1. Introduction
With the complexity of social and economic structure, bonds have been born. As an intermediate channel, the bond market communicates the surplus of funds and the demand for funds. It not only promotes the optimal allocation of resources, but also enables banks and enterprises to raise quickly, disperse risks. What’s more, it accelerates the circulation of long-term bonds through the secondary market, which improves liquidity. Because the bond market has the ability to absorb liquidity, it can alleviate the excess liquidity and optimize the economic structure. For a highly liquid and mature bond market, it can provide market benchmark interest rates and form an effective pricing mechanism. It can help to reduce transaction costs, improve the efficiency of financial markets, and even predict economic development in the future.
Moreover, the huge market for investment and financing outside the banking system, which is formed by the bond market, has greatly increased the depth and complexity of the financial market; and the diversified fixed income products provided by the bond market have improved the diversity of investment and enhanced the stability of the financial market. The different ratings of bonds by major professional rating companies provide better choices for investors with different risk preferences and affordability. At the same time, the stratification of risks shows the enhanced market flexibility. The full development of the bond market can provide a guarantee for dealing with financial risks and maintain the stability of financial markets.
All in all, the current bond market has become an inseparable part of the financial market. The same is true of Chinese bond market, but it has its own special development process compared with capitalist countries. At present, there are few studies on Chinese bond market. Therefore, this paper discusses the development process and problems of Chinese bond market, in order to help relevant researchers, understand Chinese bond market and promote the development of it.
2. Development Process and Current Situation
2.1. Development Process
Chinese bond market was founded in late 1949 and stopped issuing bonds in 1966. The bonds of this period were issued in a way of government mobilization, with a single variety, no trading market, and a small scale. In 17 years, only 3.845 billion yuan was issued.
In 1981, China 's Ministry of Finance officially issued treasury bonds, marking the official birth of the Chinese bond market. Since 1984, a small part of enterprises had begun to issue corporate bonds in response to capital needs. In 1985, in order to raise infrastructure funds, the People 's Bank of China agreed to the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China and the Agricultural Bank of China to issue financial bonds. At this stage, the bond market was mainly based on the issuance of treasury bonds, there was no formed bond trading mechanism and trading place, and the corporate fund-raising behavior had not been legally recognized and regulated [1].
In 1990, Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges were established. In 1993, the State Council promulgated the Regulations on the Administration of Corporate Bonds. In 1995, treasury bonds were successfully issued on the Shanghai Stock Exchange. During this period, the secondary market with national debt as the main component began to form, and the exchange market was dominant. Corporate bonds had undergone a transformation from the People 's Bank of China to the centralized management of the National Commission for Discipline Inspection.
In 1998, the People 's Bank of China promulgated the Interim Provisions on the Administration of the Issuance of Financial Bond Market of Policy Banks. In 1999, securities and fund companies were granted access to the interbank market. At this stage, the bond market management system had a strong planned economy characteristic, such as complex bond approval procedures, corporate bonds were similar to government bonds, based on the guarantee of large central enterprises and banks and so on. During this period, the inter-bank bond market framework was basically formed. In 2003, the birth of central bank bills marked the real rise of the interbank bond market.
At this stage, the multi-head supervision pattern of the bond market has gradually formed, and the inter-bank bond market has gradually become the main part of the Chinese bond market with various bond categories and diversified market participants [2]. As a leader, the People 's Bank of China has expanded the layout of the interbank bond market and gradually improved its infrastructure, which based on its relaxed legal environment and membership advantages. After more than half a century of evolution and development, Chinese bond market has experienced twists and turns. It sticks to enrich product categories, attract market participants, and constantly deepen market depth and complexity. It has developed into a market with a sound and mature development mechanism and become an indispensable part of Chinese financial market.
