1. Introduction
Due to the impact of the novel coronavirus epidemic and the Russia-Ukraine war in recent years, the economy of most regions has been hit to varying degrees. Some places may suffer a greater blow due to their weak national strength and lack of rich basic resources, while some developed countries are less affected due to their better economic conditions. This has caused their economic level to suffer different levels of decline. In the following article, I will take the German economy in recent years as an example to explain the economic changes in Germany in recent years and my forecast of the future economic situation.
2. Analysis of German economic situation
2.1. General overview
The German economy has withstood the impact of two COVID-19 shocks during the previous winter six months. Following a minor decrease of 0.3% in the last quarter of 2021, the economy has managed to rebound in the initial quarter of 2022, with a recent increase of just under 1% below its pre-crisis worth in late 2019.The progress of the economic recovery has come to a halt. The contact-intensive services sector experienced a resurgence in economic activity starting from January 2022, playing a crucial role in the 0.2% growth of the German economy during the initial quarter. Currently, both external and internal elements are influencing the growth of the German economy. The beginning of the year has been highly successful for the German construction industry, largely due to the high volume of orders placed and the pleasant winter weather. According to the head of the BDI, the German economy may experience a "stop-start year" as a result of the coronavirus pandemic and disruptions in the supply chain caused by the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Despite the current order book, industrial production will be affected by chips, components and raw materials for a long time.[1] The German Federal Statistics Office published data on February 8, 2019, indicating a 1.5% growth in Germany's quarterly exports for December in comparison to the previous quarter, surpassing the anticipated 0.4% increase in quarterly imports for December by 1.2% compared to the previous quarter, which also exceeded the expected 0.5%.In spite of this, the German economy has been the worst in the past five years throughout 2018.According to official data, the German economy experienced a decline in growth to 4.5 percent in 2018, compared to 22 percent in 2017, marking the lowest annual growth rate since the European debt crisis. Following the publication of the gross domestic product data, the euro experienced a decline of nearly 0.4 percent, settling at $1.14.
2.2. Manufacturing in Germany
However, it must be acknowledged that the German manufacturing sector experienced a lack of economic growth in the initial quarter. The world is going through a lot of changes in the economy and politics. The ongoing global pandemic of COVID-19, the intensification of regional disputes, and the growing protectionism of global trade between China and the United States are all having a detrimental effect on the security and stability of the international industrial chain and supply chain, making it difficult for the manufacturing industry to progress.[2] The war in Ukraine has already made its initial effects apparent in this context. The imposition of sanctions in March led to a significant decline in exports to Russia. Germany experienced a 1.2% decline in its overall goods exports within a month. Furthermore, the conflict worsened shortages in the availability of raw materials and intermediate products, particularly the German automotive sector which was forced to suspend production in March. Ultimately, the combination of bottlenecks and a significant surge in energy prices has led to an escalation in production expenses, consequently affecting the prices of producers. Consequently, there has been a decline in purchase orders for German industrial companies since the start of the year.The May annual rate of change in the German CPI is depicted in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Annual rate of change in German CPI in May
2.3. The rate of inflation in Germany
Early indications of elevated inflation in the consumer economy are also apparent. The month of May witnessed a 7.9% surge in consumer prices. Verbeke claims that due to the exceptionally low prices, she is actively seeking methods to cut costs. I used to commute to work by car, but now the cost of fuel has skyrocketed, parking is costly, and the price of gasoline has doubled, so I usually opt to take the bus or cycle to my job. In the past, we would purchase bread and yoghurt from supermarkets, however, the rapid increase in prices has compelled us to prepare them in the comfort of our own homes in order to cut costs. "As stated by Tanya Seidel, a 31-year-old homemaker. "Despite Seidel's husband's satisfactory salary as a department head at a mid-sized company, she opted to reenter the workforce due to concerns about the sustainability of her finances. [3-5] Besides energy, the cost of German cuisine has notably risen in the past few months, and it is not possible to purchase a substantial amount at the grocery store for over 100 euros. Other goods and services experienced a much more rapid increase in prices than the norm. The first quarter witnessed a lack of growth in private consumption, attributed to a significant surge in service expenditures.
