1. Introduction
On March 22, 2023, the U.S. Federal Reserve Board concluded its two -day monetary policy meeting and announced that it would increase the target range of the federal funds rate (that is, raise interest rates) by 25 basis points to between 4.75% and 5%. The interest rate has reached the highest level since September 2007. On the other hand, on March 16, 2022, the US Federal Reserve ushered in the first-rate hike of 25 basis points (since December 2018). On September 21, November 2, and December 4, 50 basis points of interest rate hikes were carried out, and four consecutive 75 basis point interest rate hikes and the final 50 basis point interest rate hikes were completed. Immediately after 2023, a 25-basis point rate hike will begin on February 25 [1].
This round of interest rate hikes has raised interest rates nine times since 2022, with a total of 475 basis points of interest rate hikes. bankruptcy liquidation. The sharp rate hike also highlights the urgency of the Federal Reserve to tighten monetary policy and control inflation.
This article uses this to analyze the impact of the Fed's sharp interest rate hike on the financial market, and to analyze how China should respond to this situation and stabilize China's own economy. This paper first studies the reasons for the Fed’s sudden and sharp interest rate increase, and then studies the impact of this interest rate increase, and then China’s measures and policies to face the impact of this interest rate increase, and finally puts forward an outlook.
2. Reasons
2.1. "Pay the Bill" for the Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic
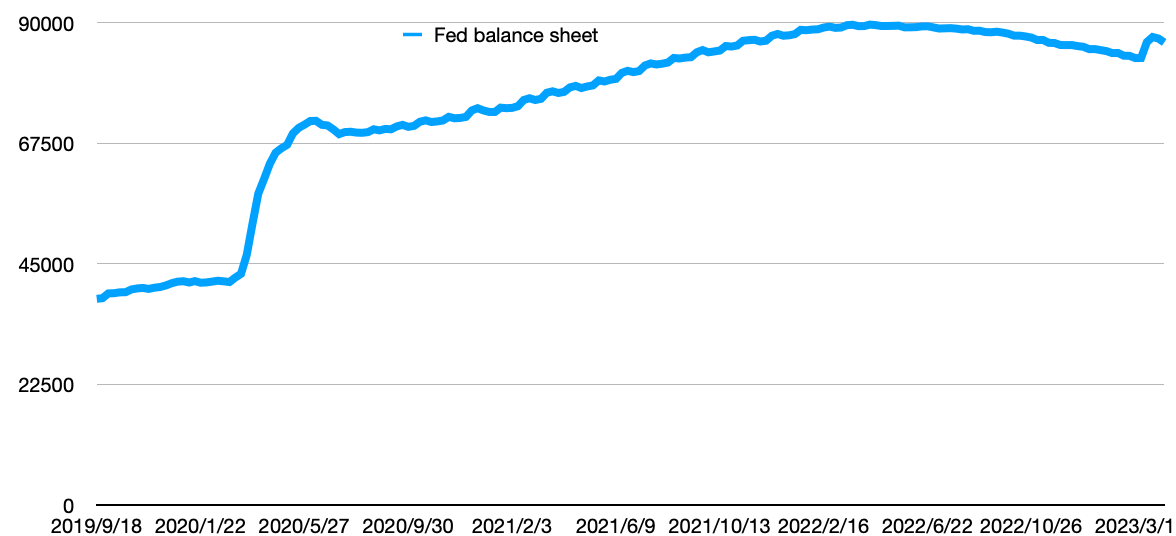
The Covid-19 pandemic is gradually dissipating, and the normal economic indicators and interest rates before the epidemic must be restored. At the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic, it spread rapidly in the United States, resulting in violent fluctuations in the capital market. A large number of economic activities were affected by the Covid-19 pandemic, resulting in a sharp rise in unemployment and exhaustion of economic activities. For this reason, the Federal Reserve cut interest rates urgently on March 3 and 15, 2020, lowering the interest rate to the range of 0 % to 0.25 % [1]. grow. The Federal Reserve is printing dollars like crazy in 2020 to stimulate the U.S. economy. According to Figure 1, the U.S. balance sheet shows that at the end of 2019, the assets of the United States were less than 5 trillion U.S. dollars, and the assets had soared to 8 trillion U.S. dollars in just over a year. This shows that the Federal Reserve has More than 3 trillion U.S. dollars of currency were printed madly, which also led to a slight depreciation of the U.S. dollar. Now that the epidemic is under control, the United States has begun to "pay" for the substantial waterproofing during the epidemic. In order to restore the US dollar index, it has begun to raise interest rates sharply.
