1. Introduction
With the increasing emphasis on efficiency in society and the waning of collective cinematic experiences, online streaming has gradually supplanted the traditional cinema-viewing mode. This trend has been particularly pronounced in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, during which the number of film screenings dramatically reduced in response to pandemic control measures, thereby severely curtailing cinema profits. As the management of the pandemic transitioned to a normalized state, the closure of dine-in facilities – a significant revenue source for cinemas – further exacerbated the challenges faced by the traditional film industry. In contrast, the inherent flexibility of streaming media, in comparison to the high demand for stable environments by traditional cinemas, has mitigated the risks of disruptions to the film industry, rendering it an increasingly favored avenue for transformation by major entertainment conglomerates. Today, with the pandemic era coming to a close, ensuring the sustainable development of streaming media has become a pressing concern. Thus, to analyze the potential trajectory of streaming media, this paper examines the developmental process and market competition within the streaming media domain. Beginning with a comprehensive analysis of the rise of the streaming media industry, using Netflix as a quintessential case study, the study subsequently juxtaposes the intense competition among various streaming platforms. Ultimately, this paper assesses the operational model of streaming media intertwined with the Metaverse concept, encompassing the fusion of “film+gaming”, along with the developmental prospects of online films tailored to the characteristics of streaming media.
2. The Rise of Streaming Media Represented by Netflix
Presently, Netflix stands as the world’s largest online streaming media service provider and production company for films and television programs, with a global footprint encompassing 17 subsidiaries. With streaming service revenue accounting for over 99%, as of 2022 Q4, Netflix has amassed a global subscriber base of 230.75 million paid users, once again surpassing Disney to secure its position as the foremost player in the North American streaming media market. However, back in the year 2000, Netflix merely occupied a downstream position within the television industry’s value chain, focusing on DVD rentals involving content aggregation and distribution. The transformative journey of Netflix commenced in 2007 when it transitioned into a full-fledged streaming platform, thereby defining the rules of the Over-The-Top (OTT) video entertainment industry. By the year 2010, its subscriber count had reached an impressive 20 million, and by the close of 2021, Netflix’s stock price had increased by over 200 times.
As demonstrated in Figure 1, a compelling narrative emerges from Netflix’s historical stock price journey. The trajectory exhibits a steadfast upward climb, characterized by a particularly marked acceleration in growth commencing from 2014. This sustained momentum culminated in an impressive milestone by the close of 2021, as the company’s stock price surged beyond the $600 per share mark. This meteoric rise is nothing short of extraordinary, signifying an exponential increase of over 200 times when juxtaposed against the valuation at the close of 2007. The remarkable ascent of Netflix’s stock price mirrors its exceptional performance and resilience within the volatile dynamics of the market. The trajectory not only underscores the successful execution of the company’s strategic vision but also serves as a testament to its ability to capture and sustain market interest. This upward trend, over the course of several years, is a testament to the enduring appeal of Netflix’s business model, content strategy, and its ability to adapt to evolving consumer preferences and industry shifts. Furthermore, this upward surge in stock value speaks to the broader transformation of the entertainment and media landscape. It signifies the ascendancy of streaming platforms and the profound impact they have had on reshaping traditional viewing habits and content distribution mechanisms. As the company’s stock price trajectory aligns with the rise of streaming services as a dominant force in the entertainment sector, it also reflects the growing investor confidence in the disruptive potential of these platforms. In a world where digital content consumption is becoming increasingly prevalent, Netflix’s stock price journey offers insights into the evolving nature of investor perceptions and expectations. The trajectory embodies not only the financial success of a company but also encapsulates the paradigm shift in how audiences engage with and consume entertainment. It serves as a contemporary case study that exemplifies the intersection of technological innovation, consumer behavior, and market dynamics in the modern media landscape.
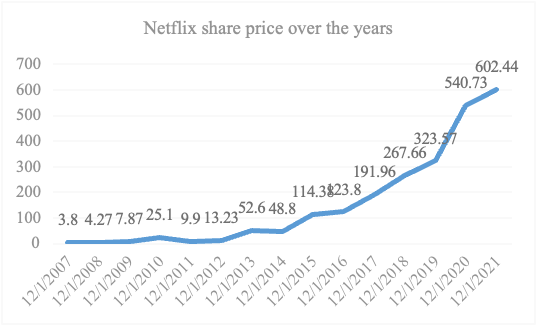
Figure 1: Netflix share price over the years (unit: dollars per share) (Photo credit: original).
