1. Introduction
Since 2020, covid-19 has accelerated the transformation of the retail industry from physical stores to the Internet, and the emergence of Metaverse is regarded as the next generation of the Internet. Metaverse provides new digital technologies and immersive virtual environments for human-computer interaction [1]. For young people represented by Generation Z, spending more than 8 hours a day focusing on the screen has become a part of daily life. These rising young affluent consumers are driving changes in the luxury industry. They have new consumption behaviors and needs, and are increasingly inclined to accept digital marketing methods [2]. Most of the well-known global luxury brands, such as Gucci, Burberry and Louis Vuitton, have added various digital product lines in the virtual space Metaverse to meet consumers' needs. Driven by the Covid-19 epidemic environment and the new consumer culture background, the traditional Marketing Mix represented by luxury goods has derived new marketing perspectives in the virtual environment, which are helpful for the marketing and innovation of luxury brands.
2. The Metaverse Emerging in luxury Brand Marketing
At the beginning of 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic that broke out worldwide has had a major impact on our daily life and work. Due to the severity and speed of the epidemic, governments around the world have taken measures such as restricting business activities and closing shopping malls and stores to control the spread of the epidemic and protect people's lives. The measures have had a negative impact on the $2.5 trillion fashion industry, leading to a sharp drop in demand for clothing and other luxury goods. At the same time, due to the collapse of the industry due to the restriction of activities, consumers' consumption concepts and behaviors have also undergone major changes [3].
Metaverse, as an emerging technological concept, was first proposed by writer Neal Stephenson in his novel Snow Crash. Metaverse is a permanent and persistent multi-user environment that blends physical reality with digital virtuality. It is based on the immersive technology of multi-sensory interaction between users and digital objects in a virtual environment, bringing users a more vivid, realistic and novel experience. According to the 2022 edition of Deloitte's "Global Powers of Luxury Goods" report, the world's top 100 luxury goods companies will have a total revenue of US$305 billion in fiscal year 2021, a year-on-year increase of 21.5%. With the receding of the COVID-19 pandemic, luxury goods companies now face new opportunities arising from the “green transition” and circular economy processes. In addition, Metaverse and Web3 are also actively promoting innovation and disruption in the luxury industry. Metaverse provides luxury companies with unprecedented opportunities to reshape the luxury experience, build brand reputation, and increase brand engagement and brand loyalty. Consumers can now interact with luxury brands’ products and their avant-garde concepts in new ways through virtual reality technology.
Famous Italian luxury fashion brand Gucci has partnered with metaverse platform Zepeto, an app and social media platform for personalizing avatars and creating virtual worlds. Users can purchase gucci clothing within the application and make their avatars wear these clothing to feel and explore gucci brand products. In addition Zepeto x Gucci also includes a gucci villa for exploration [4].
In 2020 Gucci partnered with Tennis Clash to produce exclusive gucci outfits that fans could purchase from the Gucci website that were identical to the on-screen businesses and participate in a specific tournament. This tournament also included a dedicated venue, the Gucci Open, merging the virtual and real worlds [5].
In 2021, Gucci launched its "world's first virtual sneaker" - the Gucci Virtual 25, which people can "wear" using augmented reality (AR) technology. Catering to its target market, the sneakers cost $12.99, a lot less than real-life sneakers (which cost more than $600). Also in 2021, Gucci will cooperate with Roblox to sell several Gucci rare items on the Roblox platform. Over the course of two weeks, the fashion house created a unique virtual garden exhibit that can be accessed exclusively on Roblox. The virtual exhibition is part of Gucci's Archetype, a two-week immersive multimedia experience in Florence, Italy, exploring and celebrating the brand's 100th birthday. The physical exhibition digs deep into Gucci's advertising campaign, which mainly includes inspirations such as music, art, travel and pop culture. Each venue is divided into exhibition halls according to themes, reproducing Gucci's different promotional activities. With cutting-edge technology, exquisite craftsmanship of artisans and innovative interior design, the exhibition presents a variety of immersive spaces, allowing visitors to feel as if they are in Gucci's advertising campaign [6].
In February 2022, Gucci purchased a batch of digital land on The Sandbox platform, which is a decentralized gaming community platform based on the Ethereum blockchain. Gucci built the virtual world Gucci Vault Land on this basis. As part of the Web 3.0 strategy, the project brought more new virtual experiences to the brand's Metaverse community [7].
