1. Introduction
Live Action Role Playing (LARP), also translated as Script Killing Game, is a burgeoning entertainment activity in recent years in China [1]. Analyzing this new type of entertainment, it is not difficult to realize the reason why it is so attractive to the Z generation — entertaining, interactive, and informative [2]. Besides, immersive experience is also one of the most basic characteristics of LARP games [3]. In a LARP game, consumers can express themselves, establish and maintain social connections with others, and their communication and perception in this situation can produce pleasant subjective experiences, which is called immersive experience [4]. After nearly 7 years of development, LARP has now become a mature industry chain. However, with the dramatic increase in the number of stores, there is now an oversupply in the market. There are currently about 500 more LARP stores in Beijing and Shanghai [5]. Under this condition, many offline stores are unable to attract enough customers, facing problems with market transformation or marketing strategy optimization, or they will be confronted with closing down [6]. Wang and Zhou analyzed the reasons behind this development dilemma and suggested that the market should focus on improving the govern system, formulating the content strategy, and adopting “LARP+” (i.e., integration with other industries) [5]. However, papers discussing the LARP market now are too diverse and with less depth; most of them are focusing on the current market situation or formulating related strategies for the problems that have arisen. In the face of the rapidly growing LARP market, the data-based statistical analysis articles are not sufficient to support the marketing strategy optimization of LARP merchants. Therefore, this paper starts with consumer behavior, studies consumer tendencies through statistical analysis, and determines the determining factors of LARP consumption. The research results of this article are beneficial for LARP merchants to optimize their marketing strategies.
2. Methodology
The paper mainly uses statistical methods to analyze the LARP consumer profile. Except for the gender and age proportion study, which are according to Jinyi Wu’s research, all the rest analysis was based on the data sample collected from Miquan, a professional LARP website containing almost all LARP scripts and consumption information [7]. The paper collected multiple variables of LARP scripts to analyze the consumer preference. The paper uses descriptive analysis to determine the consumer’s preference for the script. Besides, the regression analysis was performed with one-tailed test and the significance level was set at P < 0.1.
3. LARP Market Status Overview
The paper will introduce several commonly used LARP terminologies [8]. As shown in Table 1, one LARP game usually needs two outside characters: DM and NPC; LARP scripts can be divided into three categories: Exclusive Access Script, City Limited Script, and Boxed Script (price and scarcity from high to low).
Table 1: Terminology used in the LARP market.
DM (Dungeon Master) | The presenter of every LARP game. |
The presenter of every LARP game. | Collective term for works of literature, music, art, games, etc. Some LARP scripts buy IP to compose. |
NPC (Non-Player Character) | A service character in every LARP game, to move the story forward. |
Exclusive Access Script (Du Jia Quan Xian Ben) | A type of LARP scripts that only one LARP shop can own in each city. |
City Limited Script (Cheng Shi Xian Ding Ben) | A type of LARP scripts that limit the number of shop owners in each city. |
Boxed Script (He Zhuang Ben) | A type of LARP scripts that all formal shops can buy. |
In 2016, a new online variety show called “Who’s the Murder” appeared in China, which soon swept the young people and introduced a new consumer experience called “Live Action Role Playing” (LARP) games. This variety show motivated board gamers and laid the foundation for LARP development in China [5]. Since 2016, online LARP games have appeared in the form of mobile APPs and became popular in 2018. People would play LARP fully in the virtual room with suited strangers or friends. Since 2018, LARP has gradually transformed offline, which led the number of LARP shops to surge in 2019. According to the data of the Meituan Research Institute, the number of LARP offline stores drastically increased from 2400 to 12000. Until the end of 2020, this number had changed to 30,000 [9].
4. The LARP Market’s Consumer Profile
4.1. The LARP Market’s Consumer Behavior
4.1.1. The Gender and Age Proportion
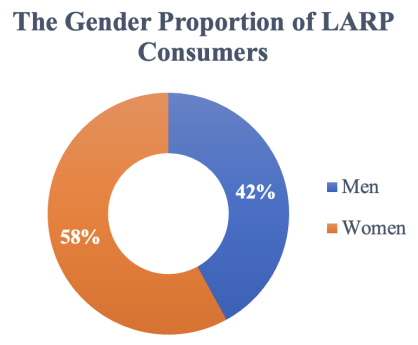
Figure 1: The gender proportion of LARP consumers.