2.2. Status Analysis
Now, Chinese bond market is in a period of steady development. For example, the issuance scale of bonds continues to expand, the structure of bond types is relatively stable, and more and more new bonds emerge in endlessly to adapt to the balanced development of all aspects of society [3]. (See Fig. 1, Fig.2 and Fig.3)
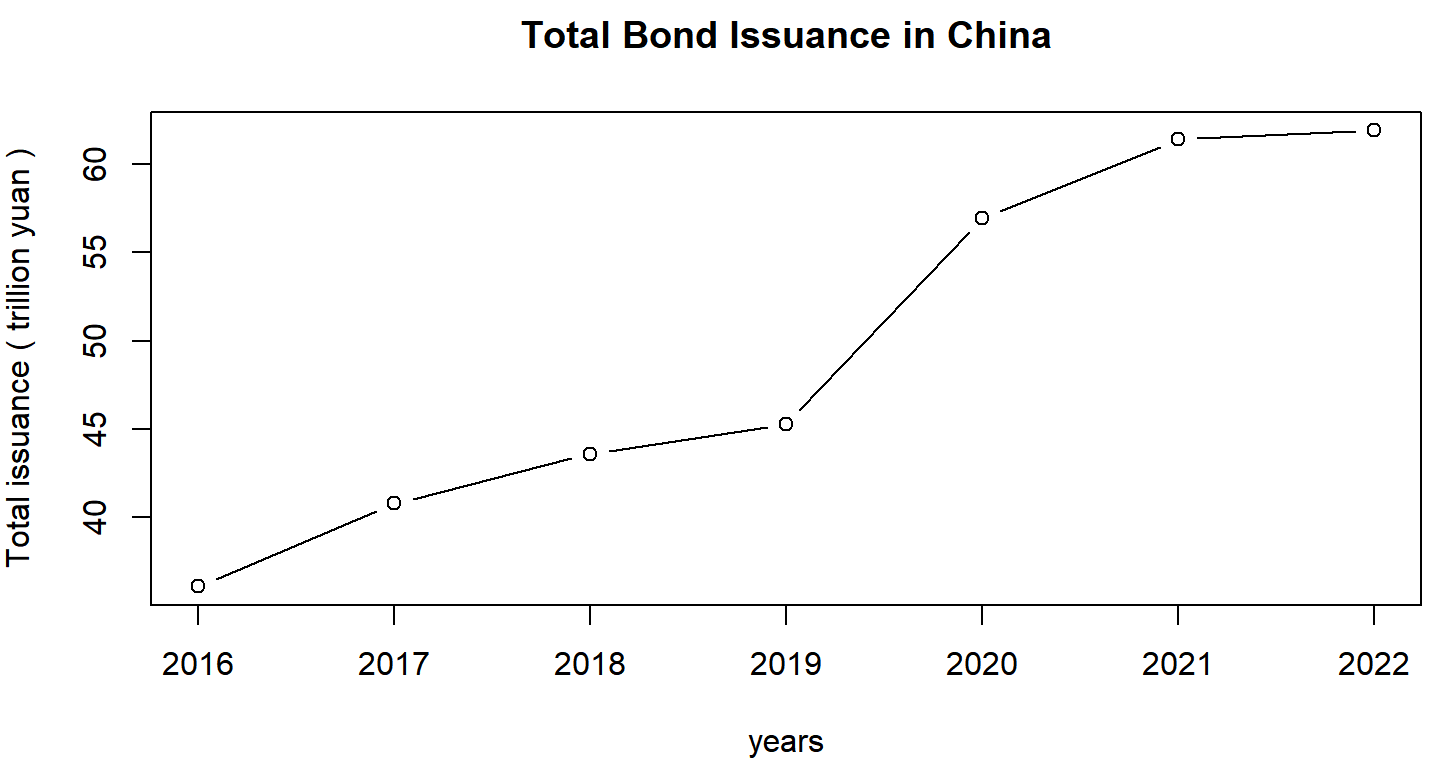
Figure 1: Total issuance.
According to the data of the People 's Bank of China 's statistical annual report, the scale of Chinese bond market has steadily expanded, the total issuance of bonds has been increasing. In 2022, the total issuance of bonds in China was 61.9 trillion yuan. There was an increase of 0.84 % year-on-year, mainly due to the impact of the epidemic, which resulting in low overall domestic economic benefits.
