

Volume 235
Published on November 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2025 Symposium: Data-Driven Decision Making in Business and Economics
With the development of big data technology, the credit reporting field has ushered in new opportunities, but some problems have also emerged as a result..This study discusses the role and types of current data analysis and the application of big data in the credit reporting field from three aspects: big data technology, the influencing factors of loan risk, and assessment efficiency. The impact of different influencing factors on borrowers' credit scores: including external environments (such as credit scores, employment history and other historical model factors). Emerging influencing factors such as legal and social acceptance, and whether the borrower's own personality is overly optimistic, etc. After taking the above factors into account, this study explored the efficiency improvements of digital Windows compared to traditional Windows from the aspects of efficiency and customer satisfaction. At the same time, inclusive finance should be taken into consideration, and credit reporting standards for less developed countries and regions should be appropriately lowered.

 View pdf
View pdf


Amid the growing importance of artificial intelligence (AI) as a strategic national priority and the increasing integration of AI-driven technologies into the real economy through policy initiatives, this paper investigates whether and how AI policies can enhance corporate accounting information quality. Drawing on a comprehensive dataset of Chinese A-share listed companies from 2012 to 2023, empirical analysis employing the difference-in-differences model demonstrates that AI policies lead to a statistically significant improvement in accounting information quality, although the positive effects exhibit a delayed impact over time. The mechanism analysis reveals that this enhancement primarily occurs through the optimization of internal corporate control systems. Furthermore, heterogeneity analysis shows that the policy effectiveness is particularly notable in large-scale enterprises, indicating that these policies yield stronger outcomes for firms with greater operational complexity. This research provides both theoretical foundations and practical guidance for governments to refine AI policy frameworks and for enterprises to develop intelligent financial governance systems that align with technological advancements.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper examines the innovations and reform directions of China's monetary policy framework in response to the evolving economic environment. With a focus on adapting to the trends of socialism with Chinese characteristics, this paper analyzes the key components of China’s monetary policy, including tools, operational targets, intermediate targets and ultimate goals. The study reveals that while China has developed a diverse set of monetary instruments, challenges remain in optimizing their use, improving interest rate liberalization, and enhancing market benchmark rates. The article proposes strategies such as clarifying the hierarchy of policy tools, fostering key operational targets, emphasizing price-based indicators, and deepening financial markets to facilitate smoother interest rate transmission. Additionally, the impact of digital RMB on the existing monetary system is discussed. The findings of this paper aim to provide valuable insights for constructing a modern monetary policy framework that supports high-quality economic growth and financial stability in China and reasonable guidance for investors.

 View pdf
View pdf


As the world is moving towards carbon neutrality, in this context, the "Industry 5.0" that is people-oriented, resilient, and sustainable has emerged, and it has formed a strong alliance with green logistics. This study explores the impact of integrating "Industry 5.0" (such as artificial intelligence, human-machine collaboration, digital twin) with green logistics (low-carbon transportation, energy-efficient warehousing, carbon tracking) on the economic and environmental performance of the logistics industry. A mixed-method approach was adopted, and quantitative panel regression analysis was employed to conduct a case study on DHL and JD Logistics. The research results indicate that the "Industry 5.0" technology is closely related to the reduction of carbon energy intensity. Companies that integrate green logistics and technology can achieve more stable and favorable economic and environmental performance. Success requires meeting three prerequisites: measurable carbon data, a transparent environment, ESG disclosure, and compliance with global reporting standards. This research has filled the existing gap in multi-company analysis, enriched the understanding of the "Industry 5.0" era, and expanded academic knowledge.

 View pdf
View pdf



Taking Chinese A-share listed companies from 2014 to 2024 as the sample, this study examines the impact of short-term debt ratio on corporate investment scale and the heterogeneous effect of property rights. The two-way fixed effects model and instrumental variable method (2SLS) are adopted to address endogeneity issues. The results show that: in the direct regression, the short-term debt ratio is significantly negatively correlated with investment; after addressing endogeneity, the two exhibit a significant positive correlation. Under the heterogeneity of property rights, the positive effect of short-term liabilities share on corporate investment is more pronounced in private enterprises than in state-owned enterprises. This study reveals the endogenous interference in the interplay between short-duration debt and investment, and provides a basis for formulating differentiated financing policies.