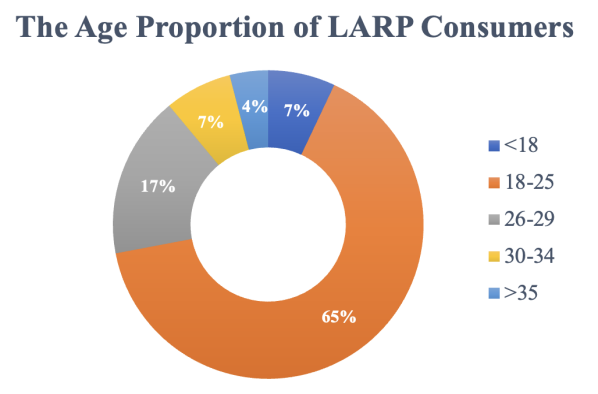
Figure 2: The age proportion of LARP consumers.
As the data shown in Figure 1, 58% of LARP consumers were women and 42% were men [8]. A possible explanation could be the fact that women are paying more attention to variety shows like “Who’s the murder” which contain more KOL. To be more specific, “Who’s the murder” Season Six was shown on December 24, 2020. Based on Baidu Index’s data for “Who’s the murder” and LARP’s search index in 2020-2021, before the variety show, the search index for LARP was 8,000 on average, whereas during the peak period of the variety show, the search index of LARP rose to 20,000 [10]. Therefore, “Who’s the murder” is an important way to draw attention to LARP. Besides, according to data from Baidu Index’s search results for “Who’s the murder” in 2022, women accounted for 67.8% [10]. Thus, such variety shows have more influence on female groups, which drives more consumption on women.
Moreover, as data shown in Figure 2, 65% of consumers fall into the 18-25 age group [8]. Young people regard the LARP games as a way to hide from reality and immerse themselves in immersive and virtual entertainment to find their true emotion [11]. They have more free time during weekends or holidays. Besides, in the information era, the promotion of the LARP game online is most easily to be accepted by young people since they are the main participants of social media. Meanwhile, young people’s consumption concept has changed: from “functionalism” to “experientialism”, which makes them different from the older generation [11]. They focus more on the emotional and spiritual needs, which also determine their consumption behaviors, and the LARP games are exactly what they need.
4.1.2. The Consumer Preference of LARP Script Plot Type
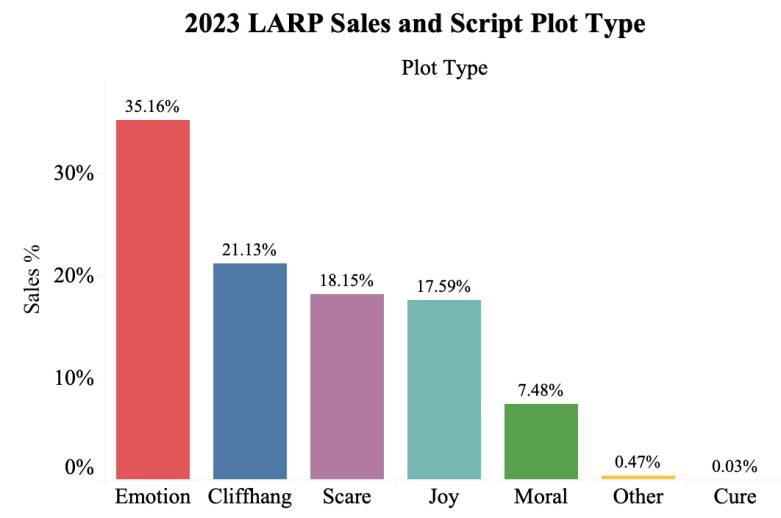
Figure 3: 2023 LARP sales and script plot type.
As shown in Figure 3, 35.16% of sales fall into the “Emotion” plot type (the script will focus on the characters emotion and moving story), which means most consumers prefer this plot type. The next three preferences are the “Cliffhanger”, “Scare”, and “Joy” type, which don’t show a great difference. The paper thinks that the reason why Emotion type is more popular is that it can easily provide an immersive experience for consumers, so it satisfies consumers’ necessities [8].
