1. Introduction
At the end of 2019, the outbreak of COVID-19 had not only brought great challenges to global public health security but also caused a huge blow to the world economy. In this case, the development for China's catering industry has also been greatly affected. In 2020, the scale of China's catering market declined by 15.4%, which is the first decline after six consecutive years of growth of Chinese catering enterprises since 2014 [1]. Many catering enterprises have taken self-rescue measures to cope with the impact and pressure brought by the COVID-19 epidemic. In the case of the world health emergency, how to adjust the marketing strategy of catering enterprises to cope with it, reduce losses and open new opportunities is the issue we should pay attention to. This paper takes McDonald's (China) as an example to study and analyze its marketing strategy during the epidemic and puts forward suggestions for catering enterprises to adjust their marketing strategy in time to cope with future emergencies. This study helps the catering industry make correct market analysis according to the market environment in the future and provides a good reference for the catering industry to change its marketing direction in the face of the world's public health emergency.
2. Analysis of the Situation of China's Catering Industry During the Epidemic
The catering industry is a food production and service industry that specializes in providing consumers with various drinks, consumption places, and facilities through instant processing, commercial sales, and service labor [2]. It is also one of the important sub-industries in the tertiary industry. The catering industry is closely related to the daily life of the Chinese people. With the rising income of Chinese residents, the catering industry has developed rapidly and become one of the fastest growing industries in China after the 21st century. The market size of China's catering industry has grown steadily in the past few years, from 2.9 trillion yuan in 2014 to 4.6 trillion yuan in 2019, with a compound annual growth rate of 10.1% during this period[3]. China's restaurant industry has a huge opportunity to grow, with per capita food expenditure in 2019 around 16.4 yuan per day, compared to 102.6 yuan per day in the United States[4]. Although China's catering industry was affected by the outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020, the size of China's restaurant market declined. However, with the normalized management of epidemic prevention and control, China's catering industry is constantly making new adjustments and attempts, while people's consumption enthusiasm is also growing. The size of China's catering market has recovered to 4.7 trillion yuan in 2021, up 18.6% year over year [3].
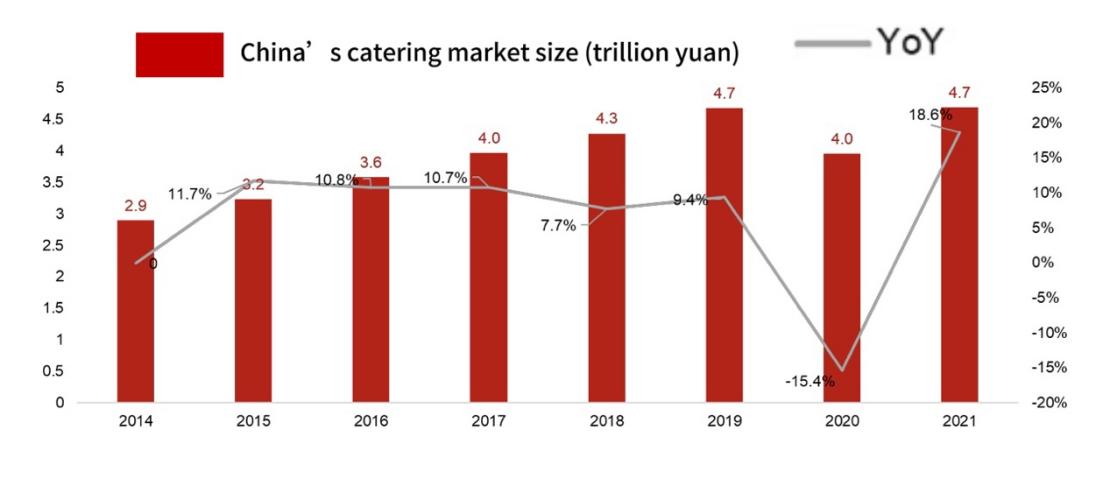
Figure 1: China's catering market size.[1].