 View pdf
View pdf


The COVID-19 pandemic has caused major disruptions in the commercial real estate market. This research paper investigates the US commercial real estate market challenges from 2020 through 2025 because of pandemic disruptions and lasting market transformations. The office sector has faced a crisis due to hybrid work adoption, which drives high vacancy rates and declining valuations. Retail and hospitality properties faced significant transformations, as e-commerce expansion and shifting travel behaviors affected their conventional customer base. While industrial real estate initially thrived during the pandemic due to logistics and e-commerce expansion, oversupply and rising costs from tariffs introduced new market threats. Cross-sector challenges including rising interest rates, reduced investor appetite, and heightened sustainability requirements have further affected the commercial real estate market. This paper argues that the difficulties of this period reflect permanent structural changes rather than temporary fluctuations, with implications for property owners, investors, and policymakers as they adapt to a redefined commercial real estate market.

 View pdf
View pdf


Based on the user lifecycle management (ULM) model, this paper explores Xiaomi Technology’s digital marketing strategies within the 'Acquisition-Conversion-Retaining’ framework. At the 'acquisition’ link in ULM, Xiaomi combined online and offline channels, focused on exact positioning, and used microblogs and social media to interact to develop a high-performance, low-cost acquisition mechanism. At the 'conversion’ link, Xiaomi optimized decision-making by making full use of the synergy effect of the ecosystem, provided situational value, and constructed trust and reputation to drive purchases across multiple categories. At the 'retaining’ link, Xiaomi emphasized emotional communication and user experience by co-creating experiences through participation in activities, while also promoting the ecosystem to maximize brand value, lifetime revenue, and foster long-term loyalty with users. Thus, Xiaomi’s success is attributed not only to its technological prowess but also to its ability to integrate user needs with brand strategy, creating sustainable interactions with users. Nonetheless, challenges remain, including full-channel synergy, authenticity control in user content ecology management, and the quality of community cooperation among ecosystem peers; this study provides relevant guidance for enterprises seeking competitive advantages or opportunities in sustainably and durably building a user-centric brand strategy in complex environments.

