1. Introduction
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterial infection with a high prevalence that is extensively dispersed worldwide, impacting around 50% of the global population. Even though around 90% of individuals infected with H. pylori do not exhibit symptoms, this infection poses significant health concerns and has become progressively more challenging to manage due to the rise in antibiotic resistance in recent times [1]. Research has indicated that the occurrence of H. pylori-positive status exhibits variability based on various parameters, including age, geographical location, living conditions, and socioeconomic position. The primary mode of H. pylori transmission appears to be through oral-oral transfer [2]. Although H. pylori infection is highly prevalent, only a certain group of patients infected with this bacterium suffer severe gastroduodenal pathology. The aetiology of H. pylori infection and its subsequent illness manifestation are thought to be regulated by a multifaceted interplay of several variables., including the host, environment, and virulence factors of the bacteria. H. pylori has successfully acclimated to the challenging conditions of the human stomach by acquiring a repertoire of virulence genes. These genes facilitate the bacterium's ability to withstand the environment characterized by acidity, navigate to the gastric epithelium, and establish adhesion to gastric epithelial cells. The presence of these virulence factors facilitates the effective establishment of colonization inside the gastric mucosa and maintains a continuous infection of H. pylori. This, in turn, induces chronic inflammation and results in tissue damage, potentially culminating in the formation of peptic ulcers or even gastric cancer [3]. The most effective treatment options now available for H. pylori infection involve the use of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and ranitidine bismuth citrate in combination with two other antibiotics, known as triple treatments. Alternatively, a quadruple therapy approach can be employed, which includes the use of bismuth, tetracycline, metronidazole, and PPI. Clarithromycin is a highly effective antibacterial agent in combating Helicobacter pylori infections. The compound in question is a macrolide that exhibits acid stability and possesses a wide range of antibacterial properties. It is efficiently absorbed by the body and has a broad distribution throughout various tissue. Additionally, it is associated with few adverse effects. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC50) of Clarithromycin against H. pylori is rather low, the efficacy of the treatment is augmented through the suppression of acid. When the PPI or ranitidine bismuth citrate is coupled with amoxicillin or metronidazole, it is possible to achieve eradication rates above 95% for susceptible organisms [4, 5].
2. Pathogen virulence factors
H. pylori are successfully acclimated to the hostile conditions in the human stomach by acquiring a repertoire of virulent genes. These genes facilitate the bacterium's ability to endure the acidic environment, navigate towards the gastric epithelium, and establish adhesion to gastric epithelial cells. The presence of these virulence factors facilitates the effective establishment of colonization inside the stomach mucosa and supports the maintenance of a prolonged H. pylori infection. This, in turn, induces chronic inflammation and results in tissue damage, potentially culminating in the formation of peptic ulcers or even gastric cancer. A multitude of research has been conducted to examine the frequency and significance of purported Helicobacter pylori virulence genes in the development of disease. Although numerous virulence factors with diverse activities have been found, the connections with diseases seem to be less apparent, particularly when considering different study groups [3].
Acid escape virulence factors:
Urease:
1. The synthesis of ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2) has the ability to neutralize stomach acidity.
2. The process of angiogenesis has been identified as a contributing factor in the progression of stomach cancer.
3. The progression of malignancies is enhanced through the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway activation.
Bacterial shape:
The helical structure of bacteria has the potential to facilitate their entry into the mucous layer, so providing a protective advantage to the bacteria.
Flagella:
1. Motility facilitates bacterial locomotion away from acidic environments.
2. Flagellin activation exhibits increased motility, hence providing protection for the bacteria.
Epithelial cells colonizing factors:
BabA:
It is capable of binding to the epithelial cell receptor, Leb, hence facilitating attachment of bacterial and colonization. Additionally, it has been observed to enhance the translocation of CagA and produce double strand breaks in host cells.
SabA:
It is a bacterial adhesin that specifically interacts with the sialyl-Lex antigen, facilitating the attachment and colonisation of bacteria.
The OipA:
It facilitates the attachment of bacteria to the gastric epithelium, resulting in potential harm to the mucosal layer. This process triggers the release of interleukin (IL)-8 and leads to the death of host cells.
