1. Introduction
Since the 21st century, the Internet has developed at a rapid pace and has become the dominant keyword in today's world [1]. Along with the rapid development of the Internet, the music industry has also stepped into the process of digitization and globalization.
In order to achieve its diversification strategy, Tencent has already opened up new frontiers in various fields such as entertainment and finance. Mergers and acquisitions of excellent companies already in existence will help Tencent quickly integrate resources, open up new business areas and achieve diversified development. Tencent's acquisition of China Music Corporation is one of many acquisitions by Tencent, but little information has been disclosed by either company about the acquisition, and few media outlets have reported on the acquisition, leaving little useful and reliable information. The purpose of this article is to consolidate and sort out information on Tencent's acquisition of China Music Corporation, fill in information gaps and provide further analysis on this basis.
Tencent, incorporated in the British Virgin Islands in November 1999, moved its registry to the British Cayman Islands in February 2004 and was listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in June 2004, the stock code is “00700.hk”, controls by agreement the main operating entity in mainland China, Shenzhen Tencent Computer Systems Limited. Initially an instant messaging software company, Tencent had well-known products such as QQ and WeChat. With the continuous development of the Internet, Tencent has gradually expanded into the fields of entertainment, finance, and information, seeking to diversify and build the Tencent ecosystem.
Tencent Music Entertainment Group (hereinafter referred to as TME), a brand of Tencent Holdings, was founded in July 2016 and listed on the New York Stock Exchange in December 2018 under the symbol "TME", with a secondary listing on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in September 2022, the stock code is “1698”. Tencent Music comprises two main businesses, namely music streaming and social entertainment, and covers four major products, namely Kugou Music, QQ Music, Kuwo Music and We Sing.
China Music Corporation (hereinafter referred to as CMC), incorporated in the Cayman Islands in 2012, controls by agreement the main operating entity in mainland China, Ocean Interactive (Beijing) Information Technology Co, and Ocean Music is a brand of it. In late 2013, Ocean Music acquired Kuwo Music, after which it began discussing a share swap merger with Kugou Music. in April 2014, Kuwo merged with Kugou to form the CMC together with the former Ocean Music.CMC is a music rights distribution and streaming platform that provides users with online music playback, artist music rights distribution, and individual and record label signings, as well as digital music licensing services, through its products Kugou Music and Kuwo Music.
Tencent's acquisition of China Music Corporation is one of many acquisitions by Tencent, but little information has been disclosed by either company about the acquisition, and few media have reported on the acquisition, leaving little useful and reliable information. The purpose of this article is to integrate and summarize the relevant information of this acquisition, analyze the strategic objectives and financial effects of Tencent's acquisition of China Music Corporation, and fill the gaps in related information on the internet.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 contains an overview of the acquisition process, as well as an analysis of the strategic purposes. Section 3 is an analysis of the financial effects of Tencent's acquisition of CMC, which will be analyzed in three parts: debt-paying ability, profitability and development capability. Section 4 focuses on the impact of the acquisition on the development of the music industry and the competitive landscape. Section 5 is the conclusion.
2. Strategic Purpose Analysis
Tencent, a giant Internet company, has a strong presence in a number of areas. Tencent has always been committed to technological innovation and business development, while through mergers and acquisitions, it can quickly expand its business scale and market share.
2.1. Overview of the Acquisition Process
On 12 July 2016, Tencent acquired a controlling stake in CMC by way of an asset injection - primarily QQ Music into CMC, then CMC acquired the assets of QQ Music, and the acquisition valued at approximately US$2.7 billion. Following the transaction, CMC was valued at approximately US$2.7 billion; Tencent Holdings will increase its stake in CMC from 16% to 61.64% [2], gaining sole control of CMC.
After this acquisition, TME was established and the integration was officially completed in January of the following year (2017). After the acquisition, the QQ Music, Kugou Music and Kuwo Music brands will remain independent, and users will continue to enjoy the same services and have access to more diversified choices.
