1. Introduction
The real estate sector plays a crucial role in the economies of numerous countries, underscoring its significance. According to a National Association of Realtors analysis, the real estate sector accounted for over 17% of the US GDP in 2021. China's real estate industry has made considerable advancements and tends to be a key driver of the nation's economic growth [1],[2].
The swift growth of the real estate market not only propels the diversification of other business models and enhances the national industrial system, but also plays a pivotal role in advancing urbanization and effectively boosting employment rates [3].
The two tools of macroeconomic policy, according to Mankiw, are monetary policy and fiscal policy. The central bank's choices about a nation's coinage, currency, and banking system are referred to as its monetary policy [4].
Keynes demonstrates that the economic instability is caused by the external demand caused by unpredictable, and the government can promote the macroeconomic balance by regulating the money supply [5].
2. Literature Review
The real estate business contributes significantly to the GDP of many nations, therefore its growth has had a significant impact on those nations' economies and the lives of their citizens. The cost of a home has also evolved into a gauge for measuring the state of the economy. A rise in housing costs may indicate an increase in the level of human production as a whole, while a decline in housing costs may indicate a recession. As a result, during periods of intense economic volatility, the government will utilize monetary policy to influence the actual economy and stabilize a nation's housing market. The remainder of this essay mainly focuses on how monetary policy specifically affects the real estate industry.
In the majority of economies, real estate, encompassing land and buildings, constitutes a substantial portion of national wealth. In specific regions, it serves as a vital pillar in supporting the local economy. In an era characterized by the mobility of capital, it is astonishing that real estate, a stationary asset, continues to hold significance [6].
In order to manage the economy, the central bank relies heavily on money supply policy, which has a profound impact on the housing market [4].
With the adoption of an accommodative monetary policy, the policy rate dropped from 6.5% in 2000 to 1% in June 2004 under the Federal Reserve's guidance [5]. This approach was acknowledged as a major factor in the recent worldwide economic downturn and the subsequent downfall of the real estate price bubble [7-9].
Before the housing bubble occurred, it is common for monetary policy to be more lenient, in 2005, Ahearne et al. conducted an analysis of housing prices and monetary policies in 18 major industrial countries [10]. Since a majority of banks in China are government-owned, monetary policy exerts substantial influence on the real estate market [5]. This study delves into the impact of monetary policy on the real estate sector, examining its effects on supply and demand, and drawing on specific examples from international real estate market. Keynes' theories about monetary policy and the models he developed are often cited [5]. This piece of writing also examines how monetary policy affects risk management and the regulatory implications it has on the industry.
3. Monetary Policy’S Effect on Real Estate Sector
3.1. Analysis the Varieties of Real Estate Market's Demand Side Caused by Monetary Policy
Monetary policy affects the cost of buying a house by adjusting the benchmark interest rate or loan interest rate.
In Keynesian monetary policy transmission mechanism, interest rate plays an important role. Interest rate is the only intermediate target and directly determines the effect of monetary policy [5].
Central bank uses open market operations to adjust loan interest rates. When monetary policy is loosened, the supply curve of the money market will be shifted to the right by central bank's behavior to increase the overall route of M2, and therefore nominal interest rate will be lowered (Fig. 1).
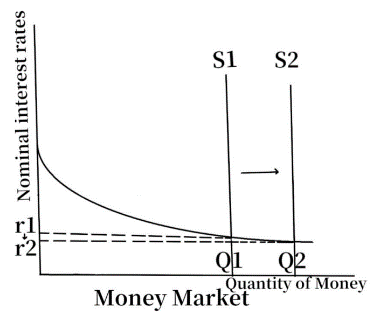
Figure 1: Money Market Diagram.
The cost of borrowing for individuals drops as a result of the interest rate on loans being equal to the nominal interest rate and decreasing. There will be a growing demand for houses as people's purchasing power increases (Fig. 2). The rate of housing turnover will rise, and housing costs will rise as a result.