The HopQ:
It facilitates the attachment of bacteria to the stomach epithelium, hence impeding the functioning of immune cells.
Epithelial cells pathogenicity factors:
CagPAI:
The genetic material under consideration encompasses a type IV secretion system (T4SS) which serves the purpose of aiding the transportation of CagA and peptidoglycan.CagT:
It functions as a critical component within the T4S system, facilitating the translocation process of CagA.
CagY:
It is capable of binding with integrin, thereby exerting influence over the immune response, facilitating bacterial persistence, and inducing modifications in the functions of the Type IV secretion system, also called T4SS.
Cagζ:
It is involved in the functioning of the Type IV Secretion System (T4SS) and has a role in facilitating the transport of CagA.
CagL:
It functions as a central protein within the Type IV secretion system (T4SS) and interacts with integrin, facilitating the CagA translocation and triggering the production of interleukin-8 (IL-8).
CagA:
It induces cellular proliferation by the process of tyrosine phosphorylation. This phosphorylation event also leads to the upregulation of IL-8 production and cell elongation. Additionally, CagA is involved in the downregulation of heat shock protein VacA:
1. It induces vacuolization in epithelial cells, leading to cellular necrosis or apoptosis.
2. The autophagy activation and subsequent rise in cellular death is augmented by endoplasmic reticulum stress.
HtrA:
It functions as a protease, responsible for the degradation of misfolded proteins. Additionally, the facilitation of CagA dissemination is of utmost importance. Moreover, it cleaves tight junction proteins, namely occludin, claudin-8, and E-cadherin.
Outer membrane vesicles:
The internalization of outer membrane vesicles, whether clathrin-dependent or independent, serves as a protective mechanism for pathogens against the detrimental impact of reactive oxygen species. Additionally, this process hinders normal cellular activities while also stimulating dendritic cell functions.
γ-glutamyl transpeptidase:
1. It is involved in transpeptidation and amino acid production, which have been found to promote cell death and suppress cellular growth and cell cycle arrest.
2. The vacuolation of epithelial cells, which leads to the death of these cells.
2. Clarithromycin
2.1. History
The discovery of Clarithromycin can be attributed to the efforts of researchers employed at Taisho Pharmaceutical, a prominent Japanese pharmaceutical business, in the year 1980. The development of the product was driven by the objective of creating a variant of the antibiotic erythromycin that would not undergo acid instability within the gastrointestinal tract, hence mitigating adverse effects such as nausea and stomachache. The pharmaceutical company Taisho initiated the process of seeking patent protection for their medicine in approximately 1980. Following this, they brought a proprietary variant of the drug, named Clarith, to the Japanese market in 1991. In the year 1985, Taisho entered a partnership with the American corporation Abbott Laboratories to acquire the international rights for their product. Additionally, Abbott Laboratories successfully obtained permission from the Food and Drug Administration for Biaxin in October 1991. The pharmaceutical product transitioned to a generic form in Europe in the year 2004, followed by its generic availability in the United States during the middle of 2005 [6].
3. Process of traditional synthesis
Comprehensive Elucidation of the Innovation
A comprehensive investigation is currently being conducted to explore the large-scale manufacture and high purity of 6-O-Methyl-erythromycin, also called Clarithromycin, a highly effective inhibitor for gram-positive bacteria. Therefore, there was a regulated methylation of the 6-hydroxyl group of erythromycins, which had been protected at the 2' and 4" positions. The current invention pertains to the manufacturing process of achieving an enhanced degree of purity for Clarithromycin (Formula I) [6].