4.1.3. The Consumer Preference of LARP Script Gameplay
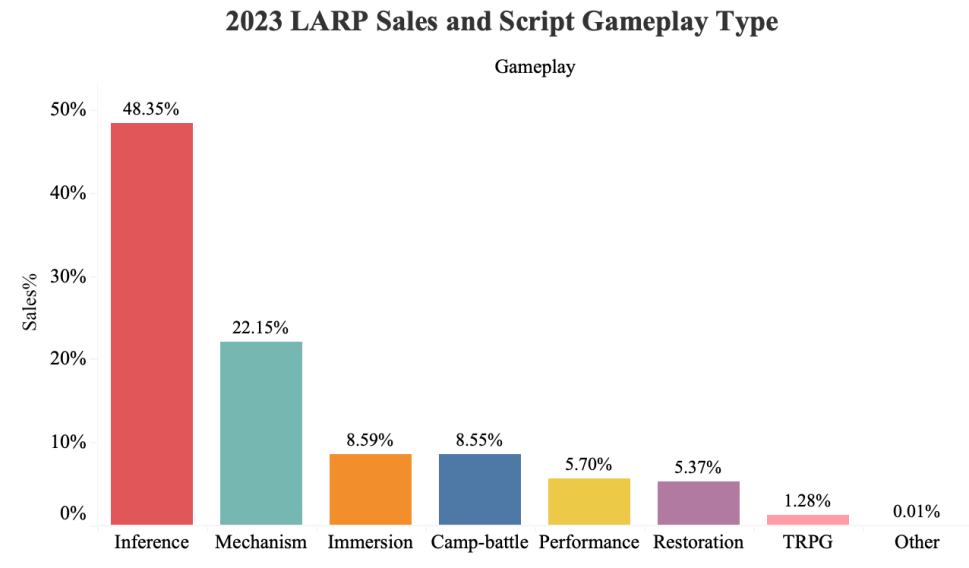
Figure 4: 2023 LARP sales and script gameplay type.
For the gameplay of LARP, almost half (48.53%) of the sales fall into the “Inference” gameplay script, in which players need to collect clues and judge the “case” according to the progress of the story [8]. The deciphering process is exciting and can help consumers gain a great sense of satisfaction when they successfully get the inference. The Mechanism type also occupies nearly a quarter of the sales (22.15%) since this type has an innovation: borrowing the storyline from the script and incorporating a tabletop game into the script. Thus, this design also attracts many players (Figure 4).
4.1.4. The Consumer Preference of LARP Script Theme
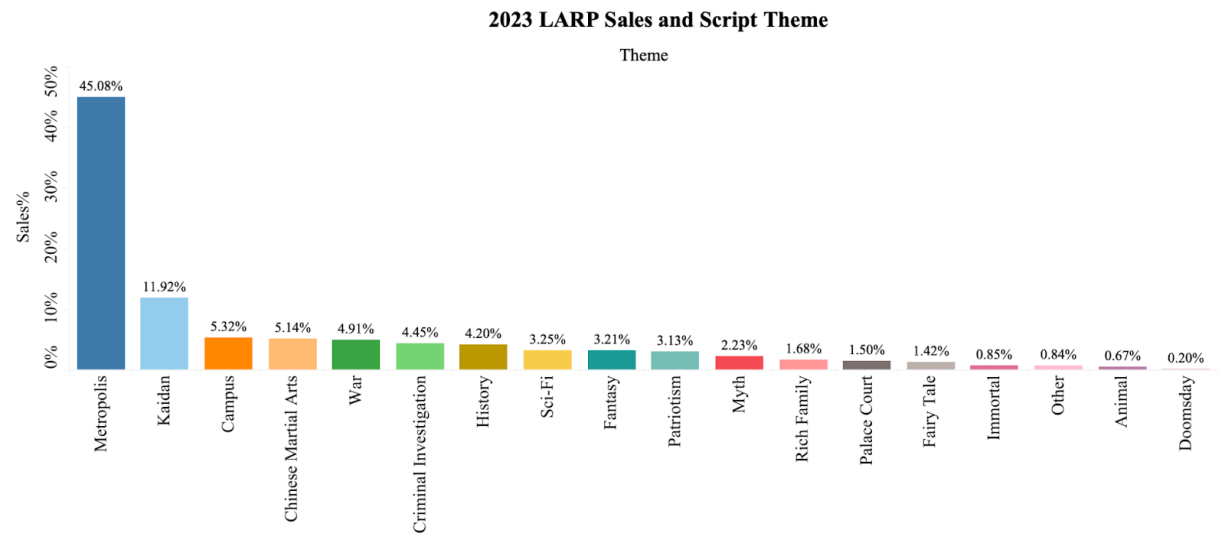
Figure 5: 2023 LARP sales and script theme.