|
Figure 1: Fed balance sheet. |
Data source: Macroview Club [2]. |
Photo credit: Original |
2.2. Russia-Ukraine Conflict
The conflict between Russia and Ukraine has slowed economic growth and accelerated inflation throughout the world. First, due to the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, the exports of Russia and Ukraine have been suppressed, and the supply of bulk commodities and energy resources has decreased, but the overall demand has not decreased, which is causing the prices of energy and bulk commodities to rise sharply. Second, as business confidence declines and investor uncertainty increases, capital will withdraw. In response to this impact, the Federal Reserve began to raise interest rates to control the sharply rising inflation, and by raising interest rates, the Federal Reserve raised the U.S. dollar index and attracted more capital to flow into the U.S. capital market to promote the development of the U.S. economy.
2.3. Runaway Inflation
During the epidemic, all countries responded to the epidemic, and their economies were severely affected. In this regard, the number of goods imported by the United States has decreased, and because the United States has printed a large number of U.S. dollars, the U.S. dollar has depreciated slightly, and the U.S. dollar index has fallen. The stimulus is more conducive to U.S. exports. Imported goods have decreased significantly, but people’s overall demand has not changed. Therefore, the price of commodities in the United States has risen significantly, and inflation has risen sharply. It only took 7 months for the CPI index to rise from 7.00% to 9.10% in December 2021. For the underestimated and out-of-control inflation rate, the Fed has no choice but to Sharp rate hike. It took only 13 months to raise interest rates by 475 basis points.
3. The Storm Caused by the Fed's Interest Rate Hike
3.1. The Raising Interest Rates
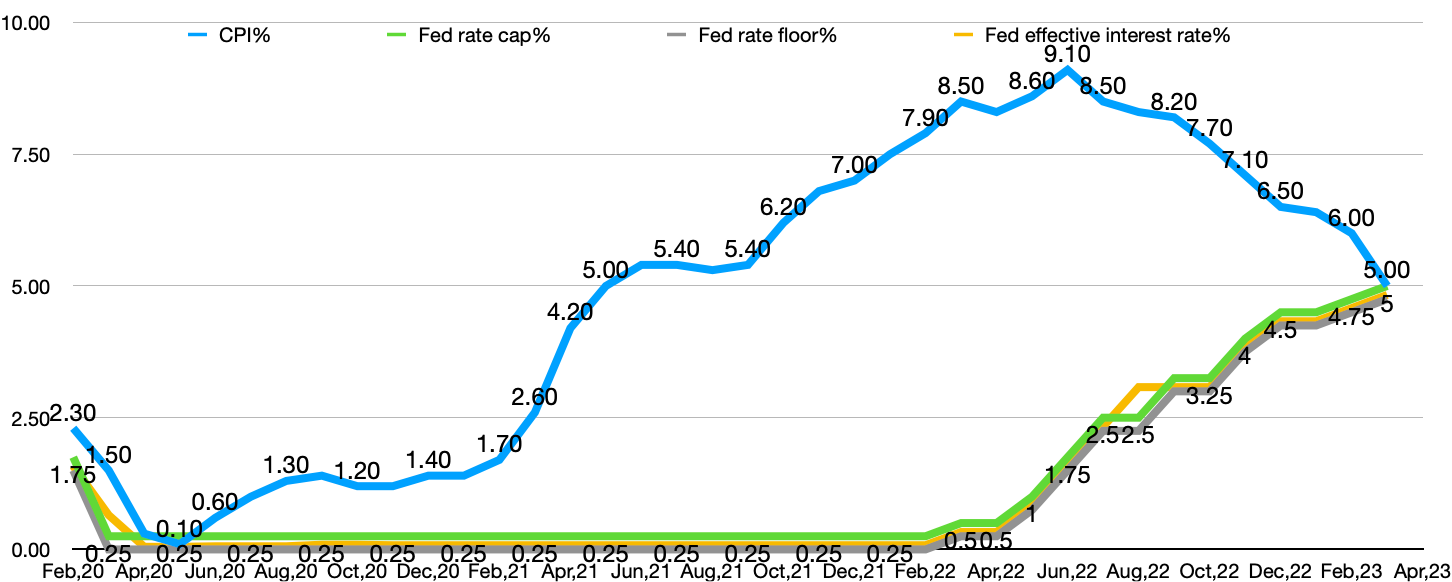
According to Figure 2, the U.S. consumer price level and the Federal Reserve interest rate icon show that the U.S. CPI increased by 8.3% year-on-year in August, which has dropped significantly from 9.1% in June and 8.5% in July, but there is still panic. The first reason This is because the decrease in the inflation rate has the influence of the base, not the decrease in the actual inflation level; the second point is that after removing