Formula (I)
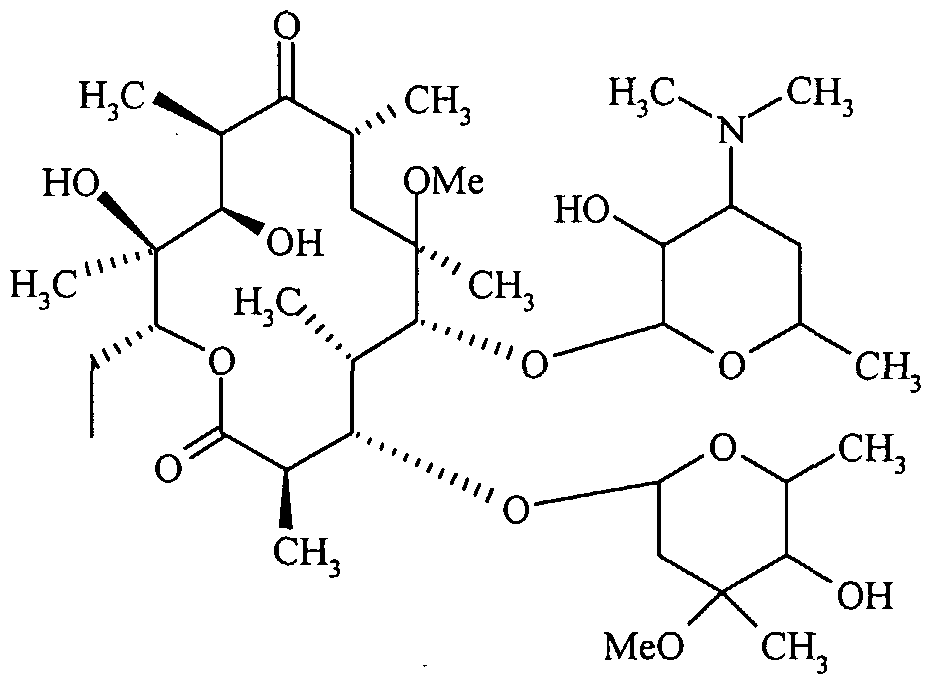
The initial iteration of Clarithromycin produced from this methodology exhibits a concentration of 6,11-O-dimethyl erythromycin-A, a possible byproduct, which is below 1.0%. The current innovation focuses on the industrial process of Clarithromycin, specifically aiming to achieve a controlled amount of side products. The finished product has been subjected to HPLC examination, which has led to the characterization of a total of eight contaminants. In accordance with a specific embodiment of the current invention, the synthesis of Clarithromycin Form II is achieved by the implementation of the subsequent reaction scheme:
(a) The reaction between Erythromycin-A and hydroxylamine hydrochloride, resulting in the formation of Erythromycin-A-9-Oxime.
The hydroxylamine hydrochloride compound is subjected to a reaction with caustic flakes in an aqueous solution of isopropyl alcohol within the range of 10°C to 20°C. This reaction results in the formation of the hydroxylamine base, which is dissolved in the solution. Subsequently, Erythromycin A is added to the solution [6].
The formula of NhLOH HCI isopropyl Alcohol
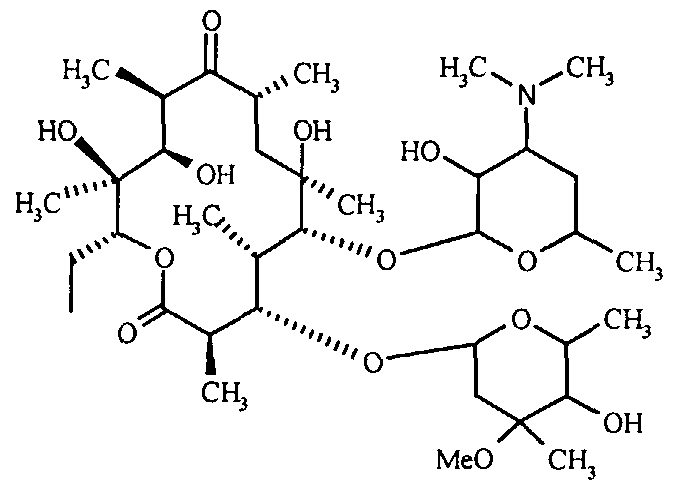
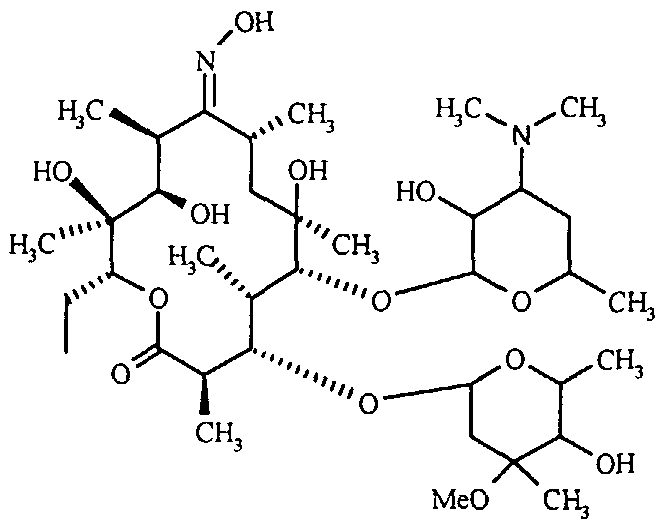
The formula of Erythromycin - A Erythromycin - A - 9 - Oxime
The pH of the reaction mixture is carefully regulated to a range from 6.5 to 7.0 with a gradual and precise supplement of glacial acetic acid. Erythromycin-A is introduced into the agitated reaction mixture, which is thereafter stirred for an additional