In accordance with the, Anti-Monopoly Law of the People's Republic of China and the Provisional Provisions on Review of Concentration of Operators(China), the State Administration of Market Supervision and Administration opened a case on 25 January 2021 to investigate the suspected illegal implementation of concentration of operators in relation to the acquisition of equity interests in CMC by Tencent Holdings Limited. As Tencent completed the registration of the change of its shareholding on 6 December 2017, it failed to make a declaration to the relevant authorities prior to that date, in violation of Article 21 of the Anti-Monopoly Law, constituting an operator concentration implemented in violation of the law [2-5].
Tencent has been ordered to refrain from entering into or indirectly entering into exclusive copyright agreements with upstream copyright owners, and to not request or indirectly request upstream copyright owners to provide it with terms more favorable than those given to other competitors. Tencent is also prohibited from using means such as high advance payments to indirectly increase the costs of competitors, or to exclude or restrict competition [2].
2.2. Expanding Market Share
Prior to this acquisition, Tencent's main business had been based on instant messaging software, but it did not hold a dominant position in terms of popular music market share. According to data from online music market researcher, in the first quarter of 2016, before Tencent's acquisition, Kugou Music and Kuwo Music held over 30% of the market share and QQ Music held 18.91% (In China, all of the following) [6].
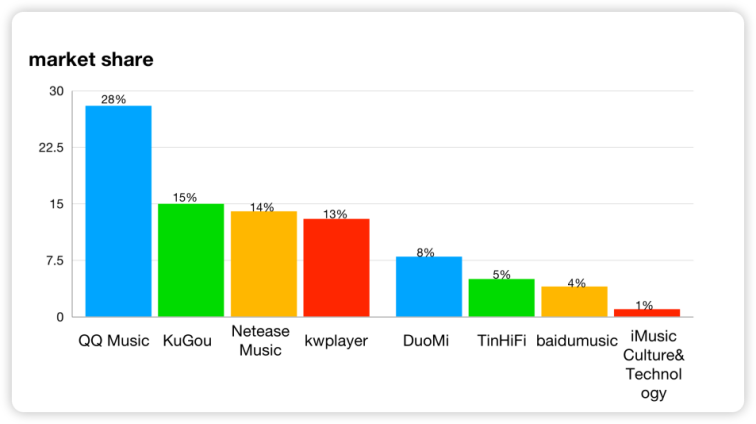
Immediately after the acquisition, Tencent set up the TME, meaning that Tencent will be more active in the music industry. The market shares of the major brands in the digital music industry after the acquisition are as follows: QQ, Kugou and Kuwo have market shares of 28%, 15% and 13% respectively. This means that TME has a 56% market share of the online music market in mainland China (Figure 1). On the one hand, this high market share has established TME as a leading player in the music industry in mainland China and is a major boost to Tencent's diversification. On the other hand, the acquisition will reduce the competition among QQ, Kugou and Kuwo, and save competition costs, thus maximising the market efficiency within the merged organisation and gaining market position in the industry [7].
|
Figure 1: Music industry market share (2016). |
Data source: Imedia [8] |
Photo credit: Original |
In terms of users, both Tencent and CMC have a large user base and the acquisition will help Tencent increase its user stickiness. The combined business and rich library of music rights will provide users with a better experience and music streaming services.