the volatile food and energy prices, the core CPI in August rose by 0.6% year-on -year, an increase of 7%. The month expanded by 0.3 percentage points; it rose by 6.3% year-on-year, and the increase was 0.4 percentage points higher than that in July. It shows that the inflation rate is not sensitive to the Fed's sudden interest rate hike, and inflation is gradually getting out of control [1,3,4,5].
|
Figure 2: US consumer price levels and Fed interest rates. |
Data source: Macroview Club [1,3,4,5] |
Photo credit: Original |
3.2. The Impact of Interest Rate Hikes on the Stock Market
The Federal Reserve raises interest rates, and the interest rate return on money deposited in the bank becomes higher. Investors are less willing to hold stocks for a long time, and are more willing to sell stocks and deposit them in the bank. Therefore, more funds are deposited in the bank and funds flow into the stock market. It will decrease, then the liquidity of the stock market will weaken, and the US stock market will plummet. During the period from April 18, 2022 to March 6, 2023, the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell from 33811.40 to 31909.64, the Nasdaq Composite Index fell from 12839.29 to 11138.89, the S & P 500 The index fell to 3861.59 from 4271.78. It can be seen that the three indexes of the U.S. stock market have decreased to varying degrees, and the Fed’s interest rate hike has caused a major blow to the U.S. stock market [6]. Uncertainty over the Fed's sharp rate hikes has also left investors hesitant about U.S. stocks, turning it into a crisis of confidence. The banking sector also suffered sharp declines, with Deutsche Bank falling by more than a quarter. According to the fund manager of BoFA Global Research, the asset allocation of US stocks in March 2023 is the least since 2018 [7]. After the Federal Reserve raised interest rates sharply, the Silicon Valley Bank of the United States could not bear the impact of bankruptcy and liquidation caused by the sharp interest rate increase. On March 13, the stocks of major US banks fell off a cliff, with a market value loss of up to 90 billion U.S. dollars. According to the previous Over the course of three trading days, the market value has evaporated by as much as US$ 190 billion. The U.S. regional banks were the hardest hit, and the share price of First Republic Bank plummeted by more than 60% [8].