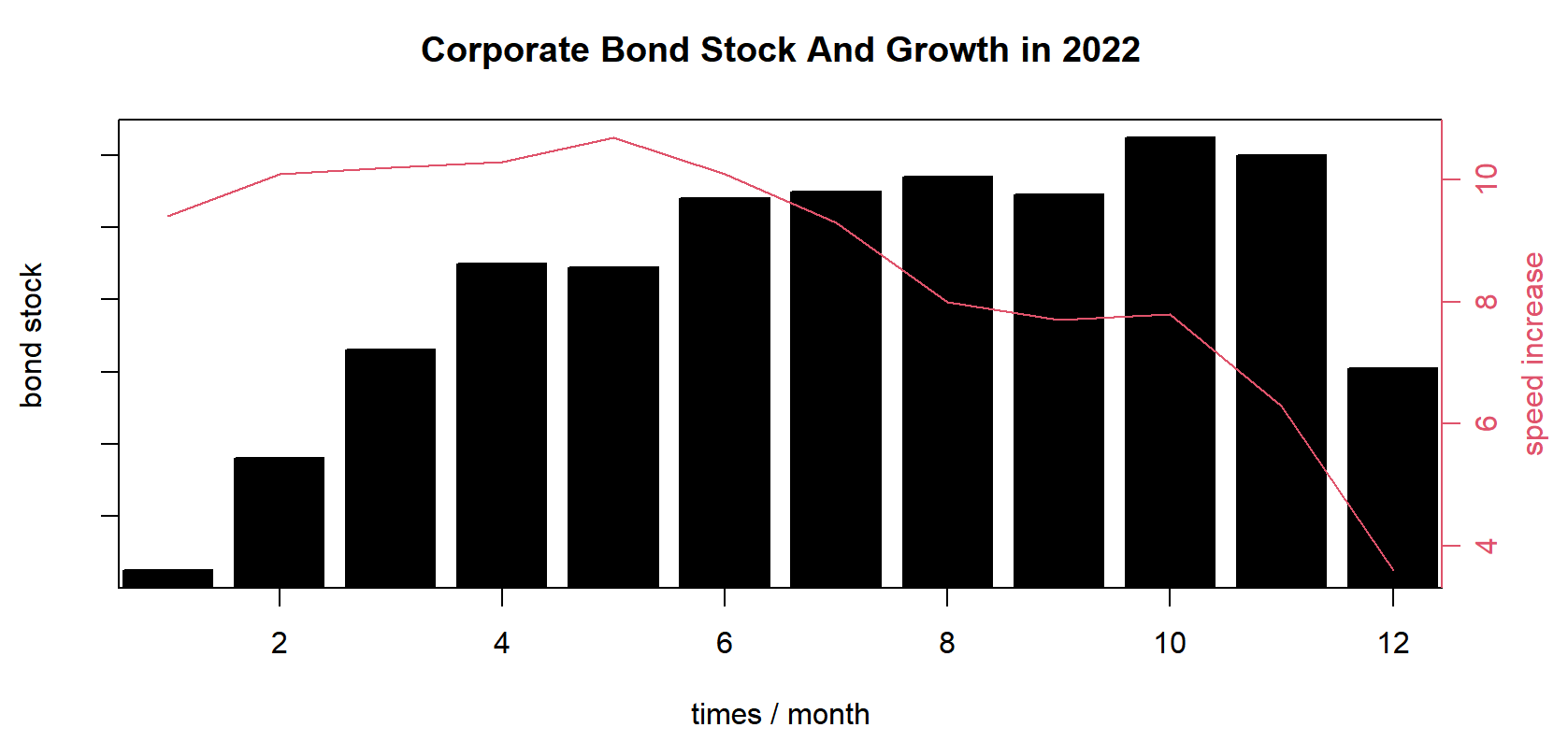
Figure 2: Corporate bond stock and the speed.
