

Volume 79
Published on February 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICGPSH 2024 Workshop: Industry 5 and Society 5 – A Study from The Global Politics and Socio-Humanity Perspective
In recent years, the unilateral decision and behavior of Japanese government in discharging Fukushima nuclear-contaminated water without any guarantee of safety and reliability, despite the international community’s skepticism , have aroused the concern and anger of the people of the world. The act of discharging the nuclear-contaminated water was carried out under the authorization and control of the Government of Japan, which is contrary to the obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, the Convention on Nuclear Safety and other conventions to which Japan is a party, so it should be subject to the corresponding national responsibility. Regarding the assumption of responsibility, as the strength of the States themselves mainly promotes international legal obligations and responsibilities, Japan should withdraw its wrongful practice and assume its corresponding duties and responsibilities as soon as possible. The ocean makes the world's countries closely connected, and all countries' interests are closely intertwined, so it is necessary to build a national responsibility mechanism for transboundary pollution under the framework of international law. Based on the existing achievements, this paper discusses and analyzes the national responsibility for transboundary pollution and its assumption and the construction of the national responsibility mechanism, taking Japan's discharge of nuclear-contaminated water as an example in order to strive to provide helpful theoretical support for judicial practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


Democracy is widely considered as a better form of regime in terms of others, such as monarchies and totalitarilism, since the freedom, human rights and equality of people in democracy regimes can be safeguarded. Meanwhile, a democratic government is under supervision of different sectors, thus preventing from abusing of power and corruption. The purpose of this article is to analyse the potential for democratic reform based on the previous studies, in order to have an implication on the factors and the future trends of democratic reform in the 21st century. This paper finds out that the process of democratic reform is getting faster as the technology and globalization progress, and the existence of social media and internet allows the faster spread of the idea of democracy, meanwhile causing a pressure to the stability of authoritarian regimes. Globalization allows countries worldwide to become more interdependent, and promotes economic activities that can further support the spread of democracy. Authoritarian regime countries who do not participate in globolization would face a problem of falling behind in econmic development and hence become less stable.

 View pdf
View pdf


International investment law always emphasizes the importance of improving the Fair and Equitable Treatment (FET) standard. Though many studies have summarized several new changes in the FET standard worldwide in recent years, there is a lack of effective evaluation and unified explanation for China’s FET standard practice. Therefore, this paper aims to expound the hidden problems and solutions to China’s application of the FET standard by exploring the developments of the FET standard in terms of treaty design and arbitration interpretations in recent years. The paper finds that states turn to impose a restriction of the scope of protection in bilateral investment treaties & international investment agreements as well as polish FET clauses in a more precise way, while the overall design of the FET standards in China remain backward. In addition, arbitration tribunals have more specific interpretations of the connotation of FET, but China's lack of arbitration experience makes it difficult to optimize FET clauses through arbitration interpretations. Therefore, this paper suggests China should specify its FET clauses in semi-closed enumeration method and more precise expression and systematically study tribunal interpretations of the FET standard elements as reference.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of globalization, cross-border data collection has become a crucial tool for countries combating transnational crime. China primarily employs international criminal judicial assistance to conduct cross-border data collection. While this approach respects national sovereignty, it faces practical challenges such as low efficiency and limited authority. In contrast, the United States and the European Union adopt a more flexible data controller model, achieving robust cross-border data collection capabilities. However, conflicts in data sovereignty and differences in legal systems hinder the direct application of these models in China. This paper employs a comparative research methodology to analyze the legislative frameworks and backgrounds of the U.S. and EU cross-border data collection approaches, identifying reasons these models are unsuitable for direct implementation in China. Building on insights from these legislative models, the paper proposes recommendations such as increasing the number of bilateral judicial assistance agreements and establishing a categorized data management system, aiming to provide a reference for China's future development in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf


When Foxconn sweatshop incident was exposed, China's society briefly paid attention to the living conditions of Chinese laborers. But when the wave of public opinion passed, no one paid attention to the exploitation of workers in foreign-owned factories, but the inadequate protection of workers in the field of labor law in China still exists. The purpose of this paper is to explore the current shortcomings of China's labor law in the field of foreign-funded factories, as well as the deficiencies in the supervision measures of foreign-funded factories, as to solve the plight of Chinese workers who are suffering from oppression. After studying the labor laws and regulations of China by consulting the labor cases of foreign-funded enterprises, the labor background of China, and combining with the current social situation, this paper finds that there are certain defects in China's labor law and certain system loopholes in the supervision of foreign-funded factories and puts forward relevant suggestions.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid development of digital technology has made international interactions more convenient and frequent, and nowadays, the rapid change and development of artificial intelligence has brought unprecedented challenges to the international law. The international community has put forward an urgent demand for the improvement and development of the international law system. On the one hand, the wide application of AI in international trade has had a great impact and influence on the global value management; on the other hand, the development of AI has put forward new challenges to the relevant rules of the WTO, which include, but are not limited to, whether the existing World Trade Organisation (WTO) treaties are applicable to AI in the context of the digital economy, such as the GATT, GATS; whether existing WTO rules are formulated with the application of AI, such as GATT, GATS; whether emerging technologies are taken into account in the formulation of existing WTO rules; and the challenge of AI to the existing legal system system. The World Trade Organisation (WTO), as the most important intergovernmental trade organisation in the world and the international community today, still plays an important role in regulating and deploying the development of AI technologies in the international trading system. Based on this, this paper takes the WTO as the research perspective to explore the impact of the digital economy and the development of artificial intelligence technology on international law, combining the existing rules system of the WTO and the characteristics of the development of artificial intelligence technology, research and argumentation to deal with the impact of the strategy, with a view to guaranteeing better development of artificial intelligence technology for the WTO, better service to mankind to offer advice.

 View pdf
View pdf


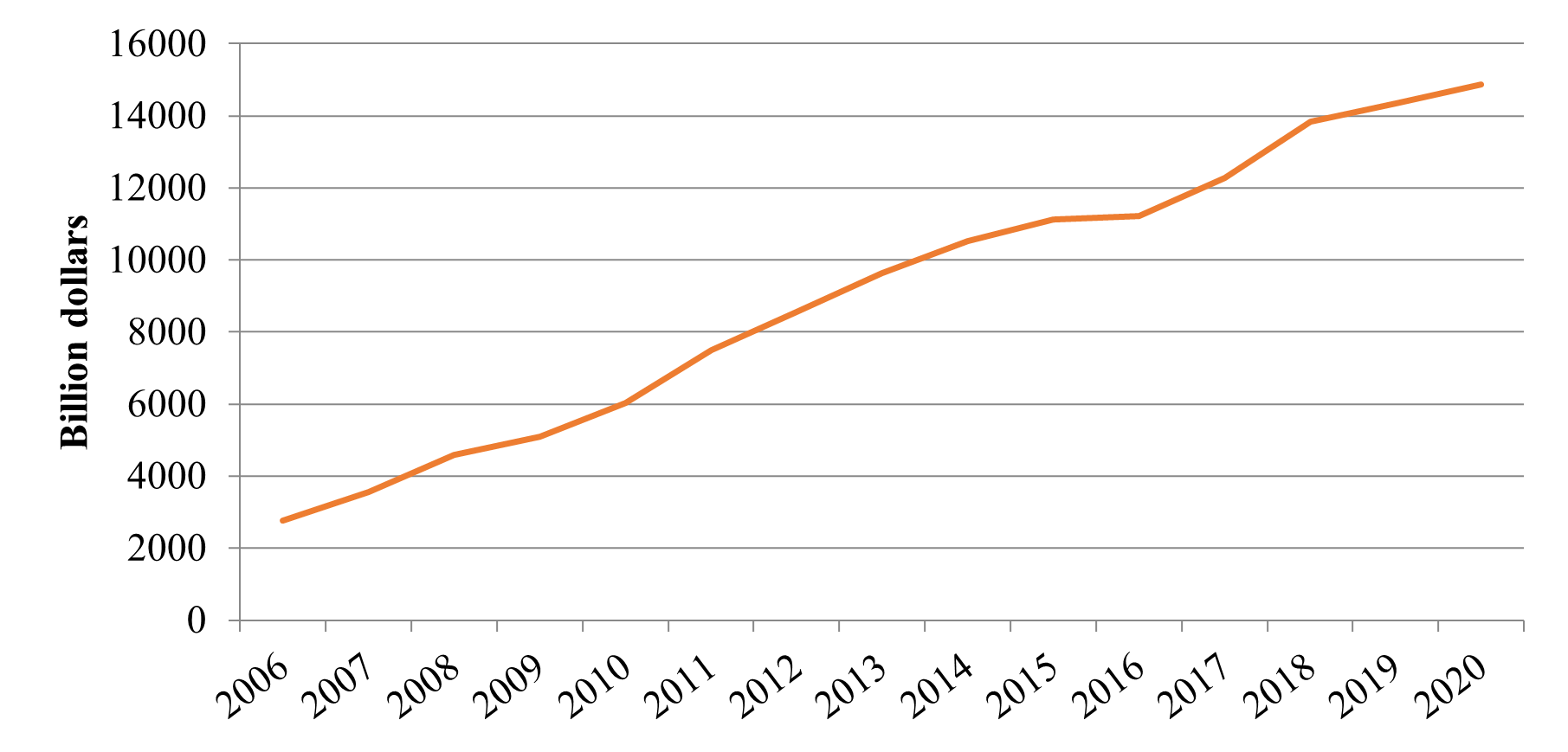
The impact of inequality has had a significant negative effect in most countries. In many countries, inequality is on an inexorable upward trend and, if allowed to continue, it will further undermine the development in societies and economies. This paper explains the effect of inequality from two perspectives, the economic development and technological advancement. Taking China as an example, the paper analyses the increase of China’s Gross Domestic Product and its investment in scientific and technological development and innovation in recent years, and analyses the corresponding impact on inequality. This paper focuses on the factors that contribute to regional inequality in China. The findings show that Western China is lagging behind in terms of development while Eastern China has a much higher level of development in spite of the fact that it is already affluent. Further, this paper suggests that, in the future, artificial intelligence can be used to enhance equality in education and to increase skilled labour in poor areas for developmental purposes.