It is anticipated that Germany's inflation rate will hit 6.8% in 2023, the highest it has been since 1974, thus hindering the revival of private spending. This could be the primary cause of the dismal atmosphere in the German retail industry. The German government's two relief packages resulted in a decrease in taxes and an increase in transfers. However, the decrease in buying power resulting from the significant surge in prices might not be compensated by a rise in net wages or an augmentation in government transfers. In Germany, disposable income is projected to increase by 6.2% this year, which is lower than the cost of living for consumers. The price reductions in the relief package, including the elimination of the EEG levy, the €9 fare on public transport, and a temporary decrease in fuel duty, have already been factored in, resulting in a reduction of inflation by approximately 0.5 percentage points this year. (Figure 2)
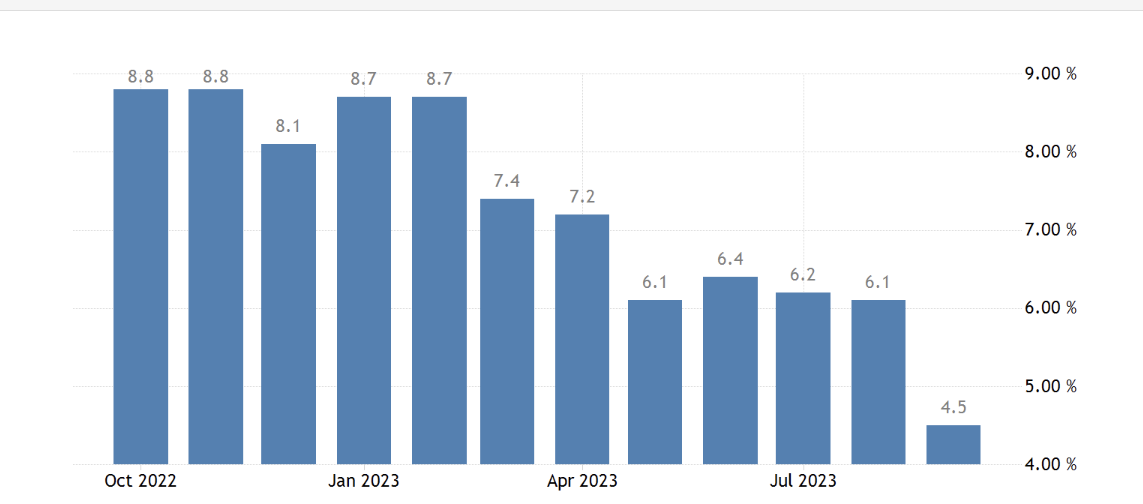
Figure 2: Tax changes in Germany in recent quarters
The tax landscape in Germany has experienced alterations in the past few quarters.
The COVID-19 pandemic is largely responsible for the current high inflation. The VAT rate in Germany, which was reduced last year as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, has been reinstated this year. The expansion of the world economy has caused a dramatic increase in the cost of oil and gas. The implementation of a carbon tax in Germany has led to an increase in the cost of energy.
In addition, some of the supply chains that have been impacted are also reducing their availability, resulting in an increase in prices.
The current high inflation can be attributed to a variety of factors. The base effect of low prices in 2020, specifically the temporary decrease in VAT rates in the latter half of the year and the decrease in mineral oil product prices in 2020 (due to their standardization at previous levels), is once again exerting a growing influence on headline inflation. The consumer price Index has only partially or to a lesser extent reflected in the significant price increases at the upstream production stage due to continued supply chain disruptions in international trade, which are also crisis-related effects.
The current increase in energy costs is the root cause of inflation, as indicated by the base effect. As an illustration, heating oil (+76.5%) and fuel (+28.4%) have become considerably pricier compared to 2020.There was a 14 percent increase in the prices of energy products. There are numerous underlying factors that contribute to this. In addition, the rise in the global economy and the consequent worldwide need for energy have caused prices to soar in international energy markets. The implementation of the CO2 tax at the start of 2021 is having a growing influence on the inflation rate of energy products. In September 2021, food prices rose at an above-average rate of 4.9%, in addition to energy prices. The lack of agricultural products, such as vegetables, was largely caused by inclement weather in Spain and Italy [6-7].
In general, inflation is increasing as a result of supply-side influences. The cost of production and intermediate goods, including energy and unprocessed foods, is rising, making consumer goods more expensive. With the exception of the energy and food categories, inflation currently stands at 2.9%, marginally surpassing the inflation target set by the European Central Bank (ECB).