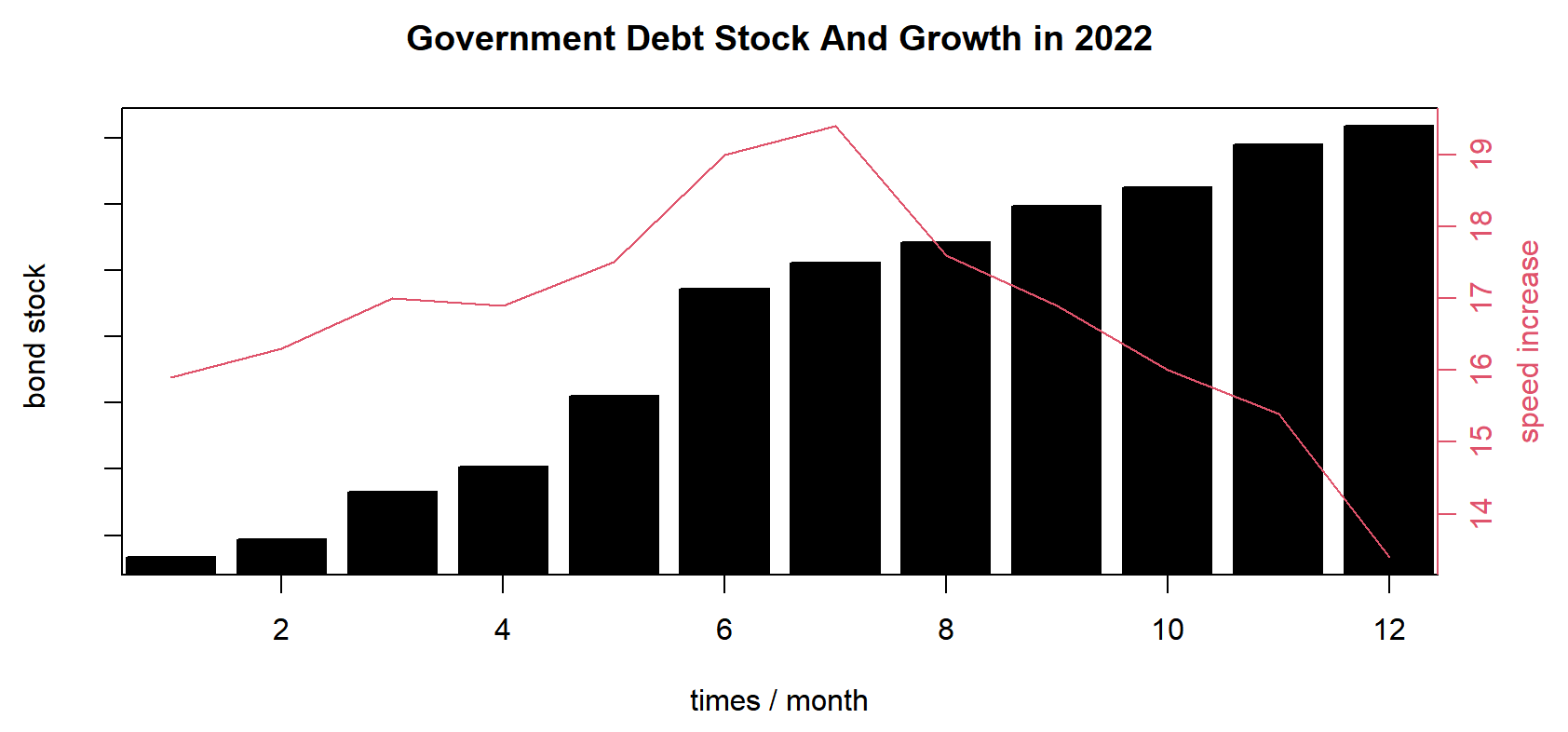
Figure 3: Government debt stock and its growth.
On the whole, in 2022, Chinese bond market ran smoothly. Although the yield of treasury bonds rose and fell, the high-level opening up of the bond market was stable and orderly, the structure of investors has been further diversified, the volume of money market transactions continued to increase, and the volume of interbank derivatives market transactions remained stable (See Table 1).
Table 1: Overview of the Chinese bond market.
