1. Introduction
In the current medical community, cancer is still an unsolved issue. Many cancer patients in the middle and late stages of the disease can only receive maintenance treatment, which has an unsatisfactory therapeutic outcome, following radiation, chemotherapy, and other forms of treatment. [1] According to survey statistics, the “number one killer” endangering women’s health is breast cancer, which has increased in occurrence by 37% in major Chinese cities over the previous ten years, particularly in the 30-54 age range. BC is able to be treated with monoclonal antibody therapy, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, or other techniques. [2] The tumor’s location, level of malignancy, stage of development, and the patient’s physical condition all influence the therapy option. Additionally, there are some experimental cancer treatments being investigated. One of the most effective cancer immunotherapies, both in terms of initial efficacy and commercial success, is PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy, which has both successfully sparked and spearheaded the BC therapeutic revolution. Although it was developed later, tumor immunotherapy has reached the clinic at an unprecedented rate, has emerged as the fifth pillar of BC treatment in recent years, and is anticipated to liberate the patient’s immune system to fight cancer to ultimately develop into a crucial tool for treating BC.
More alternatives and hope for BC patients were provided in 2022 when the FDA authorized ten novel immunotherapies, including relatlimab, the first LAG3 inhibitor, and TCR-T, the first solid tumor cell immunotherapy in history. All forms of treatment for breast cancer, including radiation, surgery, and chemotherapy, put a lot of strain on the body, and no matter what approach is used after malignant metastases have occurred, there is never a 100% cure. The goal of current BC treatment research is to eradicate cancer cells entirely while sparing healthy cells. However, because the disease has metastasized far away or spread to nearby tissues, surgical excision is frequently limited. The toxicity of chemotherapy to other normal tissues of the body. Normal tissue is also harmed by radiation. Thus, the greatest problem that humanity is currently facing is how to handle BC.
The development of human medicine and the triumph of humans over malignant tumors can be attributed to targeted therapy and immunotherapy in BC. Enhancing human longevity, promoting pleasure and quality of life, and lessening patients’ physical and psychological suffering are all benefits of BC treatment. The inhibition and promotion of BC and its impact on breast tumors have been highlighted in this paper along with the potential roles that various substances—like MUC1-C, ZEB1 mRNA, and AKT472 splicing variant subtype—may play in the advancement of human cancer research.
2. Promotion and occurrence of BC
2.1. AGTR1