3.3. The Impact of Interest Rate Hikes on the Bond Market
As the Federal Reserve sharply raised interest rates (hike rates), the most closely watched bond market volatility indicator, the ICE BofA MOVE index, soared to its highest level since the outbreak of the last major financial crisis in the United States in 2009 [9]. However, with the rise in interest rates, investors who started holding bonds in 2020 suffered floating losses, because the yield of bonds during that period was only 1.5 %. [3] The difference between the 1.5 % bond yield and the current interest rate is nearly 4%. This huge interest rate difference has caused most bond investors to suffer floating losses. For example, the Silicon Valley Bank of the United States allocated a large amount of assets in securities, so that when faced with the sale of 21 billion US dollars of liabilities, it turned a floating loss into a real loss, with a loss of 1.8 billion US dollars, and finally suffered a squeeze and declared bankruptcy [10]. The yield on the 10-year U.S. Treasury bond fell sharply following bank failures, driven by spreads reaching 4% [9]. It can be seen that the Fed's interest rate hike has put investors who previously held bonds under tremendous pressure and floating losses.
3.4. The Impact of Interest Rate Hikes on China's Financial Markets
The first is the impact on the exchange rate between China and the United States. When the Fed raises interest rates, the RMB will depreciate. In the case of a substantial interest rate increase, it will be more beneficial to the US dollar, and investors' trust in the US dollar will increase, so the United States will attract more investors' funds, and the opposite is true for the Chinese investment market in RMB. A large amount of investors' funds will flow out, which has an important impact on China's economic stability and development. As for Chinese assets, if the dollar appreciates and the renminbi depreciates, there may be cracks in the renminbi bubble economy. Especially in the real estate industry, China's real estate industry occupies a large amount of assets in China, and once the RMB bubble economy cracks, it will trigger many potential crises, such as shadow banking, illegal loans and other issues. But overall, China's economic threat is not fatal, because China's mortgage policy is relatively strict. From the perspective of cultural customs, most Chinese rely on the down payment to buy a house, regard the house as the support of a family, and have the idea that they will feel relaxed without debt, so the phenomenon of default repayment is still rare. Therefore, the threat to China's deadly economy is relatively limited [11]. Secondly, it also has a certain impact on China's international trade. With the depreciation of the RMB, it will bring good news to China's exports and become more competitive.
4. Compared with the Last Round of Fed Rate Hike
Compared with this round of Fed rate hikes, we can compare the previous round of Fed rate hikes. According to the financial crisis caused by the subprime mortgage crisis in 2007, the Federal Reserve cut interest rates repeatedly to restore the economic level of the United States. From 2007 to December 2015, the Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 425 basis points in total, down to 0.5 %. Under the loose monetary policy, the GPA of the United States quickly rose to 2.9 %, the unemployment rate dropped to 5.9%, and the core inflation rate rose to 1.7 %. The U.S. economy is on the right track and gradually recovering. The Federal Reserve announced the end of quantitative easing in 2015 and further implemented balance sheet shrinkage. The federal funds rate was raised nine times, to 2.5% in December 2018, and remained at a low rate of 3.5% in 2019 [12]. On the other hand, the frequency of interest rate hikes this time has been extremely accelerated and the range is also large. The 13 -month rate hike was 425 basis points. This is unprecedented in history, and the impact is unpredictable. Silicon Valley Bank A typical victim in the process of raising interest rates this time.