As an important industry closely related to the catering industry, tourism affects the sales growth of the catering industry to a certain extent. During the three-year period of normal epidemic management in China, policies such as centralized quarantine and home isolation have weakened residents' enthusiasm for travel and reduced their demand for travel. As a result, the tourism industry has been hit hard, and many customers have decreased in scenic spots and surrounding hotels and shopping centers. As a result, the catering industry, which is closely related to the tourism industry, has been significantly affected, and the sales revenue of the catering industry has declined sharply. At the same time, residents have fewer choices for offline catering [5], the growth of demand for delivery and the restaurants in the catering industry are often affected by the epidemic control, and are forced to suspend business, resulting in limited operating hours for stores and a decline in turnover.
During the pandemic, rising raw material costs in the catering industry, spending on epidemic protection equipment, and restrictions on the number of diners in offline catering have led to tight cash flow for many catering outlets. To reduce operating costs, many small and medium-sized catering enterprises choose to lay off employees and cut salaries. However, due to the decrease in the number of customers and the uncertainty of business hours affected by epidemic prevention and control, many catering stores have broken their capital chain and finally chosen to close their business.
3. SWOT Analysis of McDonald's in China
3.1. Strength
It has been 30 years since McDonald's entered the Chinese mainland market after opening its first McDonald's in Shenzhen in 1990. By 2023, McDonald's will have more than 3,500 restaurants in China [6]. As a catering company, McDonald's (China) has taken on its own social responsibilities while gradually promoting and expanding the Chinese market. It not only pays great attention to the growth and health of children, but also pays attention to youth employment. McDonald's (China) has launched the "Unlimited Youth" Modern Apprenticeship program, which has helped more than 10,000 young people improve their employability and support them to successfully embark on career development after graduation [6]. These actions of caring for society and giving back to it make McDonald's (China) have a good corporate image in the hearts of Chinese residents.
McDonald's (China) has always been concerned about the sustainable development of the environment, has always loved and cared for the earth, and will continue to contribute to environmental protection. McDonald's packaging has been changing, with some materials becoming leaner and others switching from plastic to paper. In 2015, McDonald's China gradually eliminated the packaging boxes of burgers and replaced them with single layer wrapping paper, reducing the amount of paper used in related product packaging by nearly 80 percent. Starting in 2018, McDonald's China piloted a "strapless lid" and a no-offer program in Beijing to encourage consumers to cut down on straw use. By 2023, all of McDonald's paper food packaging will use 100% Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certified base paper. McDonald's (China) is constantly improving, using its scale and influence, together with customers, suppliers, and the community, focusing on sustainable development, and constantly making the world a better place.
3.2. Weakness
McDonald's is targeting children. To this end, they created the image of Ronald McDonald and set up a children's playground in the restaurant. They created a large number of daily characters and games through literary and artistic works and electronic technology, and often sent people to distribute small gifts with the M logo to children in parks and kindergartens, hoping to attract child-centered family consumers. However, children do not have the ability to spend on their own, and their influence on household consumption decisions is very limited. And with the development of the times, in China, McDonald's is deeply loved by young people.
3.3. Opportunity
China has a large population base, with 1.4 billion consumers, and McDonald's (China) stores are mostly distributed in first-tier cities and southeast China. With the rapid development of China's economic level and the continuous improvement of Chinese residents' living standards and consumption power, McDonald's (China) has a huge market potential and huge potential consumers for the second and third tier cities and the central and western regions.
Advances in science and technology have led to the rapid development of China's takeout industry:
With the popularity of smartphones, more and more Chinese residents have begun to use mobile delivery apps to order food, and the online order volume of many small meals is even higher than the offline order volume [7]. People gradually realize the convenience brought by takeout service.