Bond Types | Number of Issuance Periods | Issuing Scale | ||
current year (periods) | year-on-year growth (%) | current year (billion) | year-on-year growth (%) | |
National debt | 183 | 8.28 | 97222.7 | 43.04 |
Government debt | 2328 | 7.78 | 170778.49 | 19.6 |
Local government bond | 2145 | 7.73 | 73555.79 | -1.7 |
Bank bonds | 896 | 2.05 | 58404.8 | 5.12 |
Total | 3224 | 6.12 | 229183.29 | 15.54 |
In this year, the bond market issued a total of 22.92 trillion yuan of interest bonds, an increase of 15.54 %. Among them, the issuance of national debt is 9.72 trillion yuan, with the largest increase in issuance scale, reaching 43.04 %. In the fourth quarter of 2022, the maturity scale of national debt accounted for a large proportion, resulting in more issuance of national debt in the fourth quarter. And the rhythm of national debt issuance in the whole year is relatively backward. What’s more, The overall issuance of local government bonds is ahead, but the annual issuance volume has changed little year-on-year. The policy bank debt issuance also changed little year-on-year. As of the end of 2022, the stock of interest rate bonds in Chinese bond market was 83.00 trillion yuan, a little change from the end of last year (83.61 trillion yuan). (See Fig. 4)
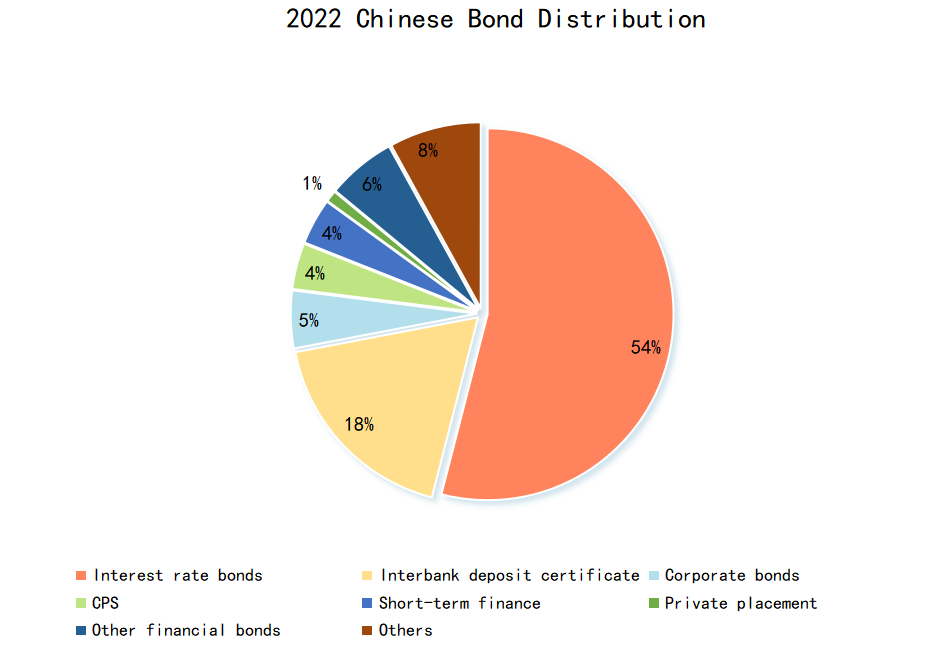
Figure 4: Bond distribution.
3. Problems
3.1. Lack of Liquidity
There are two main reasons for the inactive trading in China 's bond market: Firstly, the investment subject of Chinese bond market is commercial banks. They mainly aim at the maturity of bond holdings, resulting in lower bond turnover and lower liquidity [4]. Secondly, Chinese inter-bank bond market, the exchange bond market and the counter market are separated from each other, so that the links between the various bonds are separated [5]. The lack of liquidity in the bond market will affect the issuance of bonds, increase systemic risks, and hinder the sustained and healthy development of the bond market.
3.2. Lack of Diversity
Although Chinese bond market products have been basically complete, including more than 20 products in seven categories, its types and maturity varieties are far from rich. Chinese bonds are mainly fixed income products with a maturity of 3--20 years and there are fewer bonds of other maturity types [6].
At present, the development of interest derivatives in China is not mature, mainly including interest swaps, forward interest rate agreements, etc. There are few types of risk management tools, and the scale of transactions is small, which make market risks are not effectively controlled and dispersed.
3.3. Resource Misallocation
For a long time, Chinese enterprises have relied too much on bank indirect financing, while the proportion of direct financing in the bond market is relatively low, and there is a serious structural imbalance [7]. In 2022, the annual increase in social financing scale was 32.01 trillion yuan, 668.9 billion yuan more than the previous year. The data shows that the annual issuance of corporate credit bonds is 13.8 trillion-yuan, accounting for 22.29 %, which is lower than before and has a certain gap compared with developed markets. The slow development, small scale and low proportion of credit bonds in Chinese bond market directly restrict the financing efficiency of enterprises, increase the financing cost of enterprises, and also make the basic role of bond market in resource allocation unable to be fully played.