Netflix’s success primarily stems from its adept utilization of big data, which has transformed the streaming media industry’s role from merely content aggregation and promotion downstream of the industry value chain. Throughout its trajectory from inception to maturity, Netflix’s astute anticipation of future trends in media consumption allowed it to establish a solid user base and a substantial content library. Between 2006 and 2009, Netflix pioneered the subscription-based model that releases entire seasons at once, superseding the traditional linear broadcasting approach and innovating an entirely new business model for streaming media. While other enterprises’ streaming platforms were still in the exploratory stage from 2010 to 2018, Netflix’s profile grew substantially. It expanded its user base beyond North America to regions like East Asia and Europe, its operational framework matured, and its dominance in the streaming media industry was solidified due to its advantages of cost-effectiveness and flexible viewing experiences. A pivotal juncture in Netflix’s development occurred in 2013 when it launched the original political drama series House of Cards, which garnered resounding success and became a cornerstone of Netflix’s journey. This success motivated Netflix to continue harnessing and leveraging the commercial value of big data technology, enabling more precise content selection and creation, and fostering collaborative technological innovations. [1] In January 2019, Netflix made history by becoming the first streaming service company to join the Motion Picture Association (MPA), effectively replacing 21st Century Fox, which had been acquired by Disney that same year. This move elevated Netflix to the status of one of Hollywood’s “Big Six” film companies, signifying the streaming media industry’s long-awaited recognition and integration into the film industry.[2]
Reflecting on Netflix’s growth trajectory, aside from its technological advancements, the societal shift toward personalized media consumption has played a significant role. The use of big data to autonomously select films that align with individual preferences and the establishment of a sense of privacy within personal spaces have, to some extent, eroded the cultural support for collective cinematic experiences. As the concept propagated by the traditional film and television industry crumbled, streaming media services seized upon the audience's psychological needs. Leveraging the ubiquity of the internet and mobile devices, they dismantled barriers to content distribution, assumed control over industry distribution dynamics, and emerged as the dominant form of digital media consumption. Starting in 2019, the competition within the streaming media landscape intensified dramatically. Traditional entertainment giants like Disney, HBO, Sony, and Universal Pictures successively launched their proprietary streaming platforms. The ascent of streaming media brought about a narrowing of the theatrical release window, which not only squeezed the traditional exhibition space but also ignited a fierce battle within the industry. As the reputation of streaming media saturates the Asia-Pacific and European regions, the finite nature of the streaming media market places diverse demands on the future development of streaming platforms. The competition within the streaming media industry has led to the reconfiguration of media consumption patterns and a reshaping of industry power dynamics. The industry’s transformative course, influenced by both technological innovations and shifting social interests, continues to unfold as it navigates an evolving landscape of consumer preferences and industry trends.
3. Amidst Ailing Trees, a Flourishing Spring: Intense Competition Among Streaming Media
In 2017, Netflix’s film Okja was released in South Korea, but it faced opposition from the three major theater chains in Korea - GV, Lotte Cinema, and Megabox - due to its violation of the customary practice that films need to be screened in theaters for at least three weeks before being made available on online platforms. Nevertheless, Okja managed to achieve a commendable result, earning $597,600 in its first week across 111 theaters. While major film production companies accused Netflix of defying the rules established with theaters and encroaching on their market, they simultaneously raced against time to advance the launch of their proprietary streaming platforms. In November 2019, Disney introduced its streaming platform, Disney+. In May 2020, WarnerMedia, which had been acquired by AT&T, launched HBO MAX. With increased investments from their parent companies in production capabilities and promotional efforts, established platforms like Disney+ and HBO MAX rapidly amassed user bases through the opportunities presented by the pandemic. They continued to release sustainable new intellectual properties (IPs), putting noticeable pressure on Netflix. The once-monopolistic position of Netflix in the streaming media market began to crumble, giving way to an alternating pattern of development. For instance, between 2021 and 2022, Disney+ experienced a user growth rate of 26.5%, whereas Netflix’s user growth rate was a mere 0.04%. Despite Netflix still maintaining a larger global subscriber base of 230.5 million in the first fiscal quarter of 2023 compared to Disney+’s 157.8 million, it is evident that Disney+ has posed a substantial challenge to Netflix’s dominance.