2.3. Establishing a Complete Music Industry Chain
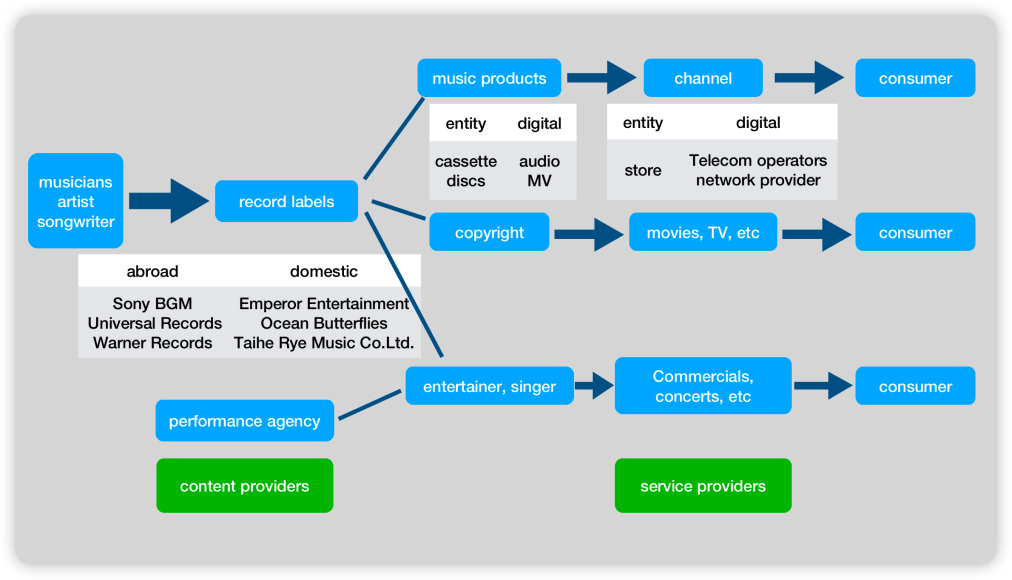
The relatively high investment required for the rights to popular music has left Tencent in a weak position when it comes to music rights and record labels, which is exactly where Tencent is short. The opposite is true for CMC. During the most difficult period for record labels, CMC signed a number of long-term exclusive music rights agents at low prices, and prior to its acquisition with Tencent, CMC had already entered into copyright partnerships with nearly 100 record labels and hoarded a large number of music rights [9]. CMC also owned two music streaming brands, Kugou Music and Kuwo Music, as well as the resources of top renowned record labels such as Warner Music and Sony Music, so CMC was One of the most powerful music rights companies of its day, with a rich, high-quality collection of music and copyright resources.
|
Figure 2: Diagram of the music industry chain. |
Data source: Tencent homepage |
Photo credit: Original |
Tencent is an Internet powerhouse, and its well-developed Internet development and use of technology are officially what Tencent is good at, so Tencent is well-placed to act as a link between content providers and consumers, connecting the two most important parts of the music industry chain. CMC and Tencent's respective strengths and weaknesses complement each other, and this acquisition will bring Tencent a complete music industry chain.
After the acquisition, TME holds the absolute leading position in terms of the total amount of copyright, and many top record companies such as Sony, Warner, Universal and Huayi have established solid strategic partnerships with it [9].
By building a complete music industry chain, TME can better integrate and manage its music resources, thereby improving the company's efficiency and profitability. For example, through its music rights management platform, TME can more effectively manage and protect its music rights and provide better services to its partners.
Building a complete music industry chain could also help TME further expand its business, creating more business opportunities and room for growth. For instance, through its music education and live music services, TME can offer its services to a wider group of users and attract more users to its platform, thereby increasing its revenue and profits.
2.4. Strengthening Tencent's Diversification and Building Tencent's Business Ecosystem
Tencent has been committed to its diversification strategy in order to reduce its reliance on the gaming business [10]. The acquisition of CMC is also part of Tencent's diversification strategy: by acquiring CMC, Tencent can quickly expand its music entertainment segment, achieve content diversification, what's more, the acquisition will help Tencent expand into international markets through CMC's overseas markets, and advance Tencent's internationalization process, which will achieve a more comprehensive diversification strategy.
Tencent has an extremely large business ecosystem, represented by social software such as WeChat and QQ, which has formed a huge user base. By acquiring CMC, Tencent can overbearingly expand its business in music entertainment, bringing more content and value to its business ecosystem, and laying a solid foundation for building an all-round Tencent.