The angiotensin II receptor, or AGTR1, has been shown to be overexpressed in some forms of vascular disease and is implicated in vasoconstriction and inflammatory signaling (BC). In this work, cell culture studies and other techniques were used to examine the function of AGTR1 in a particular subtype of BC. They found that AGTR1 is mutually exclusive with HER2 expression and overexpressed in BC’s luminal A and B subtypes. Aggressive characteristics linked to this overexpression include lower responsiveness to neoadjuvant therapy, increased lymph node metastases, and decreased overall survival. After delving deeper into the processes underlying AGTR1’s effects, the researchers discovered that the CARMA3, Bcl10, and MALT1 (CBM signalome) signaling pathway is responsible for both ligand-dependent and ligand-independent activation of NFκB. Turning on of this route stimulates the growth, migration, and invasion of cancer cells, among other intrinsic responses. Furthermore, CBM/NFκB signaling influences endothelial cells and promotes tumor angiogenesis, which have an impact on the tumor microenvironment. Aggressive behaviors are generally influenced by AGTR1 overexpression in luminal BC subtypes through a variety of mechanisms. These results imply that AGTR1 overexpression may function as a poor prognostic predictor for luminal BC. [3]
2.2. TBP RNA polypyrimidine bunchbinding protein
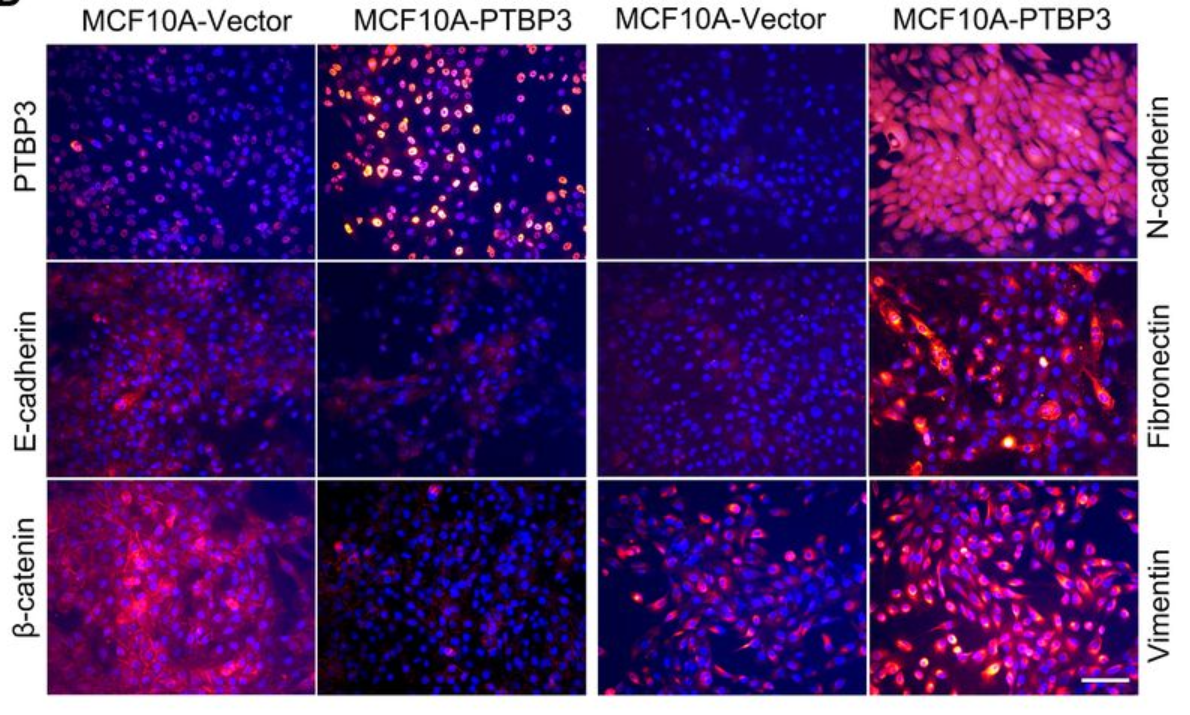
Figure 1. The driving effect of PTBP3 on EMT [4].
PTBP3 is a poorly characterized paracologue of PTBP1, which exhibits carcinogenic characteristics. As shown in Figure 1, a study focusing on PTBP3 related proteins were labeled and measured, and it was found that its overexpression can lead to the negative expression of epithelial markers, which confirms the important role of this gene in the development of breast cancer. ,in addition, this finding also shows that PTBP3 promotes the expression of EMT [4].
2.3. CA-IKk-β
Researchers created constitutively active, inducible forms of CA-IKK-β, a crucial kinase in the NFκB pathway, in breast cancer cell lines. Research has demonstrated that CA-IKKβ reversibly suppresses tumor development and E2-dependent cell proliferation in living things, pointing to a possible function for IKKβ in tumor dormancy and ER+ disease recurrence. Moreover, cell invasion and migration are encouraged by the concurrent activation of IKKβ and ER. Clinically significant invasion and metastatic gene profiles were shown to be strongly correlated with ER- and CA-IKKβ-driven gene expression, according to gene expression analysis. Mechanistically, rather than EMT, this phenotype might be caused by the proliferation of a population of stem-like cells. In summary, these results point to a function for IKKβ in stimulating the development of ER + breast cancer and imply that coactivation of the ER and canonical NFκB pathways contributes to the latent, metastatic character of ER + breast cancer. [5]
Furthermore, a study on ER+BC created a tumor transcription network in order to identify the primary features of this kind of BC from a genetic standpoint. The study’s findings suggest that RSK2’s N-terminus can interact with ERα. Simultaneously, outcomes derived from genetically altered mice suggest that anti-estrogen medications disrupt the interplay between the two elements and trigger the development of tumors. [6]
So overexpression of AGTR1, IKβ, PTBP3 controlled expression of ZEB1, RSK2 contribute to BC [7].