3.4. Threat
The fast food industry is highly competitive, and the gap between products and services in the same industry is small:
After China's accession to the WTO, more and more foreign brands of fast food entered the Chinese market. They bring advanced technology, new marketing ideas and service methods, and a unique corporate image, which all show that the competition of similar fast food restaurants like McDonald's in the Chinese market is becoming more and more fierce. In addition, KFC, as the largest competitor of McDonald's in the Chinese market, not only has similar products to McDonald's (China), but also has a higher level of localization than McDonald's (China).
With the improvement of living standards, people's food safety and health awareness are enhanced, and the nutritional requirements of their diet are increased. The fast food at McDonald's gives people the impression of "junk food", which will lead to a decrease in the loyalty of the target customers to the product. In 2015, according to the US quartz financial website, McKinsey & Company reported that only 51% of Chinese consumers said they ate Western-style fast food. That's down from 2012, when 67 percent said they ate fast food. Since then, they have moved on to healthier, greener brands. That is the message Chinese consumers are increasingly sending to Western-style fast-food chains.
4. Analysis of McDonald's (China) Marketing Strategy During the Epidemic
4.1. Fight Against the Epidemic and Take the Initiative to Assume Social Responsibilities
Immediately after the outbreak of COVID-19, McDonald's China donated RMB 1 million to the Wuhan Charity Federation, maintained close communication with local health prevention and regulatory authorities, actively listened to guidance and implemented it. Organize the Maimai volunteer team in Wuhan to send warm love meals to the medical staff of Wuhan People's Liberation Army 161 Hospital and Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University every day to cheer them up. In addition to Wuhan, free food delivery services for medical workers have been carried out in Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, and other places. As a catering company, in January 2020, at the beginning of the outbreak of the epidemic, McDonald's (China) made great efforts to overcome the limitations of the epidemic on manpower, logistics and other aspects, and made every effort to continue to operate nearly 3,000 restaurants, provide delivery services normally, and order food normally in nearly 1,500 hospitals across the country, minimizing the impact of the epidemic on the daily life of ordinary citizens. At the same time, with the support of the Ronald McDonald House Special Fund of the China Soong Ching Ling Foundation, 200,000 medical masks were purchased and imported in an emergency manner, which were successfully delivered to 11 provincial, municipal and community hospitals donated by Wuhan. In addition, McDonald's will donate nearly 2,000 goggles to Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital. McDonald's (China) has taken practical actions to show consumers that in times of crisis, catering enterprises actively assume social responsibilities and establish an excellent brand image.
4.2. Quickly Respond to the Government's Epidemic Control and Timely Implement Adjustment Strategies
During the government's epidemic control period, McDonald's (China) made every effort to ensure delivery services. According to the latest epidemic control requirements, McDonald's (China) launched a "contact-free delivery" strategy in a timely manner to deliver meals to locations negotiated with customers in advance. Delivery staff notified customers by phone when they arrived to pick up their own food, avoiding the risks caused by face-to-face contact. At the same time, offline stores have also upgraded epidemic prevention measures in a timely manner. Customers are advised to wear masks when going to the restaurant and use the restaurant's hand sanitizer to clean their hands after arriving at the restaurant. The restaurant will also check the temperature of customers at the request of the government. And pay more attention to the health and safety of food materials, actively cooperate with the inspection of relevant departments, and implement more stringent disinfection measures [8]. For the overall control of the environment, McDonald's (China) has done a good job, using accurate analysis to develop a comprehensive and sophisticated strategy to deal with public health emergencies. The impact of the epidemic on McDonald's (China) sales and turnover is greatly reduced. At the same time, it also enhances customers' brand trust in McDonald's (China).