2.4. Job prospects in Germany
The German government has always prioritized social innovation. Two-thirds of Germany's R&D investment comes from enterprises, with small and medium-sized enterprises playing a key role in it. It is anticipated that Germany's labor market will persist in its recuperation from the coronavirus pandemic. Despite the war in Ukraine, supply bottlenecks in important intermediate goods, and worsening skilled labor shortages, this momentum will slow significantly. It is anticipated that the workforce in Germany will grow by approximately 626,000 in 2022 and 190,000 in 2023.It is anticipated that the current unemployment rate will be approximately 302,000 lower than the figure from the prior year and an additional 24,000 in the upcoming year. Consequently, the unemployment rate will decrease from 5.7 percent in the previous year to an average of 5.0 percent in 2022 and 2023.2.5. The German government has been taking a proactive stance on the macroeconomy, resulting in a robust job market. Despite the low unemployment rate, there has been a steady rise in the number of people employed.[6] This year, Germany has generally adopted a neutral fiscal policy. The government's financing deficit for this year will be reduced by 50% to approximately 65 billion euros when compared to the previous year. This pattern is expected to persist until 2023.At that point, the shortfall will amount to slightly less than €12 billion. Due to the decrease in the deficit and the rise in GDP, Germany's overall government debt is projected to drop to 62.6% by 2023.The unemployment rate for them is still twice as low as that of workers with vocational education.It is anticipated that Germany will experience a 0.4% quarterly growth in its overall economic output during the second quarter of this year. The German economy is expected to rebound at a more robust rate of 1.2% and 1.4% in the latter part of 2022, followed by a gradual transition towards average growth. Overall, the German GDP is projected to increase by 2.5 percent in the current year and 3.7 percent in the upcoming year. Due to the unpredictable nature of the war in Ukraine, this forecast computes two scenarios.
3. Analysis on the economic development of Germany
Germany is one of the most economically developed countries in Europe, with a development level that is ahead of the rest of the world. In the last few years, the German economy has seen a steady rise in growth, with the aggregate, inflation rate, and employment rate all showing signs of improvement, resulting in a more prosperous economic state. What factors contribute to Germany's economic expansion? The success of the German economy is not only attributed to its sound economic strategies, but also to its advantageous trading climate, abundant resources, cutting-edge science and technology, and other elements. Robust economic strategies Germany has a well-developed system of economic policy control, and has been taking proactive fiscal measures and relaxed monetary regulations for a long time to foster economic growth. Furthermore, the German government has implemented reforms to enhance the market atmosphere, generate more employment prospects, and foster the sound growth of the economy. The trade environment is favorable. Germany has a strong trade system and has established good trade relations with the rest of the world, which provides a strong support for Germany's economic development. The German government has not only taken an active role in regional free trade agreements, but has also advanced multilateral trade talks, broadened German export markets, and invigorated German economic development. I will use apple juice as an example to illustrate Germany's import trade. Apple juice is a key component in the production of beverages, often used for blending, and is the second most popular fruit juice product globally after orange juice [8-10]. No other country produces or trades apple juice as much as China. The majority of Chinese apple juice is shipped to the United States, Japan, and Germany. In 2011, China exported 1.07 billion US dollars of apple juice, with 60 million US dollars being sent to Germany.
There is an abundance of resources. Germany is situated in Europe, boasting cutting-edge industrial technology, abundant natural resources, advantageous geographical position, as well as an excellent educational system and state-of-the-art science and technology, all of which are essential components of Germany's economic growth. The report indicated that Germany allocated 1.11 billion euros towards 7,365 in-transit projects and 1,661 new research projects in 2022.The Helmholtz Institute, renowned as one of the world's largest, received a substantial sum of 320 million euros.[9] State-of-the-art technology Germany has long been devoted to technological advancement, playing a crucial role in fostering economic growth. Germany's cutting-edge automotive production, software engineering, and cutting-edge electronic information technology have been instrumental in driving its economic growth. Germany is home to six major technologies, namely nuclear energy, automotive industry, rail transit, semiconductors, medical devices, and optical lenses [10].There is no question that these are high precision technology, the level of science and technology of a country is very strict requirements, and Germany's six major technology products are ahead of the world. This can be seen as Germany's high level of science and technology.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, Germany's economic growth has been steady and robust in recent years, largely due to its economic policies, favorable trade climate, abundant resources, and cutting-edge technology. The German government should persist in formulating and executing economic strategies, enhance the trading atmosphere, broaden export markets, bolster scientific and technological advancement, and endeavor to reach a higher level of economic growth.