This competitive landscape marks a departure from Netflix’s prior dominance as the streaming media market undergoes a dynamic shift with emerging players vying for market share. The competitive dynamics within the industry have led to intensified innovation, content creation, and user acquisition strategies, reshaping the industry’s trajectory.
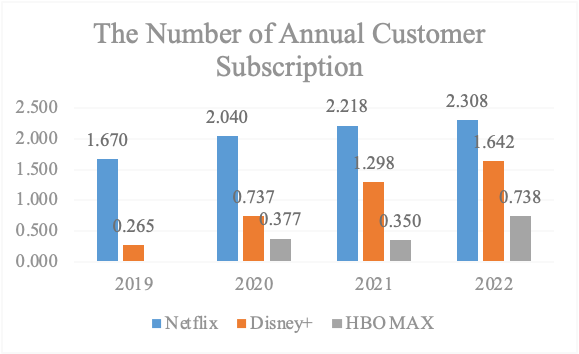
Figure 2: Global User Counts for Various Streaming Platforms (in millions) (Photo credit: original).
As depicted in Figure 2, the bar chart provides a comprehensive visualization of the global user counts attributed to Netflix, Disney+, and HBO, spanning the years from 2019 to 2022. During the entirety of 2020, Netflix’s dominion over the streaming media realm remained unchallenged and authoritative. Its commanding presence was evident, underscoring its role as a trailblazer in the industry’s landscape. However, the narrative took an intriguing turn with the arrival of 2021. A series of noteworthy technological advancements within the infrastructure of competing streaming platforms infused the industry with a newfound sense of dynamism. These developments acted as a catalyst, reshaping the competitive landscape and leading to the emergence of a harmonious equilibrium among the three prominent contenders by the close of 2020. This evolving scenario stands as a testament to the ever-shifting tides within the streaming media arena. It encapsulates the profound impact that innovation and technological strides have on the equilibrium of power among industry players. The competition, once characterized by a single dominant player, has evolved into a dynamic ecosystem where multiple platforms coexist and vie for viewers’ attention. The impetus behind this transformation lies in the unwavering dedication of each platform to hone its technological prowess and augment its repertoire of content offerings. The pursuit of excellence in these domains has become the linchpin of their strategies, representing the pivotal means through which they entice and engage their respective user bases. It’s an era defined by ceaseless innovation, where platforms are in a constant race to enhance user experiences, diversify content libraries, and introduce cutting-edge features. This monumental shift signifies a new chapter in the competition for viewers’ loyalty. The industry is experiencing an evolution marked by its responsiveness to user preferences, the integration of advanced technologies, and the infusion of creativity into content creation. The viewer is at the heart of this transformation, with platforms striving to craft immersive experiences that cater to an ever-evolving set of demands.
In essence, the streaming media landscape has entered an era defined by its adaptive spirit and its embrace of innovation. The narrative of competing giants has given way to a more intricate and balanced interplay, underscoring the resilience and adaptability that define this vibrant industry. As the competition continues to unfold, it’s the viewer who stands to gain the most – a diverse array of options, enriched content experiences, and an era of entertainment marked by its boundless potential.