5. How Should China Respond to the Impact and Challenges of the Fed's Sharp Interest Rate Hike
First, implement an independent and effective monetary policy. In the face of the Fed's sharp rise in interest rates and the depreciation of the renminbi, the People's Bank of China did not implement a policy of raising interest rates, but instead lowered them twice. Adopted a policy opposite to that of the United States. In the context of this interest rate cut, all countries have experienced the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic and the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, and they all face the problem of high inflation. The CPI of each country is as high as 10 % [13]. But China is just the opposite, the increase of China's CPI is only about 2% [13]. This is firstly due to China's good control of the Covid-19 pandemic, the adoption of correct epidemic measures, and the unblocking of the epidemic at an appropriate time according to national conditions to carry out effective economic recovery. Cutting interest rates can also stimulate the domestic investment market, improve the liquidity of domestic investment, and release the pressure on the financial market. Cutting interest rates is the most effective way. The interest rate cut by the People's Bank of China has promoted loans to more effectively promote the recovery of the real economy after the epidemic is unblocked [13]. Secondly, it is necessary to accelerate the internationalization of the renminbi. The reason why the U.S. dollar can have a strong impact on the world economy is because the U.S. dollar is equated with oil and gold, making it a means of circulation for countries around the world. Therefore, in the face of the Fed's interest rate hike, the Chinese central bank government must first ensure the stable development of the Chinese economy and reduce the security and financial crisis, and secondly, solve the dollar problem from the root. Strengthening the international circulation rate of the RMB and reducing its peg to the US dollar will reduce China's interest rate impact on the US dollar. The first step to internationalize the renminbi is to continue to maintain an open attitude and policies to carry out bilateral and multilateral trade, deepen international trade exchanges of the renminbi, and continue to actively integrate into the multilateral trading system [14].
6. Conclusion
In this article, just after China’s Covid-19 pandemic was unblocked, in the era of conflicts between Russia and Ukraine, all parts of the world are facing different degrees of inflation. In particular, the CPI in the United States has increased significantly, and it is gradually losing control. The Federal Reserve announced an emergency rate hike, and the frequency of rate hikes was so high and the rate hike rate was so large that it took only 13 months to raise the rate by 425 basis points. In the face of such a substantial interest rate hike, the whole world has been affected to varying degrees by this rate hike. The first is the capital market in the United States. Due to the increase in interest rates, the Silicon Valley Bank of the United States experienced a large-scale floating loss on the bank's bond assets, and the sale turned into an actual loss. In the end, it was severely squeezed and went bankrupt quickly. Secondly, the impact of the Federal Reserve's interest rate hike on China's financial capital market has caused a large amount of capital to flow to the US market. In the face of such challenges and crises, what policies has China adopted to deal with the disorderly flow of short-term cross-border capital caused by the Fed's interest rate hike?
Finally, this study found that any measures should be combined with the actual situation of the country itself. The monetary policy implemented by China is quite different from that of the United States and other European countries. Instead, it took the initiative to lower interest rates twice to stimulate the capital market and let the financial market release enough Vitality and liquidity, and lower interest rates to relax the loan market to promote the recovery of the real economy in China just after the epidemic was unblocked.
However, in the face of the strong connection of the U.S. dollar to the world economy, China’s financial and economic market will be stronger and stronger only if the renminbi further moves towards the international market, increases bilateral trade, reduces dependence on the U.S. dollar, and further deepens trade activities in the world economic system. Calmly respond to the adverse impact of changes in the US dollar on China.
References
[1]. Macroview Club. (2023). US Fed rate upper limit. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_fed_rate_upper_limit.
[2]. Macroview Club. (2023) US _fed_assets. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_fed_assets.
[3]. Macroview Club. (2023) US CPI. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_cpi.
[4]. Macroview Club. (2023) US fed rate. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_fed_rate.
[5]. Macroview Club. (2023) US _fed rate lower limit. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_fed_rate_lower_limit
[6]. Yahoo Finance (2023) https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/YM%3DF?p=YM%3DF.
[7]. David Randall. (2023). Analysis: Banking woes, Fed keep US market investors on edge. https://www.reuters.com/markets/us/banking-woes-fed-keep-investors-edge-nervous-us-stock-market-2023-03-25/
[8]. Reuters (2023) Morning Bid: Bank stress, bond volatility and disinflation. https://www.reuters.com/markets/global-markets-view-usa-2023-03-14/.
[9]. US Bank. (2023) How rising interest rates impact the bond market. https://www.usbank.com/investing/financial-perspectives/market-news/interest-rates-affect-bonds.html.