The German economy has withstood the impact of two COVID-19 shocks during the previous winter six months. Following a minor decrease of 0.3% in the last quarter of 2021, the economy has managed to rebound in the initial quarter of 2022, with a recent increase of just under 1% below its pre-crisis worth in late 2019.The progress of the economic recovery has come to a halt. The contact-intensive services sector experienced a resurgence in economic activity starting from January 2022, playing a crucial role in the 0.2% growth of the German economy during the initial quarter. The German construction sector has experienced a robust beginning to the year, primarily reaping the rewards of substantial orders and a balmy winter.
References
[1]. wang Lin. The German "mandatory energy saving" boost the economy difficult work [N]. China energy news, 2023-10-16 (006). The DOI: 10.28693 / n.c. Nki nshca. 2023.001710.
[2]. Inga R. Germany's economic recovery faces multiple risks By Liu Xinwei, Our correspondent
[3]. Wang Jing. Germany's central bank, in the third quarter economic growth or stalling again [N]. Economic information daily, 2023-08-23 (004). The DOI: 10.28419 / n.c. Nki NJJCK. 2023.003071.
[4]. Zhu Rui. Effect on employment of economic development of China's digital research [D]. Jilin university, 2023. The DOI: 10.27162 /, dc nki. Gjlin. 2023.000627.
[5]. Chen Ximeng. German economy into a technical recession "[N]. The economic journal, 2023-06-01 (004). The DOI: 10.28425 / n.c. Nki NJJRB. 2023.003699.
[6]. Wang Ruying. Traffic light Government's digital policy from the perspective of new economic growth theory [D]. Beijing foreign studies university, 2023. DOI: 10.26962 /, dc nki. Gbjwu. 2023.001091.
[7]. Ni X S. The new trend and experience of the European Union and Germany in actively coping with population aging [J]. Scientific Research on Aging, 2019,11(04):63-78.
[8]. [Dai H. The population policy and enlightenment of Germany entering the high-income stage. China Development Review,2023(04):94-99.]
[9]. Qin Tianhong. Germany's authoritative research institute raises this year's German economic growth forecast [N]. Economic information daily, 2023-04-07 (004). DOI: 10.28419 / n.c. Nki NJJCK. 2023.001262.
[10]. Zhang Yunxin. Research on grey multivariate prediction model driven by characteristics of energy economic system [D]. Jianghan university, 2023. DOI: 10.27800 /, dc nki. GJHDX. 2023.000033.
Cite this article
Yan,H. (2024). Reasons for Germany's Economic Success in Recent Years. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,68,172-177.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. wang Lin. The German "mandatory energy saving" boost the economy difficult work [N]. China energy news, 2023-10-16 (006). The DOI: 10.28693 / n.c. Nki nshca. 2023.001710.
[2]. Inga R. Germany's economic recovery faces multiple risks By Liu Xinwei, Our correspondent
[3]. Wang Jing. Germany's central bank, in the third quarter economic growth or stalling again [N]. Economic information daily, 2023-08-23 (004). The DOI: 10.28419 / n.c. Nki NJJCK. 2023.003071.
[4]. Zhu Rui. Effect on employment of economic development of China's digital research [D]. Jilin university, 2023. The DOI: 10.27162 /, dc nki. Gjlin. 2023.000627.
[5]. Chen Ximeng. German economy into a technical recession "[N]. The economic journal, 2023-06-01 (004). The DOI: 10.28425 / n.c. Nki NJJRB. 2023.003699.
[6]. Wang Ruying. Traffic light Government's digital policy from the perspective of new economic growth theory [D]. Beijing foreign studies university, 2023. DOI: 10.26962 /, dc nki. Gbjwu. 2023.001091.
[7]. Ni X S. The new trend and experience of the European Union and Germany in actively coping with population aging [J]. Scientific Research on Aging, 2019,11(04):63-78.
[8]. [Dai H. The population policy and enlightenment of Germany entering the high-income stage. China Development Review,2023(04):94-99.]
[9]. Qin Tianhong. Germany's authoritative research institute raises this year's German economic growth forecast [N]. Economic information daily, 2023-04-07 (004). DOI: 10.28419 / n.c. Nki NJJCK. 2023.001262.
[10]. Zhang Yunxin. Research on grey multivariate prediction model driven by characteristics of energy economic system [D]. Jianghan university, 2023. DOI: 10.27800 /, dc nki. GJHDX. 2023.000033.