After analyzing the theme of the script (Figure 5), nearly half (45.08%) of the sales are from the “Metropolis” theme, which means the whole story will expand surrounding the metropolis like the workspace, the restaurant, or other common scenes in daily life. This type of theme is the most familiar one for people since it is close to daily life; it is also the most common script theme in the LARP market, which is why it occupies the highest proportion of sales and consumer preference. Other themes like Kaidan, War, History, etc. are relatively out of reality, so they are not so attractive to players.
4.1.5. The Consumer Preference of LARP Script Difficulty
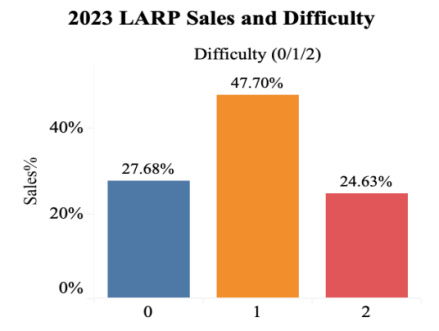
Figure 6: 2023 LARP sales and difficulty level.
LARP games currently have three difficulty levels — Easy, Advanced, and Hard —numbered from 0 to 2 in the data analysis. According to Figure 6, 47.7% of the sales are from the “Advanced” level, 27% from “Easy”, and “24%” from “Hard”. People who play LARP for the first time will always choose the Easy level to have a better experience. Generally, after the first attempt people will begin to choose the advanced level since the story is more complex and the inference part will be more challenging, which is more appropriate for most consumers. Thus, almost half of the sales fall into this difficulty level.
4.1.6. The Consumer Preference of LARP Script Issue Type
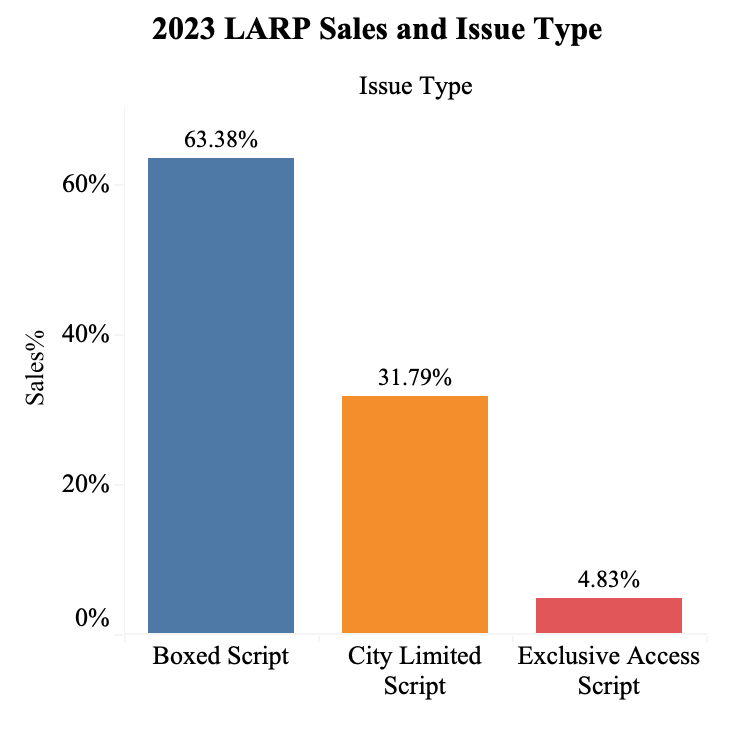
Figure 7: 2023 LARP sales and issue type.