4.3. The Cooperation of Third-Party Delivery Platforms and the Simultaneous Development of Self-Owned Delivery Construction
After the outbreak of COVID-19, many places have banned dine-in restaurants, and most catering companies can only ease their tight cash flow by taking out food. However, the high lifting fee of takeout platforms make it difficult for food enterprises to enter takeout. Platform commissions, compulsory discounts, and promotion fees make the profits of enterprises very low. But McDonald's (China) takeout strategy currently shows a great advantage. At present, the delivery capacity of China's takeout market is insufficient, while McDonald's Merdelivery has a vertically independent logistics and distribution team with high distribution efficiency, which already has certain barrier advantages. In addition, McDonald's (China) cooperates with third-party platforms to obtain orders on third-party platforms and deliver food through its own riders. And often launched "delivery fee reductions", "takeout coupons" and other strategies to attract people to buy. While gaining traffic, McDonald's (China) ensures that the brand can use its well-developed restaurant network to control product quality. "The pandemic has led to a rapid increase in demand for home delivery services." The China Cuisine Association pointed out that it is necessary for future catering enterprises to consider establishing a system by themselves or choose to cooperate with corresponding platforms with sound organizational methods and logistics systems, to make takeout a new growth point of future business.
4.4. Digitalization
In this epidemic, McDonald's was able to quickly launch "contactless order and pick up" based on the development of digital restaurants. Dual-point counters, touch-screen self-service ordering machines, dynamic electronic food cards, and convenient mobile payment will create a new consumer experience for customers. Digital restaurants not only improve the efficiency of customers' orders, but also reduce face-to-face contact between customers and employees, reducing the risk of virus transmission during the pandemic.
McDonald's launched the "i McDonald's" WeChat mini program and the McDonald's APP to provide personalized products and services. Customers can join the members through "i McDonald's", earn points when they pay by mobile phone at the counter, redeem products, and enjoy a 50% discount on membership days. During the pandemic, McDonald's introduced multiple offers through mini programs, which attracted many consumers [9]. McDonald's strengthened its relationship with customers through mini programs and apps, creating more loyal customers. The epidemic also shows the importance of customer stickiness. In the face of many takeout merchants, consumers will choose merchants they are familiar with and trust to place orders, and the customer loyalty usually accumulated will be of great use under the epidemic.
5. The Development Trend of the Catering Industry in the Post-Epidemic Era
First, at present, the utilization rate of takeout is basically stable in the first and second tier cities and is still increasing in the third tier and below cities, which means that the takeout industry has a huge consumer base and good development prospects [10]. The data showed that "after the epidemic improved, the number of users returned to rapid growth, and the utilization rate increased to 52.7 percent. In the post-epidemic era, the growth of online catering demand has promoted the continuous increase in the scale of China's takeaway market.
Second the epidemic has had a great impact on consumer thinking and behavior, and some people have developed the concept of healthy diet and fitness plasticity. At the same time, consumers pay more attention to a healthy diet and the cost of a healthy diet has also increased. In the catering industry, healthy diet will also become a mainstream trend in the future. More restaurants are attracting consumers with dishes low in sugar and fat as the focus of publicity through dish innovation. In the future, if catering brands want to maintain brand competitive advantages and increase brand awareness, they need to continue to innovate dishes, pay attention to the healthy and reasonable collocation of dishes and pay attention to the publicity of brand characteristics.
6. Conclusion
This paper mainly studies the marketing strategy of McDonald's (China) during the epidemic period. The outbreak of COVID-19 has had a great impact on economic development and, at the same time, brought great challenges to the development of the catering industry. McDonald's (China) acted timely according to the market situation, made the correct market analysis, and quickly adjusted its marketing strategy. While actively assuming social responsibilities, it adopts strategies such as improving the store elimination system, non-contact distribution, cooperating with third-party delivery platforms, synchronous development of its own delivery platform construction, and digitalization. Seeking new development directions during difficult times provides a high-quality reference for the catering industry on how to deal with public health emergencies. In the future, in the post-epidemic era, the development of the catering industry will show a trend of diversification and complexity. This paper cannot predict specific changes in the future, but the long-term sustainable development of catering enterprises is inseparable from the continuous innovation of marketing strategies.
References
[1]. The epidemic is hard to stop the recovery of the catering industry. Available at: https://www.zgswcn.com/cms/mobile_h5/wapArticleDetail.do?article_id=202208051446171049&contentType=article# (Accessed: 06 July 2023).