 View pdf
View pdf


China is in a period of high-quality development. Therefore, this paper studies the package of incremental policies issued by the People's Bank of China under the background of the great downward pressure of domestic economy and the complex international environment. This paper analyzes the policy goals and economic impact of the price fluctuation in financial assets in China. The release of this package of incremental policies is aimed at stabilizing economic growth, enhancing market confidence and creating jobs. Its key measures include lowering the required reserve ratio and interest rates, supporting the real estate market, and providing financing support for micro, small and medium-sized enterprises. On the positive side, the policy guarantees employment, stimulates consumption, and promotes the recovery of the real estate market. On the challenging side, this includes policy sustainability and insufficient consumer incentives. The package of incremental policies is particularly targeted and will have a significant impact on China's future economic development. However, its sustainability and effectiveness remain questionable, indicating the need for a gradual and orderly implementation.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article thoroughly examines the connection between political orientation and economic policies by analyzing the decision-making process and economic consequences of right-wing countries like the United States and left-wing countries such as Norway during the COVID-19 pandemic. Countries with a strong left-wing inclination might focus more on developing the public sector and social welfare, and their economic development mode tends to be closer to the welfare state model. In contrast, countries with a stronger right-wing tendency stress the function of free markets and private enterprises, and their economic development models are more similar to the free-market economy model. Nevertheless, international cooperation must be strengthened. Both left-wing and right-wing countries should discard ideological distinctions and jointly address the impact of the pandemic on the global economy to facilitate its recovery. Also, during the epidemic, vulnerable groups had been the most severely affected. The government should adopt measures to safeguard their basic livelihoods and rights, and prevent the wealth gap from further expanding. Additionally, it is essential to increase investment in education and training to enhance the skill level of workers and provide human resource support for the long-term economic development.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of expanding economic globalization, the numbers of the Multinational Corporation (MNC) have been increasing. “One Belt One Road” promotes the trade corporation between countries. In light of the MNCs implement various tax avoidance strategies, this has significant adverse impact on business environment and tax revenue. This article mainly relies on literature research and comparison of anti-tax avoidance Legal Framework between China and Canada. It explores different measures of anti-tax avoidance. China has experienced challenges with tax avoidance issue in the BRI, including lack of competitiveness of China’s Tax Rate, complexity of international taxation environment, and challenges of implementing Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Pillar II Global Minimum Tax. Furthermore, comparing the anti-tax avoidance legal framework and differences in its GAAR respectively. The purpose is to design a tax system with Chinese characteristics. Effective anti-tax measures is very crucial for ensuring fair taxation and foster competitive business environment, and increase the public trust for China.

 View pdf
View pdf