64.3% of the sales are Boxed Scripts since the price of such script is the lowest, typically 68-100 RMB. However, for City Limited Script and Exclusive Access Script, the price typically ranges from 120-160 RMB and 200-400 RMB, respectively (Figure 7).
4.2. The Driving-factors of LARP Consumer Behavior
By using the regression model in Excel, the result shows Difficulty’s P-value is 0.056, No. of Players’ P-value is 0.82, Duration’s P-value is 7.55E-06, and Price’s P-value is 1.5E-03. Thus, three variables, Difficulty Level, Duration, and Price have a significant influence since the P-value is lower than 0.1 (Alpha).
Table 2: Regression analysis result of four independent variable and sales (MS excel).
Regression Statistics | ||||||
Sample | 249 | |||||
df | SS | MS | F | Significance | ||
Regression Analysis | 4 | 1.02E11 | 2.55E10 | 1.21E+1 | 5.37E-09 | |
Residual | 244 | 5.15E11 | 2.11E09 | |||
Total | 248 | 6.17E11 | ||||
Coefficient | SE | t Stat | P-value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | |
Intercept | 1.36E05 | 2.40E04 | 5.66 | 4.13E-08 | 8.87E04 | 1.83E05 |
Difficulty | 9.71E03 | 5.07E03 | 1.92 | 0.0565 | -2.70E02 | 1.97E04 |
Players | 6.38E02 | 2.93E03 | 0.218 | 0.828 | -5.13E03 | 6.41E03 |
Duration | -1.54E04 | 3.37E03 | -4.58 | 7.55E-06 | -2.20E04 | -8.77E03 |
Price | -1.83E02 | 5.70E01 | -3.21 | 1.52E-03 | -2.95E02 | -7.06E01 |
According to this regression statistics shown in Table 2, the paper generates a LARP Sales Model which predicts the sales (1,000) of LARP script:
Sales = 13.59 + 0.97 * Difficulty Level - 1.54 * Duration Time - 0.02 * Price(1)
By using this LARP Sales Model, the merchant stores can predict the sales of a new script before selling.
5. Discussion
Before generating a model for LARP consumption prediction, the paper considered many potential models used in this project. Since there are multiple types of variables in the LARP market, including quantitative data (such as duration time, number of players, prices, and online rate) and qualitative data (such as theme type, gameplay type, plot type, and issue type), the choice of models would be important. Currently, the paper only considers the quantitative variables and one qualitative variable, “difficulty,” which is transformed into a numeric value. Therefore, there is still a lot of room to optimize the LARP sales model. The paper thinks there are several aspects that can be improved. To begin with, there can be a larger sample size for the computer to train the data, so this model can predict sales more accurately. The LARP website Miquan includes almost all scripts from 2019 to the present, which are more than 3000 scripts, and the sales are the sum since putting them on sale. As a result, there is a confounding factor — “time” — which also influences sales. Thus, by increasing the sample size, this confounding variable’s impact can be eliminated as much as possible. Secondly, since now the paper only considers the quantitative variables in the model, in the future, the research objects can include both qualitative and quantitative values, which will make the model closer to the real situation. Based on this change, the research should also reconsider the type of model to increase accuracy. Therefore, the future study can choose from Random Forest, which performs best in small sample size, and Neural Networks, which performs best in large sample size, and other machine learning methods.
6. Conclusion
As more and more stores enter the LARP market, current stores have to consider their strategies corresponding to the competitive situation. Based on the consumer preference analysis, the paper suggests that merchants should focus on women in the Z generation, as they constitute the main part of LARP consumers. Merchants can build IP from other entertainment markets such as music, film, and variety shows to attract these potential consumers. Meanwhile, merchants can utilize KOL as a tool to appeal to more customers. Moreover, merchants should pay attention to the script purchase by considering the types of script. Based on the LARP scripts sales analysis, merchants could introduce more scripts with “Emotion” plot type, “Inference” gameplay, or “Metropolis” theme, which are more popular. Furthermore, based on the regression analysis of LARP sales, the paper recommends merchants introduce more scripts with a shorter duration since the coefficient of this factor has a big negative value, which greatly influences sales. Currently, the paper focuses on the statistical analysis of the LARP markets, longing for generating a sales prediction model to provide a reference for merchants to optimize their marketing strategy. However, to tackle the competition better, the research should also analyze some successful merchants to figure out a better strategy under this competitive condition. Future research can utilize the case study method to analyze some merchants who successfully transformed or incorporated other forms of entertainment.