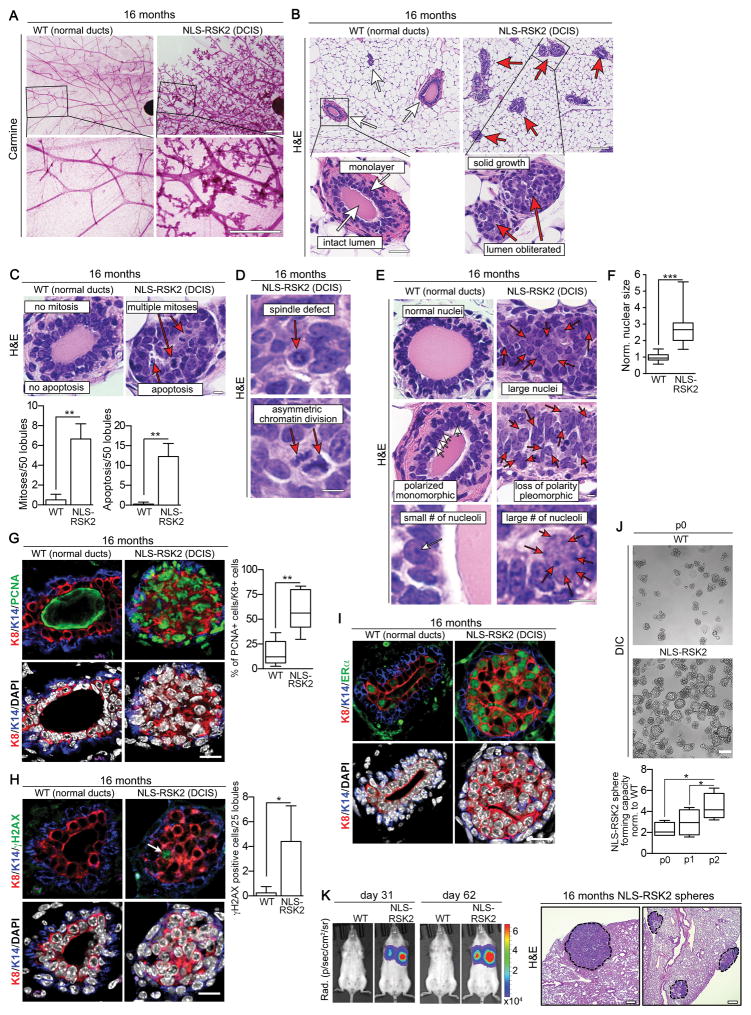
Figure 2. Comparison between RSK2 transgenic mice and WT [6]
3. BC suppression
3.1. AGTR1
The expression levels of AGTR1 were found to be higher than normal in BC patients. Researchers identified that the growth of brain metastasis is mediated by the activation of protocadherin 7 (PCDH7)-PLC-β-Ca2+-CaMKII/S100A4 signaling pathway involving astrocytes. They further evaluated the efficacy of a known drug, edelfosine, which is a selective PLC inhibitor and can inhibit the PCDH7 signaling pathway, thereby preventing brain metastasis in animal models. This study uncovers a novel signaling pathway for brain metastasis in triple-negative BC (TNBC) and provides a promising strategy for targeting organ-adaptive cancer stem cells to prevent and treat metastatic BC. [8]
The Akt pathway is well-known for its role in promoting malignant tumors. One of the isoforms of Akt3 lacks a key regulatory serine 472 phosphorylation site. While the function of the full-length Akt3 isoform (Akt3/+S472) has been studied extensively, the function of the Akt3/−S472 isoform remains unknown. In TNBC cells, specific ablation of Akt3/-S472 resulted in enhanced inhibition of breast tumor growth, despite the significantly lower expression level compared to Akt3/+S472. Overexpression of Akt3/-S472 was found to be associated with patient survival time. These effects are attributed to the induction of apoptosis mediated by upregulation of Bim, leading to the activation of Bax and caspase-3 processing. The increased endocytosis of EGFRs and subsequent attenuation of ERK result in the accumulation and stabilization of Bim. These findings reveal an unexpected pro-apoptotic function of the endogenously expressed Akt subtype, highlighting its inhibitory role in malignant tumors. [9]
Based on the above two studies, it is found that in recent years, new progress has been made in the treatment of BC, a new pathway has been discovered, and Akt has been found to play an important role in the inhibition of BC
