

Volume 124
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mathematical Physics and Computational Simulation
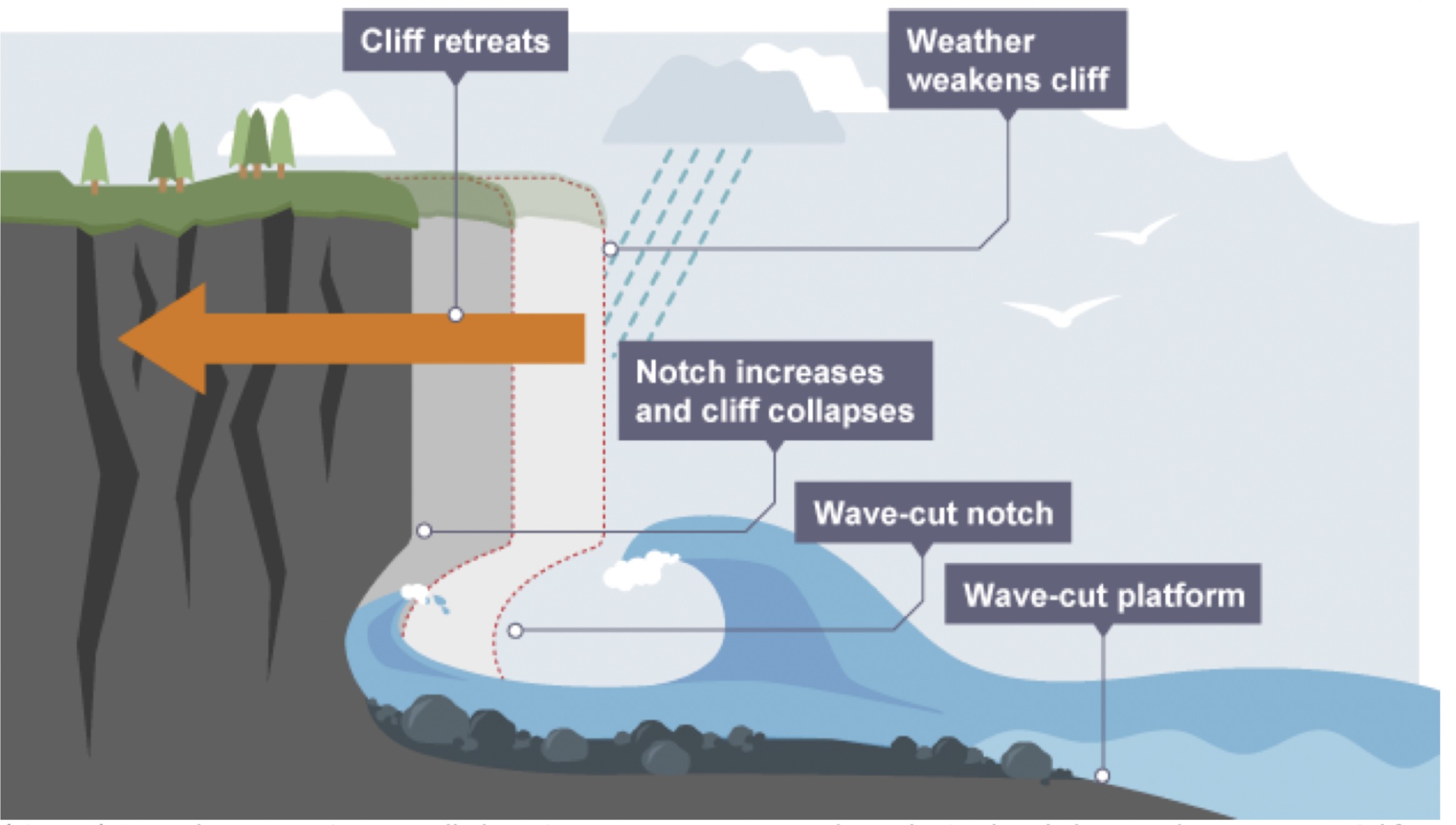
This study investigates coastal erosion at the White Cliffs of England using a wave-cut plat- form model and in situ10Be exposure testing. By integrating a salt conservation model within the Boussinesq approximation, the research aims to quantify salinity evolution in the English Channel and assess its contribution to chalk cliff instability. Results indicate that salinity-driven crystal growth reduces rock integrity by up to 55%, with pronounced seasonal variation in ero- sion rates, particularly during late winter. This interdisciplinary approach offers insight into the coupling between fluid mechanics, sediment dynamics, and climate-driven coastal change.

 View pdf
View pdf