Balenciaga and Epic Games have teamed up for the first Fortnite France luxury fashion product collaboration. Balenciaga designed four virtual outfits and an IRL limited-edition collection of hats, t-shirts, and hoodies to sell in Balenciaga stores and on Balenciaga.com [8].
Animal Crossing held the Spring Fashion Week 2020, and Valentino released 20 custom-made virtual looks from the 2020/2021 Pre-Fall men's and women's collections and brought it to Animal Crossing. In addition, Marc Jacobs has also released six specially designed looks in Animal Crossing, giving players the opportunity to wear these clothes for free on their fictional characters.
Louis Vuitton celebrates its 200th anniversary by entering the metaverse with the indie adventure game "Louis the Game." Game users need to play the protagonist Vivienne in the game and travel through six different worlds, where she needs to collect 200 candles to commemorate Louis Vuitton's birthday. The game differs from existing video games in that Metaverse allows users to move their virtual possessions between different virtual reality platforms - ownership of these items is represented by NFTs. The user avatar of the game is an anthropomorphic design of the company's letter combination. During the entire game process, the user can wear various Louis Vuitton brand-limited skins through the avatar [9].
3. Impact of Metaverse on the Luxury Market
3.1. The New Digital Marketing Marketplace
As the metaverse develops, more and more use cases are emerging in the consumer space, providing immersive retail, entertainment and education experiences, and brands can develop their own application prototypes. Morgan Stanley, a well-known financial institution, pointed out that the rise of metaverse and related factors will drive consumers' growing digital demand for fashion and luxury brands. It is estimated that by 2030, the entire industry may increase additional revenue of up to 50 billion US dollars. A recent McKinsey & Company report also assessed the marketing opportunity for the Metaverse, highlighting that selling virtual products directly to avatars is expected to be a $54 billion market. At the same time, the report pointed out that the metaverse will become a crucial market in the future of luxury marketing.
3.2. NFT Virtual Luxury Products
The emergence of NFT virtual products provides consumers with new ways to shop, exchange goods, and integrate into the Metaverse identity. According to data from Dune Analytics, an overseas statistical agency in August 2022, Nike tops the list of brands with the highest NFT revenues, with cumulative NFT sales of $185 million. It was followed by Dolce & Gabbana with sales of $25.65 million, followed by Tiffany, Gucci and Adidas with sales of $12.62 million, $11.56 million and $10.95 million respectively.
According to the survey on January 31, 2023, 36% of the respondents indicated that they are most willing to buy digital goods or NFT from luxury brands such as Chanel and Louis Vuitton. After luxury goods, sports brands are the most popular fashion type. 34% of respondents said they would buy fashion NFTs from such brands.
As Robert Triefus, executive vice president of client relations at Gucci, points out, young people are spending more and more time in areas like social media, gaming and virtual reality, becoming tech-savvy and adopting multiple identities. Pioneered, digital assets in the form of virtual fashion and non-fungible token (NFT) offer consumers a new way to shop, exchange goods, and own these identities [10].
3.3. Metaverse Gamevertising
With more and more people spending time online, video games have emerged as a new social media platform and the most attractive medium for brands to display their wares, known as Gamevertising. Gamevertising goes far beyond simple media placement in terms of branding and user experience, representing a communication paradigm shift where experiential storytelling becomes critical. The global games market could be worth $300 billion, three times the record high of $101 billion set by the global film industry in 2019, according to GlobalData. According to further estimates from research firm Technavio and others, in-game advertising will grow by $109.7 billion between 2020 and 2024. This year, Epic Games announced that their hugely successful game Fortnite had amassed 350 million registered users, and that growth looks set to continue to rise. Therefore, in the Metaverse environment, the importance of game advertising becomes even more prominent. As shown in Figure 1, according to the August 2021 Forrester Research survey of UK and US internet users, 15% of UK respondents and 22% of US respondents said brands should advertise in virtual reality. Meanwhile, 13 percent of UK respondents and 19 percent of US respondents believe brands should use virtual reality to build more brand experiences.
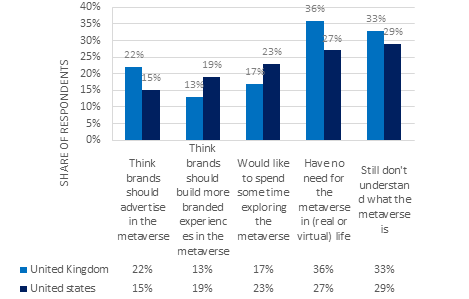
Figure 1: Brand-related attitudes towards the metaverse among UK and US internet users as of August 2021.