3.2. Metastasis of BC.
Researchers found that reversible stroma attachment mechanisms in BC cells are complicated by the regulation of Akt and AMPK. They observed that substance deprivation can trigger cell-matrix separation by stimulating AMPK activity. At the same time, substrate deprivation also inhibits Akt activity by upregulating the Akt enzyme PHLPP2. This results in a state of high pAMPK/ low pAkt, which is critical for cell survival in suspension growth. Silencing of PHLLP2 increases apoptosis in loss-nest cells and may affect the ability of autophagy and metastasis. On the other hand, when cells reattach to the matrix, Akt activity is restored through a PP2c-α-mediated mechanism, resulting in the inactivation of AMPK. This suggests that matrix reattachment can induce cells to enter a low pAMPK/ high pAkt state through an AkT-mediated approach. Breast tumor cells in the circulating state showed increased AMPK-dependent gene expression signatures, while clinical specimens from primary and metastatic BC showed AKt-related gene expression signatures. Therefore, the researchers established a double negative feedback loop between Akt and AMPK to control the balance between the matrix attachment and matrix separation states of the cells during metastasis. This feedback loop plays an important role in regulating cell growth and survival. A deeper understanding of the relationship between Akt and AMPK has important implications for the development and treatment of BC, and future studies may target these key regulatory pathways to develop new anti-cancer strategies.[10]
4. Conclusion
This work examined the drug resistance of BC as well as its pathophysiology and promotion mechanism, and it provided an overview of the findings. Breast cancer is a prevalent, grave cancer that is extremely dangerous to the health of women. Through the investigation of BC-associated signaling pathways, the tumor microenvironment, and drug resistance, new insights into the pathogenesis of BC can be gained, along with novel suggestions for treatment and prevention. Genetic mutations, hormone levels, and the microenvironment of the breast are only a few of the numerous variables that contribute to the development and propagation of BC. According to this study, Akt, AGTR1, HER2, and other crucial genes and signaling pathways are involved in the onset and progression of BC. These results offer a solid foundation for early diagnosis and risk assessment. of BC. Furthermore, one of the main obstacles of treating BC is the resilience of BC cells to medications. The method by which BC cells survive chemoradiotherapy and endocrine therapy was examined in this work. AKT and MUC1, two essential genes and signaling pathways, are involved in BC medication resistance. These findings highlight the need for more customized approaches to prevent and treat medication resistance in clinical settings. Some topics, such as the role played by various subtypes in the development of BC and the mechanism of tumor immune escape, have not, however, been thoroughly examined in this work. Additional research on these problems may yield a more thorough knowledge and workable answers. Later on, In the future, by conducting thorough research on BC-related genetic mutations and signaling pathways, more effective early diagnosis methods and personalized treatment strategies need to be further developed.