[10]. H. Geman, (2023) From Lehman to Silicon Valley Bank and Beyond: Why Are Mistakes repeated in the US banking system?. Policy Center for the New South. 16/23.
[11]. Y L v, (2019) Analysis of the impact of the Fed's interest rate hike on China's foreign exchange market. Modern Marketing (Information Edition), 105-106.
[12]. Y Yang, (2020) The Spillover Effects of Fed's Tightening Monetary Policy on China's Economy. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C475KOm_zrgu4lQARvep2SAkHr3ADhkADnVu66WViDP_3LkmKdB_OMJ-MOGwLi7HjWE1BZ0nN2Gdk1JFjPsaUp3J&uniplatform=NZKPT&src=copy
[13]. Y Chen, Z Huang, Y Zeng, (2023) Powell's "hawkish" speech, the Fed's interest rate hike expectations have increased sharply! How should China respond? https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1759794583452436733&wfr=spider&for=pc.
[14]. Y Yang (2022) The Spillover Effect of Future Fed Rate hike on China's Economy and Countermeasures. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C475KOm_zrgu4lQARvep2SAke-wuWrktdE-tSIT2YIbQ2FJ4LIc05_TmiJ2x6S1_ZDk5Ijf-ZuchQ0P4l1SPJg5y&uniplatform=NZKPT&src =copy.
Cite this article
Cai,D. (2023). The Financial Turmoil Caused by the Fed's Sharp Rate Hike: Reasons, Impacts and Countermeasures. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,36,93-98.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Macroview Club. (2023). US Fed rate upper limit. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_fed_rate_upper_limit.
[2]. Macroview Club. (2023) US _fed_assets. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_fed_assets.
[3]. Macroview Club. (2023) US CPI. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_cpi.
[4]. Macroview Club. (2023) US fed rate. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_fed_rate.
[5]. Macroview Club. (2023) US _fed rate lower limit. https://www.macroview.club/data?code=us_fed_rate_lower_limit
[6]. Yahoo Finance (2023) https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/YM%3DF?p=YM%3DF.
[7]. David Randall. (2023). Analysis: Banking woes, Fed keep US market investors on edge. https://www.reuters.com/markets/us/banking-woes-fed-keep-investors-edge-nervous-us-stock-market-2023-03-25/
[8]. Reuters (2023) Morning Bid: Bank stress, bond volatility and disinflation. https://www.reuters.com/markets/global-markets-view-usa-2023-03-14/.
[9]. US Bank. (2023) How rising interest rates impact the bond market. https://www.usbank.com/investing/financial-perspectives/market-news/interest-rates-affect-bonds.html.
[10]. H. Geman, (2023) From Lehman to Silicon Valley Bank and Beyond: Why Are Mistakes repeated in the US banking system?. Policy Center for the New South. 16/23.
[11]. Y L v, (2019) Analysis of the impact of the Fed's interest rate hike on China's foreign exchange market. Modern Marketing (Information Edition), 105-106.
[12]. Y Yang, (2020) The Spillover Effects of Fed's Tightening Monetary Policy on China's Economy. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C475KOm_zrgu4lQARvep2SAkHr3ADhkADnVu66WViDP_3LkmKdB_OMJ-MOGwLi7HjWE1BZ0nN2Gdk1JFjPsaUp3J&uniplatform=NZKPT&src=copy
[13]. Y Chen, Z Huang, Y Zeng, (2023) Powell's "hawkish" speech, the Fed's interest rate hike expectations have increased sharply! How should China respond? https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1759794583452436733&wfr=spider&for=pc.
[14]. Y Yang (2022) The Spillover Effect of Future Fed Rate hike on China's Economy and Countermeasures. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C475KOm_zrgu4lQARvep2SAke-wuWrktdE-tSIT2YIbQ2FJ4LIc05_TmiJ2x6S1_ZDk5Ijf-ZuchQ0P4l1SPJg5y&uniplatform=NZKPT&src =copy.