e-commerce platform. Based on the results, there is a positive relationship between watching short videos and purchasing from Douyin e-commerce. Also, perceived benefits, perceived costs, and perceived value all positively impact consumer purchasing aspirations. However, this research does not show any significance in the relationship between the unexpected return process and the loss of loyal customers.
4.3. Managerial Contributions
As for the practical managerial contributions, the results can generally be applied to the management of e-commerce corporations. Based on the SOR model research, watching short videos can accelerate the purchasing intentions of customers. Therefore, corporations or operators could make their own short videos to post on the platform and increase brand and product awareness. In terms of the elaboration likelihood model, the corporations and operators should be aware of their business strategies, which means they should set a customer-oriented strategy to maximize the utility of their products. When consumers make their purchase decisions, unexpected return processes cannot be avoided. Although the customers may not lose their loyalty to the brand, the corporations and operators should offer excellent post-purchase services to reduce customer complaints in their daily operations.
5. Conclusion
The growth of short videos has changed the world a lot. Looking back to the e-commerce development in Amazon, technologies and social growth accelerate the emergence of some new industries and jobs. The results of this research can contribute a lot to short video e-commerce platforms and impulse sales all over the world. Also, the results can help the scholars work on deeper research into consumer behaviors and provide some recommendations for future research directions in consumer behaviors.
Based on the results, this paper successfully studies the critical factors that lead to consumer behavior transformation. However, there are some limitations in the research due to time and other factors. The research object is based on the data collected form the Douyin e-commerce platform, which is a typical example for this area. Therefore, the author will study other e-commerce platforms to verify the feasibility of each result in this paper. Also, the research methodology is based on the survey results. Future scholars could find other innovative methodology to explore the relationships between different factors.
References
[1]. Michael K. (2021). Global Ecommerce Explained: Stats and Trends to Watch in 2021. Shopify. Retrieved from https://www.shopify.com/enterprise/global-ecommerce-statistics.
[2]. World Health Organization. (2021). Update on Omicron. WHO News. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news/item/28-11-2021-update-on-omicron.
[3]. Kenrick D. (2018). The App That Launched a Thousand Memes. Sixth Tone. Retrieved from https://www.sixthtone.com/news/1001728/the-app-that-launched-a-thousand-memes.
[4]. ByteDance Establishes E-commerce. (2020). ByteDance Establishes E-commerce Business Group. PingWest. Retrieved from: https://en.pingwest.com/w/6969.
[5]. Man Deng, Pei Deng, Baike Chen, Qirong Liang, Gaoxu Deng. (2021). Research on Tik Tok platform live streaming e-commerce to help rural revitalization based on SOR model. Academic Journal of Business & Management, 3(6), 91-94. DOI: https://doi.org/10.25236/AJBM.2021.030614.
[6]. Chu Tan Ming. (2018). [Research on consumers' willingness to choose online shopping channels based on SOR theory]. Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, (In Chinese).
[7]. Petty, R., Cacioppo, J. & Goldman, R. (1981). Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 41(5), 847-855.
[8]. Shi, J., Hu, P., Lai, K. K., & Chen, G. (2018). Determinants of users’ information dissemination behavior on social networking sites. Internet Research, 28(2), 393-418. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/IntR-01-2017-0038.
[9]. Srivastava, M., & Saini, G. K. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of the elaboration likelihood model (ELM). Journal of Consumer Marketing, 39(7), 726–743. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-12-2021-5049.
[10]. Choi, J., Lee, A. and Ok, C. (2013), “The effects of consumers’ perceived risk and benefit on attitude and behavioral intention: a study of street food”, Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 30(3), 222-237. DOI: 10.1080/10548408.2013.774916.
[11]. Zeyen Loh, & Hasnah Hassan, S. (2022). Consumers’ attitudes, perceived risks and perceived benefits towards repurchase intention of food truck products. British Food Journal, 124(4), 1314–1332. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-03-2021-0216.