4. Navigating Beyond Competition: The Path of Circumvention
Amid the intense competition prevailing in the streaming media market, streaming platforms led by Netflix have embarked on a diversified array of initiatives to chart their course. These endeavors include but are not confined to, embracing the concept of the Metaverse to expand interactive spaces for audiences and virtual content. In essence, the Metaverse constitutes a virtual realm that exists in parallel and independently from the tangible world.[3] The essence of any medium ultimately lies in its resonance with human sensations and the extension of human senses.[4] In the era of the internet, media serve as compounded extensions of multiple senses, and within the Metaverse, a multidirectional connection of sensory experiences within the virtual world is realized.[5] For Netflix, which boasts a plethora of original IPs, the Metaverse undoubtedly presents significant potential for post-sale reimaginations of exceptional series. In 2018, Netflix initiated its exploratory venture by transforming its iconic IP Black Mirror into an interactive live-action game. By integrating interactive gaming elements seamlessly into the narrative progression, the endeavor garnered substantial positive player feedback. Subsequently, in September 2021, Netflix unveiled the Netflix Games platform, tailored exclusively for its paying members. This move was accompanied by the acquisition of Night School Studio, marking Netflix’s official foray into the realm of gaming. The continuous release of game adaptations tied to popular series has gradually familiarized Netflix with its operations in the gaming industry. With the maturation of its game creation technologies and the enhancement of its autonomous innovative capabilities, the integration of “film+gaming” is steadily evolving into a comprehensive ecosystem. The empowerment of technology serves as the foundation for the rapid development of streaming platforms.[6] The Metaverse is poised to become the second battlefield in the competition within the streaming media market. To extricate themselves from the realm of copyright battles, several streaming platforms need to emulate Netflix’s operational methodologies and shift their focus towards novel industries.
5. Network Films Crafted Based on Streaming Media Characteristics
The creative process in filmmaking often takes into account the cinematic ambiance of movie theaters. However, when traditional films are viewed on personal media devices, the auditory experience can be compromised due to device limitations. The most significant distinction between streaming media and theater films in terms of viewing lies in the absence of rigid temporal and spatial constraints in streaming media viewing.[7] Audiences are no longer collectively assembled at the same physical location and time to contemplate identical content; rather, they engage in separate contemplation within diverse temporal and spatial contexts, fundamentally altering the nature of the viewing experience. In media theory, cinema is defined as organized, purposeful, rapid, and extensive information exchange activities directed at the public by professional communicators using mechanical media.[8] When streaming media platforms fail to meet the viewing demands associated with traditional cinema, streaming companies can explore adjustments in content based on the inherent nature of films. For instance, several streaming platforms like iQiyi, Youku, and Sohu have implemented a six-minute preview mechanism for non-subscribing users. As a result, many network films have strategically positioned pivotal climactic moments at this juncture to captivate audience interest. “In terms of visual presentation, network films, taking into account varying screen sizes and display standards, tend to employ more close-ups or medium shots while minimizing the use of wide-angle shots. Concerning color composition, they strive to utilize visually impactful color combinations imbued with tension, discarding superfluous secondary details to maximize the manifestation of pure aesthetics.[9] This operational mechanism in the realm of streaming media fundamentally influences the structural composition of film content and the arrangement of preview segments. As Laura Mulvey aptly states, streaming media “allows films to be slowed down or paused, creating a new mode of viewing that prompts contemplation of new meanings within the imagery itself”.[10] Emerging as a subgenre within the modernization of cinema, the novel form of network films provides a constructive response to the limitations posed by streaming media viewing in comparison to traditional theater experiences. By bridging the communicative traits of confined private media spaces, network films exemplify how streaming media is better positioned to adapt to the evolving landscape of the film industry. They enhance the competitive edge of streaming media in its rivalry with conventional cinema, presenting a more favored dimension, thus propelling streaming media further as a preferred avenue for cinematic engagement.
6. Conclusion
Throughout this discourse, it becomes evident that early streaming platforms, exemplified by Netflix, leveraged the power of big data to reshape the streaming media industry’s erstwhile position in the downstream segment of the industry value chain. As the technology matured and customer bases solidified, various entertainment enterprises subsequently introduced their proprietary streaming platforms, engendering a landscape of fierce market competition. In the realm of limited market prospects, the fusion of film and television content with the concept of the Metaverse marketing strategy has gained considerable momentum, emerging as a significant avenue for future streaming platforms to expand into diverse domains. Given the distinctive modes of communication between streaming media and traditional cinematic mediums, the emergence of network films, distinct from conventional films in their narrative structure, addresses inherent limitations in streaming media. This trend fortifies the competitiveness of streaming media in the realm of film viewing choices. The evolution of streaming media is an outcome of the confluence of technological advancement and heightened human demands. Despite persistent criticism from a contingent of traditional film enthusiasts who view it as a threat to conventional theaters, it is undeniable that the coexistence of streaming media and traditional cinema is an inevitable trajectory in the evolution of the film industry. While advocating for the preservation of the aesthetic significance of cinema as an art form and narrative medium, there exists a parallel necessity to nurture and support the development of the streaming media industry. Amid the multifaceted landscape of streaming media convergence, embarking on a transformative journey is akin to traversing a perilous mountain range. Each summit presents its own unique challenges. Yet, these challenges, however daunting, are not insurmountable; they merely necessitate a strategic detour.