duration of 28 hours at a temperature of 55°C. Following the conclusion of the reaction, the mixture is subjected to neutralization by the addition of aqueous ammonia and water. The resulting mixture is then subjected to continuous stirring for a duration of one hour. To achieve a precipitate of Erythromycin-A-9-Oxime with a yield ranging from 85% to 90%, an increased quantity of water is introduced into the reaction mixture [6].
(b) The objective of this study is to investigate the oxime protection, T, with the 4"-OH functional groups of Erythromycin-A-9-Oxime. The compound known as Erythromycin-A-9-Oxime, which was acquired through the previously mentioned process, is subjected to a reaction involving 2-methoxy propene and pyridine hydrochloride from dichloromethane. The mixture is subjected to stirring for a duration of 6 hours within a temperature range of 8°C to 120°C, after which hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) is introduced [6].
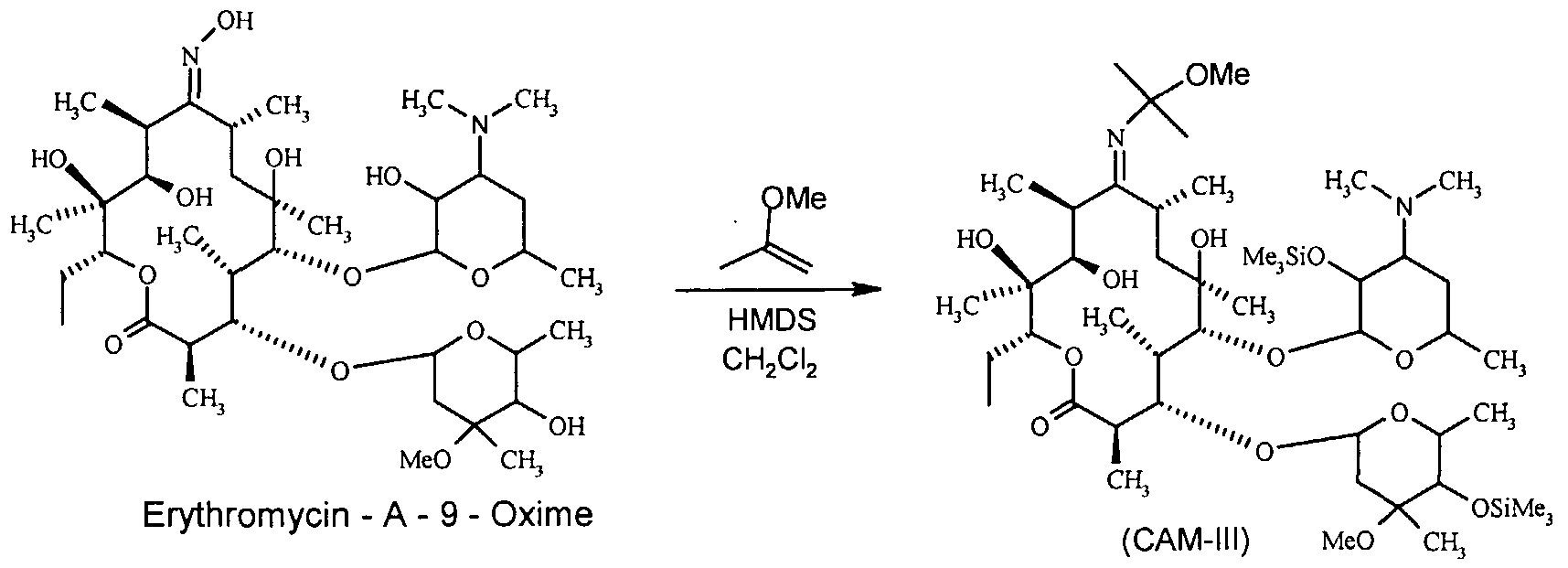
The stirring process is maintained for approximately 15 hours at a temperature consistent with the surrounding environment. Following the comprehensive protection of the oxime and 2' & 4" -OH functionalities of Erythromycin - A-9-oxime, the fully protected compound is entirely protected through conventional work-up and filtration methods. CAM-III is obtained through the process of vacuum drying, resulting in a yield of above 90%. The melting point of the substance under consideration ranges from 125 degrees Celsius to 1270 degrees Celsius [6].