References
[1]. Beltran H & Demichelis F 2021 Therapy considerations in neuroendocrine prostate cancer: what next? Endocrine-Related Cancer 28(8) T67
[2]. Zhang G Q Chen J L Luo Y Mathur M B Anagnostis P Nurmatov U & Nwaru B I 2021 Menopausal hormone therapy and women’s health: An umbrella review PLoS Med 18(8) e1003731
[3]. Prasanna Ekambaram Jia-Ying (Lloyd) Lee et al 2018 The CARMA3–Bcl10–MALT1 Signalosome Drives NFκB Activation and Promotes Aggressiveness in Angiotensin II Receptor–Positive Breast Cancer Cancer Res 1 March 78 (5) 1225–1240
[4]. Hou P Li L Chen Fet al 2018 PTBP3-mediated regulation of ZEB1 mRNA stability promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in breast cancer Cancer Res78(2) 387-398
[5]. El-Shennawy L Dubrovskyi O Kastrati I et al 2018 Coactivation of estrogen receptor and IKKβ induces a dormant metastatic phenotype in ER-positive breast cancer Cancer Res 78(4) 974-984
[6]. Ludwik K A McDonald O G et al 2018 ERα-mediated nuclear sequestration of RSK2 is required for ER+ breast cancer tumorigenesis Cancer Res 78(8) 2014-2025
[7]. Campbell T M Castro M A et al 2018 ERα binding by transcription factors NFIB and YBX1 enables FGFR2 signaling to modulate estrogen responsiveness in breast cancer Cancer Res 78(2) 410-421
[8]. Ren D Zhu X Kong Ret al 2018 Targeting brain-adaptive cancer stem cells prohibits brain metastatic colonization of triple-negative breast cancer Cancer Res 78(8) 2052-2064
[9]. Suyama K Yao J Liang Het al 2018 An Akt3 splice variant lacking the serine 472 phosphorylation site promotes apoptosis and suppresses mammary tumorigenesis Cancer Res 78(1) 103-114
[10]. Saha M Kumar S Bukhari Set al 2018 AMPK–Akt double-negative feedback loop in breast cancer cells regulates their adaptation to matrix deprivation Cancer Res 78(6) 1497-1510
Cite this article
Yao,X. (2024). Molecular mechanism and targeted therapy of breast cancer. Theoretical and Natural Science,32,293-297.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Beltran H & Demichelis F 2021 Therapy considerations in neuroendocrine prostate cancer: what next? Endocrine-Related Cancer 28(8) T67
[2]. Zhang G Q Chen J L Luo Y Mathur M B Anagnostis P Nurmatov U & Nwaru B I 2021 Menopausal hormone therapy and women’s health: An umbrella review PLoS Med 18(8) e1003731
[3]. Prasanna Ekambaram Jia-Ying (Lloyd) Lee et al 2018 The CARMA3–Bcl10–MALT1 Signalosome Drives NFκB Activation and Promotes Aggressiveness in Angiotensin II Receptor–Positive Breast Cancer Cancer Res 1 March 78 (5) 1225–1240
[4]. Hou P Li L Chen Fet al 2018 PTBP3-mediated regulation of ZEB1 mRNA stability promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in breast cancer Cancer Res78(2) 387-398
[5]. El-Shennawy L Dubrovskyi O Kastrati I et al 2018 Coactivation of estrogen receptor and IKKβ induces a dormant metastatic phenotype in ER-positive breast cancer Cancer Res 78(4) 974-984
[6]. Ludwik K A McDonald O G et al 2018 ERα-mediated nuclear sequestration of RSK2 is required for ER+ breast cancer tumorigenesis Cancer Res 78(8) 2014-2025
[7]. Campbell T M Castro M A et al 2018 ERα binding by transcription factors NFIB and YBX1 enables FGFR2 signaling to modulate estrogen responsiveness in breast cancer Cancer Res 78(2) 410-421
[8]. Ren D Zhu X Kong Ret al 2018 Targeting brain-adaptive cancer stem cells prohibits brain metastatic colonization of triple-negative breast cancer Cancer Res 78(8) 2052-2064
[9]. Suyama K Yao J Liang Het al 2018 An Akt3 splice variant lacking the serine 472 phosphorylation site promotes apoptosis and suppresses mammary tumorigenesis Cancer Res 78(1) 103-114
[10]. Saha M Kumar S Bukhari Set al 2018 AMPK–Akt double-negative feedback loop in breast cancer cells regulates their adaptation to matrix deprivation Cancer Res 78(6) 1497-1510