References
[1]. Yan, C. (2022). Exploration of the Transformation Path of Streaming Media in the Metaverse Era—Taking Netflix as an Example. News Forum, 36(05), 40-42.
[2]. Wang, T. X. (2022). From Theaters to Streaming: The Media Shift and Future of Film in the Post-Pandemic Era. Editor’s Friend, (01), 73-79.
[3]. Zhao, G., Yi, H., & Xu, Y. (2021). The Metaverse. China Translation & Publishing Corporation, 11.
[4]. McLuhan, M. (2000). Understanding Media: The Extensions of Man. Business Press, pp. 20-21.
[5]. Yu, G. (2021). The Evolutionary Logic of Future Media: Iteration, Recombination, and Upgrading of “Human Connectivity” - From the “Era of Scenes” to the “Metaverse” and to the “Inner World”. Journalism, (10), 54-60.
[6]. Kong, Z. (2021). The Paradox and Reconciliation of the Cultural Ecosystem of Digital Age Streaming Media: Modern Communication, 1.
[7]. Lv, B., & Ding, N. (2021). Innovation and Breakthroughs in Network Films in the Era of Streaming Media. Film
[8]. Li, X., & Xiu, D. (1994). Film Media and Art Theory. Huazhong Normal University Press, 58.
[9]. Shen, Y. Z. “Reconsidering the Aesthetics of Realist Cinema”. Fujian Forum (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 2006(03), 10-15.
[10]. Chang, J., & Li, S. X. (2018). Laura Mulvey: Streaming Technology Makes Cultural Democracy Possible - Contemporary Aspects of Feminist Film Theory. Journalism, (08), 4-9.
Cite this article
Tian,J. (2024). The Rise and Bypassing of Streaming Media. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,57,189-195.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Yan, C. (2022). Exploration of the Transformation Path of Streaming Media in the Metaverse Era—Taking Netflix as an Example. News Forum, 36(05), 40-42.
[2]. Wang, T. X. (2022). From Theaters to Streaming: The Media Shift and Future of Film in the Post-Pandemic Era. Editor’s Friend, (01), 73-79.
[3]. Zhao, G., Yi, H., & Xu, Y. (2021). The Metaverse. China Translation & Publishing Corporation, 11.
[4]. McLuhan, M. (2000). Understanding Media: The Extensions of Man. Business Press, pp. 20-21.
[5]. Yu, G. (2021). The Evolutionary Logic of Future Media: Iteration, Recombination, and Upgrading of “Human Connectivity” - From the “Era of Scenes” to the “Metaverse” and to the “Inner World”. Journalism, (10), 54-60.
[6]. Kong, Z. (2021). The Paradox and Reconciliation of the Cultural Ecosystem of Digital Age Streaming Media: Modern Communication, 1.
[7]. Lv, B., & Ding, N. (2021). Innovation and Breakthroughs in Network Films in the Era of Streaming Media. Film
[8]. Li, X., & Xiu, D. (1994). Film Media and Art Theory. Huazhong Normal University Press, 58.
[9]. Shen, Y. Z. “Reconsidering the Aesthetics of Realist Cinema”. Fujian Forum (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 2006(03), 10-15.
[10]. Chang, J., & Li, S. X. (2018). Laura Mulvey: Streaming Technology Makes Cultural Democracy Possible - Contemporary Aspects of Feminist Film Theory. Journalism, (08), 4-9.