3.4. Regulatory Holes
Firstly, there is a lack of a fair and effective external supervision and management system for evaluation institutions. At present, China has incorporated the rating agencies of the bond market into a unified regulatory system, but it has not verified the evaluation results of rating agencies in terms of specific regulatory content. In other words, China 's supervision of rating agencies lacks a mature and effective rating agency supervision mechanism and verification mechanism. Therefore, in the Chinese bond market, rating agencies often do not need to be responsible for their own rating results. This institutional incompleteness has greatly affected the confidence of enterprises and other entities financing in the Chinese bond market.
The second is the lack of a unified bond centralized trusteeship mechanism and issuance supporting supervision system. In recent years, the inconsistency of Chinese bond market in the custody link has intensified, leading to further segmentation of the bond market, which has seriously affected the development speed and scale of the Chinese bond market [8]. At present, Chinese bond market regulatory authorities have relatively broad regulations on bond issuance, and the information transparency of bond issuance in the market still needs to be improved. In particular, the regulations on bond underwriting are relatively rough, which only have principled regulations. The two main underwriting methods of consignment and underwriting are clarified, but there is no clear regulation on the rights and obligations of bond issuers, underwriters, distributors and investors in bond issuance transactions [9].
4. Suggestions
In view of the above problems, the following suggestions are put forward:
4.1. Improving Liquidity
First, it should enrich the participants of Chinese bond market, vigorously develop institutional investors, and continuously attract small and medium investors. Second, it should expand the types of derivatives, gradually relax derivatives trading restrictions, and strengthen risk management and control. Besides that, it should improve the market maker system, increase support for bond trading, accelerate the pace of approval, improve the efficiency of issuance, and stimulate the enthusiasm of investors.
4.2. Enriching the Investment Objects
First, improve the variety structure of Chinese bonds, from the issuer, bond maturity, coupon rate, payment methods, bond derivatives and other aspects of innovation. The second is to innovate the bond investment model, continuously meet the diversified needs of domestic and foreign investors and promote derivatives innovation.
4.3. Enhance the Optimal Allocation
The first is to continue to encourage the expansion of the proportion of direct financing from the policy level. Then, it should improve the infrastructure construction of bond issuance, trading, and settlement, and lay a solid foundation for the expansion and opening of the bond market. Thirdly, it should introduce market makers, settlement agents and token brokers to enrich the types of participants in the bond market [10]. The fourth is to continuously accelerate the pace of financial market opening up, encourage overseas entities to participate in domestic bond investment and issuance, and improve the internationalization level and international influence of Chinese bond market.
4.4. Improving the Loopholes
It draws on the experience of mature bond market from the aspects of system construction, financial supervision, information disclosure, risk management, default disposal and so on. Firstly, the integration and unification of the regulatory authorities in the bond market will improve the efficiency of supervision while reducing the cost of supervision. Secondly, Chinese bond market regulatory authorities should set up a special agency to supervise third-party rating agencies and make clear regulations on the accuracy of rating agencies ' rating results in order to achieve a fairer bond market rating mechanism [11]. Thirdly, Chinese bond market regulatory authorities should specifically formulate mandatory laws on the disclosure content, disclosure conditions, and disclosure time limits of bond issuers to regulate the information disclosure order of the bond market [12].
5. Conclusion
The bond market has the ability to absorb liquidity, alleviate excess liquidity and optimize the economic structure. And the bond market with high liquidity and mature development can not only provide market benchmark interest rates and form an effective pricing mechanism, but also reduce transaction costs and improve financial market efficiency. The existence of the bond market improves the diversity of investment and enhances the stability of the financial market.
Chinese bond market was formally born in 1981.After many reforms, it has now been in a good situation. Its overall operation is stable and the opening up is orderly. In order to adapt to the balanced development of all aspects of society, new bonds are constantly being developed.
There are four problems, insufficient liquidity, lack of diversity, inability to give full play to the basic role in resource allocation, and the existence of regulatory holes which have been accompanied by the development of Chinese bond market. Although they have not been completely eliminated, they have been in the process of improvement. This paper discusses the suggestions for improving the problems from four perspectives: improving liquidity, enriching the investment objects and investment models of the bond market, enhancing the optimal allocation ability of the bond market, and improving the loopholes in the bond market system.