[12]. Yoon, B. and Chung, Y. (2018), “Consumer attitude and visit intention toward food-trucks: targeting Millennials”, Journal of Foodservice Business Research, 21(2), 187-199.
[13]. Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., & Xu, X. (2012). Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Quarterly, 36(1), 157–178. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/41410412.
[14]. Kleijnen, M., De Ruyter, K., & Wetzels, M. (2007). An assessment of value creation in mobile service delivery and the moderating role of time consciousness. Journal of Retailing, 83(1), 33–46. DOI: https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.jretai.2006.10.004.
[15]. Rithika D., Kazuo F. & Taro K. (2021). Quantitative decision-making model to ananlyze the post-disaster consumer behavior. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 61, 102329, ISSN 2212-4209, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102329.
Cite this article
Wei,L. (2023). Critical Factors Impacting Consumer Behavior in Douyin E-commerce. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,21,254-262.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Michael K. (2021). Global Ecommerce Explained: Stats and Trends to Watch in 2021. Shopify. Retrieved from https://www.shopify.com/enterprise/global-ecommerce-statistics.
[2]. World Health Organization. (2021). Update on Omicron. WHO News. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news/item/28-11-2021-update-on-omicron.
[3]. Kenrick D. (2018). The App That Launched a Thousand Memes. Sixth Tone. Retrieved from https://www.sixthtone.com/news/1001728/the-app-that-launched-a-thousand-memes.
[4]. ByteDance Establishes E-commerce. (2020). ByteDance Establishes E-commerce Business Group. PingWest. Retrieved from: https://en.pingwest.com/w/6969.
[5]. Man Deng, Pei Deng, Baike Chen, Qirong Liang, Gaoxu Deng. (2021). Research on Tik Tok platform live streaming e-commerce to help rural revitalization based on SOR model. Academic Journal of Business & Management, 3(6), 91-94. DOI: https://doi.org/10.25236/AJBM.2021.030614.
[6]. Chu Tan Ming. (2018). [Research on consumers' willingness to choose online shopping channels based on SOR theory]. Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, (In Chinese).
[7]. Petty, R., Cacioppo, J. & Goldman, R. (1981). Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 41(5), 847-855.
[8]. Shi, J., Hu, P., Lai, K. K., & Chen, G. (2018). Determinants of users’ information dissemination behavior on social networking sites. Internet Research, 28(2), 393-418. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/IntR-01-2017-0038.
[9]. Srivastava, M., & Saini, G. K. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of the elaboration likelihood model (ELM). Journal of Consumer Marketing, 39(7), 726–743. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/JCM-12-2021-5049.
[10]. Choi, J., Lee, A. and Ok, C. (2013), “The effects of consumers’ perceived risk and benefit on attitude and behavioral intention: a study of street food”, Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 30(3), 222-237. DOI: 10.1080/10548408.2013.774916.
[11]. Zeyen Loh, & Hasnah Hassan, S. (2022). Consumers’ attitudes, perceived risks and perceived benefits towards repurchase intention of food truck products. British Food Journal, 124(4), 1314–1332. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-03-2021-0216.
[12]. Yoon, B. and Chung, Y. (2018), “Consumer attitude and visit intention toward food-trucks: targeting Millennials”, Journal of Foodservice Business Research, 21(2), 187-199.
[13]. Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., & Xu, X. (2012). Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Quarterly, 36(1), 157–178. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/41410412.
[14]. Kleijnen, M., De Ruyter, K., & Wetzels, M. (2007). An assessment of value creation in mobile service delivery and the moderating role of time consciousness. Journal of Retailing, 83(1), 33–46. DOI: https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.jretai.2006.10.004.
[15]. Rithika D., Kazuo F. & Taro K. (2021). Quantitative decision-making model to ananlyze the post-disaster consumer behavior. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 61, 102329, ISSN 2212-4209, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102329.