References
[1]. Chen, K. Research on Service Marketing Strategy Optimization of M Live Action Role Playing Store. East China Normal University, MA Thesis. (2022).
[2]. Wang, Z. H. & Zhai, G. Y. Cognitive Schema, Motivational Mechanism and Realistic Review of Youth Immersive Game Experience — Taking Script Killing as an ExampleJournal of Jining College, 44 (01), 57-64. (2023).
[3]. Feng, Z. L. A study on the immersion mechanism of script killing under the perspective of emotion.Media Forum, 6 (02), 57-59. (2023).
[4]. Feng, Z. L. A study on the immersion mechanism of script killing under the perspective of emotion.Media Forum, 6 (02), 57-59. (2023).
[5]. Wang, W. J. & Zhou, L. Y. Research on the development dilemma and countermeasures of the offline “script killing” industry [J]. Media Forum, 5 (08), 10-13+22. (2022).
[6]. Yang, N. & Zhang, Y. S. Analysis of the current situation and trend of script killing development in the entertainment industry environment. Modern Marketing (Academy Edition) (11), 87-89. (2021).
[7]. Miquan app, Retrieved May 14th, https://www.pgyer.com/jeH3.
[8]. Wu, J. Y. China Murder Mystery Game Industry Value Chain. Leadleo, Market Study. (2022).
[9]. Kang, Y. W. Script killing: offline entertainment scene with strong social attributes. Zhongtai Securities — Media Industry Generation Z Entertainment Consumption Series Research. (2021).
[10]. Baidu Index 2020, Retrieved May 3rd, index.baidu.com.
[11]. Zhang, J. T. & Zhang, Y. S. From “Script Killing” to “Secret Room Escape”: Youth Portrait,Multidimensional Causes and Risk Regula. Youth Research, (01), 78-85. (2023).
Cite this article
Jiang,Y. (2023). Consumer Behavior Analysis and Marketing Strategy Optimization in the Chinese Live Action Role Playing Market. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,39,31-38.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Chen, K. Research on Service Marketing Strategy Optimization of M Live Action Role Playing Store. East China Normal University, MA Thesis. (2022).
[2]. Wang, Z. H. & Zhai, G. Y. Cognitive Schema, Motivational Mechanism and Realistic Review of Youth Immersive Game Experience — Taking Script Killing as an ExampleJournal of Jining College, 44 (01), 57-64. (2023).
[3]. Feng, Z. L. A study on the immersion mechanism of script killing under the perspective of emotion.Media Forum, 6 (02), 57-59. (2023).
[4]. Feng, Z. L. A study on the immersion mechanism of script killing under the perspective of emotion.Media Forum, 6 (02), 57-59. (2023).
[5]. Wang, W. J. & Zhou, L. Y. Research on the development dilemma and countermeasures of the offline “script killing” industry [J]. Media Forum, 5 (08), 10-13+22. (2022).
[6]. Yang, N. & Zhang, Y. S. Analysis of the current situation and trend of script killing development in the entertainment industry environment. Modern Marketing (Academy Edition) (11), 87-89. (2021).
[7]. Miquan app, Retrieved May 14th, https://www.pgyer.com/jeH3.
[8]. Wu, J. Y. China Murder Mystery Game Industry Value Chain. Leadleo, Market Study. (2022).
[9]. Kang, Y. W. Script killing: offline entertainment scene with strong social attributes. Zhongtai Securities — Media Industry Generation Z Entertainment Consumption Series Research. (2021).
[10]. Baidu Index 2020, Retrieved May 3rd, index.baidu.com.
[11]. Zhang, J. T. & Zhang, Y. S. From “Script Killing” to “Secret Room Escape”: Youth Portrait,Multidimensional Causes and Risk Regula. Youth Research, (01), 78-85. (2023).