(c) The 6-OH group of CAM-III is subjected to methylation, followed by deprotection of the oxime and the 2' and 4'-OH functions.
To achieve this, 2',4"-O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)-erythromycin-A-9- [O- (l-methoxymethyl ethyl) oxime] is reacted with methyl iodide in the presence of potassium hydroxide powder in a suitable solvent system. This reaction results in the formation of 2',4"-disilylated-Clarithromycin-9-methoxypropyl oxime (CAM-IV). Upon further hydrolysis, CAM-IV yields Clarithromycin-9-Oxime, as illustrated below:
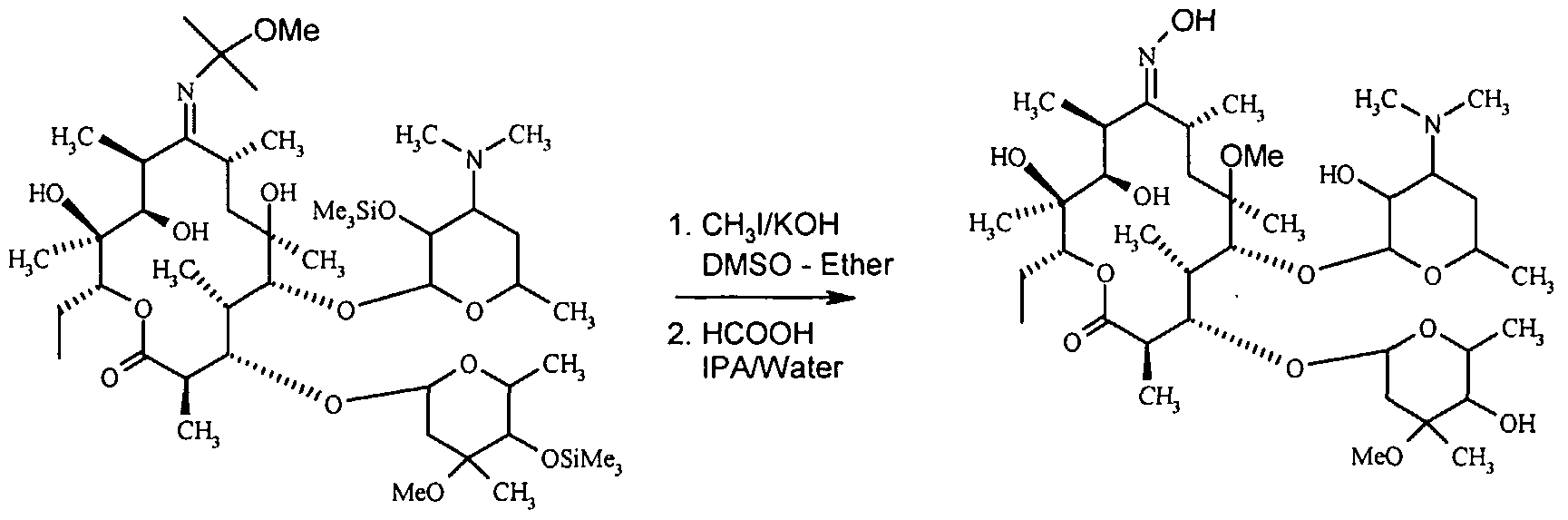
The term "computer-aided manufacturing" (CAM) pertains to the utilization of computer technology for manufacturing purposes. The chemical being examined is clarithromycin-9-oxime. One of the suitable solvent systems for this reaction includes a combination of DMSO and diethyl ether, among other potential options. The ideal proportion of diethyl ether in DMSO falls within the range of around 40% to 60%, with a preferred value of around 50%. The reaction is typically performed within the temperature range spanning between 10°C and 600°C, with a preferred range of approximately 15°C to 25°C. The duration of reactions often falls within a range of 40 minutes to 2 hours, with a favored interval of 80 to 100 minutes [6].