3.4. Virtual Reality Consumer Experience
Metaverse opens up creativity and possibility for the fashion industry not only through materials, but also through the way brands promote products based on Metaverse technology, either through marketing or through immersive consumer experiences that go beyond traditional shopping possibilities. For example, fashion lovers in different countries and regions can experience virtual display spaces and virtual wearable items produced by fashion brands through digital technology terminals. Technology can help enable efficient, more sustainable and faster business processes, improved customer service and new experiences. According to Siebel 2021, “the physical space will be reconfigured so that through an immersive experience, consumers can perceive the universe of brands and products”. Through virtual reality technology, retailers establish omni-channel integration with customers both online and offline to create a new shopping experience. Today, 81% of global consumers believe that a brand’s digital presence is as important as its physical store presence, leading to a trend towards virtual flagship stores in retail consumption.
Meanwhile, Deloitte suggested in a 2022 report that, as the metaverse matures and potentially transitions to a fully immersive mixed and augmented reality ecosystem, it will be widely used by businesses and consumers. Metaverse can provide transformational opportunities for brands and marketers to strengthen their relationships with consumers by delivering new levels of customer interaction and engagement.
4. Luxury Marketing Mix Strategy Under the Influence of Metaverse
Marketing mix is a tool used in marketing. The 4Ps classification for formulating effective marketing strategies was first proposed in 1960 by marketing professor and author E. Jerome McCarthy [11].The 4P theoretical model is widely used in the field of luxury goods, and many scholars use it to study the marketing strategies of luxury brands [12]. The four elements of Product, Price, Place and Promotion in the 4P theory closely match the consumer behavior in the luxury market. By using the 4P theory, luxury goods companies can better understand the consumption concepts of consumers in the Z-era in the Metaverse, analyze their consumption behavior characteristics, and formulate more targeted marketing strategies.
4.1. Product Strategy
The difference between traditional luxury goods and mass consumer goods lies in attributes such as design, craftsmanship, packaging and brand added value. However, in the metaverse environment, consumers' pursuit of luxury goods is not only traditional physical products and quality, but also turned to virtual NFT products. As Imran Amed, founder and CEO of The Business of Fashion puts it: "The new streetwear in the digital fashion model is screen clothing" [13]. Another important feature of the Metaverse is the interoperability between different platforms and services, which is critical to understanding how to connect a Metaverse with other Metaverses for many different purposes. Under this framework, NFT is not just a product for final sale. Its true value has two levels. The first is as a collectible, which has the symbolic characteristics of rarity and uniqueness. For example, the NFT digital shoes of the Gucci brand, which allows users to display products in SNS and virtual worlds. The second level is as a substitute for physical products, so that customers who cannot afford physical prices can also buy their favorite luxury goods, expanding the scope of potential users.
4.2. Price Strategy
The exclusivity of luxury goods enables the owners to obtain unique value and additional social status enhancement, satisfying their need to display material wealth. Virtual NFT luxury goods, on the other hand, fulfill another category of low-income consumers' need for luxury goods with their uniqueness and low prices. Metaverse's breakthrough lies in the tokenized economy and decentralized network, which makes each user asset consist of NFTs that mark ownership. Each digital asset belongs to the user and can be personalized, a uniqueness that makes the product valuable and price stable.
4.3. Place Strategy
The quality of traditional physical sales locations and services allows luxury consumers to feel the personality, culture, and other elements of the selected brand, thus generating psychological enjoyment and thus building brand loyalty. However, virtual sales locations in the metaverse environment break the limitation of physical distance, allowing consumers to access metaverse brand stores at home anytime and anywhere through virtual reality technology terminals or to feel the shopping experience of augmented reality technology offline, increasing the diversity and possibility of location experience.
4.4. Promotion Strategy
Promotional strategies can allow new and existing customers to purchase their favorite goods at relatively favorable prices while satisfying consumers' material and spiritual needs. In the metaverse environment, luxury companies can use extensive data analysis to understand consumers' needs and predict future consumption habits to better understand and tap into users' needs for personalized and cross-platform marketing. In addition, in the metaverse, users form brand community groups that help brands develop new user relationships. For example, based on Gucci's many collaborations with The Sandbox, The Sandbox co-founder Sebastien Borget said in an interview, "This approach to user-generated content has caught the eye of many cutting-edge brands that see virtual worlds as an excellent medium for engaging and creating new experiences. Behind each, The Sandbox plot is a user's story, which holds great power to build a sense of community belonging." Luxury brands use the Metaverse platform, with users acting as creators, to drive the overall brand story and deliver rich, detailed content and experiences.