Tencent's complete business ecosystem, with the user volume of its brands shared with each other, can greatly improve user stickiness and bring more revenue to Tencent. In addition, the complete business ecosystem will also bring Tencent a brand effect, which means that Tencent will enter a virtuous cycle if there are no problems in its operations and other aspects. The brand effect of Tencent as a whole will drive the development of its brands, and the development of its brands will further strengthen Tencent and consolidate its position as the dominant player on the Internet.
3. Analysis of the Financial Effects
3.1. Debt-Paying Ability
Debt-paying ability refers to the ability of a company to use its own assets to repay its debts. The increase in the amount of capital reduces the risk of loss to creditors as a result of the company's bankruptcy due to a significant increase in consolidated capital and the possibility of increased financing capacity through mergers and acquisitions.
Table 1: Tencent’s current ratio (2015-2017). | |||
YEAR | Current Assets (Bn, CNY) | Current Liabilities (Bn, CNY) | Current Ratio |
2015 | 753.21 | 500.35 | 1.5053 |
2016 | 1,553.78 | 1,244.06 | 1.2490 |
2017 | 1,491.54 | 1,011.97 | 1.4739 |
Data source: East money information Co., ltd [11] | |||
This paper uses the short-term debt-paying ability indicator Current Ratio (Table 1) and the long-term debt-paying ability indicator Asset Liability Ratio (Table 2) for analysis respectively.
Table 1 shows that Tencent's current ratio decreased by 25.63% from 1.5053 in 2015 to 1.2490 in 2016, before rising to 1.4739 in 2017. The current ratio is a crucial sign of how well an organization is doing in the short term. Internationally, it is acknowledged that a current ratio of two is ideal, meaning that it is preferable to have twice as many current assets as current liabilities so that even if half of the current assets are lost or cannot be realized immediately, the other half of the assets can still ensure the payment of current liabilities. In 2016, after the completion of the acquisition of CMC, the proportion of Tencent’s current assets decreased and the proportion of its fixed assets should have increased, as shown in Table 2. In 2016, Tencent's Asset Liability Ratio was lower than in 2015, suggesting that the acqusition did not make excessive use of the leverage, and that the acqusition made full use of and chose the role of idle assets.
Table 2 shows that there was no appreciable change in Tencent's asset liability ratio between 2017 and 2016, indicating that corporate resources had been integrated reasonably satisfactorily and that the financial impact had been positive. Total assets increased by almost three times while the gearing ratio dropped to its lowest level in the previous three years, coming very close to the ideal standard of 50%. The financial effect of the acquisition is fully reflected in the financing capacity [7].
Table 2: Tencent’s asset liability ratio (2015-2017). | |||
YEAR | Current Assets (Bn, CNY) | Current Liabilities (Bn, CNY) | Current Ratio |
2015 | 3,068.18 | 1,847.18 | 0.6020 |
2016 | 3,958.99 | 2,096.52 | 0.5296 |
2017 | 8,655.13 | 4,391.15 | 0.5137 |
Data source: East money information Co., ltd [11] | |||
3.2. Profitability
Profitability is the primary indicator of a company's survival and development. In addition to this, we also look at Net Sales Rate, ROE/ROA, gross margin and Net Asset Ratio when evaluating projects or major investments in a company. Below this paper analyse Tencent's profitability before and after this acquisition to determine whether the company has gained financial effect.
Table 3 Tencent’s operating income and operating costs (2015-2017) (Bn, CNY). | ||
YEAR | Operating Income | Operating Costs |
2015 | 1,028.63 | 416.31 |
2016 | 1,519.38 | 674.93 |
2017 | 2,377.60 | 1,208.35 |
Data source: Tencent financial statements (2015-2017) [12] | ||
As can be seen from Table 3, operating revenue increased from 2015 to 2017, with a faster rate of increase between 2015 and 2016, but the acceleration of operating cost growth was relatively small, indicating that the financial effect gained synergistic value-added after the acquisition. The increase in operating costs after the acquisition should be attributed to the large amount of capital invested after the acquisition, which led to an increase in costs. As can be seen from Table 4, Tencent's operating profit margin and net profit margin both increased after the acquisition, fully reflecting the post-acquisition financial synergy effect [7].