The description of the problems and suggestions in this paper is mainly at the theoretical level, lacking quantitative analysis. Next, it is a good idea to consider using data to prove.
References
[1]. Fan, Y.: Discuss the current situation and development of China 's bond market. Investment and Entrepreneurship 32(14), 15 (2021).
[2]. Hong, W., Meng, R.: Trends and future directions of foreign institutions participating in China 's bond market. International Finance (2), 7 (2015).
[3]. Gu, K.Z.: Analysis of the development status of China 's bond market and its future development trend. Money China 24, 11 (2013).
[4]. Zhu, R.: Research on the liquidity of China 's inter-bank bond market. CPC Central Party School, Thesis for Doctoral degree (2008).
[5]. Chen J.: Problems in the development of China 's bond market and suggestions for improvement. Shanghai Finance (4), 4 (2010).
[6]. Du, Z.Y., Xu, C.H.: Exploring the development of China 's bond market from the perspective of foreign investor demand. Journal of Hubei University of Economics: Humanities and Social Sciences 16 (7), 4 (2019).
[7]. Xu, Z.: Hot issues in the development of China 's bond market and their understanding. Financial research (2), 7 (2015).
[8]. Wang, Y.: Hot issues in the development of China 's bond market and their understanding. Finance and economics (36), 1 (2016).
[9]. Zhao, D.W., Li, W.H.: Research on China 's bond market from the perspective of regulatory technology. Jilin Financial Research (2), 5 (2021).
[10]. Dong, K.: Research on the impact of market maker system on the liquidity of interbank bond market. Southwest University of Finance and Economics, Thesis for Doctoral degree (2012).
[11]. Wu, X.Q., Tao, X.H., Zhang, T.: Several issues that need to be considered in developing China 's bond market. Finance and Trade Economy 39 (3), 12 (2018).
[12]. Paul, A., Tom, C, Prague, P., Chiang, M.J.: The Role of Mandatory Disclosure of Transaction Information in Financial Markets - Take the Corporate Bond Market as an Example. Financial Market Research (1), 10 (2014).
Cite this article
Wang,N. (2023). Reviewing the Development of Chinese Bond Market: History, Problem and Suggestions. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,24,6-12.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Fan, Y.: Discuss the current situation and development of China 's bond market. Investment and Entrepreneurship 32(14), 15 (2021).
[2]. Hong, W., Meng, R.: Trends and future directions of foreign institutions participating in China 's bond market. International Finance (2), 7 (2015).
[3]. Gu, K.Z.: Analysis of the development status of China 's bond market and its future development trend. Money China 24, 11 (2013).
[4]. Zhu, R.: Research on the liquidity of China 's inter-bank bond market. CPC Central Party School, Thesis for Doctoral degree (2008).
[5]. Chen J.: Problems in the development of China 's bond market and suggestions for improvement. Shanghai Finance (4), 4 (2010).
[6]. Du, Z.Y., Xu, C.H.: Exploring the development of China 's bond market from the perspective of foreign investor demand. Journal of Hubei University of Economics: Humanities and Social Sciences 16 (7), 4 (2019).
[7]. Xu, Z.: Hot issues in the development of China 's bond market and their understanding. Financial research (2), 7 (2015).
[8]. Wang, Y.: Hot issues in the development of China 's bond market and their understanding. Finance and economics (36), 1 (2016).
[9]. Zhao, D.W., Li, W.H.: Research on China 's bond market from the perspective of regulatory technology. Jilin Financial Research (2), 5 (2021).
[10]. Dong, K.: Research on the impact of market maker system on the liquidity of interbank bond market. Southwest University of Finance and Economics, Thesis for Doctoral degree (2012).
[11]. Wu, X.Q., Tao, X.H., Zhang, T.: Several issues that need to be considered in developing China 's bond market. Finance and Trade Economy 39 (3), 12 (2018).
[12]. Paul, A., Tom, C, Prague, P., Chiang, M.J.: The Role of Mandatory Disclosure of Transaction Information in Financial Markets - Take the Corporate Bond Market as an Example. Financial Market Research (1), 10 (2014).