The precise ratio of methyl iodide to potassium hydroxide powder is of utmost importance, as any variation from the appropriate proportion can lead to the generation of unwanted byproducts. Based on thorough examination, it has been shown that the combination of methyl iodide (1.75 moles) and potassium hydroxide (1.20 moles) results in the formation of a resultant substance containing regulated impurities. This substance can be subjected to subsequent purification processes, such as one or two re-crystallizations. An advantage of employing the methylation approach in the current study using DMSO-Diethyl ether is the capacity to isolate the ether layer subsequent to halting the reaction mixture with a 40% dimethylamine solution. The ether layer is comprised solely of the methylated product, while the DMSO layer contains impurities. The DMSO layer is subsequently employed for the retrieval of DMSO, which functions as the solvent. In the second stage of the synthesis, the methylated product, referred to as CAM-IV, undergoes a reaction with 98% formic acid in a volume ratio of 1:1 between isopropyl alcohol and water. The aforementioned reaction is conducted over a period of 30 minutes, within the temperature range observed is between 25°C and 35°C. The intended result of this chemical reaction is the synthesis of Clarithromycin-9-Oxime [6].
(d) The process of converting to Clarithromycin from Clarithromycin-9-Oxime is examined in this study.
The production process of Clarithromycin involves the conversion of Clarithromycin-9-Oxime through a reaction with sodium metabisulphite in a solution consisting of Isopropyl alcohol and water in equal proportions (1:1, v/v). This reaction is carried out at the temperature of 80°C for a period of 6 to 8 hours [6].
Formula (I)

Clarithromycιn-9-Oxιme Clarithromycin
2.3 Mechanism of actions
Macrolides exert their mechanism of action by the binding process to ribosomes, specifically targeting the peptidyl transferase loop located in domain V of the 23S ribosomal RNA. This interaction effectively hinders the translocation of aminoacyl transfer-RNA, consequently impeding the subsequent process of protein synthesis. Clarithromycin exhibits a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action, comparable to that of erythromycin. It effectively inhibits a diverse array of microorganisms encompassing both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, atypical pathogens, anaerobic organisms. Nevertheless, the development of resistance to erythromycin typically indicates a concurrent resistance to clarithromycin. It is worth mentioning that clarithromycin exhibits activity, ranging from active to moderately active, against Campylobacter species. However, it demonstrates greater activity against H. pylori compared to erythromycin, azithromycin, and roxithromycin [6].
2.4 Side effect and precautions
The most documented side effects of clarithromycin included nausea with 3.8%, diarrhea with 3.0%, stomach discomfort with 1.9%, and headache with 1.7% [6]. Taste disturbance is a frequently observed phenomenon that has a correlation with dosage. For instance, when administered concurrently with omeprazole, about two-thirds of patients reported the occurrence of a metallic taste sensation, which subsequently vanished entirely within a few days following the completion of the treatment [7]. Occasional adverse effects such as cholestasis, jaundice, hepatitis, and Steven Johnson syndrome have also been documented.