Table 4 Tencent's operating margin and net profit margin (2015-2017) (Bn, CNY). | ||
YEAR | Operating Margin | Net Profit Margin |
As at 31 December 2015 | 40% | 30% |
As at 31 December 2016 | 39% | 29% |
As at 31 December 2017 | 40% | 32% |
Data source: East money information Co., ltd [11] | ||
3.3. Development Capability
An important indicator of a company's ability to continue as a going concern is the development capacity indicator, such as sales growth rate, asset growth rate and profit growth rate. The data in Table 3 shows that sales increased by 47.76% in 2016 compared to 2015 and 56.48% in 2017 compared to 2016, which is 9 percentage points more post-acquisition than pre-acquisition, fully reflecting the post-acquisition development trend.
The calculations in Table 2 show that assets increased by 118.67% in 2017 compared to 2016 and by 29% in 2016 compared to 2015, 89 percentage points more after the acquisition than before.
Similarly, Table 4 shows that although the net profit margin in 2016 was only 29% in the year of the acquisition, which was lower than the previous year, it quickly rose to 32% in 2017, which demonstrates the strong momentum of Tencent's development and growth rate after the acquisition.
4. Impact on the Music Industry
4.1. Contributed to the Development and Popularity of Digital Music
With the rapid development and advancement of technology, the era of the Internet has arrived, and the traditional music industry will face the challenge of transformation and upgrading to cope with the wave of the Internet. The digital music industry is a major growth area for the global music market, while China's digital music market is indeed relatively lagging behind [6]. This acquisition also marks a major change in the music industry in China, making the online music platform show an increasingly active trend.
4.2. Issues that Should Concern
Calculations from figure 1 show that after this acquisition, TME's market share in China is 56%, which means that half of the Chinese music industry is in the hands of Tencent and the era of Tencent is upon us. Such a high market share would then potentially lead to a monopoly situation, which would greatly increase the barriers to entry in the music industry, while squeezing out the rest of the industry's relatively small market share, meaning that it could inhibit innovative behaviour in the industry and could also lead to an unhealthy competitive market environment.
5. Conclusion
This article analyses and studies the case of Tencent's acquisition of CMC, and focuses on the impact or significance of the acquisition on Tencent and the music industry. Tencent's acquisition of CMC to create a new TME is very much in line with Tencent's diversified development strategy. It completes Tencent's industrial chain in the music industry while complementing Tencent's business ecosystem; it expands Tencent's market share in China's music industry and, moreover, consolidates its position as an internet giant and expands its influence. Analysis of the financial effects shows that after this merger and acquisition, Tencent's debt-paying ability, profitability and development capability have all been improved compared to the previous ones. The figures tell us that Tencent is thriving, and time tells us that it is.
In addition to the opportunities and benefits of acquisition, the problems that can arise after an acquisition cannot be ignored. Tencent should take every step carefully when dealing with such a market-defining move, lest it violates local laws. Furthermore, an excessive market share could lead to monopolies and inhibit innovation, which in turn could lead to the unhealthy development of China's music industry.
The purpose of this paper is to collate information and analyse the impact and implications of this acquisition for Tencent and the Chinese music industry. However, some of the issues mentioned in the paper that require attention still exist today, such as Tencent's excessive market share in certain business segments, and the depth and breadth of this paper's research on these issues is still lacking, leaving room for further study and deeper investigation in the future.