[2]. Catering_Baidu Encyclopedia Baidu Encyclopedia. Available at: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%A4%90%E9%A5%AE%E4%B8%9A/3114646?fr= ge_ala (Accessed: 06 July 2023).
[3]. CCFA, & China Renaissance Capital. (2022). 2022 China Chain Catering Industry Report
[4]. Development status and market segment analysis of China's catering industry in 2020 - Central Kitchen engineering network. Available at: http://ckitisa.com/news/d996.html (Accessed: 06 July 2023).
[5]. Zheng, A. (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on digital economy consumption and countermeasures. Information and Communication Technology and Policy (2), 5.
[6]. Because of love, do good McDonald's official website. Available at: https://www.mcdonalds.com.cn/index/McD/mcdonalds-china/Serving-Here (Accessed: 06 July 2023).
[7]. Zhao, P. (2020). "China Takeaway Industry Survey and Research Report" released 2019 takeaway transaction volume will reach 603.5 billion yuan. Chinese food (1), 1.
[8]. Chong, L. H. Y., Yang, X., Wei, Y., Wang, Y., Alzufairi, T. A., & Aljuwaisri, R. M. R. (2022). The Impact of Covid-19 to Mcdonald’s: Its Response and Post-Pandemic Plan. Advances in Global Economics and Business Journal, 3(1), 28-38.
[9]. Huang Qiaoli, & Xu Jinqiu. (2023). Digitalization and Enterprise Resilience——Based on the Empirical Evidence of the Impact of Novel Coronavirus Infection. Journal of Shanghai University of International Business and Economics, (1), 41-56.
[10]. Kim, J., Kim, J., & Wang, Y. (2021). Uncertainty risks and strategic reaction of restaurant firms amid COVID-19: Evidence from China. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 92, 102752.
Cite this article
Wang,X. (2023). Analysis of McDonald's Marketing Strategy During the COVID-19. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,52,248-254.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. The epidemic is hard to stop the recovery of the catering industry. Available at: https://www.zgswcn.com/cms/mobile_h5/wapArticleDetail.do?article_id=202208051446171049&contentType=article# (Accessed: 06 July 2023).
[2]. Catering_Baidu Encyclopedia Baidu Encyclopedia. Available at: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%A4%90%E9%A5%AE%E4%B8%9A/3114646?fr= ge_ala (Accessed: 06 July 2023).
[3]. CCFA, & China Renaissance Capital. (2022). 2022 China Chain Catering Industry Report
[4]. Development status and market segment analysis of China's catering industry in 2020 - Central Kitchen engineering network. Available at: http://ckitisa.com/news/d996.html (Accessed: 06 July 2023).
[5]. Zheng, A. (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on digital economy consumption and countermeasures. Information and Communication Technology and Policy (2), 5.
[6]. Because of love, do good McDonald's official website. Available at: https://www.mcdonalds.com.cn/index/McD/mcdonalds-china/Serving-Here (Accessed: 06 July 2023).
[7]. Zhao, P. (2020). "China Takeaway Industry Survey and Research Report" released 2019 takeaway transaction volume will reach 603.5 billion yuan. Chinese food (1), 1.
[8]. Chong, L. H. Y., Yang, X., Wei, Y., Wang, Y., Alzufairi, T. A., & Aljuwaisri, R. M. R. (2022). The Impact of Covid-19 to Mcdonald’s: Its Response and Post-Pandemic Plan. Advances in Global Economics and Business Journal, 3(1), 28-38.
[9]. Huang Qiaoli, & Xu Jinqiu. (2023). Digitalization and Enterprise Resilience——Based on the Empirical Evidence of the Impact of Novel Coronavirus Infection. Journal of Shanghai University of International Business and Economics, (1), 41-56.
[10]. Kim, J., Kim, J., & Wang, Y. (2021). Uncertainty risks and strategic reaction of restaurant firms amid COVID-19: Evidence from China. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 92, 102752.