4.5. Game Strategy
Based on the analysis of the 4P theory and combined with the case study, this paper argues that the element of game strategy needs to be included in the marketing mix of luxury goods under the influence of the metaverse. Gaming, the preferred form of entertainment for consumers of all ages worldwide, has become a market with vast power. According to statistics, about 3 billion people worldwide play video games regularly, 46% of whom are women, and they have spent more than $100 billion on virtual goods. The multiplayer environment of metaverse platforms is more social than traditional games, such as Fortnite and Roblox, which encourage player cooperation, conversation, and real-life connections. As such, the games represent a foundational component of the Metaverse, providing a diverse community of players.
As a fast-growing industry, eSports are attracting more and more players and attention, with eSports having a following of over 518 million people in 2020. A huge user base can be obtained by combining 2.7 billion gamers worldwide, eSports fans, and viewers who watch live gaming platforms daily [14]. Therefore, for luxury brands, game marketing offers an opportunity to reach and promote young consumers and can attract and create new user groups.
Luxury brands can develop game content with metaverse platforms or independently to attract more consumers. In addition, gaming offers luxury brands the possibility to create new and unique experiences and connect with consumers more deeply. In summary, gaming strategies are an integral part of the luxury marketing mix in the metaverse environment that cannot be ignored.
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Metaverse has new implications for the luxury industry and presents unique challenges and opportunities for its portfolio marketing strategies. In this digital age full of changes and the emergence of the Z-era consumer, the potential for luxury consumption and influence is enormous in the new digital platform. Therefore, the marketing of luxury brands needs to work on the following dimensions.
First, at the product level, luxury companies should increase the content of NFT products. The uniqueness contained in NFT digital products produced based on the Metaverse platform provides customers with a strongly differentiated product experience. It brings new value to customers who own digital products. The company can create core products in a virtual space based on the special attributes of NFT products. Customers can purchase at a lower price than real products and gain higher value through secondary sales, increasing the brand's market value.
Second, regarding location strategy, the company can combine virtual reality technology and gamification design based on virtual space concept stores to bring customers the most dramatic and immersive experience, expand target customers, and improve brand favorability.
Third, companies can adopt a community-based channel strategy based on the Metaverse platform in product marketing campaigns. This includes increasing user-generated content and employing community member co-creation to expand the brand's reach and exposure, thereby increasing product sales.
Fourth, luxury companies need to develop gaming services that offer exclusive brand experiences to meet the gaming experience needs of Z-era users and expand their audience and brand reach. In addition, companies can also cooperate with large metaverse platforms to develop gaming experiences shared with others.
Based on the above research, the luxury industry is undergoing one of its most significant changes with the emergence of the metaverse. Starting in 2020, major luxury brands are aggressively moving into the Metaverse as they see an opportunity to create new profits and business models. The global personal luxury market has been rapidly growing in the last two years, showing the Metaverse's great potential in luxury marketing. Therefore, luxury goods will be the future trend in Metaverse marketing.
References
[1]. Dwivedi, Y. K., Hughes, L., Baabdullah, A. M., Ribeiro-Navarrete, S., Giannakis, M., Al-Debei, M. M., Wamba, S. F.: Metaverse beyond the hype: Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management 66, 102542 (2022).
[2]. Williams, R.: Gucci’s Robert Triefus on Testing Luxury’s Allure in the Metaverse. The Business of Fashion, (2021).
[3]. Jamali, A., Kamolova, N.: A Study of GUCCI, the Changes in its Strategies During the Pandemic and the Consumers Perception Towards the Brand`s Products. International Journal of Computational Science and Engineering, (2022).
[4]. Averbek, G. S., TÜRKYILMAZ, C. A.: SANAL EVRENDE MARKALARIN GELECEĞİ: YENİ İNTERNET DÜNYASI METAVERSE VE MARKA UYGULAMALARI. Sosyal Bilimlerde Multidisipliner Çalışmalar Teori, Uygulama ve Analizler 99, (2022).
[5]. Brienza, M. V.: Technological evolution in the luxury and fashion industry: focus on the metaverse and NFT, 35-36 (2022).