References
[1]. J. Y. Wu. (2021). A Study on the Performance of Overseas Mergers and Acquisitions of Chinese Enterprises (Master's Thesis, Soochow University). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202301&filename=1021146967.nh
[2]. State and Municipal Supervision Department (2021) NO.67, Administrative Penalty Decision of the State Administration for Market Regulation. https://www.samr.gov.cn/xw/zj/202107/P020210724302729586098.pdf
[3]. Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (2007) Anti-Monopoly Law of the People's Republic of China. In: Twenty-ninth Session of the Standing Committee of the Tenth National People's Congress. Beijing.
[4]. General Administration of Market Regulation (2020) Provisional Provisions on Review of Concentration of Operators. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-10/28/content_5555291.htm
[5]. H. H. You. (2022). Antitrust Review of Concentration of Internet Platform Operators (Master's thesis, Northwestern University). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202301&filename=1022777973.nh
[6]. Jiemian News. (2016) Tencent becomes Market Leader with China Music Corporation Acquisition - Is There still Room for Shrimp and NetEase Cloud Music? https://www.jiemian.com/article/745316.html
[7]. Y. G. Yang. (2019).Analysis of strategic M&A motivations and financial synergies of Internet companies - An example of Tencent's acquisition of China Music Group. Business Accounting(05),33-36.
[8]. Imedia homepage. https://www.imediaasia.co/
[9]. Sohu. (2017) [Observation] Online music platform giants and their digital music rights competition landscape. https://www.sohu.com/a/169467214_99957768
[10]. X. Li. (2021). A study on the performance of Tencent's acquisition of Supercell (Master's thesis, Donghua University of Technology). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202201&filename=1021852444.nh
[11]. Eastmoney homepage. https://www.eastmoney.com
[12]. Eastmoney. (2015-2017) Tencent Financial Statements.http://emweb.securities.eastmoney.com/PC_HKF10/pages/home/index.html?code=00700&type=web&color=w#/newfinancialanalysis
Cite this article
Sun,C. (2023). Tencent's Acquisition of China Music Corporation: A Case Study. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,35,14-21.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. J. Y. Wu. (2021). A Study on the Performance of Overseas Mergers and Acquisitions of Chinese Enterprises (Master's Thesis, Soochow University). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202301&filename=1021146967.nh
[2]. State and Municipal Supervision Department (2021) NO.67, Administrative Penalty Decision of the State Administration for Market Regulation. https://www.samr.gov.cn/xw/zj/202107/P020210724302729586098.pdf
[3]. Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (2007) Anti-Monopoly Law of the People's Republic of China. In: Twenty-ninth Session of the Standing Committee of the Tenth National People's Congress. Beijing.
[4]. General Administration of Market Regulation (2020) Provisional Provisions on Review of Concentration of Operators. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-10/28/content_5555291.htm
[5]. H. H. You. (2022). Antitrust Review of Concentration of Internet Platform Operators (Master's thesis, Northwestern University). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202301&filename=1022777973.nh
[6]. Jiemian News. (2016) Tencent becomes Market Leader with China Music Corporation Acquisition - Is There still Room for Shrimp and NetEase Cloud Music? https://www.jiemian.com/article/745316.html
[7]. Y. G. Yang. (2019).Analysis of strategic M&A motivations and financial synergies of Internet companies - An example of Tencent's acquisition of China Music Group. Business Accounting(05),33-36.
[8]. Imedia homepage. https://www.imediaasia.co/
[9]. Sohu. (2017) [Observation] Online music platform giants and their digital music rights competition landscape. https://www.sohu.com/a/169467214_99957768
[10]. X. Li. (2021). A study on the performance of Tencent's acquisition of Supercell (Master's thesis, Donghua University of Technology). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202201&filename=1021852444.nh
[11]. Eastmoney homepage. https://www.eastmoney.com
[12]. Eastmoney. (2015-2017) Tencent Financial Statements.http://emweb.securities.eastmoney.com/PC_HKF10/pages/home/index.html?code=00700&type=web&color=w#/newfinancialanalysis