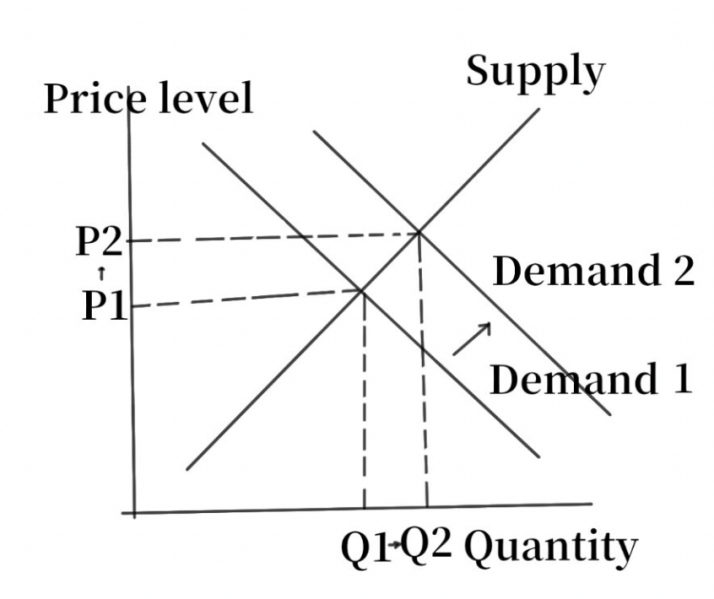
Figure 2: Supply and Demand Diagrams.
The first six months of 2023 saw a decrease in the growth rate (Fig. 3), illustrating China's real estate investment's explosive growth in 2023 [11]. It is evident that the Chinese real estate sector has faced considerable hindrances in its growth. Therefore, by decreasing mortgage rates, the government has utilized monetary policy to boost the demand side of the housing sector. The LPR (Loan Prime Rate) for the Chinese loan market on July 20, 2023, according to the National Interbank Lending Center approved by China’s People's Banking Corporation, was 3.55% for a one-year LPR and 4.2% for a five-year LPR [12]. The loan market advertised interest rates on August 21, 2023, of 3.45% for a 1-year LPR and 4.2% for a 5-year LPR. The Chinese government and central bank are attempting to increase the demand for real estate as a result.
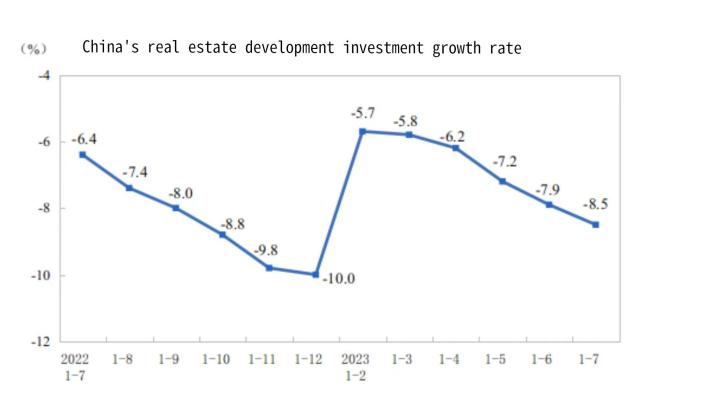
Figure 3: China’s real estate investment growth rate from January of 2022 to July of 2022; data comes from National Bureau of Statistics [12].
On the contrary, should the central bank adopt a restrictive monetary stance, it would lead to an increase in the nominal interest rate, resulting in higher borrowing costs. Because they must pay greater interest, homebuyers will decrease their desire for home purchases and the size of home loans. Home sales and home values will consequently decline.
3.2. Analysis of the Varieties of Real Estate Market's Supply Side Caused by Monetary Policy
The central bank's control of the credit market through monetary policy may have an effect on the investment and development endeavors of real estate developers. Next, utilizing the concept of loanable funds, the consequences of monetary policies on property firms will be investigated. Based on the loanable funds theory, the interest rate is established by aggregating the supply and demand for loanable funds, taking into account the equilibrium between the commodity market and the money market [13].
People are able to make more deposits when the central bank follows a loose monetary policy because the overall amount of money rises. Therefore, the supply in the loanable funds market will increase, but the demand will remain unchanged, resulting in a decrease in real interest rate (Fig. 4).