 View pdf
View pdf


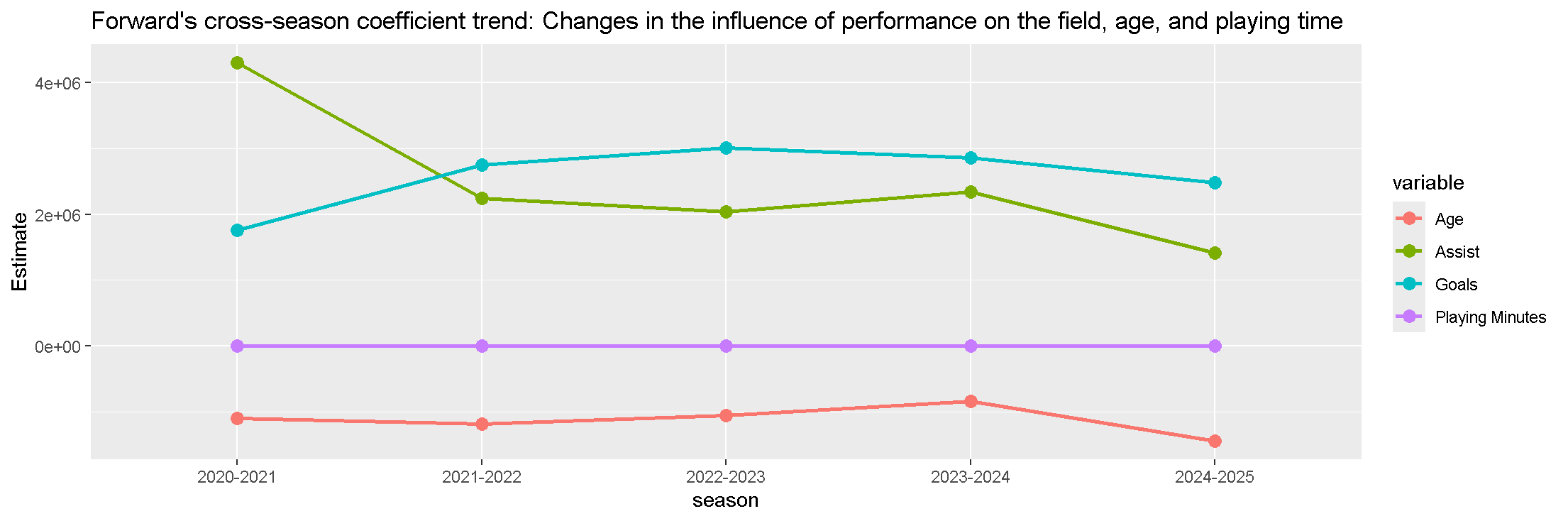
Against the backdrop of the Premier League’s high commercialization, where players’ commercial value garners significant attention from clubs, sponsors, and the media, this study aims to address gaps in existing research—such as short-term analysis, overreliance on single performance metrics, and insufficient use of panel data—by empirically examining the impact and degree of on-field performance data on Premier League players’ commercial value using panel data from the 2020–2025 seasons. Methodologically, players were categorized into four positions (forwards, midfielders, defenders, goalkeepers), with position-specific on-field indicators (e.g., goals/assists for forwards, progressive passes for midfielders, progressive passes received for defenders, and saves for goalkeepers) as independent variables and players’ market value from Transfermarkt as the dependent variable; multiple linear regression models were constructed for each position and season, with analyses conducted via the R programming language. Key findings include: models for forwards, midfielders, and defenders were highly significant (all p < 0.05) across most seasons, while the goalkeeper model was only significant in 2021–2022, 2022–2023, and 2024–2025; commercial value was driven by position-specific performance (goals for forwards, progressive passes for midfielders, progressive passes received for defenders) and age exerted a consistent negative effect on forwards/defenders, whereas traditional metrics like saves had weak explanatory power for goalkeepers (whose value relied more on unquantified factors such as tactical command); adjusted R² values fluctuated (peaking in 2022–2023 for forwards/midfielders) and remained relatively low overall, indicating on-field performance only partially explains commercial value, with unincorporated off-field factors (e.g., personal brand image) also playing critical roles. This study contributes by adopting long-term panel data and position-specific frameworks, offering practical guidance for clubs’ transfer strategies and sponsors’ partnership decisions, while its limitations (exclusion of off-field variables, narrow goalkeeper metrics) point to future research directions.

 View pdf
View pdf


Traditional Index Models have long been constrained by oversimplified assumptions limiting their accuracy in portfolio construction. This paper proposes a machine learning-enhanced Index Model framework, leveraging Random Forest algorithms whether this way can improve the accuracy of stock prediction or not. Using daily data of the OEX index (and its constituent stocks) from 2004 to 2024 as the empirical sample, this paper conducts the empirical research. The results show that the machine learning-enhanced Index Model can achieve a lower test-set MSE and higher R² compared to the traditional Index Model, indicating superior return prediction accuracy. The ability of the random forest to optimize the index model portfolio depends on the compatibility of stock features with the model. Therefore, the original random forest has the characteristics of low interpretability and high bias failure, which leads to the model being prone to failure. Moreover, this prediction constructed based on the model’s predicted returns outperform the benchmark OEX index in risk-adjusted returns and risk control. The random forest model captures the complex situations overlooked by the traditional index model, and provide more reliable input for stock prediction.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper focuses on the emerging phenomenon of ESG rating discrepancy, using Chinese A-share listed companies from 2015 to 2023 as the research sample, and employs a fixed effects model to empirically examine the impact of ESG rating discrepancy on stock price crash risk, its mechanism of action, and its heterogeneity. The study finds that ESG rating discrepancy can significantly inhibit stock price crash risk, and this conclusion remains valid after a series of robustness tests. Heterogeneity analysis shows that this inhibitory effect is more significant in non-state-owned firms, low-pollution firms, firms with low ESG scores, and firms with low media attention. Mechanism analysis confirms that ESG rating discrepancy mainly exerts its role through the "information effect": it promotes more prudent decision-making by market participants by improving stock liquidity, stabilizing investor sentiment, and intensifying analyst forecast divergence, thereby effectively weakening the herd effect and reducing crash risk. This study provides empirical evidence and policy implications for objectively viewing the market role of ESG rating discrepancy, improving the ESG rating ecosystem, and preventing and resolving financial risks.

 View pdf
View pdf