4. Overview and conclusion
Clarithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic that is developed from erythromycin, serves as the foundation on the treatment of H. pylori infection due to its favorable attributes, including a low minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), effective absorption into the mucosal lining, and minimal susceptibility to the acidic environment. The variability about the prevalence of clarithromycin resistance in H. pylori, which is the major determinant of the effectiveness of empirically prescribed conventional H. pylori eradication therapy, exhibits significant regional and international differences. The prevalence is contingent upon the selection pressure exerted by the specific group of antibiotics within a particular geographical region [8].
References
[1]. FitzGerald R, Smith SM. An Overview of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2283:1-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1302-3_1. PMID: 33765303.
[2]. de Brito BB, da Silva FAF, Soares AS, Pereira VA, Santos MLC, Sampaio MM, Neves PHM, de Melo FF. Pathogenesis and clinical management of Helicobacter pylori gastric infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Oct 7;25(37):5578-5589. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5578. PMID: 31602159; PMCID: PMC6785516.
[3]. Šterbenc A, Jarc E, Poljak M, Homan M. Helicobacter pylori virulence genes. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 7;25(33):4870-4884. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4870. PMID: 31543679; PMCID: PMC6737321.
[4]. Leung WK, Graham DY. Clarithromycin for Helicobacter pylori infection. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000 Mar;1(3):507-14. doi: 10.1517/14656566.1.3.507. PMID: 11249534.
[5]. Ansari S, Yamaoka Y. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors Exploiting Gastric Colonization and its Pathogenicity. Toxins (Basel). 2019 Nov 19;11(11):677. doi: 10.3390/toxins11110677. PMID: 31752394; PMCID: PMC6891454.
[6]. Clarithromycin. New Drug Approvals. (2021, April 4). https://newdrugapprovals.org/2021/04/01/clarithromycin/
[7]. Leung WK, Graham DY. Clarithromycin for Helicobacter pylori infection. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000 Mar;1(3):507-14. doi: 10.1517/14656566.1.3.507. PMID: 11249534.
[8]. Marques AT, Vítor JMB, Santos A, Oleastro M, Vale FF. Trends in Helicobacter pylori resistance to clarithromycin: from phenotypic to genomic approaches. Microb Genom. 2020 Mar;6(3):e000344. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000344. PMID: 32118532; PMCID: PMC7200067.
Cite this article
Chen,Y. (2024). The overview of Clarithromycin treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. Theoretical and Natural Science,46,142-148.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. FitzGerald R, Smith SM. An Overview of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2283:1-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1302-3_1. PMID: 33765303.
[2]. de Brito BB, da Silva FAF, Soares AS, Pereira VA, Santos MLC, Sampaio MM, Neves PHM, de Melo FF. Pathogenesis and clinical management of Helicobacter pylori gastric infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Oct 7;25(37):5578-5589. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5578. PMID: 31602159; PMCID: PMC6785516.
[3]. Šterbenc A, Jarc E, Poljak M, Homan M. Helicobacter pylori virulence genes. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 7;25(33):4870-4884. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4870. PMID: 31543679; PMCID: PMC6737321.
[4]. Leung WK, Graham DY. Clarithromycin for Helicobacter pylori infection. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000 Mar;1(3):507-14. doi: 10.1517/14656566.1.3.507. PMID: 11249534.
[5]. Ansari S, Yamaoka Y. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors Exploiting Gastric Colonization and its Pathogenicity. Toxins (Basel). 2019 Nov 19;11(11):677. doi: 10.3390/toxins11110677. PMID: 31752394; PMCID: PMC6891454.
[6]. Clarithromycin. New Drug Approvals. (2021, April 4). https://newdrugapprovals.org/2021/04/01/clarithromycin/
[7]. Leung WK, Graham DY. Clarithromycin for Helicobacter pylori infection. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000 Mar;1(3):507-14. doi: 10.1517/14656566.1.3.507. PMID: 11249534.
[8]. Marques AT, Vítor JMB, Santos A, Oleastro M, Vale FF. Trends in Helicobacter pylori resistance to clarithromycin: from phenotypic to genomic approaches. Microb Genom. 2020 Mar;6(3):e000344. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000344. PMID: 32118532; PMCID: PMC7200067.