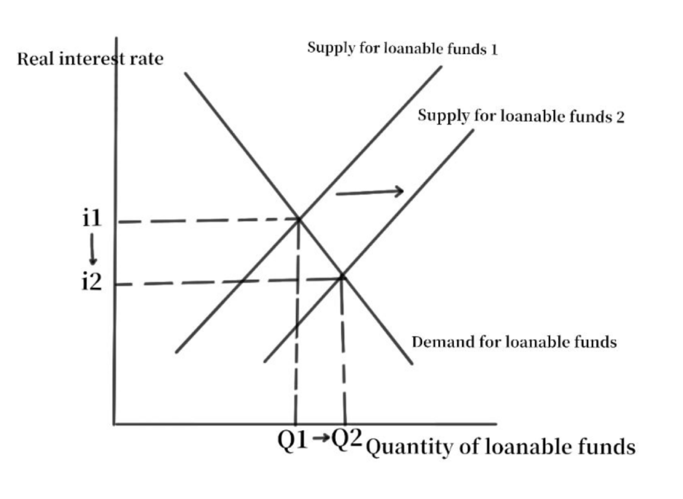
Figure 4: Loanable funds market diagram.
As everyone knows, falling real interest rates will encourage investors to put money into production. As a result, real estate developers will increase the size of their investments and development projects, increasing the supply of homes.
The real interest rate will rise instead as a result of tight monetary policy. As the opportunity cost of major real estate developers putting money into production has risen, their financing costs will increase in disguise. Therefore, the willingness of major real estate developers to invest will decline, resulting in a decrease in real estate development activities. Eventually, the supply of homes will drop.
At the same time, the central bank can also affect the real estate industry by adjusting the reserve ratio of major commercial and investment banking.
Real estate firms won't be able to borrow a lot of money if the central bank increases the reserve percentage for commercial banks, which would make it harder for them to raise more money. For real estate investors who lack financing funds, they cannot obtain funds to expand rapidly. For real estate investors with high asset-liability ratios, they may reduce housing promotions to promote sales and accelerate the return of funds.
3.3. The Role of Monetary Policy in Risk Prevention and Control
The central bank can influence the real estate market's supply and demand dynamics by implementing monetary policy, so that the economic cycle of real estate companies becomes smoother.
The central bank curbs investor enthusiasm by tightening monetary policy when it sees a risk of overheating in the property market. When the contractionary monetary policy is implemented, as discussed above, there will be a rise in both nominal interest rates and real interest rates. The demand and supply lines in this market have moved downward at the same time, resulting in house prices being suppressed.
On the contrary, when the real estate market faces downward pressure, the central bank can boost market confidence through loose monetary policy. Real and nominal interest rates will decrease after the expansionary monetary policy is put into place. The simultaneous increase in supply and demand in the housing sector will cause prices to go up. Expectations for real estate sectors have increased as a result. With growing home values, banks are more inclined to lend to homebuyers and real estate firms using homes as collateral. As a result, the real estate sector's difficulty will be lessened.
The government uses monetary policy to carry out macro-control, which can maintain the stability of housing prices that originally fluctuated greatly, and help the real estate industry to develop more stably (Fig. 5).
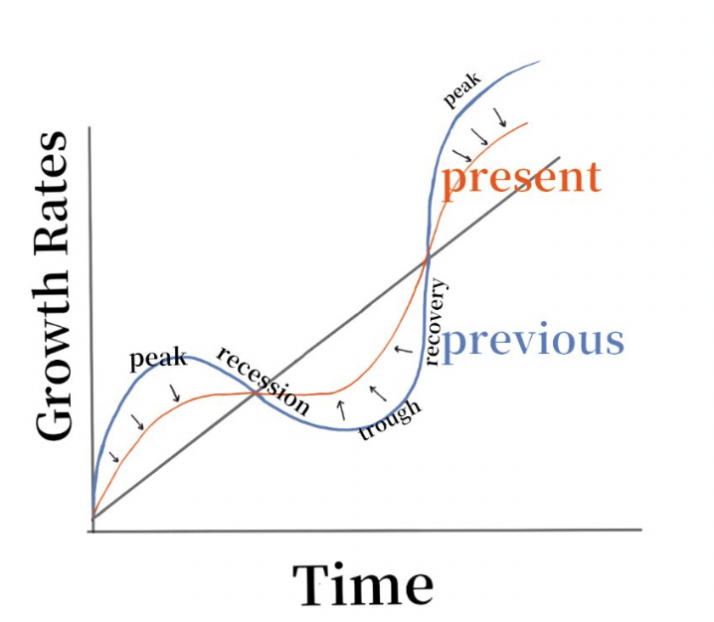
Figure 5: Business cycle diagram.