[6]. Hazan, E., Kelly, G., Khan, H., Spillecke, D., Yee, L.: Marketing in the metaverse: An opportunity for innovation and experimentation. The McKinsey Quarterly, (2022).
[7]. Yan, R.: A Sustainable Fashion Industry Business Model Revolution Based on the Metaverse: Practices and Reciprocal Processes. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management 4, 363-369 (2022).
[8]. Analytica, O.: Metaverse'brandtech'will redefine online advertising. Expert Briefings, (2022).
[9]. Papagiannis, H. . How AR is redefining retail in the pandemic. Harvard Business Review 7, (2020).
[10]. Liu, J.: Metaverse and Brand: A Study of Luxury Brand Digital Marketing Strategy-Taking Gucci as An Example. In 2022 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Cultural Industry (ICEMCI 2022), pp. 1907-1913. Atlantis Press (2022).
[11]. McCarthy, E. J., Shapiro, S. J., & Perreault, W. D.: Basic marketing (pp. 29-33). Georgetown, ON, Canada: Irwin-Dorsey(1979).
[12]. Liu, Y.:Study on independent brands in China's luxury market based on 4P theory, (2014).
[13]. Joy, A., Zhu, Y., Peña, C., Brouard, M.: Digital future of luxury brands: Metaverse, digital fashion, and non‐fungible tokens. Strategic change 31(3), 337-343 (2022).
[14]. Fakazli, A. E.: The effect of COVID-19 pandemic on digital games and eSports. International Journal of Sport Culture and Science 8(4), 335-344 (2020).
Cite this article
Gao,M.;Xu,Y.;Yan,M. (2023). Marketing Mix Strategy in the Metaverse: The Luxury Brands Case Study. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,28,230-236.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Dwivedi, Y. K., Hughes, L., Baabdullah, A. M., Ribeiro-Navarrete, S., Giannakis, M., Al-Debei, M. M., Wamba, S. F.: Metaverse beyond the hype: Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management 66, 102542 (2022).
[2]. Williams, R.: Gucci’s Robert Triefus on Testing Luxury’s Allure in the Metaverse. The Business of Fashion, (2021).
[3]. Jamali, A., Kamolova, N.: A Study of GUCCI, the Changes in its Strategies During the Pandemic and the Consumers Perception Towards the Brand`s Products. International Journal of Computational Science and Engineering, (2022).
[4]. Averbek, G. S., TÜRKYILMAZ, C. A.: SANAL EVRENDE MARKALARIN GELECEĞİ: YENİ İNTERNET DÜNYASI METAVERSE VE MARKA UYGULAMALARI. Sosyal Bilimlerde Multidisipliner Çalışmalar Teori, Uygulama ve Analizler 99, (2022).
[5]. Brienza, M. V.: Technological evolution in the luxury and fashion industry: focus on the metaverse and NFT, 35-36 (2022).
[6]. Hazan, E., Kelly, G., Khan, H., Spillecke, D., Yee, L.: Marketing in the metaverse: An opportunity for innovation and experimentation. The McKinsey Quarterly, (2022).
[7]. Yan, R.: A Sustainable Fashion Industry Business Model Revolution Based on the Metaverse: Practices and Reciprocal Processes. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management 4, 363-369 (2022).
[8]. Analytica, O.: Metaverse'brandtech'will redefine online advertising. Expert Briefings, (2022).
[9]. Papagiannis, H. . How AR is redefining retail in the pandemic. Harvard Business Review 7, (2020).
[10]. Liu, J.: Metaverse and Brand: A Study of Luxury Brand Digital Marketing Strategy-Taking Gucci as An Example. In 2022 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Cultural Industry (ICEMCI 2022), pp. 1907-1913. Atlantis Press (2022).
[11]. McCarthy, E. J., Shapiro, S. J., & Perreault, W. D.: Basic marketing (pp. 29-33). Georgetown, ON, Canada: Irwin-Dorsey(1979).
[12]. Liu, Y.:Study on independent brands in China's luxury market based on 4P theory, (2014).
[13]. Joy, A., Zhu, Y., Peña, C., Brouard, M.: Digital future of luxury brands: Metaverse, digital fashion, and non‐fungible tokens. Strategic change 31(3), 337-343 (2022).
[14]. Fakazli, A. E.: The effect of COVID-19 pandemic on digital games and eSports. International Journal of Sport Culture and Science 8(4), 335-344 (2020).