To utilize some statistics from the real estate markets in China and America to demonstrate this concept.
Figure 6 shows the China's national real estate development investment growth in 2015. As can be seen from the table, the speed of investment in real estate development in China has been declining since 2014. As a result, China began an expansionary monetary policy on October 23, 2015, to halt the real estate market's downward trend [14]. As reported by NPR, to counter a sluggish economy, the Chinese monetary authority enacted a 0.25 percentage point reduction in benchmark lending and deposit rates. Concurrently, the People's Bank of China also moved to lower the bank deposit reserve ratio by 0.5 percentage points. According to figures released by China's National Bureau of Statistics (Fig. 7), there was an uptick in the pace of China's real estate development investment, along with an increase in the growth rate of commercial housing sales area and sales in 2016 [11, 15]. This demonstrates how monetary policy is effective in limiting real estate investment and reviving market confidence. More crucially, this outcome also allows us to understand how monetary policy contributes to risk management and regulation.
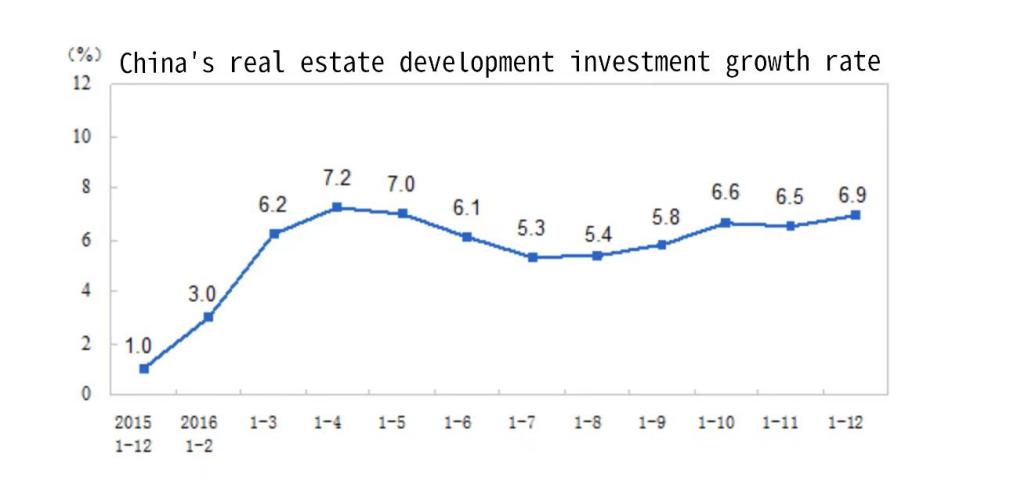
Figure 6: China’s real estate investment growth rate from December of 2015 to Decenber of 2016; data comes from National Bureau of Statistics.
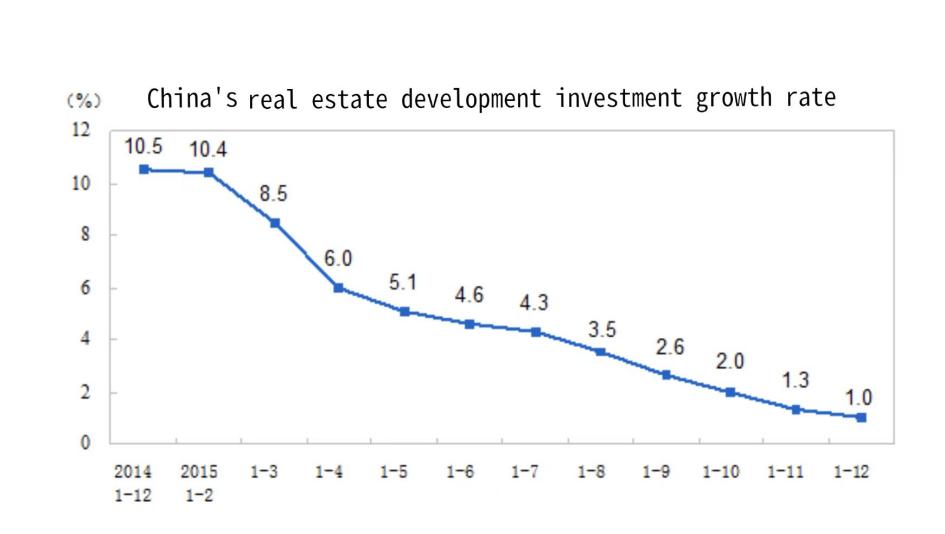
Figure 7: China’s real estate investment growth rate from December of 2014 to December of 2015; data comes from National Bureau of Statistics.
The effect of economic cycle management on the housing market will be demonstrated using data from the US housing market. As of August 19, 2023, the standard interest rate for a 30-year fixed home loan in the United States, as reported by the prominent US mortgage entity Freddie MAC [15], surpassed 7%, marking the highest mortgage rate in the country since 2002, as stated by NPR. The average interest rate on a mortgage in the US in 2022 was little over 5%. That rate was less than 3% in 2021. The U.S. housing market may experience pressure if consumers have less desire for homes as a result of high mortgage rates. June 2023 saw a decline in U.S. home sales of about 19% from the corresponding month in 2022. The Federal Reserve's attempts to manage inflation are inextricably linked to the increase in interest rates. Mortgage rates are closely related to a nation's ten-year Treasury bond yield. Mortgage rates are impacted by the increased returns that bondholders expect. The Fed must maintain high interest rates for a considerable amount of time in order to control inflation and the economic cycle.
This example does show how monetary policy influences the housing market. A few of the steps made to control the economic cycle would have an indirect effect on real estate markets.
4. Conclusion
Monetary policy, through the adjustment of interest rates and the reserve requirement ratio, has had a significant impact on the demand and supply dynamics of the real estate market, as well as housing costs.This, in essence, not only fosters the growth of the real estate sector but also contributes to reducing risks for both real estate enterprises and buyers. Reasonable macro-control has made housing prices no longer fluctuate greatly, giving people more security. The stable investment environment also gives people the confidence to better weather the economic cycle. Inevitably, different countries have different geographical locations, population sizes, and political circumstances, and the same policies may have different effects. Real-world simulations of the link between monetary policy and the housing market must also take into consideration the distinctive national conditions of each country and cannot be generalized.
References
[1]. Fung , H.‐G. , Liu , Q. W. , Huang , A. G. and Chen , M. X. (2006) . The development of China's real estate industry. The Chinese Economy.
[2]. Hinton , C. M. and Tao , Y. (2006) . Analysis on the source of competitive advantage in China's real estate industry‐E‐business applications . Journal of Technology Management in China.
[3]. Yan, N. (2019). Study on the Influence of Monetary Policy on Real Estate Price in China. Journal of Service Science and Management, 20.
[4]. N. Gregory Mankiw, 1998, Principles of economics, Dryden Press, USA.
[5]. Maynard, K. (1936). The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money. Macmillan Publishers Limited.
[6]. Haila, A. (2000). Real Estate in Global Cities: Singapore and Hong Kong as Property States. Urban Studies, 2241-2256. [Google Scholar]
[7]. John, T. (2007). Housing and monetary policy NBER Working Paper.
[8]. Jarocinski, M., Smets, F.R. (2008). House prices and the stance of monetary policy Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis Review, 90 (4), pp. 339-365
[9]. Bernanke, B. (2010). Monetary Policy and Housing Bubbles Annual meeting of the American Economic Association
[10]. Ahearne, A.G., Ammer, J., Doyle, B.M., Kole, L.S., Robert, F. (2005). Martin House prices and monetary policy: A cross-country study, Federal Reserve System Board of Governors International Finance Discussion Paper
[11]. National Bureau of Statistics. (2023). Basic situation of national real estate market in the first half of 2023 (in Chinese). 17 July 2023. <http://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202307/t20230715_1941273.html>. National Bureau of Statistics. (2016). National real estate development investment and sales in 2015, 19 January 2016. (in Chinese).
[12]. The People's Bank of China. (2023). The National Interbank Lending Center was authorized to publish the Loan Market Quotation Rate (LPR) announcement (in Chinese). <http://www.pbc.gov.cn/zhengcehuobisi/125207/125213/125440/3876551/5033439/index.html>.
[13]. Robertson and Ohlin, 1937, Loanable—Funds Theory of Interest.
[14]. Chappell, B. (2015). China Cuts Interest Rates by Quarter of A Percentage Point. 23 October 2015. <https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2015/10/23/451098626/china-cuts-interest-rates-by-quarter-of-a-percentage-point>.
[15]. Simon, S., Horsley, S. (2023). Mortgage rates are at a record high. Here's what that means for home buying, 19 August 2023. <https://www.npr.org/2023/08/19/1194846063/mortgage-rates-are-at-a-record-high-heres-what-that-means-for-home-buying>.
Cite this article
Chen,Y. (2024). Analysis of the Impact of Monetary Policy on the Housing Market. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,60,236-242.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Fung , H.‐G. , Liu , Q. W. , Huang , A. G. and Chen , M. X. (2006) . The development of China's real estate industry. The Chinese Economy.
[2]. Hinton , C. M. and Tao , Y. (2006) . Analysis on the source of competitive advantage in China's real estate industry‐E‐business applications . Journal of Technology Management in China.
[3]. Yan, N. (2019). Study on the Influence of Monetary Policy on Real Estate Price in China. Journal of Service Science and Management, 20.
[4]. N. Gregory Mankiw, 1998, Principles of economics, Dryden Press, USA.
[5]. Maynard, K. (1936). The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money. Macmillan Publishers Limited.
[6]. Haila, A. (2000). Real Estate in Global Cities: Singapore and Hong Kong as Property States. Urban Studies, 2241-2256. [Google Scholar]
[7]. John, T. (2007). Housing and monetary policy NBER Working Paper.
[8]. Jarocinski, M., Smets, F.R. (2008). House prices and the stance of monetary policy Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis Review, 90 (4), pp. 339-365
[9]. Bernanke, B. (2010). Monetary Policy and Housing Bubbles Annual meeting of the American Economic Association
[10]. Ahearne, A.G., Ammer, J., Doyle, B.M., Kole, L.S., Robert, F. (2005). Martin House prices and monetary policy: A cross-country study, Federal Reserve System Board of Governors International Finance Discussion Paper
[11]. National Bureau of Statistics. (2023). Basic situation of national real estate market in the first half of 2023 (in Chinese). 17 July 2023. <http://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202307/t20230715_1941273.html>. National Bureau of Statistics. (2016). National real estate development investment and sales in 2015, 19 January 2016. (in Chinese).
[12]. The People's Bank of China. (2023). The National Interbank Lending Center was authorized to publish the Loan Market Quotation Rate (LPR) announcement (in Chinese). <http://www.pbc.gov.cn/zhengcehuobisi/125207/125213/125440/3876551/5033439/index.html>.
[13]. Robertson and Ohlin, 1937, Loanable—Funds Theory of Interest.
[14]. Chappell, B. (2015). China Cuts Interest Rates by Quarter of A Percentage Point. 23 October 2015. <https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2015/10/23/451098626/china-cuts-interest-rates-by-quarter-of-a-percentage-point>.
[15]. Simon, S., Horsley, S. (2023). Mortgage rates are at a record high. Here's what that means for home buying, 19 August 2023. <https://www.npr.org/2023/08/19/1194846063/mortgage-rates-are-at-a-record-high-heres-what-that-means-for-home-buying>.









